Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Superfast assembly and synthesis of gold nanostructures using nanosecond low-temperature compression via magnetic pulsed power
Superfast assembly and synthesis of gold nanostructures using nanosecond low-temperature compression via magnetic pulsed power
Gold nanostructures have shape-dependent properties, making synthetic control over their morphology critical. Here, the authors use dynamic compression to obtain a variety of gold nanoarchitectures, which are formed at very fast timescales by the controlled coalescence of spherical particle arrays.
- Binsong Li
- , Kaifu Bian
- & Hongyou Fan
-
Article
| Open Access Oriented graphene nanoribbons embedded in hexagonal boron nitride trenches
Oriented graphene nanoribbons embedded in hexagonal boron nitride trenches
Graphene nanoribbons are promising candidates for 2D material electrical interconnects; however, the top-down fabrication of nanoribbons has remained a challenge. Here, Chenet al. have used a hexagonal boron nitride template to grow narrow, integrated graphene nanoribbons with small bandgaps.
- Lingxiu Chen
- , Li He
- & Mianheng Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access Local self-uniformity in photonic networks
Local self-uniformity in photonic networks
The interaction between photonic bandgap materials and light is largely determined by the wavelength-scale material structure. Here, Sellerset al. develop a new metric of network structural order and demonstrate its connection to the photonic bandgap of an amorphous gyroid network.
- Steven R. Sellers
- , Weining Man
- & Marian Florescu
-
Article
| Open Access Bio-inspired self-shaping ceramics
Bio-inspired self-shaping ceramics
Shaping ceramics into complex forms is a formidable goal. Here, the authors present an approach to self-shaping ceramics, inspired by self-folding processes in plants, in which the ceramic microstructure is embedded with aligned platelets that control the orientation of heat-induced shrinkage.
- Fabio L. Bargardi
- , Hortense Le Ferrand
- & André R. Studart
-
Article
| Open Access Kaleidoscopic imaging patterns of complex structures fabricated by laser-induced deformation
Kaleidoscopic imaging patterns of complex structures fabricated by laser-induced deformation
Complex surface micro- and nanostructures can be useful in many device applications, but are challenging in terms of controllability, low cost and high throughput. Here the authors have fabricated quasi 3D structures by the thermal deformation of simple two-dimensional laser-induced patterns.
- Haoran Zhang
- , Fengyou Yang
- & Qian Liu
-
Correspondence
| Open Access Correspondence: Strongly-driven Re+CO2 redox reaction at high-pressure and high-temperature
Correspondence: Strongly-driven Re+CO2 redox reaction at high-pressure and high-temperature
- D. Santamaria-Perez
- , C. McGuire
- & A. Muñoz
-
Correspondence
| Open Access Correspondence: Reply to ‘Strongly-driven Re+CO2 redox reaction at high-pressure and high-temperature’
Correspondence: Reply to ‘Strongly-driven Re+CO2 redox reaction at high-pressure and high-temperature’
- Mario Santoro
- , Federico A. Gorelli
- & Julien Haines
-
Article
| Open Access A stable lithium-rich surface structure for lithium-rich layered cathode materials
A stable lithium-rich surface structure for lithium-rich layered cathode materials
Surface modification of high-capacity lithium-rich layered oxides for improved capacity retention is an active area of battery materials research. Here authors demonstrate lithium-rich layered surfaces with a framework matching the host's, but with nickel atoms regularly arranged between layers.
- Sangryun Kim
- , Woosuk Cho
- & Jang Wook Choi
-
Article
| Open Access All-gas-phase synthesis of UiO-66 through modulated atomic layer deposition
All-gas-phase synthesis of UiO-66 through modulated atomic layer deposition
Thin films of metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) are promising for catalysis, gas storage, and microelectronics. Here, the authors introduce a vapour-phase synthesis of UiO-66 thin films, beginning with modulated atomic layer deposition of porous, amorphous films, followed by acetic acid vapour-enabled crystallization to the MOF structure.
- Kristian Blindheim Lausund
- & Ola Nilsen
-
Article
| Open Access Structure-conserving spontaneous transformations between nanoparticles
Structure-conserving spontaneous transformations between nanoparticles
Ambient chemical transformations between nanoparticles are poorly explored in materials science. Here, the authors find that two atomically precise, isomorphic clusters of gold and silver can convert between each other in solution through a series of alloy clusters, preserving structure, topology, and metal-ligand stoichiometry.
- K. R. Krishnadas
- , Ananya Baksi
- & Thalappil Pradeep
-
Article
| Open Access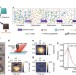 Nanoscale probing of electron-regulated structural transitions in silk proteins by near-field IR imaging and nano-spectroscopy
Nanoscale probing of electron-regulated structural transitions in silk proteins by near-field IR imaging and nano-spectroscopy
Silk protein fibres are exceptionally strong, owing to their high β-sheet nanocrystal content. Here, the authors use an electron beam to guide silk β-sheet crystals through structural transitions, and visualize the changes by infrared near-field optics, achieving close to molecular-level resolution.
- Nan Qin
- , Shaoqing Zhang
- & Tiger H. Tao
-
Article
| Open Access Synthesis of sodium polyhydrides at high pressures
Synthesis of sodium polyhydrides at high pressures
The only known compound of sodium and hydrogen is ionic NaH, but theory predicts the existence of polyhydrides at high pressure. Here, the authors report observations of the formation of polyhydrides above 40 GPa and 2000 K, supporting the idea of multicentre bonding in a material with unusual stoichiometry.
- Viktor V. Struzhkin
- , Duck Young Kim
- & Alexander F. Goncharov
-
Article
| Open Access Rational design of carbon nitride photocatalysts by identification of cyanamide defects as catalytically relevant sites
Rational design of carbon nitride photocatalysts by identification of cyanamide defects as catalytically relevant sites
Graphitic carbon nitride is a promising hydrogen evolution photocatalyst, although there is limited understanding of its mechanistic operation. Here, the authors employ molecular heptazine-based model catalysts to identify catalytically relevant defects and to rationally design a highly active carbon nitride photocatalyst.
- Vincent Wing-hei Lau
- , Igor Moudrakovski
- & Bettina V. Lotsch
-
Article
| Open Access Discovery of earth-abundant nitride semiconductors by computational screening and high-pressure synthesis
Discovery of earth-abundant nitride semiconductors by computational screening and high-pressure synthesis
Nitride semiconductors are attractive for various applications. Here a computational screening study identifies a number of possible ternary nitrides as promising candidates, including a phase that the authors synthesize for the first time via a high-pressure route.
- Yoyo Hinuma
- , Taisuke Hatakeyama
- & Fumiyasu Oba
-
Article
| Open Access Sugary interfaces mitigate contact damage where stiff meets soft
Sugary interfaces mitigate contact damage where stiff meets soft
Robust attachment between living tissues and inert materials is challenging to achieve. Here, Hwang and co-workers look at the molecular level between tissue and embedded byssal threads of Atrina pectinata and how this affects tenacity, toughness, and robustness.
- Hee Young Yoo
- , Mihaela Iordachescu
- & Dong Soo Hwang
-
Article
| Open Access Bio-based polycarbonate as synthetic toolbox
Bio-based polycarbonate as synthetic toolbox
With growing concerns over the sustainability of petroleum-based polymers, poly(limonene carbonate) is offered as a renewable alternative. Here, Greiner and co-workers have managed to tune the properties of poly(limonene carbonate) by carrying out several different chemical modifications.
- O. Hauenstein
- , S. Agarwal
- & A. Greiner
-
Article
| Open Access High-flexibility combinatorial peptide synthesis with laser-based transfer of monomers in solid matrix material
High-flexibility combinatorial peptide synthesis with laser-based transfer of monomers in solid matrix material
Peptide arrays are used in areas such as measuring protein-protein interactions, but achieving high density in synthesis is challenging. Here, the authors report a method for the combinatorial synthesis of high density peptides arrays by laser driven sequential transfer of monomers onto acceptor surfaces.
- Felix F. Loeffler
- , Tobias C. Foertsch
- & Alexander Nesterov-Mueller
-
Article
| Open Access Pie-like electrode design for high-energy density lithium–sulfur batteries
Pie-like electrode design for high-energy density lithium–sulfur batteries
Lithium-sulfur batteries are a promising candidate for next-generation battery technologies. Here, the authors report a pie-like structured electrode in which sulfur is confined in multichannel carbon nanofibers which is then coated by amino-functionalized graphene, leading to good balance between electrochemical performance and cell energy density.
- Zhen Li
- , Jin Tao Zhang
- & Xiong Wen (David) Lou
-
Article
| Open Access Assembling an alkyl rotor to access abrupt and reversible crystalline deformation of a cobalt(II) complex
Assembling an alkyl rotor to access abrupt and reversible crystalline deformation of a cobalt(II) complex
Molecular motion can potentially be harnessed to control macroscopic properties such as size and shape. Here, the authors show that the phase transition of a cobalt(II) complex with an n-butyl group on its ligands, results in a reversible crystal deformation at the structural phase transition temperature.
- Sheng-Qun Su
- , Takashi Kamachi
- & Osamu Sato
-
Article
| Open Access Evidence of covalent synergy in silicon–sulfur–graphene yielding highly efficient and long-life lithium-ion batteries
Evidence of covalent synergy in silicon–sulfur–graphene yielding highly efficient and long-life lithium-ion batteries
Silicon anodes are promising for lithium-ion battery development, but suffer from problems such as undesired volume expansion and solid-electrolyte interface formation. Here, the authors report a hierarchical silicon-sulfur-graphene composite anode which mitigates the problems leading to high performance.
- Fathy M. Hassan
- , Rasim Batmaz
- & Zhongwei Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Non-covalent synthesis of supermicelles with complex architectures using spatially confined hydrogen-bonding interactions
Non-covalent synthesis of supermicelles with complex architectures using spatially confined hydrogen-bonding interactions
Ubiquitous in nature, hierarchical architectures are less commonly achieved in synthetic functional materials. Here, the authors design and carefully assemble block copolymer micelles into complex supermicelles using hydrogen bonding in orthogonal combination with other non-covalent interactions.
- Xiaoyu Li
- , Yang Gao
- & Ian Manners
-
Article
| Open Access Controllable synthesis of molybdenum tungsten disulfide alloy for vertically composition-controlled multilayer
Controllable synthesis of molybdenum tungsten disulfide alloy for vertically composition-controlled multilayer
The band gap modulation of two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenide alloy is essential for successful applications. Here, we show a controllable synthesis of Mo1−xWxS2 alloy and vertically composition-controlled Mo1−xWxS2multilayer, which is promising as a photoactive material.
- Jeong-Gyu Song
- , Gyeong Hee Ryu
- & Hyungjun Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Solubility design leading to high figure of merit in low-cost Ce-CoSb3 skutterudites
Solubility design leading to high figure of merit in low-cost Ce-CoSb3 skutterudites
Thermoelectric materials have the potential to convert waste heat into electricity. Although some of the more viable thermoelectric materials are based on expensive rare earth elements, here the authors replace Yb with low-cost Ce by engineering Ce solubility, thereby making Ce-CoSb3 a competitive thermoelectric.
- Yinglu Tang
- , Riley Hanus
- & G. Jeffrey Snyder
-
Article
| Open Access Creating semiconductor metafilms with designer absorption spectra
Creating semiconductor metafilms with designer absorption spectra
Ultrathin semiconductor metafilms can be designed to achieve near-unity absorption in specific spectral regions. Here, Kim et al. engineer nanoscale optical resonances in sub-50-nm-thick germanium nanobeams metafilms to demonstrate near-unity absorption in one or more desired wavelength regions.
- Soo Jin Kim
- , Pengyu Fan
- & Mark L. Brongersma
-
Article
| Open Access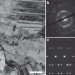 Transition of dislocation nucleation induced by local stress concentration in nanotwinned copper
Transition of dislocation nucleation induced by local stress concentration in nanotwinned copper
Metallic materials with a nanometre-scaled lamella structure can have properties that are very different from their coarser-grained counterparts. Here, the authors demonstrate how dislocations in such a material—nanotwinned copper—can nucleate in two distinctly different mechanisms depending on local stress
- N. Lu
- , K. Du
- & H. Q. Ye
-
Article
| Open Access Rational design of crystalline supermicroporous covalent organic frameworks with triangular topologies
Rational design of crystalline supermicroporous covalent organic frameworks with triangular topologies
Covalent organic frameworks are currently arousing considerable interest due to their desirable properties for a wide range of applications. Here, Jiang et al. report two such materials with triangular topologies which exhibit high hole mobility arising from extensive π-cloud delocalisation.
- Sasanka Dalapati
- , Matthew Addicoat
- & Donglin Jiang
-
Article |
 Resonant tunnelling in a quantum oxide superlattice
Resonant tunnelling in a quantum oxide superlattice
Quantum mechanical resonant tunnelling is believed to be only feasible in semiconductor-based heterostructures due to high crystalline quality required, which restricts the number of viable materials. Here, the authors demonstrate resonant tunnelling in a deliberately designed complex-oxide superlattice.
- Woo Seok Choi
- , Sang A. Lee
- & Ho Nyung Lee
-
Article
| Open Access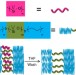 Membranes with artificial free-volume for biofuel production
Membranes with artificial free-volume for biofuel production
The free-volume of a polymer is a key parameter in its ability to permit through transport of small molecules. Here, the authors develop a way of introducing different degrees of artificial free-volume to a polymer membrane, and thus tailor its penetrability for applications including biofuel purification.
- Nikos Petzetakis
- , Cara M. Doherty
- & Nitash P. Balsara
-
Article |
 Design and discovery of a novel half-Heusler transparent hole conductor made of all-metallic heavy elements
Design and discovery of a novel half-Heusler transparent hole conductor made of all-metallic heavy elements
Materials that are both electrically conducting and transparent to light are vital for optoelectronic devices, but are rare. Here, the authors perform a quantum mechanical search for such materials and identify the compound TaIrGe as an unexpected possibility, which they then synthesize.
- Feng Yan
- , Xiuwen Zhang
- & Alex Zunger
-
Article
| Open Access High-performance flexible perovskite solar cells exploiting Zn2SnO4 prepared in solution below 100 °C
High-performance flexible perovskite solar cells exploiting Zn2SnO4 prepared in solution below 100 °C
There has been impressive progress in the development of perovskite solar cells in recent years, but the best performing systems tend to be fabricated on glass surfaces. Here, the authors present a cell built on a polymer substrate, allowing flexibility whilst maintaining high efficiency.
- Seong Sik Shin
- , Woon Seok Yang
- & Sang Il Seok
-
Article
| Open Access Atomically thin resonant tunnel diodes built from synthetic van der Waals heterostructures
Atomically thin resonant tunnel diodes built from synthetic van der Waals heterostructures
The family of two-dimensional materials is ever growing, but greater functionality can be realized by combining them together. Here, the authors report the direct synthesis of multijunction heterostructures made from graphene, tungsten diselenide and either molybdenum disulphide or molybdenum diselenide.
- Yu-Chuan Lin
- , Ram Krishna Ghosh
- & Joshua A. Robinson
-
Article
| Open Access The solvation of electrons by an atmospheric-pressure plasma
The solvation of electrons by an atmospheric-pressure plasma
Free, or solvated, electrons in a solution are known to form at the interface between a liquid and a gas. Here, the authors use absorption spectroscopy in a total internal reflection geometry to probe solvated electrons generated at a plasma in contact with the surface of an aqueous solution
- Paul Rumbach
- , David M. Bartels
- & David B. Go
-
Article
| Open Access Rhodium-catalysed C(sp2)–C(sp2) bond formation via C–H/C–F activation
Rhodium-catalysed C(sp2)–C(sp2) bond formation via C–H/C–F activation
Fluoroalkenes are found widely in biologically active compounds, but their introduction can be difficult or laborious. Here, the authors report a C–H/C–F activation strategy to introduce monofluoroalkenes into organic molecules in one step with good to excellent yields.
- Panpan Tian
- , Chao Feng
- & Teck-Peng Loh
-
Article
| Open Access A palladium-catalysed multicomponent coupling approach to conjugated poly(1,3-dipoles) and polyheterocycles
A palladium-catalysed multicomponent coupling approach to conjugated poly(1,3-dipoles) and polyheterocycles
The requirement for multistep synthesis can render the fabrication of highly substituted polymers particularly troublesome. Here, the authors take advantage of metal-catalysed multicomponent polymerization to synthesize a large family of such materials with ease from single-pot reactions.
- David C. Leitch
- , Laure V. Kayser
- & Bruce A. Arndtsen
-
Article
| Open Access Enabling unassisted solar water splitting by iron oxide and silicon
Enabling unassisted solar water splitting by iron oxide and silicon
Water splitting using earth-abundant materials promises a low cost solution to the problem of large scale energy storage. Here, the authors fabricate a haematite and silicon-based high-efficiency water splitting device, which operates without the need for an externally applied bias.
- Ji-Wook Jang
- , Chun Du
- & Dunwei Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Crystallization of DNA-coated colloids
Crystallization of DNA-coated colloids
DNA-coated colloids have failed to achieve their promise of programmable self-assembly because they stick to each other like Velcro. Here Wang et al.overcome this problem by making clickable smooth colloids that are coated with short single-stranded DNA at high density.
- Yu Wang
- , Yufeng Wang
- & David J. Pine
-
Article
| Open Access Synthesis of three-dimensionally interconnected sulfur-rich polymers for cathode materials of high-rate lithium–sulfur batteries
Synthesis of three-dimensionally interconnected sulfur-rich polymers for cathode materials of high-rate lithium–sulfur batteries
There is intensive research underway into the cathode development of lithium–sulphur batteries. Here, the authors present a battery with organosulfur-containing polymers as the cathode active materials which displays promising electrochemical performance.
- Hoon Kim
- , Joungphil Lee
- & Moon Jeong Park
-
Article
| Open Access General synthesis of complex nanotubes by gradient electrospinning and controlled pyrolysis
General synthesis of complex nanotubes by gradient electrospinning and controlled pyrolysis
Nanowires and nanotubes are ideal candidates for energy applications but inorganic multielement oxides are less well studied. Here, the authors propose a gradient-electrospinning followed by controlled-pyrolysis method to synthesize various controllable one dimensional metal oxide nanostructures.
- Chaojiang Niu
- , Jiashen Meng
- & Liqiang Mai
-
Article |
 A carbon nanotube wall membrane for water treatment
A carbon nanotube wall membrane for water treatment
Carbon nanotubes have been proposed for many forms of water treatment, although ultrafiltration nanotube-based membranes with very high flow rates remain rare. Here, the authors fabricate a membrane delivering water permeability close to 30,000 litres per square meter per hour at 1 bar.
- Byeongho Lee
- , Youngbin Baek
- & Yong Hyup Kim
-
Article
| Open Access High-speed multiple-mode mass-sensing resolves dynamic nanoscale mass distributions
High-speed multiple-mode mass-sensing resolves dynamic nanoscale mass distributions
Nanomechanical resonators are sensitive to tiny changes in their mass. Here, the authors demonstrate a method for quickly measuring many resonator modes and use it to analyse the mass and position of multiple nanoparticles flowing in a fluid channel with a precision of 40 attograms and 150 nm, respectively.
- Selim Olcum
- , Nathan Cermak
- & Scott R. Manalis
-
Article
| Open Access Spatially and temporally resolved gas distributions around heterogeneous catalysts using infrared planar laser-induced fluorescence
Spatially and temporally resolved gas distributions around heterogeneous catalysts using infrared planar laser-induced fluorescence
Visualization of the gas distribution around working catalyst is crucial for understanding structure–activity relationships. Here, the authors show that gas distribution can be imaged in situwith high spatial and temporal resolution using infrared planar laser-induced fluorescence.
- Johan Zetterberg
- , Sara Blomberg
- & Edvin Lundgren
-
Article
| Open Access Triangular prism-shaped β-peptoid helices as unique biomimetic scaffolds
Triangular prism-shaped β-peptoid helices as unique biomimetic scaffolds
β-Peptoids are based on N-alkylated β-aminopropionic acid residues, which have been inspired by the more intensely studied peptoids and β-peptides. Here, the authors report X-ray crystal structures of oligomeric β-peptoids demonstrating secondary structures with this backbone.
- Jonas S. Laursen
- , Pernille Harris
- & Christian A. Olsen
-
Article
| Open Access Tunable solid-state fluorescent materials for supramolecular encryption
Tunable solid-state fluorescent materials for supramolecular encryption
Solid-state fluorescent materials show promise for potential applications in security and anti-counterfeiting technologies. Here, the authors report a heterorotaxane which has found application in security inks with highly tunable solid-state fluorescence through supramolecular encapsulation.
- Xisen Hou
- , Chenfeng Ke
- & J. Fraser Stoddart
-
Article
| Open Access Accelerated sintering in phase-separating nanostructured alloys
Accelerated sintering in phase-separating nanostructured alloys
In sintering, powders of small grains are packed together to form shapes or grain structures that cannot be achieved by melt casting. Here, the authors demonstrate the fast sintering of a nanostructured alloy at low temperatures, preserving its nanoscale grain structure.
- Mansoo Park
- & Christopher A. Schuh
-
Article
| Open Access Temperature-triggered chemical switching growth of in-plane and vertically stacked graphene-boron nitride heterostructures
Temperature-triggered chemical switching growth of in-plane and vertically stacked graphene-boron nitride heterostructures
Targeted synthesis of vertically stacked graphene (G) and hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN) heterostructures remains a challenge. Here, the authors achieve the selective, CVD growth of h-BN-G and G/h-BN through a temperature-triggered switching reaction.
- Teng Gao
- , Xiuju Song
- & Zhongfan Liu
-
Article |
 Self-templated chemically stable hollow spherical covalent organic framework
Self-templated chemically stable hollow spherical covalent organic framework
Hollow, spherical nano/microstructures are potentially useful for energy and drug delivery applications. Here, the authors show that these structures can be fabricated from covalent organic frameworks, and exploit their chemical stability and mesoporous structures for enzyme encapsulation.
- Sharath Kandambeth
- , V. Venkatesh
- & Rahul Banerjee
-
Article
| Open Access A photofunctional bottom-up bis(dipyrrinato)zinc(II) complex nanosheet
A photofunctional bottom-up bis(dipyrrinato)zinc(II) complex nanosheet
The creation of functional 2D bottom-up nanosheets woven from molecular components remains a large challenge. Here, a bottom-up nanosheet featuring a photofunctional bis(dipyrrinato)zinc(II) complex motif is synthesized using interfacial syntheses, enabling a photoelectric conversion system.
- Ryota Sakamoto
- , Ken Hoshiko
- & Hiroshi Nishihara
-
Article
| Open Access Ternary metal fluorides as high-energy cathodes with low cycling hysteresis
Ternary metal fluorides as high-energy cathodes with low cycling hysteresis
Transition metal fluorides have high theoretical specific capacities as cathodes for lithium ion batteries, but low working potentials and poor energy efficiency limit their practical applications. Here, the authors report a group of ternary metal fluorides, which may overcome these problems.
- Feng Wang
- , Sung-Wook Kim
- & Jason Graetz
-
Article |
 Rational design of a chalcogenopyrylium-based surface-enhanced resonance Raman scattering nanoprobe with attomolar sensitivity
Rational design of a chalcogenopyrylium-based surface-enhanced resonance Raman scattering nanoprobe with attomolar sensitivity
Raman imaging offers great potential in biomedical imaging due to the combination of specificity and sensitivity. Here, the authors show nanoparticles functionalized with a chalcogenopyrylium reporter molecule, giving bright probes with low limits of detection for in vivoimaging.
- Stefan Harmsen
- , Matthew A. Bedics
- & Moritz F. Kircher

 Electrically driven cation exchange for in situ fabrication of individual nanostructures
Electrically driven cation exchange for in situ fabrication of individual nanostructures