Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article |
 Compressive forces stabilize microtubules in living cells
Compressive forces stabilize microtubules in living cells
Microtubules respond to mechanical compression by deforming, becoming more stable, which results in CLASP2 recruitment to the distorted shaft—a process crucial for cell migration through confined spaces.
- Yuhui Li
- , Ondřej Kučera
- & Manuel Théry
-
News & Views |
 Mechanotransduction mediated by microtubules
Mechanotransduction mediated by microtubules
Integrin-mediated substrate-rigidity sensing triggers microtubule acetylation, modulating mechanosensitive cellular responses and focal adhesion dynamics, subsequently promoting actomyosin organization and collective cell migration.
- Kseniia Porshneva
- & Guillaume Montagnac
-
Article |
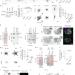 Microtubules tune mechanosensitive cell responses
Microtubules tune mechanosensitive cell responses
Substrate-rigidity-dependent microtubule acetylation is now shown to be triggered by mechanosensing at focal adhesions, and in turn controls the mechanosensitivity of Yes-associated protein (YAP) translocation, focal adhesion distribution, actomyosin contractility and cell migration.
- Shailaja Seetharaman
- , Benoit Vianay
- & Sandrine Etienne-Manneville
-
Article |
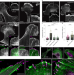 Correlative cryo-ET identifies actin/tropomyosin filaments that mediate cell–substrate adhesion in cancer cells and mechanosensitivity of cell proliferation
Correlative cryo-ET identifies actin/tropomyosin filaments that mediate cell–substrate adhesion in cancer cells and mechanosensitivity of cell proliferation
The role of actin/tropomyosin filaments in the assembly of cell–substrate adhesions has been investigated and it is now shown by cryo-electron tomography that they are essential for adhesion assembly and also regulate mechanosensing, matrix remodelling and transformation of cells towards a cancer phenotype.
- Maria Lastra Cagigas
- , Nicole S. Bryce
- & Edna C. Hardeman
-
News & Views |
 Stress fibres and the cortex work in tandem
Stress fibres and the cortex work in tandem
Stress fibres form a fully integrated meshwork with the submembranous contractile actin cortex that generates and propagates traction forces across the entire cell.
- Guillaume Charras
-
Article |
 Self-repair protects microtubules from destruction by molecular motors
Self-repair protects microtubules from destruction by molecular motors
Molecular motors destroy a microtubule lattice as they walk on it, but it is now shown that a self-healing process incorporates new dimers in the damaged regions and prevents microtubule disassembly.
- Sarah Triclin
- , Daisuke Inoue
- & Manuel Théry
-
Article |
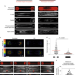 Stress fibres are embedded in a contractile cortical network
Stress fibres are embedded in a contractile cortical network
The mechanism of stress fibre assembly by the coalescence of actin filaments in the cell cortex has now been found to account for the transmission of mechanical forces throughout the entire cell along stress fibres.
- Timothée Vignaud
- , Calina Copos
- & Laetitia Kurzawa
-
News & Views |
 Syndecan-4 forces integrins to cooperate
Syndecan-4 forces integrins to cooperate
While integrin-based adhesions are thought to underlie many aspects of cell response to localized tension, another matrix receptor, syndecan-4, has now been shown to act as a mechanosensor, which triggers cell-wide integrin activation and adhesion reinforcement.
- Christophe Guilluy
- & Monika E. Dolega
-
News & Views |
 Pushing the limit on laminopathies
Pushing the limit on laminopathies
Mutations in lamins in skeletal muscle cells have been shown to reduce nuclear stability, increase nuclear envelope rupture, and induce DNA damage and cell death. New research shows that limiting mechanical loads can rescue myofibre function and viability.
- Joel C. Eissenberg
- & Susana Gonzalo
-
News & Views |
 Life and death agendas of actin filaments
Life and death agendas of actin filaments
Cancer cells have now been shown to lack rigidity-sensing due to alteration in cytoskeletal sensor proteins, but can be reversed from a transformed to a rigidity-dependent growth state by the sensor proteins, resulting in restoration of contractility and adhesion.
- Edna C. Hardeman
- & Peter W. Gunning
-
Article |
 Mutant lamins cause nuclear envelope rupture and DNA damage in skeletal muscle cells
Mutant lamins cause nuclear envelope rupture and DNA damage in skeletal muscle cells
Lamin mutations responsible for muscular dystrophy are shown to reduce nuclear envelope stability, resulting in mechanically induced nuclear envelope rupture, DNA damage and activation of DNA damage response pathways that lead to muscle cell death. Preventing nuclear envelope damage by reducing cytoskeletal forces on the nucleus improves muscle fibre health and function.
- Ashley J. Earle
- , Tyler J. Kirby
- & Jan Lammerding
-
Article |
 Taxanes convert regions of perturbed microtubule growth into rescue sites
Taxanes convert regions of perturbed microtubule growth into rescue sites
Anticancer drugs such as Taxol can affect microtubule dynamics and organization in cells. Direct visualization of the action of such drugs has shown that they can trigger local and cooperative changes in microtubule lattice and induce formation of stable microtubule regions that promote rescues.
- Ankit Rai
- , Tianyang Liu
- & Anna Akhmanova
-
Letter |
 Cellular nanoscale stiffness patterns governed by intracellular forces
Cellular nanoscale stiffness patterns governed by intracellular forces
High-spatial-resolution mechanical imaging reveals that intracellular forces generate cellular nanoscale stiffness patterns.
- Nicola Mandriota
- , Claudia Friedsam
- & Ozgur Sahin
-
Article |
 A mechano-signalling network linking microtubules, myosin IIA filaments and integrin-based adhesions
A mechano-signalling network linking microtubules, myosin IIA filaments and integrin-based adhesions
Crosstalk between microtubules and the actin cytoskeleton of cells is important in elucidating integrin-mediated adhesion and mechanotransduction. It is now shown that microtubule-mediated control of focal adhesions and podosomes occurs via KANK family proteins.
- Nisha Bte Mohd Rafiq
- , Yukako Nishimura
- & Alexander D. Bershadsky
-
News & Views |
 Self-healing microtubules
Self-healing microtubules
The walls of microtubules can self-repair bending-induced damage.
- Bela M. Mulder
- & Marcel E. Janson
-
News & Views |
 Fleeting defects line up
Fleeting defects line up
Short-lived topological defects in active liquid crystals can exhibit long-range, long-lived orientational order.
- Denis Bartolo
-
News & Views |
 Playful topology
Playful topology
The combination of topological constraints and deformability in an active system of microtubules and molecular motors leads to rich dynamic behaviour.
- Julia M. Yeomans
-
News & Views |
 Bundles from boundaries
Bundles from boundaries
Using a micropatterning technique, the architecture of actin networks is revealed to be influenced by the spatial organization of actin filament nucleation. Considering the geometric boundaries within live cells, implications in the realm of actin-induced cell functions are vast.
- Denis Wirtz
- & Shyam B. Khatau
-
Letter |
 Nucleation geometry governs ordered actin networks structures
Nucleation geometry governs ordered actin networks structures
Actin filaments are a principal component of the cell cytoskeleton. Using micropatterning methods, physical influences on the growth of highly ordered actin structures are investigated. The spatial organization of actin nucleation sites is discovered to play an important role in establishing the architecture of actin networks.
- Anne-Cécile Reymann
- , Jean-Louis Martiel
- & Manuel Théry

 The laminin–keratin link shields the nucleus from mechanical deformation and signalling
The laminin–keratin link shields the nucleus from mechanical deformation and signalling