News & Views |
Featured
-
-
-
News & Views |
 A light-switched yin and yang pair
A light-switched yin and yang pair
In 1972, Baird showed theoretically that the electron counting rule for aromaticity and antiaromaticity in the lowest ππ* triplet state is opposite to that in the electronic ground state. A pair of compounds that manifests this reversal in character has now been identified and characterized experimentally for the first time.
- Henrik Ottosson
- & K. Eszter Borbas
-
Correspondence |
Reply to 'Entropic factors also contribute to the high melting points of polyhedral alkanes'
- Sason Shaik
- & Santiago Alvarez
-
News & Views |
 Searching sequence space
Searching sequence space
Short peptides are among the most intriguing building blocks in nanotechnology, but it would be very challenging to experimentally study the properties of large numbers of different sequences. Now, a computational analysis of all 8,000 possible tripeptides has been used to identify those with interesting self-assembly behaviour.
- Ehud Gazit
-
-
News & Views |
 Docking points
Docking points
The flexibility and structural dynamics of proteins pose a big challenge for those trying to discover new bioactive compounds. Now, by using guiding crystallographic data, a method that uses the energetic balance between protein conformers to weight docking scores is shown to aid the hunt for new ligands.
- Xavier Barril
-
Article |
 Incorporation of protein flexibility and conformational energy penalties in docking screens to improve ligand discovery
Incorporation of protein flexibility and conformational energy penalties in docking screens to improve ligand discovery
The adoption of multiple conformations by proteins presents a challenge for ligand discovery using docking simulations. Now, a method for representing the conformational behaviour of a flexible protein in docking screens, which is guided by experimental crystallography data, is shown to predict protein conformation, ligand pose and aid the discovery of new ligands.
- Marcus Fischer
- , Ryan G. Coleman
- & Brian K. Shoichet
-
Article |
 A transferable model for singlet-fission kinetics
A transferable model for singlet-fission kinetics
Understanding the process of exciton fission, which occurs in certain organic materials, could lead to the development of more efficient photovoltaic devices. Here, an expression derived from first principles is used to accurately characterize the singlet fission rate of a wide array of materials, reproducing a transition from weak to strong coupling as a function of molecular separation.
- Shane R. Yost
- , Jiye Lee
- & Troy Van Voorhis
-
News & Views |
 A stitch in time
A stitch in time
Lengthy molecular dynamics simulations of complex systems at the atomic scale usually require supercomputers. Now, by stitching together many shorter independent simulations run 'in the cloud', this requirement has been circumvented, allowing two milliseconds of the dynamics of a G-protein-coupled receptor to be simulated.
- Xavier Deupi
-
Article |
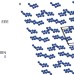 Calculations predict a stable molecular crystal of N8
Calculations predict a stable molecular crystal of N8
Polynitrogen compounds are of interest on a fundamental level and as potential high-energy-density materials. A crystalline solid that consists of two isomeric forms of N8 molecules held together by weak van der Waals interactions has now been predicted to exist, and to be stable even at low pressures.
- Barak Hirshberg
- , R. Benny Gerber
- & Anna I. Krylov
-
Article |
 Cloud-based simulations on Google Exacycle reveal ligand modulation of GPCR activation pathways
Cloud-based simulations on Google Exacycle reveal ligand modulation of GPCR activation pathways
Two milliseconds of molecular dynamics simulations of a major drug-target G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) has been carried out using Google's Exacycle cloud computing platform. Markov state models were used to aggregate independent simulations into a statistical model that provides an atomistic description of GPCR ligand-modulated activation pathways.
- Kai J. Kohlhoff
- , Diwakar Shukla
- & Vijay S. Pande
-
-
-
-
News & Views |
 Inverse solvent design
Inverse solvent design
Choosing a solvent for a particular reaction is often a matter of personal preference or the result of limited screening. Now, a computational method allows identification of a solvent that will enhance the kinetics of a reaction prior to running a wet experiment.
- Donald G. Truhlar
-
Article |
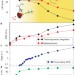 The Janus-faced role of external forces in mechanochemical disulfide bond cleavage
The Janus-faced role of external forces in mechanochemical disulfide bond cleavage
Using ab initio simulations external mechanical forces are shown to trigger structural changes to disulfide bridges that result in conformations that are less susceptible to nucleophilic attack. This finding is crucial for the interpretation of recent force microscopy experiments, and could be important for understanding protein regulation.
- Przemyslaw Dopieralski
- , Jordi Ribas-Arino
- & Dominik Marx
-
News & Views |
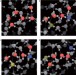 Wired-up water
Wired-up water
The splitting of water molecules into protons and hydroxide ions, and their recombination, occurs by proton transfer along hydrogen-bond wires. Now, first principle simulations of the recombination reaction reveal new atomic-scale details of the process showing that compression of the wire plays an important role.
- David Chandler
- , Christoph Dellago
- & Phillip Geissler
-
Perspective |
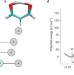 Good vibrations in enzyme-catalysed reactions
Good vibrations in enzyme-catalysed reactions
This Perspective discusses contemporary ideas for enzymatic reactions that invoke a role for fast 'promoting' (or 'compressive') motions or vibrations that, in principle, can facilitate enzyme-catalysed reactions. With an emphasis on hydrogen-transfer reactions, experimental, theoretical and computational approaches that have lent evidence to this controversial hypothesis are discussed.
- Sam Hay
- & Nigel S. Scrutton
-
Article |
 Large-scale screening of hypothetical metal–organic frameworks
Large-scale screening of hypothetical metal–organic frameworks
Chemists are able to prepare a wide variety of metal–organic frameworks by connecting together inorganic and organic building blocks of all sorts of shapes and properties. Now, a large-scale computational screening approach that simulates thousands of hypothetical MOFs from previously synthesized ones can help identify just which materials should be pursued.
- Christopher E. Wilmer
- , Michael Leaf
- & Randall Q. Snurr
-
Article |
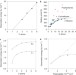 Dihydrogen contacts in alkanes are subtle but not faint
Dihydrogen contacts in alkanes are subtle but not faint
Intermolecular non-polar H···H interactions between polyhedrane molecules may be as attractive as classical hydrogen bonds. A theoretical study identifies the chemical and structural factors that favour such attractive interactions.
- Jorge Echeverría
- , Gabriel Aullón
- & Santiago Alvarez
-
News & Views |
 Model, make, measure
Model, make, measure
Computational studies have been used to accurately model the properties of a metal–organic framework. The material, subsequently synthesized, lived up to the predicted high surface area and sorption ability.
- George K. H. Shimizu
-

 Making a bad calculation
Making a bad calculation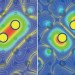 Electrides explained
Electrides explained Reduction to practice
Reduction to practice Model citizens
Model citizens United they are strong
United they are strong Defying cavity
Defying cavity