Featured
-
-
Research Briefing |
 Site-selective episulfonium formation on protein surfaces
Site-selective episulfonium formation on protein surfaces
Covalent protein conjugation facilitates the study of biological processes and the synthesis of therapeutic biomacromolecules. A method that uses vinyl thianthrenium reagents for the site-selective formation of highly reactive episulfonium species on proteins is demonstrated. These in situ-formed intermediates react with diverse nucleophiles, providing access to protein conjugates in one step without purification.
-
Article |
 Electrochemical labelling of hydroxyindoles with chemoselectivity for site-specific protein bioconjugation
Electrochemical labelling of hydroxyindoles with chemoselectivity for site-specific protein bioconjugation
Current electrochemical-based protein labelling methods suffer from limited site-selectivity and off-target reactivity owing to required radical/electrophilic reagents. Now an electrochemical strategy enables chemoselective labelling of proteins at a site-specifically incorporated 5-hydroxytryptophan residue using aromatic amines as coupling partners. This approach works on various proteins, including a full-length antibody, and is compatible with established click reactions.
- Conor Loynd
- , Soumya Jyoti Singha Roy
- & Abhishek Chatterjee
-
Article
| Open Access A SAM analogue-utilizing ribozyme for site-specific RNA alkylation in living cells
A SAM analogue-utilizing ribozyme for site-specific RNA alkylation in living cells
Ribozyme-mediated post-transcriptional RNA modification is a powerful method for site-specific RNA labelling and analysis of RNA functions. Now, an alkyltransferase ribozyme—termed SAMURI—has been shown to catalyse the transfer of a propargyl group from a stabilized synthetic S-adenosylmethionine analogue to a specific adenosine on the target RNA within cells.
- Takumi Okuda
- , Ann-Kathrin Lenz
- & Claudia Höbartner
-
Article
| Open Access Chemical generation of checkpoint inhibitory T cell engagers for the treatment of cancer
Chemical generation of checkpoint inhibitory T cell engagers for the treatment of cancer
Three-protein conjugates, which have so far been produced using protein-engineering strategies, can now be generated using a chemical approach that enables the addition of small-molecule functionality. Checkpoint inhibitory T cell engagers (CiTEs) were assembled and shown to have enhanced in vitro potency compared to a traditional T cell engager.
- Peter A. Szijj
- , Melissa A. Gray
- & Vijay Chudasama
-
Article
| Open Access Site-specific bioorthogonal protein labelling by tetrazine ligation using endogenous β-amino acid dienophiles
Site-specific bioorthogonal protein labelling by tetrazine ligation using endogenous β-amino acid dienophiles
An enzymatic reaction installs endogenous β-amino acids in proteins with unique reactivity. Now it has been shows that this reaction can be used for site-specific modification with tetrazine dienophiles to introduce labels onto target proteins. Applications include generation of a radiolabel chelator-modified Her2-binding Affibody and intracellular, fluorescently labelled cell division protein FtsZ.
- Daniel Richter
- , Edgars Lakis
- & Jörn Piel
-
Article |
 Tubulin engineering by semi-synthesis reveals that polyglutamylation directs detyrosination
Tubulin engineering by semi-synthesis reveals that polyglutamylation directs detyrosination
Microtubules carry patterns of post-translational modifications that are important for the regulation of key cellular processes. Now a semi-synthetic method facilitates the production of tubulins with defined post-translational modifications. Using these designer tubulins, polyglutamylation of α-tubulin is found to promote its detyrosination by enhancing the activity of the carboxypeptidase vasohibin/small vasohibin-binding protein.
- Eduard Ebberink
- , Simon Fernandes
- & Charlotte Aumeier
-
Article |
 Reversible 2′-OH acylation enhances RNA stability
Reversible 2′-OH acylation enhances RNA stability
Stabilization of RNAs for storage, transport and biological application remains a profound challenge. Now, it has been shown that reversible 2′-OH acylation with easily accessible acylimidazoles unlocks efficient protection of RNA. RNA can be deprotected by non-basic nucleophiles or spontaneously in cells to restore RNA functions.
- Linglan Fang
- , Lu Xiao
- & Eric T. Kool
-
News & Views |
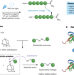 Shining light on diselenide bonds
Shining light on diselenide bonds
Post-translational modification of proteins is widely used for studying biological processes; however, competing reactions can provide numerous challenges. Now, a visible-light photocatalytic diselenide contraction enables the highly chemoselective functionalization of selenopeptides and proteins under mild conditions.
- Nicholas A. Fitzpatrick
- & Patricia Z. Musacchio
-
Article |
 Post-translational backbone-acyl shift yields natural product-like peptides bearing hydroxyhydrocarbon units
Post-translational backbone-acyl shift yields natural product-like peptides bearing hydroxyhydrocarbon units
Despite recent advances in engineering of in vitro translation systems, direct ribosomal incorporation of hydroxyhydrocarbon moieties—which can endow peptides with unique biochemical/folding properties—remains challenging. Now, incorporation of translation-compatible azide/hydroxy acids and their post-translational tandem backbone-acyl shifts have enabled in vitro ribosomal synthesis of peptides containing various hydroxyhydrocarbon units.
- Tomohiro Kuroda
- , Yichao Huang
- & Hiroaki Suga
-
Article |
 Genetically encoded chemical crosslinking of RNA in vivo
Genetically encoded chemical crosslinking of RNA in vivo
Protein–RNA interactions regulate RNA fate and function, and are generally non-covalent and reversible. Genetically introducing a latent bioreactive amino acid into a protein is now shown to enable the protein to covalently crosslink a bound RNA molecule in vivo. This method offers innovative avenues for developing protein–RNA research and applications.
- Wei Sun
- , Nanxi Wang
- & Lei Wang
-
Article |
 Light-activated tetrazines enable precision live-cell bioorthogonal chemistry
Light-activated tetrazines enable precision live-cell bioorthogonal chemistry
Developing stimuli-responsive bioorthogonal tetrazine ligations remains highly challenging, but a versatile approach that uses photocaged dihydrotetrazines has now been developed. Photouncaging results in the spontaneous formation of reactive tetrazines that rapidly react with dienophiles such as trans-cyclooctenes. As a demonstration, the method was used for live-cell labelling with single-cell precision and light-triggered drug delivery.
- Luping Liu
- , Dongyang Zhang
- & Neal K. Devaraj
-
Article
| Open Access Photocaged 5′ cap analogues for optical control of mRNA translation in cells
Photocaged 5′ cap analogues for optical control of mRNA translation in cells
Analogues of mRNA 5′ caps containing a photo-cleavable group have now been developed. These so-called FlashCaps can be used for routine in vitro transcription to make long mRNAs containing a cap. In cells, the capped mRNAs are translationally muted; however, upon irradiation by light, the photo-cleavable group is removed without leaving any remaining modification and mRNA is then translated into the corresponding protein.
- Nils Klöcker
- , Florian P. Weissenboeck
- & Andrea Rentmeister
-
Article |
 Wittig reagents for chemoselective sulfenic acid ligation enables global site stoichiometry analysis and redox-controlled mitochondrial targeting
Wittig reagents for chemoselective sulfenic acid ligation enables global site stoichiometry analysis and redox-controlled mitochondrial targeting
Triphenylphosphonium ylides (Wittig reagents) that selectively react with sulfenic acids—a pivotal post-translational cysteine modification in redox biology—are developed. This bioconjugation method enables a site-specific proteome-wide stoichiometry analysis of S-sulfenylation, and visualization of redox-dependent changes in mitochondrial cysteine oxidation and the redox-triggered generation of triphenylphosphonium for the controlled delivery of small molecules to mitochondria.
- Yunlong Shi
- , Ling Fu
- & Kate S. Carroll
-
Article |
 Site-selective tyrosine bioconjugation via photoredox catalysis for native-to-bioorthogonal protein transformation
Site-selective tyrosine bioconjugation via photoredox catalysis for native-to-bioorthogonal protein transformation
Regioselective chemical modification of wild-type proteins remains challenging. Now, by harnessing the varied SOMOphilicity of native tyrosine residues through photoredox catalysis, a site-selective bioconjugation method has been developed. This technology directly incorporates bioorthogonal formyl groups in one step, forming structurally defined fluorescent conjugates that can be rapidly diversified to biorelevant products.
- Beryl X. Li
- , Daniel K. Kim
- & David W. C. MacMillan
-
News & Views |
 Finding the sweet spot for chaperone activity
Finding the sweet spot for chaperone activity
Although critically important for protein function, post-translational modifications are complex and notoriously difficult to study. Now, the effects of O-GlcNAcylation on chaperone activity and the accompanying inhibition of amyloid fibril formation have been revealed, potentially yielding new routes to combat neurodegeneration.
- Sheena E. Radford
- & Theodoros K. Karamanos
-
Article |
 Cellular uptake of large biomolecules enabled by cell-surface-reactive cell-penetrating peptide additives
Cellular uptake of large biomolecules enabled by cell-surface-reactive cell-penetrating peptide additives
Robust delivery of proteins into cells is challenging, but it has now been shown that by conjugating arginine-rich cell-penetrating peptides to the surface of cells, proteins containing a cell-penetrating peptide can be delivered efficiently into them. Using a thiol-reactive cell-penetrating peptide enables thiol-containing proteins to be delivered by simple co-incubation.
- Anselm F. L. Schneider
- , Marina Kithil
- & Christian P. R. Hackenberger
-
Article |
 A far-red hybrid voltage indicator enabled by bioorthogonal engineering of rhodopsin on live neurons
A far-red hybrid voltage indicator enabled by bioorthogonal engineering of rhodopsin on live neurons
Voltage imaging is a powerful technique for studying electrical signalling in neurons. A palette of bright and sensitive voltage indicators has now been developed via enzyme-mediated ligation and Diels–Alder cycloaddition. Among these, a far-red indicator faithfully reports neuronal action potential dynamics with an excitation spectrum orthogonal to optogenetic actuators and green/red-emitting biosensors.
- Shuzhang Liu
- , Chang Lin
- & Peng Zou
-
News & Views |
 Decorating proteins with LACE
Decorating proteins with LACE
Labelling proteins at internal sites holds promise for generating novel protein conjugates in a programmable fashion. Now, a chemoenzymatic approach, dubbed LACE, enables the site-specific modification of recombinant proteins that contain a short genetically encoded tag.
- Maximilian Fottner
- & Kathrin Lang
-
Article |
 In situ chromatin interactomics using a chemical bait and trap approach
In situ chromatin interactomics using a chemical bait and trap approach
Proteins that interact with histone post-translational modifications have now been identified using an approach based on split-intein mediated histone semisynthesis. Histone modifications and disease-relevant mutations were installed into native chromatin with an adjacent photocross-linker to enable in situ cross-linking. This strategy enabled the determination of chromatin-relevant interactomes and represents a powerful tool for exploring epigenetic regulation and dysregulation at the molecular level.
- Antony J. Burton
- , Michael Haugbro
- & Tom W. Muir
-
Perspective |
 Proteomimetics as protein-inspired scaffolds with defined tertiary folding patterns
Proteomimetics as protein-inspired scaffolds with defined tertiary folding patterns
The complexity of proteins has inspired chemists to seek artificial mimetics of protein structure and function. Historically, most such work has focused on analogues of small, isolated segments; however, there is growing interest in mimicry of larger, intact tertiary folds. This Perspective surveys the emerging body of work on these agents, termed ‘proteomimetics’, discusses their construction and outlines some of the remaining challenges.
- W. Seth Horne
- & Tom N. Grossmann
-
Article |
 Protein engineering through tandem transamidation
Protein engineering through tandem transamidation
A method for engineering chemically modified proteins has now been developed using a chemoenzymatic cascade of sortase-mediated transpeptidation and protein trans-splicing. Using this one-pot approach enabled the generation of site-specifically modified proteins in vitro and in isolated cell nuclei.
- Robert E. Thompson
- , Adam J. Stevens
- & Tom. W. Muir
-
News & Views |
 Diverse engineering
Diverse engineering
Methods for generating molecular diversity provide a route to screen a wider section of chemical space, to discover compounds with useful biological properties. Now, a complexity-to-diversity strategy has enabled the discovery of a multi-cyclic structure from a complex natural product that induces ferroptotic cell death in cancer cells.
- Tatiana Cañeque
- & Raphaël Rodriguez
-
Article |
 Diverse compounds from pleuromutilin lead to a thioredoxin inhibitor and inducer of ferroptosis
Diverse compounds from pleuromutilin lead to a thioredoxin inhibitor and inducer of ferroptosis
A set of stereochemically complex and structurally diverse compounds were created from the diterpene natural product pleuromutilin using the complexity-to-diversity strategy. Phenotypic screening identified a compound that induces rapid ferroptotic death of cancer cells. Experiments to probe the mechanism revealed the compound to be an inhibitor of thioredoxin.
- Evijola Llabani
- , Robert W. Hicklin
- & Paul J. Hergenrother
-
Article |
 Dual chemical probes enable quantitative system-wide analysis of protein prenylation and prenylation dynamics
Dual chemical probes enable quantitative system-wide analysis of protein prenylation and prenylation dynamics
Two chemical probes, YnF and YnGG, that enable the identification of prenylated peptides and global analysis of protein prenylation using quantitative chemical proteomics have now been developed. Prenylation dynamics in response to pharmacological inhibition of prenyl-transferase enzymes were also studied. As a final demonstration, defective Rab prenylation in a model of the retinal degenerative disease choroideremia was also quantified.
- Elisabeth M. Storck
- , Julia Morales-Sanfrutos
- & Edward W. Tate
-
Article |
 A chemoselective strategy for late-stage functionalization of complex small molecules with polypeptides and proteins
A chemoselective strategy for late-stage functionalization of complex small molecules with polypeptides and proteins
The preparation of conjugates between proteins and small molecules is often challenging and requires several synthetic steps to functionalize each component for conjugation. Now, a conjugation methodology that leverages an electrophilic Se–S bond of selenocysteine to create bioconjugates between polypeptides and complex small molecules has been described.
- Daniel T. Cohen
- , Chi Zhang
- & Bradley L. Pentelute
-
Article |
 Mining the cellular inventory of pyridoxal phosphate-dependent enzymes with functionalized cofactor mimics
Mining the cellular inventory of pyridoxal phosphate-dependent enzymes with functionalized cofactor mimics
A chemical proteomic strategy has now been developed for profiling pyridoxal-phosphate dependent enzymes (PLP-DEs) in cells. Pyridoxal-based probes are phosphorylated in situ and bind to cellular PLP-DEs as cofactor mimics. The method accessed 73% of the Staphylococcus aureus PLP-dependent proteome and annotated uncharacterized proteins as novel PLP-DEs.
- Annabelle Hoegl
- , Matthew B. Nodwell
- & Stephan A. Sieber
-
Article |
 Ribosomal synthesis and folding of peptide-helical aromatic foldamer hybrids
Ribosomal synthesis and folding of peptide-helical aromatic foldamer hybrids
The extent to which peptide synthesis by the ribosome can tolerate the inclusion of non-peptidic components is not clear. Yet such hybrids would expand the range of ribosomally synthesized structures. Now it has been shown that tRNAs acylated by aromatic foldamers can initiate the ribosomal synthesis of non-cyclic and cyclic foldamer–peptide hybrid molecules. The oligo-aryl segments contain folding information that can control peptide conformation in the hybrids.
- Joseph M. Rogers
- , Sunbum Kwon
- & Ivan Huc
-
Review Article |
 Fluorescent nucleobases as tools for studying DNA and RNA
Fluorescent nucleobases as tools for studying DNA and RNA
The emergence of synthetic fluorescent nucleobases that can be incorporated into DNA and RNA in place of their natural counterparts has enabled new tools and technologies with applications in chemistry, biology and biomedicine. This Review discusses chemical insights into canonical and non-canonical nucleobase designs, relating structure to properties.
- Wang Xu
- , Ke Min Chan
- & Eric T. Kool
-
Article |
 Cell-permeable nanobodies for targeted immunolabelling and antigen manipulation in living cells
Cell-permeable nanobodies for targeted immunolabelling and antigen manipulation in living cells
Delivery of antibodies into living cells enables the labelling and manipulation of intracellular antigens; however, transporting antibodies into the cytosol in a functional state is difficult. Now, a modular strategy for creating cell-permeable nanobodies capable of targeting intracellular antigens has been developed. The cell-permeable nanobodies are formed by site-specific attachment of cyclic arginine-rich cell-penetrating peptides to camelid-derived single-chain antibody fragments.
- Henry D. Herce
- , Dominik Schumacher
- & Christian P. R. Hackenberger
-
Article |
 Engineering live cell surfaces with functional polymers via cytocompatible controlled radical polymerization
Engineering live cell surfaces with functional polymers via cytocompatible controlled radical polymerization
A cytocompatible controlled radical polymerization method has now been developed that initiates polymer synthesis directly on the surface of living cells. This method achieves significantly enhanced polymer grafting and enables active manipulation of cellular phenotypes.
- Jia Niu
- , David J. Lunn
- & Craig J. Hawker
-
News & Views |
 The missing link
The missing link
The targeted release of bioactive molecules to diseased tissues has the potential to improve therapeutic efficacy, but not all drugs contain a free functional group that can be easily attached to an antibody. Now, a linker technology has been developed to enable the traceless release of tertiary and heteroaryl amine-containing drugs.
- Tiago Rodrigues
- & Gonçalo J. L. Bernardes
-
Article |
 Chemoproteomic profiling and discovery of protein electrophiles in human cells
Chemoproteomic profiling and discovery of protein electrophiles in human cells
A chemical proteomic strategy is described for the discovery of protein-bound electrophilic groups in human cells. Using this approach, the dynamic regulation of the pyruvoyl catalytic cofactor in S-adenosyl-L-methionine decarboxylase was characterized and an N-terminal glyoxylyl modification on secernin proteins was discovered.
- Megan L. Matthews
- , Lin He
- & Benjamin F. Cravatt
-
News & Views |
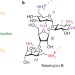 Shields for small molecules
Shields for small molecules
Nucleic acid aptamers have been employed to shield small molecules so that one among many similar reactive functional groups can be modified. This provides access to new chemical entities with potentially interesting properties while avoiding the use of covalent protecting groups.
- Scott K. Silverman
-
Article |
 Chemically homogeneous and thermally reversible oxidation of epitaxial graphene
Chemically homogeneous and thermally reversible oxidation of epitaxial graphene
Graphene oxide produced via the standard Hummers method possesses a high degree of chemical inhomogeneity and limited reversibility. Now, it has been shown that an alternative ultra-high-vacuum approach for oxidizing epitaxial graphene yields uniform epoxy functionalization with thermal reversibility at temperatures as low as 260 °C.
- Md. Zakir Hossain
- , James E. Johns
- & Mark C. Hersam

 Deciphering functional roles of protein succinylation and glutarylation using genetic code expansion
Deciphering functional roles of protein succinylation and glutarylation using genetic code expansion