Original Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Rapid Communication |
 Mussel-inspired interfacial ultrathin films for cellular adhesion on the wrinkled surfaces of hydrophobic fluids
Mussel-inspired interfacial ultrathin films for cellular adhesion on the wrinkled surfaces of hydrophobic fluids
Inspired by mussel adhesion, polydopamine ultrathin films were formed at silicone oil/water interfaces even in neutral solutions. The MCF-7 cells successfully adhered to the oil/water interface without aggregation during cell growth. The interfacial wrinkles were induced by changes in the oil volume and the compressive stress, and the MCF-7 cells adhered to the oil/water interface and were arranged along the wrinkles. The polydopamine interfacial films provide new opportunities to investigate the relationships between toughness and patterns for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine.
- Hiroya Abe
- , Tomoya Ina
- & Matsuhiko Nishizawa
-
Focus Review |
 Functionalization of acyclic xenonucleic acid with modified nucleobases
Functionalization of acyclic xenonucleic acid with modified nucleobases
Nucleobase modification of acyclic XNA oligomers achieved functionalization for use as a novel fluorescent probe and photoswitching system. A linear probe, composed of serinol nucleic acid (SNA) and 5-perylenylethynyl uracil residues, enabled quantitative detection of target RNA through a visually observable change in fluorescent color and intensity. A photoresponsive SNA with two 8-pyrenylvinyl adenine (PVA) residues established photocontrol of SNA/RNA duplex formation and dissociation. Using a combination of 8-naphthylvinyl adenine (NVA) and PVA demonstrated orthogonal photocontrol system. Thus, nucleobase modifications further expand the utility of acyclic XNA in bionanotechnology.
- Keiji Murayama
- , Yuuhei Yamano
- & Hiroyuki Asanuma
-
Focus Review
| Open Access Bridging polymer chemistry and cryobiology
Bridging polymer chemistry and cryobiology
This review outlines the research across the areas of polymer chemistry and cryobiology We discuss the solutions to problems in cryobiology from the viewpoint of polymeric materials science and the applications of polymer-based cryobiology for biomedical applications. We explain how the recent advances in polymer research have enabled the development of innovative polymeric cryoprotectants with novel mechanisms and the development of state-of-the-art methods for the intracellular delivery of substances, such as drugs, using a cryobiological technique called the freeze-concentration effect.
- Kazuaki Matsumura
- , Robin Rajan
- & Sana Ahmed
-
Focus Review |
 Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)-based temperature- and pH-responsive polymer materials for application in biomedical fields
Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)-based temperature- and pH-responsive polymer materials for application in biomedical fields
Among stimuli-responsive polymers, thermoresponsive poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (PNIPAAm) is the most widely investigated. PNIPAAm-based polymers can undergo appropriate changes in response to their external environment. In this focus review, recent advancements in the applications of stimuli-responsive polymers based on PNIPAAm in biomedical fields are summarized, with an emphasis on our own research. In particular, a summary of the design of polymers for application in the separation and purification of (bio)pharmaceutical products and controlled cellular uptake is provided.
- Yuki Hiruta
-
Original Article
| Open Access Structural and mechanical properties of biodegradable poly(lactic acid) and pectin composites: using bionucleating agent to improve crystallization behavior
Structural and mechanical properties of biodegradable poly(lactic acid) and pectin composites: using bionucleating agent to improve crystallization behavior
PLA-pectin biocomposites were prepared at pectin contents from 2 to 8% w/w. The mechanical properties of PLA-pectin were considerably improved after the annealing process, especially at 4% w/w of pectin according to being the best dispersion indicated by SEM and synchrotron-based FT-IR mapping. Moreover, pectin aids in the crystallization of PLA confirmed by in situ SR-WAXS. The crystallization rate and crystallinity were maximum at 8% w/w pectin addition. Finally, the pectin dispersion is the main factor in determining the mechanical and thermal properties of biocomposites.
- Apiwat Satsum
- , Wutthikrai Busayaporn
- & Chokchai Wanapu
-
Original Article |
 Accelerated transgene expression of pDNA/polysaccharide complexes by solid-phase reverse transfection and analysis of the cell transfection mechanism
Accelerated transgene expression of pDNA/polysaccharide complexes by solid-phase reverse transfection and analysis of the cell transfection mechanism
We developed pDNA/polysaccharide complexes suitable for reverse transfection (RTF) and investigated their transfection mechanisms. The pDNA/chitosan/hyaluronic acid ternary complexes showed excellent transfection efficiency in RTF compared with the conventional forward transfection (FTF). The ternary complexes were taken up via macropinocytosis in RTF. Furthermore, the ternary complexes in RTF were transported to late endosomes via microtubules, and were remarkably accumulated in the nucleus. These results suggest that the cell transfection efficiency of the ternary complexes in RTF was enhanced by their efficient delivery to the nucleus via late endosomes.
- Takahiro Arai
- , Yu Aiki
- & Toshinori Sato
-
Focus Review |
 A new approach to explore the mechanoresponsiveness of microtubules and its application in studying dynamic soft interfaces
A new approach to explore the mechanoresponsiveness of microtubules and its application in studying dynamic soft interfaces
Recent studies on exploration of mechanical deformation of microtubules under tensile and compressive stress, using a newly developed methodology, have been reviewed. In the first part of this review article, development of the methodology and its utility in studying the mechanoresponsiveness of microtubules have been described. In the second part, applications of the recently developed methodology in studying dynamic soft interfaces have been elaborately discussed.
- Arif Md. Rashedul Kabir
- & Akira Kakugo
-
Focus Review |
 Intracellular self-assembly of supramolecular gelators to selectively kill cells of interest
Intracellular self-assembly of supramolecular gelators to selectively kill cells of interest
Peptides conjugated with hydrophobic moieties are typical examples of supramolecular gelators (low molecular weight gelators, LMWGs), which can be designed or programmed to self-assemble to form nanofibers/nanosheets in response to stimuli or microenvironments. In the last decade, several groups have reported that the self-assembly of small gelator molecules achieved inside living cells or on the surfaces of living cells induced selective cell death. This focused review outlines the self-assembly of small gelator molecules inside or around living cells that control cell fate.
- Tatsuo Maruyama
- & Witta Kartika Restu
-
Original Article |
 Development of chitinous nanofiber-based flexible composite hydrogels capable of cell adhesion and detachment
Development of chitinous nanofiber-based flexible composite hydrogels capable of cell adhesion and detachment
Chitinous nanofibers (NFs) exhibit a specific physiological activity not observed in the powdered form. Herein, we aimed to develop a cell-adhesive chitinous NF-based flexible hydrogel. The desired cell-adhesive flexible hydrogel was obtained by introducing cationic groups and vinyl polymerizable functional groups on the surface deacetylated chitin NFs as well as copolymerizing it with N-isopropylacrylamide monomer in an aqueous system. Cells adhered to the gel could be detached by cooling to 4 °C. The composite hydrogel fabricated here may be useful as a cell culture scaffold material in regenerative medicine.
- Kenki Goto
- & Yoshikuni Teramoto
-
Original Article |
 Efficient synthesis, characterization, and application of biobased scab-bionic hemostatic polymers
Efficient synthesis, characterization, and application of biobased scab-bionic hemostatic polymers
A series of polymeric hemostatic materials are prepared in one-step, by using biobased lactic acid monomers and mature hemostatic drugs (4-aminomethylbenzoic acid or tranexamic acid) through direct melt polycondensation. These materials are powdery with rough and irregular surfaces, and the powder particle size is ~8–30 μm, which is beneficial to the application, immediate hemostasis and scab-bionic membrane forming. Moreover, after the degradation of these materials at 37 °C, more monomers will be released, resulting in a higher efficiency and long-term hemostatic function.
- Jian-Yun Lin
- , Shi-He Luo
- & Zhao-Yang Wang
-
Original Article |
 Sonoporation-based labeling of mesenchymal stem cells with polymeric MRI contrast agents for live-cell tracking
Sonoporation-based labeling of mesenchymal stem cells with polymeric MRI contrast agents for live-cell tracking
We optimized the sonoporation of a suspension culture with microbubbles for labeling and MR tracking of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). When water was used as the transmission medium between the acoustic probe and cell suspension, microbubbles gently collapsed with minimal cell damage. Under this condition, the number of labeled MSCs was 25%, which is 3.3-fold greater than the number of MSCs labeled using the conventional electroporation system, and the cell viability was maintained at approximately 80%. The MRI signal could be clearly observed for 2.0 × 106 MSCs.
- Atsushi Mahara
- , Naoki Kobayashi
- & Tetsuji Yamaoka
-
Invited Review |
 Characterization of polymer materials based on structure analyses of vicinal water
Characterization of polymer materials based on structure analyses of vicinal water
Susceptible situation of water molecules in the vicinity of lopsidedly charged copolymer films (upper) and a zwitterionic copolymer film. The charge-neutralized polymer surface is less perturbative to the structure of vicinal water. The image first published in Kobunshi 39, 445 (Hot Topics) (2014).
- Hiromi Kitano
-
Original Article |
 A peptide release system using a photo-cleavable linker in a cell array format for cell-toxicity analysis
A peptide release system using a photo-cleavable linker in a cell array format for cell-toxicity analysis
A novel peptide-array format system with a photo-cleavage linker for cellular toxicity analysis was constructed. In this system, a peptide was immobilized on a commercially available plate bottom via the photo-cleavable linker. UV light irradiation on the desired wells releases the peptide from the plate bottom, and then the cytotoxic behavior of the peptide can be monitored.
- Takashi Kakiyama
- , Kenji Usui
- & Hisakazu Mihara
-
Original Article |
 Hydrogel scaffolds composed of genetically synthesized self-assembling peptides for three-dimensional cell culture
Hydrogel scaffolds composed of genetically synthesized self-assembling peptides for three-dimensional cell culture
Two and three times repeats of the self-assembling peptide RADA16 (RADARADARADARADA), namely RADA16x2 and RADA16x3, were genetically produced. The peptides were expressed as fusion proteins while retaining the activity of the fusion partner protein. The expressed peptides exhibited both fibril formation and cell adhesive activity. Moreover, the hydrogels formed by the peptides via addition of a medium provided a three-dimensional environment for cell proliferation.
- Masayasu Mie
- , Mayu Oomuro
- & Eiry Kobatake
-
Note |
 Enzymatic emulsifier-free emulsion polymerization to prepare polystyrene particles using horseradish peroxidase as a catalyst
Enzymatic emulsifier-free emulsion polymerization to prepare polystyrene particles using horseradish peroxidase as a catalyst
Monodisperse polystyrene particles were prepared by enzymatic emulsifier-free emulsion polymerization using a horseradish peroxidase (HRP)/H2O2/β-diketone system in water. The resultant polymer particles were stabilized by the β-diketone moieties located at the surface of the particle. Enzymatic emulsifier-free emulsion polymerization might offer a practical method for the preparation of polymer particles under mild enzymatic conditions (that is, room temperature and surfactant-free).
- Michinari Kohri
- , Satoshi Uzawa
- & Takayuki Nakahira
-
Original Article |
 Characterization and structural determination of 3A-amino-3A-deoxy-(2AS, 3AS)-cyclodextrins by NMR spectroscopy
Characterization and structural determination of 3A-amino-3A-deoxy-(2AS, 3AS)-cyclodextrins by NMR spectroscopy
The proton and carbon NMR resonances have been assigned for 3A-amino-3A-deoxy(2AS,3AS)-α-, β- and γ-CyDs (3α, 3β and 3γ). In these CyDs, a glucose residue has been replaced by an altro-pyranose unit with an axial hydroxyl group. Assignments were made with one-dimensional NMR and COSY, TOCSY, ROESY and CHSHF (heteronuclear shift correlation) spectra. Titration by NMR shift changes gave amino-group pKa values of 7.73 and 8.84 for 3β (left) and 6A-amino-6A-deoxy-β-CyD (6β, right), respectively.
- Keiko Takahashi
- , Keita Andou
- & Shoji Fujiwara
-
Original Article |
 Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)-modified silica beads with hyperbranched polysiloxysilane for three-dimensional cell cultivation
Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)-modified silica beads with hyperbranched polysiloxysilane for three-dimensional cell cultivation
The objective of this study is to establish an immobilization method of PNIPAM on silica beads surface-modified by HBPS, which could be applied to cell cultivation. The PNIPAM-modified silica beads with enough loading of N-isopropylacrylamide (cleaved PNIPAM Mn=14 800 and 23 700) shows controlled cell adhesion and detachment due to lower critical solution temperature behavior of PNIPAM.
- Bo Ra Park
- , Yuta Nabae
- & Masa-aki Kakimoto
-
Original Article |
 Change in local dynamics of bacteriorhodopsin with retinal isomerization under pressure as studied by fast magic angle spinning NMR
Change in local dynamics of bacteriorhodopsin with retinal isomerization under pressure as studied by fast magic angle spinning NMR
Bacteriorhodopsin (bR) has a retinal with all-trans and 13-cis, 15-syn configurations whose isomeric ratio is close to 1 in the dark and the population of 13-cis, 15-syn configuration can be increased under the pressurized condition. Increase of pressure by fast magic angle spinning (MAS) induced dynamics change at around Ala81 and Ala84 in bR together with retinal isomerization from all-trans to 13-cis configurations. We demonstrated that fast MAS NMR provides a pressure sauce for investigating the structure and dynamics change of biomacromolecules.
- Izuru Kawamura
- , Satoru Yamaguchi
- & Akira Naito
-
Original Article |
 Preparation of stimulus-sensitive gel particles with a DNA-dye complex and their pH sensitivity
Preparation of stimulus-sensitive gel particles with a DNA-dye complex and their pH sensitivity
Poly(acrylic acid) (PAAc) gel particles with DNA–ethidium bromide (EtBr) was synthesized and pH-sensitivity and fluorescence property were evaluated for applying to optical micro-pH sensor. Swelling ratio of PAAc gel particles with DNA–EtBr complexes were regularly changed with pH and the gel particle responded to pH for about 60 s. Furthermore, fluorescence intensity of PAAc gel particles with DNA–EtBr complexes were detected with high-sensitivity and changed in response to pH as shown in figure (The left shows the gel particles in pH 2.1 and the right shows in pH 11).
- Takashi Nishiyama
- , Yoshiharu Kagami
- & Norio Tsubokawa
-
Note |
 Near-infrared fluorescent nanoparticle of low-bandgap π-conjugated polymer for in vivo molecular imaging
Near-infrared fluorescent nanoparticle of low-bandgap π-conjugated polymer for in vivo molecular imaging
Polymer nanoparticles (PNPs) that consist of a low-bandgap conjugated polymer, co-poly(2,3-diphenylthieno[3,4-b]pyrazine-alt-9,9-dioctylfluorene), were prepared for the photoluminescence in vivo imaging in the near infrared region. The emission efficiency was enhanced by the fluorescent resonance energy transfer from the conjugated polymer to a silicon naphthalocyanine dye. The dye-doped conjugated PNPs enabled the bright fluorescence imaging of live mice.
- Hiroyuki Aoki
- , Jun-ichi Kakuta
- & Shinzaburo Ito
-
Rapid Communication |
 Segmental orientation of a single polymer chain in Langmuir–Blodgett films studied by defocus fluorescence imaging
Segmental orientation of a single polymer chain in Langmuir–Blodgett films studied by defocus fluorescence imaging
- Hiroyuki Aoki
- , Toshiaki Takahashi
- & Shinzaburo Ito
-
Invited Article |
 Polyelectrolyte multilayers-modified membrane filter for rapid immunoassay: protein condensation by centrifugal permeation
Polyelectrolyte multilayers-modified membrane filter for rapid immunoassay: protein condensation by centrifugal permeation
Polyelectrolyte multilayers-modified membrane filter, leading to achieve rapid immunoassay as compared with the conventional enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) system. The antigen–antibody reaction was carried out by the centrifugal permeation of antigen solution allowing the local condensation of the antigen molecules in the proximity of the primary antibody. Hence, the incubation time for the antigen–antibody reaction was just permeation time, 3 min, which overcomes the molecular diffusion as rate-limiting factor compared with conventional ELISA method.
- Heyun Shen
- , Junji Watanabe
- & Mitsuru Akashi
-
Original Article |
 Chiral recognition ability of cellulose derivatives bearing pyridyl and bipyridyl residues as chiral stationary phases for high-performance liquid chromatography
Chiral recognition ability of cellulose derivatives bearing pyridyl and bipyridyl residues as chiral stationary phases for high-performance liquid chromatography
The cellulose derivatives bearing pyridyl and bipyridyl residues were synthesized, and their recognition abilities as chiral stationary phases for high-performance liquid chromatography were evaluated. Among them, the cellulose derivatives with regioselective substitution of bipyridyl residues exhibited a relatively high chiral recognition. The recognition ability of the derivatives was significantly influenced by the coordination of a Cu(II) ion to the bipyridyl residues. In addition, the derivatives were also used for the ligand-exchange chromatography with an eluent containing a copper salt in order to directly separate amino acids without derivatization.
- Yasunaka Katoh
- , Yasutaka Tsujimoto
- & Yoshio Okamoto
-
Original Article |
 Uniform poly(methyl methacrylate) stereostars: synthesis, separation and stereocomplex formation
Uniform poly(methyl methacrylate) stereostars: synthesis, separation and stereocomplex formation
Isotactic (it-) and syndiotactic (st-) uniform poly(methyl methacrylate)s (PMMAs) with hydroxyl end group, isolated by supercritical fluid chromatography (SFC), were reacted with benzene-1,3,5-tricarbonyl trichloride, and two types of uniform three-arm star-PMMAs with different stereoregular arms, [it/it/st]- and [it/st/st]-3-star-PMMAs, were isolated by SFC from the product mixture. The stereocomplex formation of these stereostar PMMAs was examined in acetone. Although both stereostar PMMAs formed intramolecular stereocomplexes, the [it/st/st]-3-star-PMMA, in particular, was found to form two types of intramolecular stereocomplexes with different hydrodynamic volumes because of different compositions of it- and st-PMMA arms involved in the stereocomplexes.
- Takafumi Nishiura
- , Yoshinori Abe
- & Tatsuki Kitayama
-
Original Article |
 Preparation methods of alginate micro-hydrogel particles and evaluation of their electrophoresis behavior for possible electronic paper ink application
Preparation methods of alginate micro-hydrogel particles and evaluation of their electrophoresis behavior for possible electronic paper ink application
For the purpose of an electric paper application, alginate hydrogel particles were prepared. To increase their zeta potential for well response by electric fields, their surface were modified chemically. Electro-response behaviors were observed between comb-shaped electrodes. It was found that surface-modified alginate hydrogel particles were well responded by applied low voltage 4–9 V.
- Daisaku Kaneko
- , Nguyen Quyen Thi le
- & Tatsuo Kaneko
-
Original Article |
 Highly efficient enzymatic catalysis for cyclocarbonate polymerization
Highly efficient enzymatic catalysis for cyclocarbonate polymerization
PPMC with a high Mn of up to 6.0 × 104 g mol−1 can be readily afforded under the catalysis of an immobilized lipase from Candida antarctica (Novozym-435). The result sounds attractive, as presently the low catalytic efficiency is known as the main restriction for the industrialization of enzyme catalysis.
- Xiao-hua Luo
- , Jun Feng
- & Ren-xi Zhuo
-
Original Article |
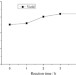 Synthesis of antibacterial polymers from 2-dimethylamino ethyl methacrylate quaternized by dimethyl sulfate
Synthesis of antibacterial polymers from 2-dimethylamino ethyl methacrylate quaternized by dimethyl sulfate
An antibacterial quaternary ammonium acrylic monomer 1 was synthesized by quaternization of 2-dimethylamino ethyl methacrylate with dimethyl sulfate. This synthetic route was able to obtain the quaternary ammonium monomer 1 of high yield and low cost. The corresponding homopolymers were then synthesized by free radical polymerization using potassium persulfate as the initiator and H2O as the solvent. Interestingly, it was found that 2 had significantly higher antibacterial activity than 1, although 1 exhibited moderate antibacterial activity.
- Huajiang Zuo
- , Dingcai Wu
- & Ruowen Fu
-
Rapid Communication |
 Local conformation of serine residues in a silk model peptide, (Ala–Gly–Ser–Gly–Ala–Gly)5, studied with solid-state NMR:REDOR
Local conformation of serine residues in a silk model peptide, (Ala–Gly–Ser–Gly–Ala–Gly)5, studied with solid-state NMR:REDOR
- Yu Suzuki
- & Tetsuo Asakura
-
Invited Article |
 Enantioseparation using amylose esters as chiral stationary phases for high-performance liquid chromatography
Enantioseparation using amylose esters as chiral stationary phases for high-performance liquid chromatography
Novel amylose ester derivatives were synthesized and their chiral recognition abilities as chiral stationary phases for high-performance liquid chromatography were evaluated. Among the prepared derivatives, the nonsubstituted cinnamate derivative showed a relatively high chiral recognition, and interestingly, its ability was influenced by the preparation conditions of packing materials using silica gel as a support.
- Yuri Sugiura
- , Chiyo Yamamoto
- & Yoshio Okamoto
-
Review |
 Synthesis and structure determination of helical polymers
Synthesis and structure determination of helical polymers
The recent remarkable progress in structural investigations of helical polymers by high-resolution atomic force microscopy provides their exact helical structures including helical pitch and handedness. Seeing is believing!
- Eiji Yashima
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Analytical biochemistry
- Behavioural methods
- Bioinformatics
- Biological models
- Biophysical methods
- Cytological techniques
- Electrophysiology
- Epigenetics analysis
- Experimental organisms
- Gene delivery
- Gene expression analysis
- Genetic engineering
- Genetic techniques
- Genomic analysis
- High-throughput screening
- Imaging
- Immunological techniques
- Isolation, separation and purification
- Lab-on-a-chip
- Mass spectrometry
- Metabolomics
- Microbiology techniques
- Microscopy
- Molecular engineering
- Nanobiotechnology
- Optogenetics
- Proteomic analysis
- Sensors and probes
- Sequencing
- Software
- Optical spectroscopy
- Structure determination

 Construction of peptide/plasmid DNA complexes for plant gene transfection via the basic leucine zipper domain
Construction of peptide/plasmid DNA complexes for plant gene transfection via the basic leucine zipper domain