Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access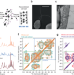 Molecular-level architecture of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii’s glycoprotein-rich cell wall
Molecular-level architecture of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii’s glycoprotein-rich cell wall
Chlamydomonas reinhardtii produces a glycoprotein-rich cell wall. Using nuclear magnetic resonance and mass spectrometry approaches, this study reveals unprecedented details on its protein and carbohydrate content, and provide an atomic-level architecture model.
- Alexandre Poulhazan
- , Alexandre A. Arnold
- & Isabelle Marcotte
-
Article
| Open Access An intranasal live-attenuated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine limits virus transmission
An intranasal live-attenuated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine limits virus transmission
In this study, the authors evaluated the protective capacity of a mucosal, live-attenuated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine and show that it induces systemic and mucosal humoral immunity, protects from clinical disease symptoms, and prevents virus transmission in hamsters more efficiently than an intramuscular mRNA vaccine.
- Julia M. Adler
- , Ricardo Martin Vidal
- & Jakob Trimpert
-
Article
| Open Access Fluorogenic CRISPR for genomic DNA imaging
Fluorogenic CRISPR for genomic DNA imaging
Conventional CRISPR-based approaches to monitor genomic loci can be hampered by high background and nonspecific nucleolar signal. Here, the authors propose a fluorogenic CRISPR (fCRISPR) tool that allows for high-contrast and sensitive imaging of genomic DNA.
- Zhongxuan Zhang
- , Xiaoxiao Rong
- & Xing Li
-
Article
| Open Access DeepFocus: fast focus and astigmatism correction for electron microscopy
DeepFocus: fast focus and astigmatism correction for electron microscopy
High-throughput electron microscopy demands minimal human intervention and high image quality. Here, authors introduce DeepFocus, a data-driven method for aberration correction in electron microscopy, robust for low SNR images, fast and easily adaptable to microscopes and samples. Peer Review Information: Nature Communications thanks Yang Zhang and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work. A peer review file is available.
- P. J. Schubert
- , R. Saxena
- & J. Kornfeld
-
Article
| Open Access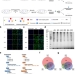 Nuclear and cytoplasmic specific RNA binding proteome enrichment and its changes upon ferroptosis induction
Nuclear and cytoplasmic specific RNA binding proteome enrichment and its changes upon ferroptosis induction
The reported assay shows a subcellular-specific RNA labeling method for efficient enrichment and deep profiling of nuclear and cytoplasmic RBPs, the authors apply this to investigate changes of subcellular-specific RBP-RNA interactions in ferroptosis.
- Haofan Sun
- , Bin Fu
- & Weijie Qin
-
Article
| Open Access Expanded palette of RNA base editors for comprehensive RBP-RNA interactome studies
Expanded palette of RNA base editors for comprehensive RBP-RNA interactome studies
RNA base-editors are often used in methods for RNA binding protein (RBP) target discovery. Here the authors present a new RBP target discovery method, PRINTER, and suggest optimal RNA base-editors for dual-RBP studies, emphasizing the importance of matching rBEs’ editing biases with RBPs’ binding preferences.
- Hugo C. Medina-Munoz
- , Eric Kofman
- & Gene W. Yeo
-
Article
| Open Access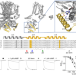 A high affinity switch for cAMP in the HCN pacemaker channels
A high affinity switch for cAMP in the HCN pacemaker channels
Cyclic AMP modulation of HCN channels underlies beta adrenergic stimulation of heart rate. Here, authors describe an intramolecular mechanism that controls cAMP affinity of the cyclic nucleotide binding domain of these channels.
- Alessandro Porro
- , Andrea Saponaro
- & Anna Moroni
-
Article
| Open Access Identification of a highly conserved neutralizing epitope within the RBD region of diverse SARS-CoV-2 variants
Identification of a highly conserved neutralizing epitope within the RBD region of diverse SARS-CoV-2 variants
Most recent SARS-CoV-2 variants showed exceptional immune evasion properties. Here, the authors identify a highly conserved epitope within the RBD targeted by a broad spectrum neutralizing antibody BA7535 that shows therapeutic antiviral potency in mouse studies.
- Yanqun Wang
- , An Yan
- & Jincun Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access BacPE: a versatile prime-editing platform in bacteria by inhibiting DNA exonucleases
BacPE: a versatile prime-editing platform in bacteria by inhibiting DNA exonucleases
Prime editing in bacteria is currently inefficient. Here the authors report BacPE, a versatile prime editing platform in Escherichia coli that works by inhibiting 3′→5′ DNA exonucleases, highlighting the intrinsic genetic factors that are adverse to efficient prime editing.
- Hongyuan Zhang
- , Jiacheng Ma
- & Quanjiang Ji
-
Article
| Open Access Chemically-defined and scalable culture system for intestinal stem cells derived from human intestinal organoids
Chemically-defined and scalable culture system for intestinal stem cells derived from human intestinal organoids
Challenges in reproducibility and large-scale expansion limit the current applicability of human intestinal organoids. Here, the authors present a feeder-free, chemically-defined culture method for enrichment of intestinal stem cells isolated from 3D human intestinal organoids.
- Ohman Kwon
- , Hana Lee
- & Mi-Young Son
-
Article
| Open Access Intraocular liver spheroids for non-invasive high-resolution in vivo monitoring of liver cell function
Intraocular liver spheroids for non-invasive high-resolution in vivo monitoring of liver cell function
Longitudinal monitoring of liver function in vivo is hindered by the lack of high-resolution non-invasive imaging techniques. Here, the authors show a crucial and unique tool for longitudinal in vivo imaging of liver spheroids at cellular resolution to study liver physiology and disease.
- Francesca Lazzeri-Barcelo
- , Nuria Oliva-Vilarnau
- & Per-Olof Berggren
-
Article
| Open Access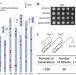 Large-scale genomic rearrangements boost SCRaMbLE in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Large-scale genomic rearrangements boost SCRaMbLE in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Synthetic Chromosome Rearrangement and Modification by LoxP-mediated Evolution (SCRaMbLE) is a promising tool to study genomic rearrangements. Here the authors present an engineered yeast strain with 83 sparsely distributed loxPsym sites across the genome can genrerate large-scale genomic rearrangements, which benefits cell fitness under stress and boosts the SCRaMbLE system when combined with synthetic chromosomes.
- Li Cheng
- , Shijun Zhao
- & Junbiao Dai
-
Article
| Open Access SiFT: uncovering hidden biological processes by probabilistic filtering of single-cell data
SiFT: uncovering hidden biological processes by probabilistic filtering of single-cell data
Cells simultaneously encode multiple signals, some harder to recover. Here, authors introduce SiFT (Signal FilTering), a kernel-based projection method, revealing underlying biological processes in single-cell data.
- Zoe Piran
- & Mor Nitzan
-
Article
| Open Access Human coronavirus OC43-elicited CD4+ T cells protect against SARS-CoV-2 in HLA transgenic mice
Human coronavirus OC43-elicited CD4+ T cells protect against SARS-CoV-2 in HLA transgenic mice
The origin of SARS-CoV-2 cross-reactive T cells in unexposed humans is unclear. Here, the authors use HLA transgenic mouse models of sequential infections with human coronavirus OC43 and SARSCoV-2 and show that OC43 elicits cross-protective immunity against SARS-CoV-2, which partially depends on CD4 + T cells.
- Rúbens Prince dos Santos Alves
- , Julia Timis
- & Sujan Shresta
-
Article
| Open Access Life-history stage determines the diet of ectoparasitic mites on their honey bee hosts
Life-history stage determines the diet of ectoparasitic mites on their honey bee hosts
Varroa and Tropilaelaps mites threaten honeybee health. This study finds that mites alter feeding habits depends on their own, and hosts’, life history stage. Mites feed on the host hemolymph when parasitizing pupae during their reproductive stage but consume fat body during their dispersal stage.
- Bin Han
- , Jiangli Wu
- & Shufa Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Anti-correlated feature selection prevents false discovery of subpopulations in scRNAseq
Anti-correlated feature selection prevents false discovery of subpopulations in scRNAseq
Typical single-cell RNAseq pipelines will subcluster homogeneous cells. Here, authors present a computational algorithm for accurately identifying cell-type marker genes in single-cell data analysis with a low false discovery rate.
- Scott R. Tyler
- , Daniel Lozano-Ojalvo
- & Eric E. Schadt
-
Article
| Open Access Rapid and visual identification of β-lactamase subtypes for precision antibiotic therapy
Rapid and visual identification of β-lactamase subtypes for precision antibiotic therapy
The rapid identification of drug-resistant bacteria is vital for effective treatment and to avoid antibiotic misuse. Here authors report a paper-based sensor which utilises chromogenic carbapenem and cephalosporin substrates for the identification and discrimination of β-lactamase subtypes.
- Wenshuai Li
- , Jingqi Li
- & Dingbin Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Shape-changing electrode array for minimally invasive large-scale intracranial brain activity mapping
Shape-changing electrode array for minimally invasive large-scale intracranial brain activity mapping
The invasiveness of extensive craniotomy hinders large-scale cortex mapping. Here, the authors developed a flexible, shape-changing electrode array which enables minimally invasive implantation and achieves high spatiotemporal resolution brain mapping.
- Shiyuan Wei
- , Anqi Jiang
- & Xiaojie Duan
-
Article
| Open Access A one-two punch targeting reactive oxygen species and fibril for rescuing Alzheimer’s disease
A one-two punch targeting reactive oxygen species and fibril for rescuing Alzheimer’s disease
Toxic amyloid-beta plaque and harmful inflammation are two leading hallmarks of Alzheimer’s disease (AD), and precise AD therapy is elusive due to the lack of dual-targeting therapy function, limited blood-brain barrier penetration, and low imaging sensitivity. Here, the authors address these issues by designing a near-infrared-II aggregation-induced emission nanotheranostic for precise AD therapy.
- Jiefei Wang
- , Ping Shangguan
- & Ben Zhong Tang
-
Article
| Open Access Ratiometric fluorescent sensing of pyrophosphate with sp³-functionalized single-walled carbon nanotubes
Ratiometric fluorescent sensing of pyrophosphate with sp³-functionalized single-walled carbon nanotubes
Inorganic pyrophosphate is a key molecule in many biological processes. Here, the authors develop an optical sensor that enables its ratiometric detection in the near infrared with functionalized single-walled carbon nanotubes.
- Simon Settele
- , C. Alexander Schrage
- & Jana Zaumseil
-
Article
| Open Access Folding pathway of a discontinuous two-domain protein
Folding pathway of a discontinuous two-domain protein
Here, using single molecule FRET, the unfolding and folding of a discontinuous two-domain protein was studied. The authors find that a dynamic, intermediate population entropically limits the rate of folding while the order of domain folding is kept in a slow-folding mutant.
- Ganesh Agam
- , Anders Barth
- & Don C. Lamb
-
Article
| Open Access Programmable RNA base editing with photoactivatable CRISPR-Cas13
Programmable RNA base editing with photoactivatable CRISPR-Cas13
Cas13 systems suffer from a lack of spatiotemporal control. Here the authors report paCas13, a light-inducible Cas13 system created by fusing Magnet with fragment pairs; they also report padCas13, a light-inducible base-editing system by fusing ADAR2 to catalytically inactive paCas13 fragments.
- Jeonghye Yu
- , Jongpil Shin
- & Won Do Heo
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular quantitative trait loci in reproductive tissues impact male fertility in cattle
Molecular quantitative trait loci in reproductive tissues impact male fertility in cattle
Investigating the genetics of male fertility requires comprehensive genotype and phenotype data. Here, the authors characterize the transcriptional complexity of bovine male reproductive tissues to identify loci associated with male fertility.
- Xena Marie Mapel
- , Naveen Kumar Kadri
- & Hubert Pausch
-
Article
| Open Access Self-renewing human naïve pluripotent stem cells dedifferentiate in 3D culture and form blastoids spontaneously
Self-renewing human naïve pluripotent stem cells dedifferentiate in 3D culture and form blastoids spontaneously
Blastoids are emerging models for early embryo development exploration in vitro. Here, authors found self-renewing human naïve PSCs spontaneously and efficiently give rise to blastoids upon three-dimensional suspension culture.
- Mingyue Guo
- , Jinyi Wu
- & José C. R. Silva
-
Article
| Open Access Nanoparticle-based DNA vaccine protects against SARS-CoV-2 variants in female preclinical models
Nanoparticle-based DNA vaccine protects against SARS-CoV-2 variants in female preclinical models
Here the authors screen different lipid nanoparticle (LNP) formulations for intramuscular delivery of plasmid DNA and uptake by antigen-presenting cells. The lead LNP exhibits immunogenicity and protection in small animal models that is comparable to approved SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine formulations.
- Lays Cordeiro Guimaraes
- , Pedro Augusto Carvalho Costa
- & Pedro Pires Goulart Guimaraes
-
Article
| Open Access Antibody-dependent enhancement of toxicity of myotoxin II from Bothrops asper
Antibody-dependent enhancement of toxicity of myotoxin II from Bothrops asper
The recent emergence of monoclonal antibodies able to neutralize snake toxins have revolutionized the approach of developing novel therapies to treat snakebite envenoming, at least in animal models. Here, the authors show antibody-dependent enhancement of toxicity (ADET) for a toxin derived from snake venom and highlight the importance of this phenomenon when testing therapeutic antibodies against snake venoms in animal models.
- Christoffer V. Sørensen
- , Julián Fernández
- & Andreas H. Laustsen
-
Article
| Open Access Reprogramming mechanism dissection and trophoblast replacement application in monkey somatic cell nuclear transfer
Reprogramming mechanism dissection and trophoblast replacement application in monkey somatic cell nuclear transfer
Somatic cloning of rhesus monkey has not been successful until now. Here, authors report epigenetic abnormalities in SCNT embryos and placentas and develop a trophoblast replacement method that enables them to successful clone of a healthy male rhesus monkey.
- Zhaodi Liao
- , Jixiang Zhang
- & Qiang Sun
-
Article
| Open Access DiffDomain enables identification of structurally reorganized topologically associating domains
DiffDomain enables identification of structurally reorganized topologically associating domains
Topologically associating domains (TADs) are critical structural units in 3D genome organization, and their reorganization between health and disease states is associated with essential genome functions. However, computational methods for identifying reorganized TADs are still in the early stages of development. Here, the authors present an algorithm leveraging random matrix theory to identify reorganized TADs.
- Dunming Hua
- , Ming Gu
- & Dechao Tian
-
Article
| Open Access Massively parallel profiling of RNA-targeting CRISPR-Cas13d
Massively parallel profiling of RNA-targeting CRISPR-Cas13d
Systematic understanding of CRISPR enzyme RNA binding specificity and cleavage is lacking. Here the authors report RNA chip-hybridised association-mapping platform (RNA-CHAMP), a workflow that repurposes next generation DNA sequencing chips to measure the binding affinity for RNA targets.
- Hung-Che Kuo
- , Joshua Prupes
- & Ilya J. Finkelstein
-
Article
| Open Access Direct RNA sequencing coupled with adaptive sampling enriches RNAs of interest in the transcriptome
Direct RNA sequencing coupled with adaptive sampling enriches RNAs of interest in the transcriptome
It can be difficult to find rare transcripts when sequencing a transcriptome. Here the authors show adaptive sampling on direct RNA runs to increase the likelihood of finding less frequent ones while selectively ejecting the higher-abundance transcripts.
- Jiaxu Wang
- , Lin Yang
- & Yue Wan
-
Article
| Open Access Single-sided magnetic resonance-based sensor for point-of-care evaluation of muscle
Single-sided magnetic resonance-based sensor for point-of-care evaluation of muscle
Magnetic resonance imaging is a useful clinical tool, but its widespread use is constrained by size, cost, and time. Here, the authors report the development of a magnetic resonance sensor for the clinical detection of muscle tissue, allowing for new point-of-care quantitative diagnostic measurements
- Sydney E. Sherman
- , Alexa S. Zammit
- & Michael J. Cima
-
Article
| Open Access Non-Faradaic optoelectrodes for safe electrical neuromodulation
Non-Faradaic optoelectrodes for safe electrical neuromodulation
Nanoscale optoelectrodes hold the potential to optically stimulate individual neuron. Here, the authors form nanoscale capacitive optoelectrodes by incorporating zinc porphyrin into nanorods, coated by TiO2, a design that allows for far-field optical modulation of neurons with efficiency and negligible side effects.
- Jian Chen
- , Yanyan Liu
- & Wenbo Bu
-
Article
| Open Access A full-body transcription factor expression atlas with completely resolved cell identities in C. elegans
A full-body transcription factor expression atlas with completely resolved cell identities in C. elegans
Invariant cell lineage in C. elegans enables the analysis of transcriptional regulatory mechanisms controlling the fate of each cell at spatiotemporal resolution. Here, the authors develop a tool automating C. elegans cell identification and create an expression atlas of 620 transcription factors.
- Yongbin Li
- , Siyu Chen
- & Xiao Liu
-
Article
| Open Access VESPA: an optimized protocol for accurate metabarcoding-based characterization of vertebrate eukaryotic endosymbiont and parasite assemblages
VESPA: an optimized protocol for accurate metabarcoding-based characterization of vertebrate eukaryotic endosymbiont and parasite assemblages
DNA sequencing methods for characterizing microbial communities are well developed for bacteria, archaea and fungi, but less so for eukaryotic parasites and commensals. Here, the authors present an optimized and validated metabarcoding protocol for host-associated eukaryotic communities.
- Leah A. Owens
- , Sagan Friant
- & Tony L. Goldberg
-
Editorial
| Open AccessEfficient genetic improvement of orphan crops cannot follow the old path
Orphan crops hold the potential to diversify our food systems. Considering their unique characteristics, our deep understanding of major crops, and the availability of modern genomic tools, taking a different research path from what major crops have gone through could accelerate the genetic improvement of orphan crops.
-
Article
| Open Access Single-cell mapping of lipid metabolites using an infrared probe in human-derived model systems
Single-cell mapping of lipid metabolites using an infrared probe in human-derived model systems
Current metabolic imaging studies are limited by low resolution and low specificity. Here, the authors present a single-cell metabolic imaging platform to monitor lipid metabolism with high specificity in various human-derived 2D and 3D culture systems.
- Yeran Bai
- , Carolina M. Camargo
- & Kenneth S. Kosik
-
Article
| Open Access Conformational coupling of the sialic acid TRAP transporter HiSiaQM with its substrate binding protein HiSiaP
Conformational coupling of the sialic acid TRAP transporter HiSiaQM with its substrate binding protein HiSiaP
Tripartite ATP-independent periplasmic (TRAP) transporters use an extra substrate binding protein to transport a variety of substrates in bacteria and archaea. Here the authors use a disulfide engineering approach to lock the TRAP transporter HiSiaPQM from H. influenzae in different conformational states for characterisation.
- Martin F. Peter
- , Jan A. Ruland
- & Gregor Hagelueken
-
Article
| Open Access Gene drive and genetic sex conversion in the global agricultural pest Ceratitis capitata
Gene drive and genetic sex conversion in the global agricultural pest Ceratitis capitata
Homing-based gene drives are novel interventions promising the area-wide, species-specific genetic control of harmful insect populations. Here the authors demonstrate the feasibility of a gene drive approach for the genetic control of the agricultural pest, the medfly, based on complete female-to-male sex conversion.
- Angela Meccariello
- , Shibo Hou
- & Nikolai Windbichler
-
Article
| Open Access PIEZO1 loss-of-function compound heterozygous mutations in the rare congenital human disorder Prune Belly Syndrome
PIEZO1 loss-of-function compound heterozygous mutations in the rare congenital human disorder Prune Belly Syndrome
PIEZO1 is a mechanosensitive ion channel. Here, authors identify PIEZO1 human mutations in Prune Belly Syndrome. At a single molecule level these mutations exhibit loss-of-function characteristics.
- Nathalia G. Amado
- , Elena D. Nosyreva
- & Ruhma Syeda
-
Article
| Open Access Enhancing geometric representations for molecules with equivariant vector-scalar interactive message passing
Enhancing geometric representations for molecules with equivariant vector-scalar interactive message passing
Utilising geometric information and reducing computational costs are key challenges in the molecular modelling field. Here, authors propose ViSNet, which efficiently extracts geometric features, accurately predicts molecular properties, and drives simulations with interpretability.
- Yusong Wang
- , Tong Wang
- & Tie-Yan Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Muscle abnormalities worsen after post-exertional malaise in long COVID
Muscle abnormalities worsen after post-exertional malaise in long COVID
In this longitudinal, case-controlled, cohort design study, authors show that post-exertional malaise is associated with severe exercise-induced myopathy, local and systemic metabolic disturbances and infiltration of amyloid-containing deposits in skeletal muscles of patients with long COVID.
- Brent Appelman
- , Braeden T. Charlton
- & Rob C. I. Wüst
-
Article
| Open Access Drosophila activins adapt gut size to food intake and promote regenerative growth
Drosophila activins adapt gut size to food intake and promote regenerative growth
While activins are critical regulators of early development, their role in maintaining adult tissue homeostasis remains obscure. Here the authors explore the role of activins in promoting intestinal regeneration and nutrient-dependent gut resizing in Drosophila.
- Christian F. Christensen
- , Quentin Laurichesse
- & Ditte S. Andersen
-
Article
| Open Access Angiogenesis-on-a-chip coupled with single-cell RNA sequencing reveals spatially differential activations of autophagy along angiogenic sprouts
Angiogenesis-on-a-chip coupled with single-cell RNA sequencing reveals spatially differential activations of autophagy along angiogenic sprouts
The functional heterogeneity of autophagy in endothelial cells during angiogenesis remains incompletely understood. Here, the authors apply a 3D angiogenesis-on-a-chip coupled with single-cell RNA sequencing to find distinct autophagy functions in two different endothelial cell populations during angiogenic sprouting.
- Somin Lee
- , Hyunkyung Kim
- & Noo Li Jeon
-
Comment
| Open Access From lab to life: how wearable devices can improve health equity
From lab to life: how wearable devices can improve health equity
Wearable devices can provide personalised medicine at the point of need, potentially increasing access to health services and therefore improving health equity. Here the authors discuss their experiences developing wearable devices for vulnerable patient populations, including neonates and pregnant individuals.
- Jessica R. Walter
- , Shuai Xu
- & John A. Rogers
-
Article
| Open Access ECOLE: Learning to call copy number variants on whole exome sequencing data
ECOLE: Learning to call copy number variants on whole exome sequencing data
Copy number variants (CNV) are shown to contribute to the etiology of various genetic disorders. Here, authors present ECOLE, a deep learning-based somatic and germline CNV caller for WES data. Utilising a variant of the transformer architecture, the model is trained to call CNVs per exon.
- Berk Mandiracioglu
- , Furkan Ozden
- & A. Ercument Cicek
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic stability of Sgt2 enables selective and privileged client handover in a chaperone triad
Dynamic stability of Sgt2 enables selective and privileged client handover in a chaperone triad
Newly synthesized tail-anchored membrane proteins (TAs) are relayed in a chaperone triad, Hsp70, Sgt2, and Get3, for delivery to the endoplasmic reticulum. Here, the authors show how the conformational dynamics of the cochaperone Sgt2 generates a decision point to enable efficient and selective TA targeting.
- Hyunju Cho
- , Yumeng Liu
- & Shu-ou Shan
-
Article
| Open Access Hijacking of internal calcium dynamics by intracellularly residing viral rhodopsins
Hijacking of internal calcium dynamics by intracellularly residing viral rhodopsins
Rhodopsins are ubiquitous light-driven membrane proteins that have diverse functions in nature, and value as optogenetics tools. Here the authors characterise type 1 viral channelrhodopsins, showing that they regulate intracellular calcium and can be used for the photocontrol of muscle contraction in vivo.
- Ana-Sofia Eria-Oliveira
- , Mathilde Folacci
- & Michel Vivaudou
-
Article
| Open Access Decoding the gene regulatory network of endosperm differentiation in maize
Decoding the gene regulatory network of endosperm differentiation in maize
The cereal endosperm constitutes most of the grain by volume. Here the authors use single-cell analysis of maize developing endosperm to decode gene regulatory networks that likely control endosperm growth and offer a framework for crop improvement.
- Yue Yuan
- , Qiang Huo
- & Zeyang Ma
-
Article
| Open Access Optogenetic spatial patterning of cooperation in yeast populations
Optogenetic spatial patterning of cooperation in yeast populations
Microbial communities are the siege of complex metabolic interactions including cooperation and competition. Here, the authors report the utilization of optogenetics and spatial light-patterning to activate the expression of the invertase SUC2 at selected locations and selectively switch cooperation and competition roles of the yeast cells.
- Matthias Le Bec
- , Sylvain Pouzet
- & Pascal Hersen
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Analytical biochemistry
- Behavioural methods
- Bioinformatics
- Biological models
- Biophysical methods
- Cytological techniques
- Electrophysiology
- Epigenetics analysis
- Experimental organisms
- Gene delivery
- Gene expression analysis
- Genetic engineering
- Genetic techniques
- Genomic analysis
- High-throughput screening
- Imaging
- Immunological techniques
- Isolation, separation and purification
- Lab-on-a-chip
- Mass spectrometry
- Metabolomics
- Microbiology techniques
- Microscopy
- Molecular engineering
- Nanobiotechnology
- Optogenetics
- Proteomic analysis
- Sensors and probes
- Sequencing
- Software
- Optical spectroscopy
- Structure determination

 Nanoparticle enrichment mass-spectrometry proteomics identifies protein-altering variants for precise pQTL mapping
Nanoparticle enrichment mass-spectrometry proteomics identifies protein-altering variants for precise pQTL mapping