Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Discovery and remodeling of Vibrio natriegens as a microbial platform for efficient formic acid biorefinery
Discovery and remodeling of Vibrio natriegens as a microbial platform for efficient formic acid biorefinery
Formic acid (FA) is a promising CO2-equivalent feedstock for onecarbon biorefinery, but microbial host that can efficiently utilize FA is unavailable. Here, the authors engineer a non-native closed loop in Vibrio natriegens and demonstrate its application in promoting FA utilization.
- Jinzhong Tian
- , Wangshuying Deng
- & Yang Gu
-
Article
| Open Access Regulation of species metabolism in synthetic community systems by environmental pH oscillations
Regulation of species metabolism in synthetic community systems by environmental pH oscillations
Most synthetic communities are unidirectional or two-way interaction without dynamic feedback. Here, the authors report a dynamic feedback system involving artificial cell species, biological cell species, and their environment using pH-sensitive molecule that phase-shift between fluid and gel phases.
- Shubin Li
- , Yingming Zhao
- & Xiaojun Han
-
Article
| Open Access Enhancing photosynthetic CO2 fixation by assembling metal-organic frameworks on Chlorella pyrenoidosa
Enhancing photosynthetic CO2 fixation by assembling metal-organic frameworks on Chlorella pyrenoidosa
Concentrating CO2 around Rubisco is critical to improve photosynthetic efficiency for biomass yield. Here, the authors report the self-assembly of metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) on the surface of green alga Chlorella pyrenoidosa to enhance the photosynthetic carbon fixation.
- Dingyi Li
- , Hong Dong
- & Can Li
-
Article
| Open Access Droplet-based high-throughput single microbe RNA sequencing by smRandom-seq
Droplet-based high-throughput single microbe RNA sequencing by smRandom-seq
Population level transcriptomics measurements miss bacterial heterogeneity. Here the authors report smRandom-seq, a droplet-based high-throughput single-microbe RNA-seq assay, using random primers for in situ cDNA generation, droplets for single-microbe barcoding, and CRISPR-based rRNA depletion.
- Ziye Xu
- , Yuting Wang
- & Yongcheng Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Precise in-field molecular diagnostics of crop diseases by smartphone-based mutation-resolved pathogenic RNA analysis
Precise in-field molecular diagnostics of crop diseases by smartphone-based mutation-resolved pathogenic RNA analysis
On-site crop disease diagnostics is critical for precise application of pesticides. Here, the authors report an in-field molecular diagnostic tool for wheat pathogens using a nucleic acid amplification-free, gene mutation-resolved and smartphone-integrated genetic assay.
- Ting Zhang
- , Qingdong Zeng
- & Ruijie Deng
-
Article
| Open Access Bi-terminal fusion of intrinsically-disordered mussel foot protein fragments boosts mechanical strength for protein fibers
Bi-terminal fusion of intrinsically-disordered mussel foot protein fragments boosts mechanical strength for protein fibers
High-yield production of well-performing protein materials is challenging due to their high molecular weights and repetitive sequences. Here the authors develop a method to boost the strength of low molecular-weight protein materials by bi-terminal fusion of intrinsically-disordered mussel foot protein fragments, while achieving high yield.
- Jingyao Li
- , Bojing Jiang
- & Fuzhong Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Spatial profiling of microbial communities by sequential FISH with error-robust encoding
Spatial profiling of microbial communities by sequential FISH with error-robust encoding
Spatial analysis of microbiomes at single cell resolution is challenging. Here the authors report a highly multiplexed method for spatial profiling, sequential error-robust fluorescence in situ hybridisation (SEER-FISH), and show that this allows mapping of microbial communities at micron-scale.
- Zhaohui Cao
- , Wenlong Zuo
- & Lei Dai
-
Article
| Open Access Engineered hypermutation adapts cyanobacterial photosynthesis to combined high light and high temperature stress
Engineered hypermutation adapts cyanobacterial photosynthesis to combined high light and high temperature stress
Cyanobacteria mutants with improved tolerance to combined high light and high temperature (HLHT) are rarely reported. Here, the authors use a hypermutation system for adaptive laboratory evolution and identify a mutant with improved HLHT tolerance by enhancing expression of shikimate kinase.
- Huili Sun
- , Guodong Luan
- & Xuefeng Lu
-
Article
| Open Access Quantitative dose-response analysis untangles host bottlenecks to enteric infection
Quantitative dose-response analysis untangles host bottlenecks to enteric infection
Here, using Citrobacter rodentium colonization of mice as a model, the authors characterize the impact of pathogen dose on the number of bacteria that initiate infection in the mouse gut, providing a framework for quantifying the host bottlenecks that eliminate pathogens to protect from infection.
- Ian W. Campbell
- , Karthik Hullahalli
- & Matthew K. Waldor
-
Article
| Open Access Orthogonal glycolytic pathway enables directed evolution of noncanonical cofactor oxidase
Orthogonal glycolytic pathway enables directed evolution of noncanonical cofactor oxidase
Engineering enzymes to accept noncanonical cofactor biomimetics is difficult. Here, the authors establish a self-sufficient growth selection method and demonstrate its application in engineering the Lactobacillus pentosus NADH oxidase to efficiently recycle reduced nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMNH).
- Edward King
- , Sarah Maxel
- & Han Li
-
Article
| Open Access Absolute protein quantification using fluorescence measurements with FPCountR
Absolute protein quantification using fluorescence measurements with FPCountR
A challenge in synthetic biology is the empirical characterisation of genetic parts. Here the authors present FPCountR, a validated method and accompanying R package that enables the precise quantification of fluorescent protein reporters per bacterial cell to be enumerated in ‘proteins per cell’ or nanomolar units without requiring protein purification.
- Eszter Csibra
- & Guy-Bart Stan
-
Article
| Open Access Rapid antibiotic susceptibility testing and species identification for mixed samples
Rapid antibiotic susceptibility testing and species identification for mixed samples
Rapid antibiotic susceptibility testing (AST) is needed. Here the authors report a method for phenotypic AST at the single cell level, using a microfluidic chip that allows for subsequent genotyping with in situ FISH; they apply this to a mixed sample of 7 species and 4 antibiotics.
- Vinodh Kandavalli
- , Praneeth Karempudi
- & Johan Elf
-
Article
| Open Access Engineering consortia by polymeric microbial swarmbots
Engineering consortia by polymeric microbial swarmbots
Most attempts to co-cultivate the artificial microbial communities fail mostly due to the mismatched rates of consumption and production of nutrients among subpopulations. Here, the authors develop a microbial swarmbot mediated spatial segregation method to assemble stably coexisting consortia with both flexibility and precision.
- Lin Wang
- , Xi Zhang
- & Zhuojun Dai
-
Article
| Open Access Enhancing bioreactor arrays for automated measurements and reactive control with ReacSight
Enhancing bioreactor arrays for automated measurements and reactive control with ReacSight
Small-scale bioreactors are increasingly used in quantitative biology. Here, the authors report ReacSight, a software solution to connect reactor arrays with sensitive measurement devices using low-cost pipetting robots and provide applications leveraging optogenetic control in yeast.
- François Bertaux
- , Sebastián Sosa-Carrillo
- & Gregory Batt
-
Article
| Open Access Mitigation of SARS-CoV-2 transmission at a large public university
Mitigation of SARS-CoV-2 transmission at a large public university
Safely opening university campuses has been a major challenge during the COVID-19 pandemic. Here, the authors describe a program of public health measures employed at a university in the United States which, combined with other non-pharmaceutical interventions, allowed the university to stay open in fall 2020 with limited evidence of transmission.
- Diana Rose E. Ranoa
- , Robin L. Holland
- & Martin D. Burke
-
Article
| Open Access High-throughput identification and quantification of single bacterial cells in the microbiota
High-throughput identification and quantification of single bacterial cells in the microbiota
Here, Jin et al., develop a method called Barcoding Bacteria for Identification and Quantification (BarBIQ), which allows to both characterize the global microbiome and to identify and quantify single-cell bacterial members in a high-throughput manner.
- Jianshi Jin
- , Reiko Yamamoto
- & Katsuyuki Shiroguchi
-
Article
| Open Access A dual-reporter system for investigating and optimizing protein translation and folding in E. coli
A dual-reporter system for investigating and optimizing protein translation and folding in E. coli
Heterologous expression of recombinant proteins often results in misfolding, aggregation and degradation. Here, we show an in vivo dual-biosensor system that simultaneously assesses protein translation and protein folding, thereby enabling rapid screening of expression strains as well as mutant libraries.
- Ariane Zutz
- , Louise Hamborg
- & Alex Toftgaard Nielsen
-
Article
| Open Access Glycan remodeled erythrocytes facilitate antigenic characterization of recent A/H3N2 influenza viruses
Glycan remodeled erythrocytes facilitate antigenic characterization of recent A/H3N2 influenza viruses
Here, Broszeit et al. show that circulating A/H3N2 viruses have evolved binding specificity to α2,6-sialosides on extended LacNAc moieties and therefore cannot agglutinate erythrocytes. Applying glycan remodeling allows to install functional receptors on erythrocytes and promotes identification of newly circulating variants to facilitate vaccine design.
- Frederik Broszeit
- , Rosanne J. van Beek
- & Geert-Jan Boons
-
Article
| Open Access Transforming biorefinery designs with ‘Plug-In Processes of Lignin’ to enable economic waste valorization
Transforming biorefinery designs with ‘Plug-In Processes of Lignin’ to enable economic waste valorization
The current biorefineries yield lignin with inadequate fractionation for bioconversion, yet substantial changes of these biorefinery designs could jeopardize carbohydrate efficiency and increase capital costs. Here the authors resolve the dilemma by designing ‘plug-in processes of lignin’ to enable economic waste valorization.
- Zhi-Hua Liu
- , Naijia Hao
- & Joshua S. Yuan
-
Article
| Open Access A comprehensive influenza reporter virus panel for high-throughput deep profiling of neutralizing antibodies
A comprehensive influenza reporter virus panel for high-throughput deep profiling of neutralizing antibodies
Understanding the human antibody response to influenza A virus strains is important for vaccine development. Here, Creanga et al. generate a panel of 55 replication-deficient reporter viruses representing diversity of human H1N1 and H3N2, and pandemic subtypes and characterize the neutralization profile of 24 antibodies and polyclonal sera.
- Adrian Creanga
- , Rebecca A. Gillespie
- & Masaru Kanekiyo
-
Article
| Open Access Plasmodium vivax infection compromises reticulocyte stability
Plasmodium vivax infection compromises reticulocyte stability
During Plasmodium intra-erythrocytic developmental, parasites compromise the structural integrity of host red-blood cells. Here, Clark et al. develop a flow cytometric osmotic stability assay to show that P. vivax infection destabilizes host reticulocytes, which are less stable than P. falciparum-infected normocytes.
- Martha A. Clark
- , Usheer Kanjee
- & Manoj T. Duraisingh
-
Article
| Open Access In-situ generation of large numbers of genetic combinations for metabolic reprogramming via CRISPR-guided base editing
In-situ generation of large numbers of genetic combinations for metabolic reprogramming via CRISPR-guided base editing
To obtain optimal yield and productivity in bioproduction, expression of pathway genes must be appropriately coordinated. Here, the authors report repurposing of base editors for simultaneous regulation of multiple gene expression and demonstrate its application in industrially important and model microorganisms.
- Yu Wang
- , Haijiao Cheng
- & Yanhe Ma
-
Article
| Open Access HIV-1 diversity considerations in the application of the Intact Proviral DNA Assay (IPDA)
HIV-1 diversity considerations in the application of the Intact Proviral DNA Assay (IPDA)
The intact proviral DNA assay quantifies the genomically intact HIV reservoir, but assay failure due to HIV-1 polymorphism has been observed. Here, the authors report a 28% failure rate in a cohort of people with HIV-1, and note within-host HIV-1 diversity as a further challenge to IPDA accuracy.
- Natalie N. Kinloch
- , Yanqin Ren
- & R. Brad Jones
-
Article
| Open Access Engineered fluoride sensitivity enables biocontainment and selection of genetically-modified yeasts
Engineered fluoride sensitivity enables biocontainment and selection of genetically-modified yeasts
Non-antibiotic selection systems could also serve as biocontainment strategies. Here the authors present a fluoride sensitivity selection system for use in yeast.
- Justin I. Yoo
- , Susanna Seppälä
- & Michelle A. OʼMalley
-
Article
| Open Access A fast impedance-based antimicrobial susceptibility test
A fast impedance-based antimicrobial susceptibility test
There is an urgent need to develop simple and fast antimicrobial susceptibility tests. Here, Spencer et al. describe a label-free test that can deliver results within an hour, consisting of a 30-min antibiotic treatment followed by single-cell analysis of phenotypic responses with microfluidic impedance cytometry.
- Daniel C. Spencer
- , Teagan F. Paton
- & Hywel Morgan
-
Article
| Open Access Sensitive detection of a bacterial pathogen using allosteric probe-initiated catalysis and CRISPR-Cas13a amplification reaction
Sensitive detection of a bacterial pathogen using allosteric probe-initiated catalysis and CRISPR-Cas13a amplification reaction
The detection of pathogens in food and clinical samples remains a challenge. Here, Shen et al. present a detection system, involving a combination of nucleic acid-based allosteric probes and CRISPR-Cas13a components, that can detect very low numbers of a bacterial pathogen in milk and serum samples without isolation.
- Jinjin Shen
- , Xiaoming Zhou
- & Da Xing
-
Article
| Open Access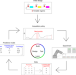 Towards a fully automated algorithm driven platform for biosystems design
Towards a fully automated algorithm driven platform for biosystems design
Existing efforts have been focused on one of the elements in the automation of the design, build, test, and learn (DBTL) cycle for biosystems design. Here, the authors integrate a robotic system with machine learning algorithms to fully automate the DBTL cycle and apply it in optimizing the lycopene biosynthetic pathway.
- Mohammad HamediRad
- , Ran Chao
- & Huimin Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Targeting metabolic driving and intermediate influx in lysine catabolism for high-level glutarate production
Targeting metabolic driving and intermediate influx in lysine catabolism for high-level glutarate production
The efficiency of producing glutarate, a valuable platform C5 compound, by engineered E. coli is low. Here, the authors achieve high titer and yield of glutarate production by pushing and pulling carbon flux in the native pathway and increasing intermediate influx using newly identified transporters.
- Wenna Li
- , Lin Ma
- & Qipeng Yuan
-
Article
| Open Access Inherent biomechanical traits enable infective filariae to disseminate through collecting lymphatic vessels
Inherent biomechanical traits enable infective filariae to disseminate through collecting lymphatic vessels
Stimuli affecting migration of filaria in host tissues are unclear. Using in situ imaging, Kilarski et al. here show that universal adaptations of nematodes allow Litomosoides sigmodontis infective larvae to mechanically break into pre-collecting lymphatics and follow the direction of flow towards the lymph node.
- Witold W. Kilarski
- , Coralie Martin
- & Melody A. Swartz
-
Article
| Open Access Vibrio sp. dhg as a platform for the biorefinery of brown macroalgae
Vibrio sp. dhg as a platform for the biorefinery of brown macroalgae
Brown macroalgae is a good candidate feedstock for biorefinery, but the major carbohydrate alginate cannot be digested by current industrial microbes. Here, the authors isolate Vibrio sp. dhg and engineer it to produce value-added biochemicals from alginate using newly developed genetic tools.
- Hyun Gyu Lim
- , Dong Hun Kwak
- & Gyoo Yeol Jung
-
Article
| Open Access Blood meal-induced inhibition of vector-borne disease by transgenic microbiota
Blood meal-induced inhibition of vector-borne disease by transgenic microbiota
Vector alteration strategies are emerging as attractive tools for malaria transmission control. Here, Shane et al. engineer a bacterial strain, isolated from mosquitoes, to produce an antiplasmodial protein in the presence of blood meal, causing the mosquitoes to become refractory to Plasmodium infection.
- Jackie L. Shane
- , Christina L. Grogan
- & David J. Lampe
-
Article
| Open Access De novo targeting to the cytoplasmic and luminal side of bacterial microcompartments
De novo targeting to the cytoplasmic and luminal side of bacterial microcompartments
Bacterial microcompartments (BMCs) are protein-bound organelles encapsulating segments of metabolic pathways. Here the authors utilize specific de novo coiled-coil protein-protein interactions to display proteins on the outer or inner surface of BMCs.
- Matthew J. Lee
- , Judith Mantell
- & Martin J. Warren
-
Article
| Open Access Programmed loading and rapid purification of engineered bacterial microcompartment shells
Programmed loading and rapid purification of engineered bacterial microcompartment shells
Bacterial microcompartments are protein-bound organelles encapsulating segments of metabolic pathways. Here the authors functionalise shell proteins to facilitate facile purification and enable cargo encapsulation via covalent linkage.
- Andrew Hagen
- , Markus Sutter
- & Cheryl A. Kerfeld
-
Article
| Open Access Optically-controlled bacterial metabolite for cancer therapy
Optically-controlled bacterial metabolite for cancer therapy
Targeting tumors with bacteria as vehicles for metabolite therapy suffers from low efficiency and robustness. Here, the authors combine carbon nitride with nitric oxide generation enzyme-positive E. coli for photo-controlled metabolite therapy (PMT) and observe increased effects both in vitro and in tumor-bearing mice.
- Di-Wei Zheng
- , Ying Chen
- & Xian-Zheng Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Performance of the Trioplex real-time RT-PCR assay for detection of Zika, dengue, and chikungunya viruses
Performance of the Trioplex real-time RT-PCR assay for detection of Zika, dengue, and chikungunya viruses
The Trioplex real-time RT-PCR assay was developed for detection of Zika virus infections in areas with dengue and chikungunya transmission. Here, Santiago et al. describe the optimization and clinical performance of the assay, showing high sensitivity for detection and differentiation of the three viruses.
- Gilberto A. Santiago
- , Jesús Vázquez
- & Jorge L. Muñoz-Jordan

 Microevolution, reinfection and highly complex genomic diversity in patients with sequential isolates of Mycobacterium abscessus
Microevolution, reinfection and highly complex genomic diversity in patients with sequential isolates of Mycobacterium abscessus