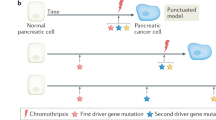
Abstract
Efficient metastasis is believed as the result of multiple genetic, epigenetic and/or post-translational events in the lifetime of a carcinoma. At the genetic level, these events may be categorized into those that occur during carcinogenesis, and those that occur during subclonal evolution. This review summarizes current knowledge of the genetics of pancreatic cancer from its initiation within a normal cell until the time that is has disseminated to distant organs, many features of which can be extrapolated to other solid tumor types. The implications of these findings to personalize genome analyses of an individual patient’s tumor are also discussed.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nguyen DX, Massagué J . Genetic determinants of cancer metastasis. Nat Rev Genet 2007; 8: 341–352.
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA . Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 2011; 144: 646–674.
Nguyen DX, Bos PD, Massagué J . Metastasis: from dissemination to organ-specific colonization. Nat Rev Cancer 2009; 9: 274–284.
Fidler IJ . The biology of cancer metastasis. Semin Cancer Biol 2011; 21: 71.
Langley RR, Fidler IJ . The seed and soil hypothesis revisited—the role of tumor-stroma interactions in metastasis to different organs. Int J Cancer 2011; 128: 2527–2535.
Comen E, Norton L, Massagué J . Clinical implications of cancer self-seeding. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2011; 8: 369–377.
Maitra A, Hruban RH . Pancreatic cancer. Annu Rev Pathol 2008; 3: 157–188.
Matthaei H, Schulick RD, Hruban RH, Maitra A . Cystic precursors to invasive pancreatic cancer. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2011; 8: 141–150.
Wu J, Jiao Y, Dal Molin M, Maitra A, de Wilde RF, Wood LD et al. Whole-exome sequencing of neoplastic cysts of the pancreas reveals recurrent mutations in components of ubiquitin-dependent pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2011; 108: 21188–21193.
Macgregor-Das AM, Iacobuzio-Donahue CA . Molecular pathways in pancreatic carcinogenesis. J Surg Oncol 2013; 107: 8–14.
Hruban RH, Goggins M, Parsons J, Kern SE . Progression model for pancreatic cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2000; 6: 2969–2972.
Yachida S, Iacobuzio-Donahue CA . The pathology and genetics of metastatic pancreatic cancer. Arch Pathol Lab Med 2009; 133: 413–422.
Sohn TA, Yeo CJ, Cameron JL, Koniaris L, Kaushal S, Abrams RA et al. Resected adenocarcinoma of the pancreas-616 patients: results, outcomes, and prognostic indicators. J Gastrointest Surg 2000; 4: 567–579.
Stathis A, Moore MJ . Advanced pancreatic carcinoma: current treatment and future challenges. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2010; 7: 163–172.
Siegel R, Ward E, Brawley O, Jemal A . Cancer statistics, 2011: the impact of eliminating socioeconomic and racial disparities on premature cancer deaths. CA Cancer J Clin 2011; 61: 212–236.
Hidalgo M . Pancreatic cancer. N Engl J Med 2010; 362: 1605–1617.
Hruban RH, Adsay NV, Albores-Saavedra J, Compton C, Garrett ES, Goodman SN et al. Pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia: a new nomenclature and classification system for pancreatic duct lesions. Am J Surg Pathol 2001; 25: 579–586.
Kanda M, Matthaei H, Wu J, Hong S-M, Yu J, Borges M et al. Presence of somatic mutations in most early-stage pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia 2012 Gastroenterology 142: 730–733.e9.
Wilentz RE, Geradts J, Maynard R, Offerhaus GJ, Kang M, Goggins M et al. Inactivation of the p16 (INK4A) tumor-suppressor gene in pancreatic duct lesions: loss of intranuclear expression. Cancer Res 1998; 58: 4740–4744.
Wilentz RE, Su GH, Dai JL, Sparks AB, Argani P, Sohn TA et al. Immunohistochemical labeling for dpc4 mirrors genetic status in pancreatic adenocarcinomas: a new marker of DPC4 inactivation. Am J Pathol 2000; 156: 37–43.
Jones S, Zhang X, Parsons DW, Lin JC-H, Leary RJ, Angenendt P et al. Core signaling pathways in human pancreatic cancers revealed by global genomic analyses. Science 2008; 321: 1801–1806.
Balakrishnan A, Bleeker FE, Lamba S, Rodolfo M, Daniotti M, Scarpa A et al. Novel somatic and germline mutations in cancer candidate genes in glioblastoma, melanoma, and pancreatic carcinoma. Cancer Res 2007; 67: 3545–3550.
Shain AH, Giacomini CP, Matsukuma K, Karikari CA, Bashyam MD, Hidalgo M et al. Convergent structural alterations define SWItch/Sucrose NonFermentable (SWI/SNF) chromatin remodeler as a central tumor suppressive complex in pancreatic cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2012; 109: E252–E259.
Biankin AV, Waddell N, Kassahn KS, Gingras M-C, Muthuswamy LB, Johns AL et al. Pancreatic cancer genomes reveal aberrations in axon guidance pathway genes. Nature 2012; 491: 399–405.
Attwooll C, Oddi S, Cartwright P, Prosperini E, Agger K, Steensgaard P et al. A novel repressive E2F6 complex containing the polycomb group protein, EPC1, that interacts with EZH2 in a proliferation-specific manner. J Biol Chem 2005; 280: 1199–1208.
Guo Z, Kozlov S, Lavin MF, Person MD, Paull TT . ATM activation by oxidative stress. Science 2010; 330: 517–521.
Ballard MS, Hinck L . A roundabout way to cancer. Adv Cancer Res 2012; 114: 187–235.
Iacobuzio-Donahue CA, Fu B, Yachida S, Luo M, Abe H, Henderson CM et al. DPC4 gene status of the primary carcinoma correlates with patterns of failure in patients with pancreatic cancer. J Clin Oncol 2009; 27: 1806–1813.
Li D, Xie K, Wolff R, Abbruzzese JL . Pancreatic cancer. Lancet 2004; 363: 1049–1057.
Blackford A, Serrano OK, Wolfgang CL, Parmigiani G, Jones S, Zhang X et al. SMAD4 gene mutations are associated with poor prognosis in pancreatic cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2009; 15: 4674–4679.
Tascilar M, Skinner HG, Rosty C, Sohn T, Wilentz RE, Offerhaus GJ et al. The SMAD4 protein and prognosis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 2001; 7: 4115–4121.
Massagué J . TGFbeta in cancer. Cell 2008; 134: 215–230.
Zhou S, Buckhaults P, Zawel L, Bunz F, Riggins G, Dai JL et al. Targeted deletion of Smad4 shows it is required for transforming growth factor beta and activin signaling in colorectal cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1998; 95: 2412–2416.
Zawel L, Dai JL, Buckhaults P, Zhou S, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B et al. Human Smad3 and Smad4 are sequence-specific transcription activators. Mol Cell 1998; 1: 611–617.
Grau AM, Zhang L, Wang W, Ruan S, Evans DB, Abbruzzese JL et al. Induction of p21waf1 expression and growth inhibition by transforming growth factor beta involve the tumor suppressor gene DPC4 in human pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells. Cancer Res 1997; 57: 3929–3934.
Dai JL, Bansal RK, Kern SE . G1 cell cycle arrest and apoptosis induction by nuclear Smad4/Dpc4: phenotypes reversed by a tumorigenic mutation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1999; 96: 1427–1432.
Dai JL, Turnacioglu KK, Schutte M, Sugar AY, Kern SE . Dpc4 transcriptional activation and dysfunction in cancer cells. Cancer Res 1998; 58: 4592–4597.
Peng B, Fleming JB, Breslin T, Grau AM, Fojioka S, Abbruzzese JL et al. Suppression of tumorigenesis and induction of p15(ink4b) by Smad4/DPC4 in human pancreatic cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res 2002; 8: 3628–3638.
Murakami M, Suzuki M, Nishino Y, Funaba M . Regulatory expression of genes related to metastasis by TGF-beta and activin A in B16 murine melanoma cells. Mol Biol Rep 2010; 37: 1279–1286.
Nishimori H, Ehata S, Suzuki HI, Katsuno Y, Miyazono K . Prostate cancer cells and bone stromal cells mutually interact with each other through bone morphogenetic protein-mediated signals. J Biol Chem 2012; 287: 20037–20046.
Park C-Y, Kim D-K, Sheen YY . EW-7203, a novel small molecule inhibitor of transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) type I receptor/activin receptor-like kinase-5, blocks TGF-β1-mediated epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in mammary epithelial cells. Cancer Sci 2011; 102: 1889–1896.
Yachida S, White C, Naito Y, Zhong Y, Brosnan JA, Macgregor-Das AM et al. Clinical significance of the genetic landscape of pancreatic cancer and implications for identification of potential long term survivors. Clin Cancer Res 2012; 18: 6339–6347.
Morton JP, Timpson P, Karim SA, Ridgway RA, Athineos D, Doyle B et al. Mutant p53 drives metastasis and overcomes growth arrest/senescence in pancreatic cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2010; 107: 246–251.
Oshima M, Keiichi O, Shinobu M, Reiji H, Takashi M, Yasuyuki S et al. Immunohistochemically detected expression of three major genes (CDKN2A/p16, TP53 and SMAD4/DPC4) strongly predicts survival in patients with resectable pancreatic cancer. Ann Surg 2013, (in press).
Crane CH, Iacobuzio-Donahue CA . Keys to personalized care in pancreatic oncology. J Clin Oncol 2012; 30: 4049–4050.
Crane CH, Varadhachary GR, Yordy JS, Staerkel GA, Javle MM, Safran H et al. Phase II trial of cetuximab, gemcitabine, and oxaliplatin followed by chemoradiation with cetuximab for locally advanced (T4) pancreatic adenocarcinoma: correlation of Smad4(Dpc4) immunostaining with pattern of disease progression. J Clin Oncol 2011; 29: 3037–3043.
Talmadge JE, Fidler IJ . AACR centennial series: the biology of cancer metastasis: historical perspective. Cancer Res 2010; 70: 5649–5669.
Mani SA, Guo W, Liao M-J, Eaton EN, Ayyanan A, Zhou AY et al. The epithelial-mesenchymal transition generates cells with properties of stem cells. Cell 2008; 133: 704–715.
Ma L, Young J, Prabhala H, Pan E, Mestdagh P, Muth D et al. miR-9, a MYC/MYCN-activated microRNA, regulates E-cadherin and cancer metastasis. Nat Cell Biol 2010; 12: 247–256.
Oskarsson T, Acharyya S, XH-F Zhang, Vanharanta S, Tavazoie SF, Morris PG et al. Breast cancer cells produce tenascin C as a metastatic niche component to colonize the lungs. Nat Med 2011; 17: 867–874.
Calon A, Espinet E, Palomo-Ponce S, Tauriello DVF, Iglesias M, Céspedes MV et al. Dependency of colorectal cancer on a TGF-β-driven program in stromal cells for metastasis initiation. Cancer Cell 2012; 22: 571–584.
Semenza GL . Cancer-stromal cell interactions mediated by hypoxia-inducible factors promote angiogenesis, lymphangiogenesis, and metastasis. Oncogene 2013; 32: 4057–4063.
Rabinovich GA, Gabrilovich D, Sotomayor EM . Immunosuppressive strategies that are mediated by tumor cells. Annu Rev Immunol 2007; 25: 267–296.
Yachida S, Jones S, Bozic I, Antal T, Leary R, Fu B et al. Distant metastasis occurs late during the genetic evolution of pancreatic cancer. Nature 2010; 467: 1114–1117.
Jones S, Chen W-D, Parmigiani G, Diehl F, Beerenwinkel N, Antal T et al. Comparative lesion sequencing provides insights into tumor evolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2008; 105: 4283–4288.
Iacobuzio-Donahue CA . Genetic evolution of pancreatic cancer: lessons learnt from the pancreatic cancer genome sequencing project. Gut 2012; 61: 1085–1094.
Campbell PJ, Yachida S, Mudie LJ, Stephens PJ, Pleasance ED, Stebbings LA et al. The patterns and dynamics of genomic instability in metastatic pancreatic cancer. Nature 2010; 467: 1109–1113.
Larsson L-G . Oncogene- and tumor suppressor gene-mediated suppression of cellular senescence. Semin Cancer Biol 2011; 21: 367–376.
Liu W, Laitinen S, Khan S, Vihinen M, Kowalski J, Yu G et al. Copy number analysis indicates monoclonal origin of lethal metastatic prostate cancer. Nat Med 2009; 15: 559–565.
Navin N, Kendall J, Troge J, Andrews P, Rodgers L, McIndoo J et al. Tumour evolution inferred by single-cell sequencing. Nature 2011; 472: 90–94.
Navin N, Krasnitz A, Rodgers L, Cook K, Meth J, Kendall J et al. Inferring tumor progression from genomic heterogeneity. Genome Res 2010; 20: 68–80.
Grubor V, Krasnitz A, Troge JE, Meth JL, Lakshmi B, Kendall JT et al. Novel genomic alterations and clonal evolution in chronic lymphocytic leukemia revealed by representational oligonucleotide microarray analysis (ROMA). Blood 2009; 113: 1294–1303.
Egan JB, Shi C-X, Tembe W, Christoforides A, Kurdoglu A, Sinari S et al. Whole-genome sequencing of multiple myeloma from diagnosis to plasma cell leukemia reveals genomic initiating events, evolution, and clonal tides. Blood 2012; 120: 1060–1066.
Gerlinger M, Rowan AJ, Horswell S, Larkin J, Endesfelder D, Gronroos E et al. Intratumor heterogeneity and branched evolution revealed by multiregion sequencing. N Engl J Med 2012; 366: 883–892.
Nik-Zainal S, Van Loo P, Wedge DC, Alexandrov LB, Greenman CD, Lau KW et al. The life history of 21 breast cancers. Cell 2012; 149: 994–1007.
Turajlic S, Furney SJ, Lambros MB, Mitsopoulos C, Kozarewa I, Geyer FC et al. Whole genome sequencing of matched primary and metastatic acral melanomas. Genome Res 2012; 22: 196–207.
Magee JA, Piskounova E, Morrison SJ . Cancer stem cells: impact, heterogeneity, and uncertainty. Cancer Cell 2012; 21: 283–296.
Li C, Heidt DG, Dalerba P, Burant CF, Zhang L, Adsay V et al. Identification of pancreatic cancer stem cells. Cancer Res 2007; 67: 1030–1037.
Salnikov AV, Liu L, Platen M, Gladkich J, Salnikova O, Ryschich E et al. Hypoxia induces EMT in low and highly aggressive pancreatic tumor cells but only cells with cancer stem cell characteristics acquire pronounced migratory potential. PLoS ONE 2012; 7: e46391.
Gisselsson D . Intratumor diversity and clonal evolution in cancer—a skeptical standpoint. Adv Cancer Res 2011; 112: 1–9.
Bozic I, Antal T, Ohtsuki H, Carter H, Kim D, Chen S et al. Accumulation of driver and passenger mutations during tumor progression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2010; 107: 18545–18550.
Shin EJ, Canto MI . Pancreatic cancer screening. Gastroenterol Clin North Am 2012; 41: 143–157.
Canto MI, Hruban RH, Fishman EK, Kamel IR, Schulick R, Zhang Z et al. Frequent detection of pancreatic lesions in asymptomatic high-risk individuals. Gastroenterology 2012; 142: 796–804.
Haeno H, Gonen M, Davis MB, Herman JM, Iacobuzio-Donahue CA, Michor F . Computational modeling of pancreatic cancer reveals kinetics of metastasis suggesting optimum treatment strategies. Cell 2012; 148: 362–375.
Egawa S, Takeda K, Fukuyama S, Motoi F, Sunamura M, Matsuno S . Clinicopathological aspects of small pancreatic cancer. Pancreas 2004; 28: 235–240.
Warshaw AL, Lillemoe KD, Fernandez-del Castillo C . Pancreatic surgery for adenocarcinoma. Curr Opin Gastroenterol 2012; 28: 488–493.
Stratton MR . Exploring the genomes of cancer cells: progress and promise. Science 2011; 331: 1553–1558.
Garnett MJ, Edelman EJ, Heidorn SJ, Greenman CD, Dastur A, Lau KW et al. Systematic identification of genomic markers of drug sensitivity in cancer cells. Nature 2012; 483: 570–575.
Barretina J, Caponigro G, Stransky N, Venkatesan K, Margolin AA, Kim S et al. The Cancer Cell Line Encyclopedia enables predictive modelling of anticancer drug sensitivity. Nature 2012; 483: 603–607.
Diaz LA, Williams RT, Wu J, Kinde I, Hecht JR, Berlin J et al. The molecular evolution of acquired resistance to targeted EGFR blockade in colorectal cancers. Nature 2012; 486: 537–540.
Misale S, Yaeger R, Hobor S, Scala E, Janakiraman M, Liska D et al. Emergence of KRAS mutations and acquired resistance to anti-EGFR therapy in colorectal cancer. Nature 2012; 486: 532–536.
Shoushtari AN, Szmulewitz RZ, Rinker-Schaeffer CW . Metastasis-suppressor genes in clinical practice: lost in translation? Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2011; 8: 333–342.
Goedegebuure P, Mitchem JB, Porembka MR, Tan MCB, Belt BA, Wang-Gillam A et al. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells: general characteristics and relevance to clinical management of pancreatic cancer. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 2011; 11: 734–751.
Porembka MR, Mitchem JB, Belt BA, Hsieh C-S, Lee H-M, Herndon J et al. Pancreatic adenocarcinoma induces bone marrow mobilization of myeloid-derived suppressor cells which promote primary tumor growth. Cancer Immunol Immunother 2012; 61: 1373–1385.
Hiraoka N, Onozato K, Kosuge T, Hirohashi S . Prevalence of FOXP3+ regulatory T cells increases during the progression of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and its premalignant lesions. Clin Cancer Res 2006; 12: 5423–5434.
Yang L, Huang J, Ren X, Gorska AE, Chytil A, Aakre M et al. Abrogation of TGF beta signaling in mammary carcinomas recruits Gr-1+CD11b+ myeloid cells that promote metastasis. Cancer Cell 2008; 13: 23–35.
Olive KP, Jacobetz MA, Davidson CJ, Gopinathan A, McIntyre D, Honess D et al. Inhibition of Hedgehog signaling enhances delivery of chemotherapy in a mouse model of pancreatic cancer. Science 2009; 324: 1457–1461.
Provenzano PP, Cuevas C, Chang AE, Goel VK, Hoff Von DD, Hingorani SR . Enzymatic targeting of the stroma ablates physical barriers to treatment of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Cancer Cell 2012; 21: 418–429.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by NCI CA140599 (CID).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yachida, S., Iacobuzio-Donahue, C. Evolution and dynamics of pancreatic cancer progression. Oncogene 32, 5253–5260 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2013.29
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2013.29
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
p53-driven lipidome influences non-cell-autonomous lysophospholipids in pancreatic cancer
Biology Direct (2022)
-
Poor dental health and risk of pancreatic cancer: a nationwide registry-based cohort study in Sweden, 2009–2016
British Journal of Cancer (2022)
-
Prevalence, features, and explanations of missed and misinterpreted pancreatic cancer on imaging: a matched case–control study
Abdominal Radiology (2022)
-
NUAK2 and RCan2 participate in the p53 mutant pro-tumorigenic network
Biology Direct (2021)
-
Preclinical models of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: challenges and opportunities in the era of precision medicine
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2021)