Abstract
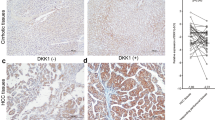
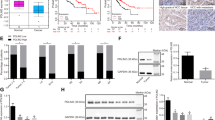
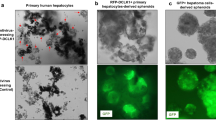
Deregulation of Wnt/β-catenin pathway is a hallmark of major gastrointestinal cancers including hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The oncogenic role of β-catenin is well defined but reasons for its accumulation in HCC remain unclear. Dickkopf 4 (DKK4) acts as a negative regulator of Wnt/β-catenin pathway but its functional role in liver carcinogenesis has not been studied. We investigated the role of DKK4 in β-catenin regulation in HCC. Reduced expression of DKK4 was found in 47% (38/81) of HCC, as measured by quantitative real time PCR. Ectopic expression of DKK4 in two HCC cell lines, PLC/PRF/5 (PLC) and MHCC97L (97L), attenuated β-catenin responsive luciferase activity, and decreased both β-catenin and cyclin D1 protein levels. To study the effect of DKK4 on cell growth and tumourigenicity, two stable HCC cell lines were established from PLC and 97L cells. Functional assays demonstrated that overexpression of DKK4 hampered cell proliferation, reduced colony formation and retarded cell migration. When DKK4-expressing 97L stable cells were used to induce tumour xenografts in nude mice (n=8), reduction in tumour sizes was observed (P=0.027). Furthermore, immunohistochemical studies showed that decreased expression of DKK4 was associated with β-catenin accumulation in HCC tissues. Additionally, inhibition of the proteasome using specific inhibitor in DKK4-expressing 97L stable cells masked the effect of β-catenin. Our findings suggest a potential tumour suppressive role of DKK4 as well as that of an important regulator of HCC.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguilera O, Fraga MF, Ballestar E, Paz MF, Herranz M, Espada J et al. (2006). Epigenetic inactivation of the Wnt antagonist DICKKOPF-1 (DKK-1) gene in human colorectal cancer. Oncogene 25: 4116–4121.
Apte U, Thompson MD, Cui S, Liu B, Cieply B, Monga SP . (2008). Wnt/beta-catenin signaling mediates oval cell response in rodents. Hepatology 47: 288–295.
Baehs S, Herbst A, Thieme SE, Perschl C, Behrens A, Scheel S et al. (2009). Dickkopf-4 is frequently down-regulated and inhibits growth of colorectal cancer cells. Cancer Lett 276: 152–159.
Blitzer JT, Nusse R . (2006). A critical role for endocytosis in Wnt signaling. BMC Cell Biol 7: 28.
Chamorro MN, Schwartz DR, Vonica A, Brivanlou AH, Cho KR, Varmus HE . (2005). FGF-20 and DKK1 are transcriptional targets of beta-catenin and FGF-20 is implicated in cancer and development. EMBO J 24: 73–84.
Chen TC, Hsieh LL, Ng KF, Jeng LB, Chen MF . (1998). Absence of APC gene mutation in the mutation cluster region in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett 134: 23–28.
de La Coste A, Romagnolo B, Billuart P, Renard CA, Buendia MA, Soubrane O et al. (1998). Somatic mutations of the beta-catenin gene are frequent in mouse and human hepatocellular carcinomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95: 8847–8851.
Dignam JD, Lebovitz RM, Roeder RG . (1983). Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res 11: 1475–1489.
Ding Z, Qian YB, Zhu LX, Xiong QR . (2009). Promoter methylation and mRNA expression of DKK-3 and WIF-1 in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 15: 2595–2601.
Fatima S, Lee NP, Luk JM . (2011). Dickkopfs and Wnt/beta-catenin signalling in liver cancer. World J Clin Oncol 2: 311–325.
Gonzalez FJ . (2006). Role of beta-catenin in the adult liver. Hepatology 43: 650–653.
Gonzalez-Sancho JM, Aguilera O, Garcia JM, Pendas-Franco N, Pena C, Cal S et al. (2005). The Wnt antagonist DICKKOPF-1 gene is a downstream target of beta-catenin/TCF and is downregulated in human colon cancer. Oncogene 24: 1098–1103.
Hao K, Luk JM, Lee NP, Mao M, Zhang C, Ferguson MD et al. (2009). Predicting prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma after curative surgery with common clinicopathologic parameters. BMC Cancer 9: 389.
Hirata H, Hinoda Y, Majid S, Chen Y, Zaman MS, Ueno K et al. (2011). DICKKOPF-4 activates the noncanonical c-Jun-NH2 kinase signaling pathway while inhibiting the Wnt-canonical pathway in human renal cell carcinoma. Cancer 117: 1649–1660.
Hirata H, Hinoda Y, Nakajima K, Kawamoto K, Kikuno N, Kawakami K et al. (2009). Wnt antagonist gene DKK2 is epigenetically silenced and inhibits renal cancer progression through apoptotic and cell cycle pathways. Clin Cancer Res 15: 5678–5687.
Hu J, Dong A, Fernandez-Ruiz V, Shan J, Kawa M, Martinez-Anso E et al. (2009). Blockade of Wnt signaling inhibits angiogenesis and tumor growth in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res 69: 6951–6959.
Huang H, Fujii H, Sankila A, Mahler-Araujo BM, Matsuda M, Cathomas G et al. (1999). Beta-catenin mutations are frequent in human hepatocellular carcinomas associated with hepatitis C virus infection. Am J Pathol 155: 1795–1801.
Inagawa S, Itabashi M, Adachi S, Kawamoto T, Hori M, Shimazaki J et al. (2002). Expression and prognostic roles of beta-catenin in hepatocellular carcinoma: correlation with tumor progression and postoperative survival. Clin Cancer Res 8: 450–456.
Ishii H, Baffa R, Numata SI, Murakumo Y, Rattan S, Inoue H et al. (1999). The FEZ1 gene at chromosome 8p22 encodes a leucine-zipper protein, and its expression is altered in multiple human tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96: 3928–3933.
Ito K, Lim AC, Salto-Tellez M, Motoda L, Osato M, Chuang LS et al. (2008). RUNX3 attenuates beta-catenin/T cell factors in intestinal tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell 14: 226–237.
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D . (2011). Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 61: 69–90.
Kemp W, Pianko S, Nguyen S, Bailey MJ, Roberts SK . (2005). Survival in hepatocellular carcinoma: impact of screening and etiology of liver disease. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 20: 873–881.
Krieghoff E, Behrens J, Mayr B . (2006). Nucleo-cytoplasmic distribution of beta-catenin is regulated by retention. J Cell Sci 119: 1453–1463.
Krupnik VE, Sharp JD, Jiang C, Robison K, Chickering TW, Amaravadi L et al. (1999). Functional and structural diversity of the human Dickkopf gene family. Gene 238: 301–313.
Lee EJ, Jo M, Rho SB, Park K, Yoo YN, Park J et al. (2009a). Dkk3, downregulated in cervical cancer, functions as a negative regulator of beta-catenin. Int J Cancer 124: 287–297.
Lee NP, Chen L, Lin MC, Tsang FH, Yeung C, Poon RT et al. (2009b). Proteomic expression signature distinguishes cancerous and nonmalignant tissues in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Proteome Res 8: 1293–1303.
Lee NP, Leung KW, Cheung N, Lam BY, Xu MZ, Sham PC et al. (2008). Comparative proteomic analysis of mouse livers from embryo to adult reveals an association with progression of hepatocellular carcinoma. Proteomics 8: 2136–2149.
Lee NP, Tong MK, Leung PP, Chan VW, Leung S, Tam PC et al. (2006). Kidney claudin-19: localization in distal tubules and collecting ducts and dysregulation in polycystic renal disease. FEBS Lett 580: 923–931.
Lee NP, Tsang FH, Shek FH, Mao M, Dai H, Zhang C et al. (2010). Prognostic significance and therapeutic potential of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A (eIF5A) in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Cancer 127: 968–976.
Liao C, Zhao M, Song H, Uchida K, Yokoyama KK, Li TP . (2000). Identification of the gene for a novel liver-related putative tumor suppressor at a high-frequency loss of heterozygosity region of chromosome 8p23 in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 32: 721–727.
Liao CH, Yeh CT, Huang YH, Wu SM, Chi HC, Tsai MM et al. (2011). Dickkopf 4 positively regulated by the thyroid hormone receptor suppresses cell invasion in human hepatoma cells. Hepatology.
Liu AM, Poon RT, Luk JM . (2010). MicroRNA-375 targets Hippo-signaling effector YAP in liver cancer and inhibits tumor properties. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 394: 623–627.
Liu LX, Lee NP, Chan VW, Xue W, Zender L, Zhang C et al. (2009). Targeting cadherin-17 inactivates Wnt signaling and inhibits tumor growth in liver carcinoma. Hepatology 50: 1453–1463.
Logan CY, Nusse R . (2004). The Wnt signaling pathway in development and disease. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 20: 781–810.
Lu WJ, Lee NP, Kaul SC, Lan F, Poon RT, Wadhwa R et al. (2011). Induction of mutant p53-dependent apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting stress protein mortalin. Int J Cancer 129: 1806–1814.
MacDonald BT, Tamai K, He X . (2009). Wnt/beta-catenin signaling: components, mechanisms, and diseases. Dev Cell 17: 9–26.
Maehata T, Taniguchi H, Yamamoto H, Nosho K, Adachi Y, Miyamoto N et al. (2008). Transcriptional silencing of Dickkopf gene family by CpG island hypermethylation in human gastrointestinal cancer. World J Gastroenterol 14: 2702–2714.
Mao B, Niehrs C . (2003). Kremen2 modulates Dickkopf2 activity during Wnt/LRP6 signaling. Gene 302: 179–183.
Mao B, Wu W, Davidson G, Marhold J, Li M, Mechler BM et al. (2002). Kremen proteins are Dickkopf receptors that regulate Wnt/beta-catenin signalling. Nature 417: 664–667.
Mao BY, Wu W, Li Y, Hoppe D, Stannek P, Glinka A et al. (2001). LDL-receptor-related protein 6 is a receptor for Dickkopf proteins. Nature 411: 321–325.
Matsui A, Yamaguchi T, Maekawa S, Miyazaki C, Takano S, Uetake T et al. (2009). DICKKOPF-4 and -2 genes are upregulated in human colorectal cancer. Cancer Sci 100: 1923–1930.
Morin PJ, Sparks AB, Korinek V, Barker N, Clevers H, Vogelstein B et al. (1997). Activation of beta-catenin-Tcf signaling in colon cancer by mutations in beta-catenin or APC. Science 275: 1787–1790.
Nakamura T, Matsumoto K . (2008). The functions and possible significance of Kremen as the gatekeeper of Wnt signalling in development and pathology. J Cell Mol Med 12: 391–408.
Nejak-Bowen KN, Monga SP . (2011). Beta-catenin signaling, liver regeneration and hepatocellular cancer: sorting the good from the bad. Semin Cancer Biol 21: 44–58.
Niehrs C . (2006). Function and biological roles of the Dickkopf family of Wnt modulators. Oncogene 25: 7469–7481.
Niida A, Hiroko T, Kasai M, Furukawa Y, Nakamura Y, Suzuki Y et al. (2004). DKK1, a negative regulator of Wnt signaling, is a target of the beta-catenin/TCF pathway. Oncogene 23: 8520–8526.
Orford K, Crockett C, Jensen JP, Weissman AM, Byers SW . (1997). Serine phosphorylation-regulated ubiquitination and degradation of beta-catenin. J Biol Chem 272: 24735–24738.
Pendas-Franco N, Garcia JM, Pena C, Valle N, Palmer HG, Heinaniemi M et al. (2008). DICKKOPF-4 is induced by TCF/beta-catenin and upregulated in human colon cancer, promotes tumour cell invasion and angiogenesis and is repressed by 1alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. Oncogene 27: 4467–4477.
Pineau P, Nagai H, Prigent S, Wei Y, Gyapay G, Weissenbach J et al. (1999). Identification of three distinct regions of allelic deletions on the short arm of chromosome 8 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene 18: 3127–3134.
Sakanaka C . (2002). Phosphorylation and regulation of beta-catenin by casein kinase I epsilon. J Biochem 132: 697–703.
Sato H, Suzuki H, Toyota M, Nojima M, Maruyama R, Sasaki S et al. (2007). Frequent epigenetic inactivation of DICKKOPF family genes in human gastrointestinal tumors. Carcinogenesis 28: 2459–2466.
Semenov MV, Tamai K, Brott BK, Kuhl M, Sokol S, He X . (2001). Head inducer Dickkopf-1 is a ligand for Wnt coreceptor LRP6. Curr Biol 11: 951–961.
Shih YL, Hsieh CB, Lai HC, Yan MD, Hsieh TY, Chao YC et al. (2007). SFRP1 suppressed hepatoma cells growth through Wnt canonical signaling pathway. Int J Cancer 121: 1028–1035.
Takagi H, Sasaki S, Suzuki H, Toyota M, Maruyama R, Nojima M et al. (2008). Frequent epigenetic inactivation of SFRP genes in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastroenterol 43: 378–389.
Takemaru K, Yamaguchi S, Lee YS, Zhang Y, Carthew RW, Moon RT . (2003). Chibby, a nuclear beta-catenin-associated antagonist of the Wnt/Wingless pathway. Nature 422: 905–909.
Taniguchi K, Roberts LR, Aderca IN, Dong X, Qian C, Murphy LM et al. (2002). Mutational spectrum of beta-catenin, AXIN1, and AXIN2 in hepatocellular carcinomas and hepatoblastomas. Oncogene 21: 4863–4871.
Tung EK, Mak CK, Fatima S, Lo RC, Zhao H, Zhang C et al. (2011). Clinicopathological and prognostic significance of serum and tissue Dickkopf-1 levels in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Int 31: 1494–1504.
Urakami S, Shiina H, Enokida H, Hirata H, Kawamoto K, Kawakami T et al. (2006). Wnt antagonist family genes as biomarkers for diagnosis, staging, and prognosis of renal cell carcinoma using tumor and serum DNA. Clin Cancer Res 12: 6989–6997.
Wiesman KC, Wei L, Baughman C, Russo J, Gray MR, Castellot JJ . (2010). CCN5, a secreted protein, localizes to the nucleus. J Cell Commun Signal 4: 91–98.
Wong CM, Fan ST, Ng IO . (2001). beta-Catenin mutation and overexpression in hepatocellular carcinoma: clinicopathologic and prognostic significance. Cancer 92: 136–145.
Wu Y, Zhang Y, Zhang H, Yang X, Wang Y, Ren F et al. (2010). p15RS attenuates Wnt/{beta}-catenin signaling by disrupting {beta}-catenin.TCF4 Interaction. J Biol Chem 285: 34621–34631.
Yang B, Du Z, Gao YT, Lou C, Zhang SG, Bai T et al. (2010). Methylation of Dickkopf-3 as a prognostic factor in cirrhosis-related hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 16: 755–763.
Yamamoto H, Sakane H, Michiue T, Kikuchi A . (2008). Wnt3a and Dkk1 regulate distinct internalization pathways of LRP6 to tune the activation of beta-catenin signaling. Dev Cell 15: 37–48.
Yi X, Luk JM, Lee NP, Peng J, Leng X, Guan XY et al. (2008). Association of mortalin (HSPA9) with liver cancer metastasis and prediction for early tumor recurrence. Mol Cell Proteomics 7: 315–325.
Yu B, Yang X, Xu Y, Yao G, Shu H, Lin B et al. (2009). Elevated expression of DKK1 is associated with cytoplasmic/nuclear beta-catenin accumulation and poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinomas. J Hepatol 50: 948–957.
Yuan BZ, Miller MJ, Keck CL, Zimonjic DB, Thorgeirsson SS, Popescu NC . (1998). Cloning, characterization, and chromosomal localization of a gene frequently deleted in human liver cancer (DLC-1) homologous to rat RhoGAP. Cancer Res 58: 2196–2199.
Yue W, Sun Q, Dacic S, Landreneau RJ, Siegfried JM, Yu J et al. (2008). Downregulation of Dkk3 activates beta-catenin/TCF-4 signaling in lung cancer. Carcinogenesis 29: 84–92.
Zeng X, Tamai K, Doble B, Li S, Huang H, Habas R et al. (2005). A dual-kinase mechanism for Wnt co-receptor phosphorylation and activation. Nature 438: 873–877.
Zhang K, Watanabe M, Kashiwakura Y, Li SA, Edamura K, Huang P et al. (2010). Expression pattern of REIC/Dkk-3 in various cell types and the implications of the soluble form in prostatic acinar development. Int J Oncol 37: 1495–1501.
Zhang LH, Qin LX, Ma ZC, Ye SL, Liu YK, Ye QH et al. (2003). Allelic imbalance regions on chromosomes 8p, 17p and 19p related to metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma: comparison between matched primary and metastatic lesions in 22 patients by genome-wide microsatellite analysis. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 129: 279–286.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Bhavin M Thakkar of the National University of Singapore, Singapore for his assistance in immunohistochemical studies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fatima, S., Lee, N., Tsang, F. et al. Dickkopf 4 (DKK4) acts on Wnt/β-catenin pathway by influencing β-catenin in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene 31, 4233–4244 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.580
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.580
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Sensitization of hepatocellular carcinoma cells towards doxorubicin and sorafenib is facilitated by glucose-dependent alterations in reactive oxygen species, P-glycoprotein and DKK4
Journal of Biosciences (2020)
-
LRP16 prevents hepatocellular carcinoma progression through regulation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling
Journal of Molecular Medicine (2018)
-
Dickkopf-4 is frequently overexpressed in epithelial ovarian carcinoma and promotes tumor invasion
BMC Cancer (2017)
-
Differential effects on lung and bone metastasis of breast cancer by Wnt signalling inhibitor DKK1
Nature Cell Biology (2017)
-
Serine peptidase inhibitor Kazal type 1 (SPINK1) as novel downstream effector of the cadherin-17/β-catenin axis in hepatocellular carcinoma
Cellular Oncology (2017)