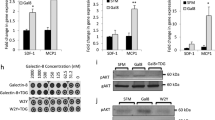
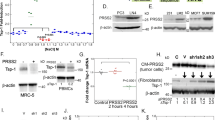
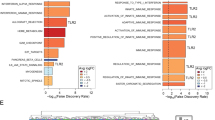
Abstract
Pancreatic adenocarcinoma upregulated factor (PAUF) is overproduced in certain types of cancer. However, little is known of the tumorigenic function of PAUF. In this study, we report the X-ray crystal structure of PAUF and reveal that PAUF is a mammalian lectin normally found in plant lectins. We also identify PAUF as an endogenous ligand of Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) and TLR4 by screening extracellular domain receptor pools. We further confirmed the specificity of the PAUF–TLR2 interaction. PAUF induces extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) phosphorylation and activates the IKK-β-mediated TPL2/MEK/ERK signaling pathway through TLR2. In agreement with the result of TLR2-mediated ERK activation by PAUF, PAUF induces increased expression of the protumorigenic cytokines RANTES and MIF in THP-1 cells. However, PAUF does not fully activate Iκ-B-α signaling pathways in THP-1 cells, and fails to translocate the p65 subunit of the nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) complex into the nucleus, resulting in no NF-κB activation. Surprisingly, we found that PAUF also associated with the CXC chemokine receptor (CXCR4)–TLR2 complex and inhibited CXCR4-dependent, TLR2-mediated NF-κB activation. Together, these findings suggest that the new cancer-associated ligand, PAUF, may activate TLR-mediated ERK signaling to produce the protumorigenic cytokines, but inhibits TLR-mediated NF-κB signaling, thereby facilitating tumor growth and escape from innate immune surveillance.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adachi H, Takano K, Morikawa M, Kanaya S, Yoshimura M, Mori Y et al. (2003). Application of a two-liquid system to sitting-drop vapour-diffusion protein crystallization. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 59: 194–196.
Akira S, Takeda K . (2004). Toll-like receptor signalling. Nat Rev Immunol 4: 499–511.
Azenshtein E, Luboshits G, Shina S, Neumark E, Shahbazian D, Weil M et al. (2002). The CC chemokine RANTES in breast carcinoma progression: regulation of expression and potential mechanisms of promalignant activity. Cancer Res 62: 1093–1102.
Bach JP, Rinn B, Meyer B, Dodel R, Bacher M . (2008). Role of MIF in inflammation and tumorigenesis. Oncology 75: 127–133.
Banerjee A, Gugasyan R, McMahon M, Gerondakis S . (2006). Diverse Toll-like receptors utilize Tpl2 to activate extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) in hemopoietic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103: 3274–3279.
Barre A, Bourne Y, Van Damme EJ, Peumans WJ, Rouge P . (2001). Mannose-binding plant lectins: different structural scaffolds for a common sugar-recognition process. Biochimie 83: 645–651.
Bourne Y, Zamboni V, Barre A, Peumans WJ, Van Damme EJ, Rouge P . (1999). Helianthus tuberosus lectin reveals a widespread scaffold for mannose-binding lectins. Structure 7: 1473–1482.
Chen R, Alvero AB, Silasi DA, Steffensen KD, Mor G . (2008). Cancers take their Toll—the function and regulation of Toll-like receptors in cancer cells. Oncogene 27: 225–233.
Cho J, Melnick M, Solidakis GP, Tsichlis PN . (2005). Tpl2 (tumor progression locus 2) phosphorylation at Thr290 is induced by lipopolysaccharide via an Ikappa-B Kinase-beta-dependent pathway and is required for Tpl2 activation by external signals. J Biol Chem 280: 20442–20448.
Folkman J . (1990). What is the evidence that tumors are angiogenesis dependent? J Natl Cancer Inst 82: 4–6.
Greten FR, Eckmann L, Greten TF, Park JM, Li ZW, Egan LJ et al. (2004). IKKbeta links inflammation and tumorigenesis in a mouse model of colitis-associated cancer. Cell 118: 285–296.
Hajishengallis G, Wang M, Liang S, Triantafilou M, Triantafilou K . (2008). Pathogen induction of CXCR4/TLR2 cross-talk impairs host defense function. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105: 13532–13537.
Huang B, Zhao J, Li H, He KL, Chen Y, Chen SH et al. (2005). Toll-like receptors on tumor cells facilitate evasion of immune surveillance. Cancer Res 65: 5009–5014.
Huang B, Zhao J, Shen S, Li H, He KL, Shen GX et al. (2007). Listeria monocytogenes promotes tumor growth via tumor cell toll-like receptor 2 signaling. Cancer Res 67: 4346–4352.
Jemal A, Tiwari RC, Murray T, Ghafoor A, Samuels A, Ward E et al. (2004). Cancer statistics, 2004. CA Cancer J Clin 54: 8–29.
Jeyaprakash AA, Katiyar S, Swaminathan CP, Sekar K, Surolia A, Vijayan M . (2003). Structural basis of the carbohydrate specificities of jacalin: an X-ray and modeling study. J Mol Biol 332: 217–228.
Jeyaprakash AA, Srivastav A, Surolia A, Vijayan M . (2004). Structural basis for the carbohydrate specificities of artocarpin: variation in the length of a loop as a strategy for generating ligand specificity. J Mol Biol 338: 757–770.
Jouault T, El Abed-El Behi M, Martinez-Esparza M, Breuilh L, Trinel PA, Chamaillard M et al. (2006). Specific recognition of Candida albicans by macrophages requires galectin-3 to discriminate Saccharomyces cerevisiae and needs association with TLR2 for signaling. J Immunol 177: 4679–4687.
Ju G, Labriola-Tompkins E, Campen CA, Benjamin WR, Karas J, Plocinski J et al. (1991). Conversion of the interleukin 1 receptor antagonist into an agonist by site-specific mutagenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88: 2658–2662.
Kelly MG, Alvero AB, Chen R, Silasi DA, Abrahams VM, Chan S et al. (2006). TLR-4 signaling promotes tumor growth and paclitaxel chemoresistance in ovarian cancer. Cancer Res 66: 3859–3868.
Kim SA, Lee Y, Jung DE, Park KH, Park JY, Gang J et al. (2009). Pancreatic adenocarcinoma up-regulated factor (PAUF), a novel up-regulated secretory protein in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Cancer Sci 100: 828–836.
Lee Y, Kim SJ, Park HD, Park EH, Huang SM, Jeon SB et al. (2010). PAUF functions in the metastasis of human pancreatic cancer cells and upregulates CXCR4 expression. Oncogene 29: 56–67.
Li Y, Komai-Koma M, Gilchrist DS, Hsu DK, Liu FT, Springall T et al. (2008). Galectin-3 is a negative regulator of lipopolysaccharide-mediated inflammation. J Immunol 181: 2781–2789.
Li YM, Pan Y, Wei Y, Cheng X, Zhou BP, Tan M et al. (2004). Upregulation of CXCR4 is essential for HER2-mediated tumor metastasis. Cancer Cell 6: 459–469.
Liu FT, Rabinovich GA . (2005). Galectins as modulators of tumour progression. Nat Rev Cancer 5: 29–41.
Miettinen M, Veckman V, Latvala S, Sareneva T, Matikainen S, Julkunen I . (2008). Live Lactobacillus rhamnosus and Streptococcus pyogenes differentially regulate Toll-like receptor (TLR) gene expression in human primary macrophages. J Leukoc Biol 84: 1092–1100.
Morse RJ, Yamamoto T, Stroud RM . (2001). Structure of Cry2Aa suggests an unexpected receptor binding epitope. Structure 9: 409–417.
Nishihira J, Ishibashi T, Fukushima T, Sun B, Sato Y, Todo S . (2003). Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF): its potential role in tumor growth and tumor-associated angiogenesis. Ann NY Acad Sci 995: 171–182.
Raman D, Baugher PJ, Thu YM, Richmond A . (2007). Role of chemokines in tumor growth. Cancer Lett 256: 137–165.
Raz A, Lotan R . (1987). Endogenous galactoside-binding lectins: a new class of functional tumor cell surface molecules related to metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev 6: 433–452.
Shimizu T, Vassylyev DG, Kido S, Doi Y, Morikawa K . (1994). Crystal structure of vitelline membrane outer layer protein I (VMO-I): a folding motif with homologous Greek key structures related by an internal three-fold symmetry. EMBO J 13: 1003–1010.
Singh S, Sadanandam A, Singh RK . (2007). Chemokines in tumor angiogenesis and metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev 26: 453–467.
Strieter RM, Burdick MD, Mestas J, Gomperts B, Keane MP, Belperio JA . (2006). Cancer CXC chemokine networks and tumour angiogenesis. Eur J Cancer 42: 768–778.
Triantafilou M, Lepper PM, Briault CD, Ahmed MA, Dmochowski JM, Schumann C et al. (2008). Chemokine receptor 4 (CXCR4) is part of the lipopolysaccharide ‘sensing apparatus’. Eur J Immunol 38: 192–203.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by grants from the National Creative Research Initiative Center Program, World Class University (WCU) program and the 21st Century Frontier Functional Human Genome Project of the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology in Korea. We thank Sang Yong Hong for technical support with the cloning work. We thank the staff of Beamline 4A at the Pohang Accelerator Laboratory, Korea, for assistance in data collection and Dr Hyun Kyu Song of Korea University for help with MAD data analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website ()
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, H., Lee, Y., Oh, Y. et al. Pancreatic adenocarcinoma upregulated factor promotes metastasis by regulating TLR/CXCR4 activation. Oncogene 30, 201–211 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.401
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.401
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Pancreatic cancer induces muscle wasting by promoting the release of pancreatic adenocarcinoma upregulated factor
Experimental & Molecular Medicine (2021)
-
Inflammation and tumor progression: signaling pathways and targeted intervention
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy (2021)
-
Interactions between tumor-derived proteins and Toll-like receptors
Experimental & Molecular Medicine (2020)
-
Porphyromonas gingivalis: Immune Subversion Activities and Role in Periodontal Dysbiosis
Current Oral Health Reports (2020)
-
Elevated expression of pancreatic adenocarcinoma upregulated factor (PAUF) is associated with poor prognosis and chemoresistance in epithelial ovarian cancer
Scientific Reports (2018)