Abstract
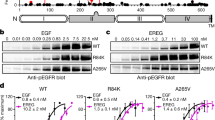
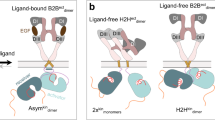
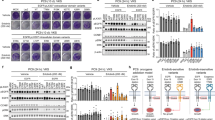
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is a receptor tyrosine kinase that is commonly activated by mutation in non–small cell lung cancer. The mechanism of this oncogenic activation is not completely understood, but in contrast to that of the wild-type EGFR, it is proposed to be independent of kinase domain dimerization. Mechanistic studies on EGFR have mainly relied on cell-based assays or isolated kinase domain measurements. Here we show, using purified, near full-length human EGFR proteins (tEGFRs), that two oncogenic mutants are fully active independently of EGF and highly resistant to the therapeutic and endogenous inhibitors cetuximab, lapatinib and MIG6. Based on the pattern of inhibition and the effects of additional asymmetric kinase dimer interface mutations, we propose that these oncogenic EGFR mutants drive and strongly depend on the formation of the asymmetric kinase dimer for activation, which has implications for drug design and cancer treatment strategies.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$189.00 per year
only $15.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schlessinger, J. Cell signaling by receptor tyrosine kinases. Cell 103, 211–225 (2000).
Hynes, N.E. & Lane, H.A. ERBB receptors and cancer: the complexity of targeted inhibitors. Nat. Rev. Cancer 5, 341–354 (2005).
Wheeler, D.L., Dunn, E.F. & Harari, P.M. Understanding resistance to EGFR inhibitors-impact on future treatment strategies. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 7, 493–507 (2010).
Stamos, J., Sliwkowski, M.X. & Eigenbrot, C. Structure of the epidermal growth factor receptor kinase domain alone and in complex with a 4-anilinoquinazoline inhibitor. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 46265–46272 (2002).
Lynch, T.J. et al. Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N. Engl. J. Med. 350, 2129–2139 (2004).
Paez, J.G. et al. EGFR mutations in lung cancer: correlation with clinical response to gefitinib therapy. Science 304, 1497–1500 (2004).
Pao, W. et al. EGF receptor gene mutations are common in lung cancers from “never smokers” and are associated with sensitivity of tumors to gefitinib and erlotinib. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101, 13306–13311 (2004).
Wood, E.R. et al. A unique structure for epidermal growth factor receptor bound to GW572016 (Lapatinib): relationships among protein conformation, inhibitor off-rate, and receptor activity in tumor cells. Cancer Res. 64, 6652–6659 (2004).
Cameron, D.A. & Stein, S. Drug Insight: intracellular inhibitors of HER2–clinical development of lapatinib in breast cancer. Nat. Clin. Pract. Oncol. 5, 512–520 (2008).
Li, S. et al. Structural basis for inhibition of the epidermal growth factor receptor by cetuximab. Cancer Cell 7, 301–311 (2005).
Mano, M. & Humblet, Y. Drug Insight: panitumumab, a human EGFR-targeted monoclonal antibody with promising clinical activity in colorectal cancer. Nat. Clin. Pract. Oncol. 5, 415–425 (2008).
Schlessinger, J. Ligand-induced, receptor-mediated dimerization and activation of EGF receptor. Cell 110, 669–672 (2002).
Jura, N. et al. Mechanism for activation of the EGF receptor catalytic domain by the juxtamembrane segment. Cell 137, 1293–1307 (2009).
Garrett, T.P. et al. Crystal structure of a truncated epidermal growth factor receptor extracellular domain bound to transforming growth factor alpha. Cell 110, 763–773 (2002).
Ogiso, H. et al. Crystal structure of the complex of human epidermal growth factor and receptor extracellular domains. Cell 110, 775–787 (2002).
Ferguson, K.M. et al. EGF activates its receptor by removing interactions that autoinhibit ectodomain dimerization. Mol. Cell 11, 507–517 (2003).
Adak, S., DeAndrade, D. & Pike, L.J. The tethering arm of the EGF receptor is required for negative cooperativity and signal transduction. J. Biol. Chem. 286, 1545–1555 (2011).
Macdonald, J.L. & Pike, L.J. Heterogeneity in EGF-binding affinities arises from negative cooperativity in an aggregating system. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 105, 112–117 (2008).
Zhang, X., Gureasko, J., Shen, K., Cole, P.A. & Kuriyan, J. An allosteric mechanism for activation of the kinase domain of epidermal growth factor receptor. Cell 125, 1137–1149 (2006).
Zhang, X. et al. Inhibition of the EGF receptor by binding of MIG6 to an activating kinase domain interface. Nature 450, 741–744 (2007).
Yun, C.H. et al. Structures of lung cancer-derived EGFR mutants and inhibitor complexes: mechanism of activation and insights into differential inhibitor sensitivity. Cancer Cell 11, 217–227 (2007).
Carey, K.D. et al. Kinetic analysis of epidermal growth factor receptor somatic mutant proteins shows increased sensitivity to the epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, erlotinib. Cancer Res. 66, 8163–8171 (2006).
Guha, U. et al. Comparisons of tyrosine phosphorylated proteins in cells expressing lung cancer-specific alleles of EGFR and KRAS. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 105, 14112–14117 (2008).
Gilmer, T.M. et al. Impact of common epidermal growth factor receptor and HER2 variants on receptor activity and inhibition by lapatinib. Cancer Res. 68, 571–579 (2008).
Mulloy, R. et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor mutants from human lung cancers exhibit enhanced catalytic activity and increased sensitivity to gefitinib. Cancer Res. 67, 2325–2330 (2007).
Okabe, T. et al. Differential constitutive activation of the epidermal growth factor receptor in non-small cell lung cancer cells bearing EGFR gene mutation and amplification. Cancer Res. 67, 2046–2053 (2007).
Qiu, C. et al. In vitro enzymatic characterization of near full length EGFR in activated and inhibited states. Biochemistry 48, 6624–6632 (2009).
Reeves, P.J., Callewaert, N., Contreras, R. & Khorana, H.G. Structure and function in rhodopsin: high-level expression of rhodopsin with restricted and homogeneous N-glycosylation by a tetracycline-inducible N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase I-negative HEK293S stable mammalian cell line. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99, 13419–13424 (2002).
Sato, J.D. et al. Biological effects in vitro of monoclonal antibodies to human epidermal growth factor receptors. Mol. Biol. Med. 1, 511–529 (1983).
Wang, D., Huang, X.Y. & Cole, P.A. Molecular determinants for Csk-catalyzed tyrosine phosphorylation of the Src tail. Biochemistry 40, 2004–2010 (2001).
Seeliger, M.A. et al. High yield bacterial expression of active c-Abl and c-Src tyrosine kinases. Protein Sci. 14, 3135–3139 (2005).
Levinson, N.M. et al. A Src-like inactive conformation in the abl tyrosine kinase domain. PLoS Biol. 4, e144 (2006).
Red Brewer, M. et al. The juxtamembrane region of the EGF receptor functions as an activation domain. Mol. Cell 34, 641–651 (2009).
Macdonald-Obermann, J.L. & Pike, L.J. The intracellular juxtamembrane domain of the epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor is responsible for the allosteric regulation of EGF binding. J. Biol. Chem. 284, 13570–13576 (2009).
Thiel, K.W. & Carpenter, G. Epidermal growth factor receptor juxtamembrane region regulates allosteric tyrosine kinase activation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 104, 19238–19243 (2007).
Qiao, Y., Molina, H., Pandey, A., Zhang, J. & Cole, P.A. Chemical rescue of a mutant enzyme in living cells. Science 311, 1293–1297 (2006).
Bose, R. et al. Phosphoproteomic analysis of Her2/neu signaling and inhibition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103, 9773–9778 (2006).
Zhu, J. et al. Protein array identification of substrates of the Epstein-Barr virus protein kinase BGLF4. J. Virol. 83, 5219–5231 (2009).
Segel, I.H. Enzyme Kinetics: Behavior and Analysis of Rapid Equilibrium and Steady-State Enzyme Systems (Wiley, New York, 1993).
Azam, M., Seeliger, M.A., Gray, N.S., Kuriyan, J. & Daley, G.Q. Activation of tyrosine kinases by mutation of the gatekeeper threonine. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 15, 1109–1118 (2008).
Acknowledgements
We thank the US National Institutes of Health (GM099321 to D.J.L. and CA074305 to P.A.C.) for financial support and A. Mildvan and J. Stivers for helpful discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Z.W., D.J.L. and P.A.C. conceived of the project and designed the research. Z.W., M.K.T., P.A.L., K.K. and S.H. conducted experiments. All authors helped analyze the results and wrote the paper.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–6 and Supplementary Methods (PDF 749 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Z., Longo, P., Tarrant, M. et al. Mechanistic insights into the activation of oncogenic forms of EGF receptor. Nat Struct Mol Biol 18, 1388–1393 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.2168
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.2168
This article is cited by
-
Molecular basis for cooperative binding and synergy of ATP-site and allosteric EGFR inhibitors
Nature Communications (2022)
-
Molecular insight into the affinity, specificity and cross-reactivity of systematic hepatocellular carcinoma RALT interaction profile with human receptor tyrosine kinases
Amino Acids (2021)
-
Basic Amino Acids Within the Juxtamembrane Domain of the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Regulate Receptor Dimerization and Auto-phosphorylation
The Protein Journal (2020)
-
Mechanisms of receptor tyrosine kinase activation in cancer
Molecular Cancer (2018)
-
Overcoming resistance to HER2 inhibitors through state-specific kinase binding
Nature Chemical Biology (2016)