Abstract
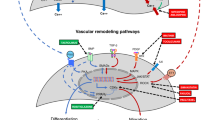
Hepatopulmonary syndrome (HPS) is a serious vascular complication of liver disease that occurs in 5–32% of patients with cirrhosis. The presence of HPS markedly increases mortality. No effective medical therapies are currently available and liver transplantation is the only established treatment option for HPS. The definition and diagnosis of HPS are established by the presence of a triad of liver disease with intrapulmonary vascular dilation that causes abnormal arterial gas exchange. Experimental biliary cirrhosis induced by common bile duct ligation in the rat reproduces the pulmonary vascular and gas exchange abnormalities of human HPS and serves as a pertinent animal model. Pulmonary microvascular dilation and angiogenesis are two central pathogenic features that drive abnormal pulmonary gas exchange in experimental HPS, and thus might underlie HPS in humans. Defining the mechanisms involved in the microvascular alterations of HPS has the potential to lead to effective medical therapies. This Review focuses on the current understanding of the pathogenesis, clinical features and management of HPS.
Key Points
-
HPS is a common finding in patients with cirrhosis that increases mortality in this context
-
HPS is defined by the triad of liver disease with intrapulmonary vascular dilatation causing abnormal oxygenation
-
No effective medical therapies for HPS exist and liver transplantation is the only treatment option
-
Chronic common bile duct ligation in the rat is the only established experimental model of human HPS
-
Excess lung production of gaseous vasodilators, nitric oxide and carbon monoxide contributes to vasodilatation in human and experimental HPS
-
Pulmonary angiogenesis has an additive role in the development of experimental HPS
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rodriguez-Roisin, R. & Krowka, M. J. Hepatopulmonary syndrome—a liver-induced lung vascular disorder. N. Engl. J. Med. 358, 2378–2387 (2008).
Schenk, P. et al. Hepatopulmonary syndrome: prevalence and predictive value of various cut offs for arterial oxygenation and their clinical consequences. Gut 51, 853–859 (2002).
Swanson, K., Wiesner, R. & Krowka, M. Natural history of hepatopulmonary syndrome: impact of liver transplantation. Hepatology 41, 1122–1129 (2005).
Arguedas, M., Abrams, G. A., Krowka, M. J. & Fallon, M. B. Prospective evaluation of outcomes and predictors of mortality in patients with hepatopulmonary syndrome undergoing liver transplantation. Hepatology 37, 192–197 (2003).
Arguedas, M., Singh, H., Faulk, D. & Fallon, M. B. Utility of pulse oximetry screening for hepatopulmonary syndrome. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 5, 749–754 (2007).
Fallon, M. B. et al. Impact of hepatopulmonary syndrome on quality of life and survival in liver transplant candidates. Gastroenterology 135, 1168–1175 (2008).
Krowka, M. J. & Cortese, D. A. Hepatopulmonary syndrome: an evolving perspective in the era of liver transplantation. Hepatology 11, 138–141 (1990).
Battaglia, S. E., Pretto, J. J., Irving, L. B., Jones, R. M. & Angus, P. W. Resolution of gas exchange abnormalities and intrapulmonary shunting following liver transplantation. Hepatology 25, 1228–1232 (1997).
Benjaminov, F. S. et al. Portopulmonary hypertension in decompensated cirrhosis with refractory ascites. Gut 52, 1355–1362 (2003).
Castro, M. et al. Frequency and clinical implications of increased pulmonary artery pressures in liver transplantation. Mayo Clin. Proc. 71, 543–551 (1996).
Hadengue, A., Benhayoun, M., Lebrec, D. & Benhamou, J. Pulmonary hypertension complicating portal hypertension: prevalence and relation to splanchnic hemodynamics. Gastroenterology 100, 520–528 (1991).
Hoeper, M. M., Krowka, M. J. & Strassburg, C. P. Portopulmonary hypertension and hepatopulmonary syndrome. Lancet 363, 1461–1468 (2004).
Mantz, F. & Craige, E. Portal axis thrombosis with spontaneous portocaval shunt and resultant cor pulmonale. AMA Arch. Pathol. 52, 91–97 (1951).
McDonnell, P., Toye, P. & Hutchins, G. Primary pulmonary hypertension and cirrhosis: are they related? Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 127, 437–441 (1983).
Plevak, D., Krowka, M., Rettke, S., Dunn, W. & Southorn, P. Successful liver transplantation in patients with mild to moderate pulmonary hypertension. Transplant. Proc. 25, 1840 (1993).
Rodriguez-Roisin, R. et al. Pulmonary–hepatic vascular disorders (PHD). Eur. Respir. J. 24, 861–880 (2004).
Austin, M. J. et al. Safety and efficacy of combined use of sildenafil, bosentan, and iloprost before and after liver transplantation in severe portopulmonary hypertension. Liver Transpl. 14, 287–291 (2008).
Chua, R., Keogh, A. & Miyashita, M. Novel use of sildenafil in the treatment of portopulmonary hypertension. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 24, 498–500 (2005).
Halank, M. et al. Use of oral endothelin-receptor antagonist bosentan in the treatment of portopulmonary hypertension. Transplantation 77, 1775–1776 (2004).
Minder, S. et al. Intravenous iloprost bridging to orthotopic liver transplantation in portopulmonary hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 24, 703–707 (2004).
Gough, M. S. & White, R. J. Sildenafil therapy is associated with improved hemodynamics in liver transplantation candidates with pulmonary arterial hypertension. Liver Transpl. 15, 30–36 (2009).
Ioachimescu, O. C., Mehta, A. C. & Stoller, J. K. Hepatopulmonary syndrome following portopulmonary hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 29, 1277–1280 (2007).
Jones, F. D. et al. The coexistence of portopulmonary hypertension and hepatopulmonary syndrome. Anesthesiology 90, 626–629 (1999).
Aucejo, F. et al. Pulmonary hypertension after liver transplantation in patients with antecedent hepatopulmonary syndrome: a report of 2 cases and review of the literature. Liver Transpl. 12, 1278–1282 (2006).
Martinez-Palli, G. et al. Severe portopulmonary hypertension after liver transplantation in a patient with preexisting hepatopulmonary syndrome. J. Hepatol. 31, 1075–1079 (1999).
Mal, H. et al. Pulmonary hypertension following hepatopulmonary syndrome in a patient with cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 31, 360–364 (1999).
Pham, D. M., Subramanian, R. & Parekh, S. Coexisting hepatopulmonary syndrome and portopulmonary hypertension: implications for liver transplantation. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 44, e136–e140 (2010).
Abrams, G., Nanda, N., Dubovsky, E., Krowka, M. & Fallon, M. Use of macroaggregated albumin lung perfusion scan to diagnose hepatopulmonary syndrome: a new approach. Gastroenterology 114, 305–310 (1998).
Martinez, G. et al. Hepatopulmonary syndrome associated with cardiorespiratory disease. J. Hepatol. 30, 882–889 (1999).
Abrams, G. A., Jaffe, C. C., Hoffer, P. B., Binder, H. J. & Fallon, M. B. Diagnostic utility of contrast echocardiography and lung perfusion scan in patients with hepatopulmonary syndrome. Gastroenterology 109, 1283–1288 (1995).
Martinez, G. et al. Hepatopulmonary syndrome in candidates for liver transplantation. J. Hepatol. 34, 756–758 (2001).
Abrams, G. & Fallon, M. The hepatopulmonary syndrome. Clin. Liver Dis. 1, 185–200 (1997).
Binay, K. et al. Hepatopulmonary syndrome in inferior vena cava obstruction responding to cavoplasty. Gastroenterology 118, 192–196 (2000).
Gupta, D. et al. Prevalence of hepatopulmonary syndrome in cirrhosis and extrahepatic portal venous obstruction. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 96, 3395–3399 (2001).
Fuhrmann, V. et al. Hepatopulmonary syndrome in patients with hypoxic hepatitis. Gastroenterology 131, 69–75 (2006).
Regev, A. et al. Transient hepatopulmonary syndrome in a patient with acute hepatitis A. J. Viral Hep. 8, 83–86 (2001).
Teuber, G. et al. Pulmonary dysfunction in non-cirrhotic patients with chronic viral hepatitis. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 13, 311–318 (2002).
Lee, D. & Lepler, L. Severe intrapulmonary shunting associated with metastatic carcinoid. Chest 115, 1203–1207 (1999).
Law, Y. M. et al. Cardiopulmonary manifestations of portovenous shunts from congenital absence of the portal vein: pulmonary hypertension and pulmonary vascular dilatation. Pediatr. Transplant. 15, E162–E168 (2011).
Gupta, N. A. et al. Pediatric hepatopulmonary syndrome is seen with polysplenia/interrupted inferior vena cava and without cirrhosis. Liver Transpl. 13, 680–686 (2007).
Kinane, T. B. & Westra, S. J. Case records of the Massachusetts General Hospital. Weekly clinicopathological exercises. Case 31–2004. A four-year-old boy with hypoxemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 351, 1667–1675 (2004).
O'Leary, J. G., Rees, C. R., Klintmalm, G. B. & Davis, G. L. Inferior vena cava stent resolves hepatopulmonary syndrome in an adult with a spontaneous inferior vena cava–portal vein shunt. Liver Transpl. 15, 1897–1900 (2009).
McFaul, R., Tajik, A., Mair, D., Danielson, G. & Seward, J. Development of pulmonary arteriovenous shunt after superior vena cava-right pulmonary artery (glenn) anastamosis. Report of four cases. Circulation 55, 212–216 (1977).
Srivastava, D. et al. Hepatic venous blood and the development of pulmonary arteriovenous malformations in congenital heart disease. Circulation 92, 1217–1222 (1995).
Duncan, B. W. & Desai, S. Pulmonary arteriovenous malformations after cavopulmonary anastomosis. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 76, 1759–1766 (2003).
Lee, J., Menkis, A. H. & Rosenberg, H. C. Reversal of pulmonary arteriovenous malformation after diversion of anomalous hepatic drainage. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 65, 848–849 (1998).
Rodriguez-Roison, R., Agusti, A. G. & Roca, J. The hepatopulmonary syndrome: new name, old complexities. Thorax 47, 897–902 (1992).
Lange, P. A. & Stoller, J. K. The hepatopulmonary syndrome. Ann. Intern. Med. 122, 521–529 (1995).
Fallon, M., Mulligan, D., Gish, R. & Krowka, M. Model for end-stage liver disease (MELD) exception for hepatopulmonary syndrome. Liver Transpl. 12, s105–s107 (2006).
Krowka, M. J. et al. Hepatopulmonary syndrome and portopulmonary hypertension: a report of the multicenter liver transplant database. Liver Transpl. 10, 174–182 (2004).
Schenk, P. et al. Prognostic significance of the hepatopulmonary syndrome in patients with cirrhosis. Gastroenterology 125, 1042–1052 (2003).
Abrams, G. A., Sanders, M. K. & Fallon, M. B. Utility of pulse oximetry in the detection of arterial hypoxemia in liver transplant candidates. Liver Transpl. 8, 391–396 (2002).
Palma, D. T. & Fallon, M. B. The hepatopulmonary syndrome. J. Hepatol. 45, 617–625 (2006).
Crapo, R. O., Jensen, R. L., Hegewald, M. & Tashkin, D. P. Arterial blood gas reference values for sea level and an altitude of 1,400 meters. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 160, 1525–1531 (1999).
Cardús, J. et al. Increase in pulmonary ventilation-perfusion inequality with age in healthy individuals. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 156, 648–653 (1997).
Harris, E., Kenyon, A., Nisbet, H., Seelye, E. & Whitlock, R. The normal alveolar-arterial oxygen-tension gradient in man. Clin. Sci. Mol. Med. 46, 89–104 (1974).
Krowka, M. J., Dickson, E. R. & Cortese, D. A. Hepatopulmonary syndrome. Clinical observations and lack of therapeutic response to somatostatin analogue. Chest 104, 515–521 (1993).
Anel, R. M. & Sheagren, J. N. Novel presentation and approach to management of hepatopulmonary syndrome with use of antimicrobial agents. Clin. Infect. Dis. 32, E131–E136 (2001).
Poterucha, J. J. et al. Failure of hepatopulmonary syndrome to resolve after liver transplantation and successful treatment with embolotherapy. Hepatology 21, 96–100 (1995).
Molleston, J. P. et al. Brain abscess in hepatopulmonary syndrome. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 29, 225–226 (1999).
Stickland, M. K. et al. Intra-pulmonary shunt and pulmonary gas exchange during exercise in humans. J. Physiol. 561, 321–329 (2004).
Berthelot, P., Walter, J. G., Sherlock, S. & Reid, L. Arterial changes in the lungs in cirrhosis of the liver-lung spider nevi. N. Engl. J. Med. 274, 291–298 (1966).
Herve, P. et al. Pulmonary vascular disorders in portal hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 11, 1153–1166 (1998).
Roberts, D. N., Arguedas, M. R. & Fallon, M. B. Cost-effectiveness of screening for hepatopulmonary syndrome in liver transplant candidates. Liver Transpl. 13, 206–214 (2007).
Krowka, M. et al. Hepatopulmonary syndrome: a prospective study of relationships between severity of liver disease, pao2 response to 100% oxygen, and brain uptake after 99mTc MAA lung scanning. Chest 118, 615–624 (2000).
Krowka, M. J. & Cortese, D. A. Hepatopulmonary syndrome. Current concepts in diagnostic and therapeutic considerations. Chest 105, 1528–1537 (1994).
Sussman, N. L., Kochar, R. & Fallon, M. B. Pulmonary complications in cirrhosis. Curr. Opin. Organ Transplant. 16, 281–288 (2011).
Aller, R. et al. Diagnosis of hepatopulmonary syndrome with contrast transesophageal echocardiography: advantages over contrast transthoracic echocardiography. Dig. Dis. Sci. 44, 1243–1248 (1999).
Vedrinne, J. M. et al. Comparison of transesophageal and transthoracic contrast echocardiography for detection of an intrapulmonary shunt in liver disease. Chest 111, 1236–1240 (1997).
Fischer, C. H. et al. Role of contrast-enhanced transesophageal echocardiography for detection of and scoring intrapulmonary vascular dilatation. Echocardiography 27, 1233–1237 (2010).
Ryu, J. K. & Oh, J. H. Hepatopulmonary syndrome: angiography and therapeutic embolization. Clin. Imaging 27, 97–100 (2003).
Saad, N. E. A., Lee, D. E., Waldman, D. L. & Saad, W. E. A. Pulmonary arterial coil embolization for the management of persistent type I hepatopulmonary syndrome after liver transplantation. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 18, 1576–1580 (2007).
Koksal, D. et al. Evaluation of intrapulmonary vascular dilatations with high-resolution computed thorax tomography in patients with hepatopulmonary syndrome. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 40, 77–83 (2006).
Suga, K., Kawakami, Y., Iwanaga, H., Tokuda, O. & Matsunaga, N. Findings of hepatopulmonary syndrome on breath-hold perfusion spect-ct fusion images. Ann. Nucl. Med. 23, 413–419 (2009).
Schraufnagel, D., Malik, R., Goel, V., Ohara, N. & Chang, S. Lung capillary changes in hepatic cirrhosis in rats. Am. J. Physiol. 272, L139–L147 (1997).
Schraufnagel, D. & Kay, J. Structural and pathologic changes in the lung vasculature in chronic liver disease. Clin. Chest Med. 17, 1–15 (1996).
Gómez, F. et al. Effects of nebulized ng-nitro-l-arginine methyl ester in patients with hepatopulmonary syndrome. Hepatology 43, 1084–1091 (2006).
Gómez, F. et al. Gas exchange mechanism of orthodeoxia in hepatopulmonary syndrome. Hepatology 40, 660–666 (2004).
Chang, S. W. & O'Hara, N. Increased pulmonary vascular permeability in rats with biliary cirrhosis: role of thomboxane A2. Am. J. Physiol. 264, L245–L252 (1993).
Chang, S. W. & O'Hara, N. Pulmonary circulatory dysfunction in rats with biliary cirrhosis. An animal model of the hepatopulmonary syndrome. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 145, 798–805 (1992).
Chang, S. W. & O'Hara, N. Chronic biliary obstruction induces pulmonary intravascular phagocytosis and endotoxin sensitivity in rats. J. Clin. Invest. 94, 2009–2019 (1994).
Chang, S. W. & O'Hara, N. Pulmonary circulatory dysfunction in rats with biliary cirrhosis. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 148, 798–805 (1992).
Fallon, M. B. et al. The role of endothelial nitric oxide synthase in the pathogenesis of a rat model of hepatopulmonary syndrome. Gastroenterology 113, 606–614 (1997).
Fallon, M. B., Abrams, G. A., McGrath, J. W., Hou, Z. & Luo, B. Common bile duct ligation in the rat: a model of intrapulmonary vasodilatation and hepatopulmonary syndrome. Am. J. Physiol. 272, G779–G784 (1997).
Luo, B., Abrams, G. A. & Fallon, M. B. Endothelin-1 in the rat bile duct ligation model of hepatopulmonary syndrome: correlation with pulmonary dysfunction. J. Hepatol. 29, 571–578 (1998).
Zhang, J. et al. Analysis of pulmonary heme oxygenase-1 and nitric oxide synthase alterations in experimental hepatopulmonary syndrome. Gastroenterology 125, 1441–1451 (2003).
Georgiev, P. et al. Characterization of time-related changes after experimental bile duct ligation. Br. J. Surg. 95, 646–656 (2008).
Groszmann, R. J., Vorobioff, J. & Riley, E. Splanchnic hemodynamics in portal-hypertensive rats: measurement with gamma-labeled microspheres. Am. J. Physiol. 242, G156–G160 (1982).
Vorobioff, J., Bredfeldt, J. & Grosszmann, R. J. Hyperdynamic circulation in a portal hypertensive rat model: a primary factor for maintenance of chronic portal hypertension. Am. J. Physiol. 244, G52–G57 (1983).
Abraldes, J. G. et al. Mild increases in portal pressure upregulate vascular endothelial growth factor and endothelial nitric oxide synthase in the intestinal microcirculatory bed, leading to a hyperdynamic state. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 290, G980–G987 (2006).
Luo, B. et al. ET-1 and TNF-α in HPS: analysis in prehepatic portal hypertension and biliary and nonbiliary cirrhosis in rats. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 286, G294–G303 (2004).
Luo, B. et al. Increased pulmonary vascular endothelin b receptor expression and responsiveness to endothelin-1 in cirrhotic and portal hypertensive rats: a potential mechanism in experimental hepatopulmonary syndrome. J. Hepatol. 38, 556–563 (2003).
Geerts, A. et al. Comparison of three research models of portal hypertension in mice: Macroscopic, histological and portal pressure evaluation. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 89, 251–263 (2008).
Mejias, M. et al. Beneficial effects of sorafenib on splanchnic, intrahepatic, and portocollateral circulations in portal hypertensive and cirrhotic rats. Hepatology 49, 1245–1256 (2009).
Laleman, W. et al. A stable model of cirrhotic portal hypertension in the rat: thioacetamide revisited. Eur. J. Clin. Invest. 36, 242–249 (2006).
Zhang, J. et al. Pulmonary angiogenesis in a rat model of hepatopulmonary syndrome. Gastroenterology 136, 1070–1080 (2009).
Zhang, M., Luo, B., Chen, S. J., Abrams, G. A. & Fallon, M. B. Endothelin-1 stimulation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase in the pathogenesis of hepatopulmonary syndrome. Am. J. Physiol. 277, G944–G952 (1999).
Zhang, X.-J. et al. Intrapulmonary vascular dilatation and nitric oxide in hypoxemic rats with chronic bile duct ligation. J. Hepatol. 39, 724–730 (2003).
Miyamoto, A. et al. Effect of chronic methylene blue administration on hypoxemia in rats with common bile duct ligation. Hepatol. Res. 40, 622–632 (2010).
Nunes, H. et al. Role of nitric oxide in hepatopulmonary syndrome in cirrhotic rats. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 164, 879–885 (2001).
Brussino, L. et al. Effect on dyspnoea and hypoxaemia of inhaled ng-nitro-l-arginine methyl ester in hepatopulmonary syndrome. Lancet 362, 43–44 (2003).
Luo, B. et al. Cholangiocyte endothelin-1 and transforming growth factor-beta1 production in rat experimental hepatopulmonary syndrome. Gastroenterology 129, 682–695 (2005).
Tang, L. et al. Modulation of pulmonary endothelial endothelin b receptor expression and signaling: Implications for experimental hepatopulmonary syndrome. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 292, L1467–L1472 (2007).
Ling, Y. et al. The role of endothelin-1 and the endothelin b receptor in the pathogenesis of experimental hepatopulmonary syndrome. Hepatology 39, 1593–1602 (2004).
Zhang, J. et al. Attenuation of experimental hepatopulmonary syndrome in endothelin b receptor-deficient rats. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 296, G704–G708 (2009).
Schroeder, R. A., Ewing, C. A., Sitzmann, J. V. & Kuo, P. C. Pulmonary expression of inos and ho-1 protein is upregulated in a rat model of prehepatic portal hypertension. Dig. Dis. Sci. 45, 2405–2410 (2000).
Carter, E. P. et al. Regulation of heme oxygenase-1 by nitric oxide during hepatopulmonary syndrome. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 283, L346–L353 (2002).
Roberts, K. E. et al. Genetic risk factors for hepatopulmonary syndrome in patients with advanced liver disease. Gastroenterology 139, 130–139e124 (2010).
Thenappan, T. et al. A central role for CD68+ macrophages in hepatopulmonary syndrome. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 183, 1080–1091 (2011).
Bosch, J. Vascular deterioration in cirrhosis: the big picture. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 41, S247–S253 (2007).
Dimmeler, S. et al. Activation of nitric oxide synthase in endothelial cells by akt-dependent phosphorylation. Nature 399, 601–605 (1999).
Dimmeler, S. & Zeiher, A. M. Akt takes center stage in angiogenesis signaling. Circ. Res. 86, 4–5 (2000).
Fernandez, M. et al. Reversal of portal hypertension and hyperdynamic splanchnic circulation by combined vascular endothelial growth factor and platelet-derived growth factor blockade in rats. Hepatology 46, 1208–1217 (2007).
Tugues, S. et al. Antiangiogenic treatment with sunitinib ameliorates inflammatory infiltrate, fibrosis, and portal pressure in cirrhotic rats. Hepatology 46, 1919–1926 (2007).
Lee, J., Semela, D., Iredale, J. & Shah, V. Sinusoidal remodeling and angiogenesis: a new function for the liver-specific pericyte? Hepatology 45, 817–825 (2007).
Fernandez, L. G. et al. Differential vascular growth in postpneumonectomy compensatory lung growth. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 133, 309–316 (2007).
Gill, S. et al. Role of pulmonary intravascular macrophages in endotoxin-induced lung inflammation and mortality in a rat model. Respir. Res. 9, 69 (2008).
Zhang, J. et al. Pentoxifylline attenuation of experimental hepatopulmonary syndrome. J. Appl. Physiol. 102, 949–955 (2007).
Rabiller, A. et al. Prevention of gram-negative translocation reduces the severity of hepatopulmonary syndrome. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 166, 514–517 (2002).
Sztrymf, B. et al. Prevention of hepatopulmonary syndrome by pentoxifylline in cirrhotic rats. Eur. Respir. J. 23, 752–758 (2004).
Hemprich, U., Papadakos, P. J. & Lachmann, B. Respiratory failure and hypoxemia in the cirrhotic patient including hepatopulmonary syndrome. Curr. Opin. Anaesthesiol. 23, 133–138 (2010).
Agusti, A. G. N., Roca, J. & Rodriguez-Roisin, R. Mechanisms of gas exchange impairment in patients with liver cirrhosis. Clin. Chest Med. 17, 49–66 (1996).
Krowka, M. J. et al. Hepatopulmonary syndrome: a prospective study of relationships between severity of liver disease, PaO2 response to 100% oxygen, and brain uptake after 99mTc MAA lung scanning. Chest 118, 615–624 (2000).
Cremona, G. et al. Elevated exhaled nitric oxide in patients with hepatopulmonary syndrome. Eur. Respir. J. 8, 1883–1885 (1995).
Rolla, G., Brussino, L. & Colagrande, P. Exhaled nitric oxide and impaired oxygenation in cirrhotic patients before and after liver transplantation. Ann. Intern. Med. 129, 375–378 (1998).
Rolla, G. et al. Exhaled nitric oxide and oxygenation abnormalities in hepatic cirrhosis. Hepatology 26, 842–847 (1997).
Arguedas, M. R., Drake, B. B., Kapoor, A. & Fallon, M. B. Carboxyhemoglobin levels in cirrhotic patients with and without hepatopulmonary syndrome. Gastroenterology 128, 328–333 (2005).
Sood, G. et al. Utility of a dyspnea–fatigue index for screening liver transplant candidates for hepatopulmonary syndrome. Hepatology 28, 2319 (1998).
Robin, E. D., Laman, D., Horn, B. R. & Theodore, J. Platypnea related to orthodeoxia caused by true vascular lung shunts. N. Engl. J. Med. 294, 941–943 (1976).
Martinez, G. P. et al. Hepatopulmonary syndrome in candidates for liver transplantation. J. Hepatol. 34, 651–657 (2001).
Palma, D. T., Philips, G. M., Arguedas, M. R., Harding, S. M. & Fallon, M. B. Oxygen desaturation during sleep in hepatopulmonary syndrome. Hepatology 47, 1257–1263 (2008).
McAdams, H. P. et al. The hepatopulmonary syndrome: radiologic findings in 10 patients. Am. J. Roentgenol. 166, 1379–1385 (1996).
Fallon, M. & Abrams, G. Pulmonary dysfunction in chronic liver disease. Hepatology 32, 859–865 (2000).
Lima, B. et al. Frequency, clinical characteristics, and respiratory parameters of hepatopulmonary syndrome. Mayo Clin. Proc. 79, 42–48 (2004).
Yigit, I., Hacievliyagil, S., Seckin, Y., Öner, R. & Karincaoglu, M. The relationship between severity of liver cirrhosis and pulmonary function tests. Dig. Dis. Sci. 53, 1951–1956 (2008).
Møller, S., Krag, A., Madsen, J. L., Henriksen, J. H. & Bendtsen, F. Pulmonary dysfunction and hepatopulmonary syndrome in cirrhosis and portal hypertension. Liver Int. 29, 1528–1537 (2009).
Tumgor, G. et al. Childhood cirrhosis, hepatopulmonary syndrome and liver transplantation. Pediatr. Transplant. 12, 353–357 (2008).
Whitworth, J. R., Ivy, D. D., Gralla, J., Narkewicz, M. R. & Sokol, R. J. Pulmonary vascular complications in asymptomatic children with portal hypertension. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 49, 607–612 (2009).
El-Shabrawi, M. H. et al. 99mTechnetium-macroaggregated albumin perfusion lung scan versus contrast enhanced echocardiography in the diagnosis of the hepatopulmonary syndrome in children with chronic liver disease. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 22, 1006–1012 (2010).
Gupta, S. et al. Norfloxacin therapy for hepatopulmonary syndrome: a pilot randomized controlled trial. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 8, 1095–1098 (2010).
Abrams, G. A. & Fallon, M. B. Treatment of hepatopulmonary syndrome with allium sativum l (garlic): a pilot trial. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 27, 232–235 (1998).
Sani, M. N., Kianifar, H. R., Kianee, A. & Khatami, G. Effect of oral garlic on arterial oxygen pressure in children with hepatopulmonary syndrome. World J. Gastroenterol. 12, 2427–2431 (2006).
De, B. K. et al. The role of garlic in hepatopulmonary syndrome: a randomized controlled trial. Can. J. Gastroenterol. 24, 183–188 (2010).
Akyüz, F. et al. Is there any medical therapeutic option in hepatopulmonary syndrome? A case report. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 16, 126–128 (2005).
Tanikella, R., Philips, G., Faulk, D., Kawut, S. & Fallon, M. Pilot study of pentoxifylline in hepatopulmonary syndrome. Liver Transpl. 14, 1199–1203 (2008).
Gupta, L. B. et al. Pentoxifylline therapy for hepatopulmonary syndrome: a pilot study. Arch. Intern. Med. 168, 1820–1823 (2008).
Iqbal, C. W. et al. Liver transplantation for pulmonary vascular complications of pediatric end-stage liver disease. J. Pediatr. Surg. 43, 1813–1820 (2008).
Krug, S., Seyfarth, H.-J., Hagendorff, A. & Wirtz, H. Inhaled iloprost for hepatopulmonary syndrome: Improvement of hypoxemia. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 19, 1140–1143 (2007).
Lau, E. M. T., McCaughan, G. & Torzillo, P. J. Improvement in hepatopulmonary syndrome after methadone withdrawal: a case report with implications for disease mechanism. Liver Transpl. 16, 870–873 (2010).
Reigler, J. L., Lang, K. A., Johnson, S. P. & Westerman, J. H. Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt improves oxygenation in hepatopulmonary syndrome. Gastroenterology 109, 978–983 (1995).
Selim, K. M., Akriviadis, E. A., Zuckerman, E., Chen, D. & Reynolds, T. B. Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt: a successful treatment for hepatopulmonary syndrome. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 93, 455–458 (1998).
Allgaier, H. P. et al. Hepatopulmonary syndrome: Successful treatment by transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic stent-shunt (tips). J. Hepatol. 23, 102–105 (1995).
Paramesh, A. et al. Improvement of hepatopulmonary syndrome after transjugular intrahepatic portasystemic shunting: case report and review of literature. Pediatr. Transplant. 7, 157–162 (2003).
Corley, D. A., Scharschmidt, B., Bass, N., Somberg, K. & Gold, W. Lack of efficacy of tips for hepatopulmonary syndrome. Gastroenterology 113, 728–731 (1997).
Morikawa, N. et al. Resolution of hepatopulmonary syndrome after ligation of a portosystemic shunt in a pediatric patient with an abernethy malformation. J. Pediatr. Surg. 43, e35–e38 (2008).
Gupta, S. et al. Improved survival after liver transplantation in patients with hepatopulmonary syndrome. Am. J. Transplant. 10, 354–363 (2010).
Motomura, T. et al. Living donor liver transplantation for end-stage liver disease with severe hepatopulmonary syndrome: report of a case. Surg. Today 41, 436–440 (2011).
Chen, K. & Li, B. Reversal of severe hepatopulmonary syndrome in chronic hepatic cirrhosis by living donor liver transplantation: Report of two cases. Surg. Today 41, 441–443 (2011).
Schiller, O. et al. Nitric oxide for post-liver-transplantation hypoxemia in pediatric hepatopulmonary syndrome: case report and review. Pediatr. Transplant. 15, E130–E134 (2011).
Durand, P. et al. Reversal of hypoxemia by inhaled nitric oxide in children with severe hepatopulmonary syndrome, type 1, during and after liver transplantation. Transplantation 65, 437–439 (1998).
Taniai, N. et al. Reversal of hypoxemia by inhaled nitric oxide in a child with hepatopulmonary syndrome after living-related liver transplantation. Transplant. Proc. 34, 2791–2792 (2002).
Meyers, C., Low, L., Kaufman, L., Druger, G. & Wong, L. Trendelenburg positioning and continuous lateral rotation improve oxygenation in heaptopulmonary syndrome after liver transplantation. Liver Transpl. Surg. 6, 510–512 (1998).
Taille, C. et al. Liver transplantation for hepatopulmonary syndrome: a ten-year experience in Paris, France. Transplantation 79, 1482–1489 (2003).
Deberaldini, M. et al. Hepatopulmonary syndrome: morbidity and survival after liver transplantation. Transplant. Proc. 40, 3512–3516 (2008).
Schiffer, E. et al. Hepatopulmonary syndrome increases the postoperative mortality rate following liver transplantation: a prospective study in 90 patients. Am. J. Transplant. 6, 1430–1437 (2006).
De Palma, M., Murdoch, C., Venneri, M. A., Naldini, L. & Lewis, C. E. Tie2-expressing monocytes: regulation of tumor angiogenesis and therapeutic implications. Trends Immunol. 28, 545–550 (2007).
Elsheikh, E. et al. Only a specific subset of human peripheral-blood monocytes has endothelial-like functional capacity. Blood 106, 2347–2355 (2005).
Venneri, M. A. et al. Identification of proangiogenic tie2-expressing monocytes (TEMS) in human peripheral blood and cancer. Blood 109, 5276–5285 (2007).
Schenk, P., Madl, C., Rezale-Majd, S., Lehr, S. & Muller, C. Methylene blue improves the hepatopulmonary syndrome. Ann. Intern. Med. 133, 701–706 (2000).
Rolla, G., Bucca, C. & Brussino, L. Methylene blue in the hepatopulmonary syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 331, 1098 (1994).
Almeida, J. A. et al. Deleterious effect of nitric oxide inhibition in chronic hepatopulmonary syndrome. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 19, 341–346 (2007).
Tekin, A. et al. Effects of caffeic acid phenethyl ester (cape) on hepatopulmonary syndrome. Inflammation 34, 614–619 (2011).
Tieppo, J. et al. Quercetin administration ameliorates pulmonary complications of cirrhosis in rats. J. Nutr. 139, 1339–1346 (2009).
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the support of NIH grant 5DKR01DK056804 (M. B. Fallon) and an award from the American Heart Association (J. Zhang).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Both authors contributed equally to all aspects of this article.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Fallon, M. Hepatopulmonary syndrome: update on pathogenesis and clinical features. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 9, 539–549 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrgastro.2012.123
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nrgastro.2012.123
This article is cited by
-
Quercetin ameliorates acute lung injury in a rat model of hepatopulmonary syndrome
BMC Complementary Medicine and Therapies (2022)
-
Does Biliodigestive Anastomosis Have Any Effect on the Reversal of Hepatopulmonary Syndrome in a Biliary Cirrhosis Experimental Model?
Digestive Diseases and Sciences (2019)
-
Late complications of biliary atresia: hepatopulmonary syndrome and portopulmonary hypertension
Pediatric Surgery International (2017)
-
Inhibition of autophagy ameliorates pulmonary microvascular dilation and PMVECs excessive proliferation in rat experimental hepatopulmonary syndrome
Scientific Reports (2016)
-
Hepatopulmonary Syndrome
Digestive Diseases and Sciences (2015)