Abstract
Arising from G. Yeretssian et al. Nature 474, 96–99 (2011)10.1038/nature09982.
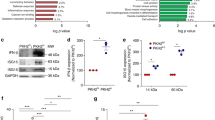
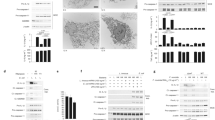
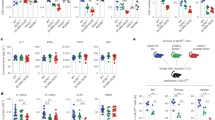
Innate immune signalling mediated by the nucleotide-binding and oligomerization domain (NOD) receptors for pathogen-associated constituents regulates the response to intracellular peptidoglycans present in Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria. Recently, Yeretssian et al.1 reported that the pro-apoptotic BH3-only BCL2 family member BID is essential for NOD-mediated immune signalling. This was on the basis of their finding that bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs) from Bid−/− mice failed to activate NF-κB and extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), and were unable to secrete inflammatory cytokines after stimulation with NOD ligands, and that BID-deficient mice were also defective in mounting a cytokine response to in vivo challenge with NOD ligands. Using the same strain of Bid−/− mice used by Yeretssian et al.1, we found that the mice responded like wild-type mice to NOD ligands, and that the levels of NF-κB or ERK activation and cytokine secretion from Bid−/− BMDMs were indistinguishable from the wild-type response. We therefore propose that the non-apoptotic role of BID in inflammation and innate immunity should be reassessed.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yeretssian, G. et al. Non-apoptotic role of BID in inflammation and innate immunity. Nature 474, 96–99 (2011)
Kaufmann, T., Gugasyan, R., Gerondakis, S., Dixit, V. M. & Strasser, A. Loss of the BH3-only protein Bid does not rescue RelA-deficient embryos from TNF-R1-mediated fatal hepatocyte destruction. Cell Death Differ. 14, 637–639 (2007)
Kobayashi, K. et al. RICK/Rip2/CARDIAK mediates signalling for receptors of the innate and adaptive immune systems. Nature 416, 194–199 (2002)
Saiki, I. & Fidler, I. J. Synergistic activation by recombinant mouse interferon-gamma and muramyl dipeptide of tumoricidal properties in mouse macrophages. J. Immunol. 135, 684–688 (1985)
Yin, X. M. et al. Bid-deficient mice are resistant to Fas-induced hepatocellular apoptosis. Nature 400, 886–891 (1999)
Jost, P. J. et al. XIAP discriminates between type I and type II FAS-induced apoptosis. Nature 460, 1035–1039 (2009)
Kaufmann, T. et al. The BH3-only protein bid is dispensable for DNA damage- and replicative stress-induced apoptosis or cell-cycle arrest. Cell 129, 423–433 (2007)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
Competing Financial Interests Declared none.
PowerPoint slides
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nachbur, U., Vince, J., O’Reilly, L. et al. Is BID required for NOD signalling?. Nature 488, E4–E6 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11366
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11366
This article is cited by
-
Hepatocyte-specific Bid depletion reduces tumor development by suppressing inflammation-related compensatory proliferation
Cell Death & Differentiation (2015)
-
A RIPK2 inhibitor delays NOD signalling events yet prevents inflammatory cytokine production
Nature Communications (2015)
-
NOD proteins: regulators of inflammation in health and disease
Nature Reviews Immunology (2014)
-
Yeretssian et al. reply
Nature (2012)
-
Correction: Corrigendum: Yeretssian et al. reply
Nature (2012)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.