Abstract
BACKGROUND:
Circulating angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) was identified as a predictor of weight loss maintenance in overweight/obese women of the Diogenes project.
OBJECTIVE:
To investigate whether ACE acted also as a predictor in men of the Diogenes study and to compare it with that in women.
DESIGN:
Subjects, who lost ⩾8% of body weight induced by low-caloric diet in an 8-week weight loss period, were assigned to weight loss maintenance with dietary intervention for 6 months.
SUBJECTS:
125 overweight/obese healthy men from eight European countries who completed whole intervention.
MEASUREMENTS:
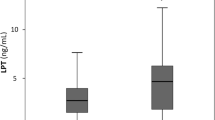
Concentrations and activity of serum ACE at baseline and after the 8-week weight loss, in addition to anthropometric and physiological parameters.
RESULTS:
Serum ACE concentration decreased by 11.3±10.6% during the weight loss period in men. A greater reduction is associated with less body weight regain during the maintenance period (r=0.227, P=0.012). ACE change was able to predict a weight regain ⩽20% after 6 months, with an odds ratio of 1.59 (95% confidence interval (CI): 1.09–2.33, P=0.016) for every 10% reduction, which was independent of body mass index and weight loss. The prediction power was weaker in men than in women, but without a significant sex difference (P=0.137). In pooled subjects (N=218), the odds ratio was 1.96 (95% CI: 1.46–2.64, P<0.001).
CONCLUSIONS:
A greater reduction of ACE during weight loss is favorable for weight maintenance in both men and women. This can offer useful information for personalized advice to improve weight loss maintenance. It also confirms the role of ACE in the metabolic pathways of weight regulation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
World Health Organization. Global Health Risks: Mortality and Burden of Disease Attributable to Selected Major Risks. World Health Organization: Geneva, 2009.
Poirier P, Giles TD, Bray GA, Hong YL, Stern JS, Pi-Sunyer FX et al. Obesity and cardiovascular disease: pathophysiology, evaluation, and effect of weight loss - an update of the 1997 American Heart Association Scientific Statement on obesity and heart disease from the Obesity Committee of the Council on Nutrition, Physical Activity, and Metabolism. Circulation 2006; 113: 898–918.
Wing RR, Phelan S . Long-term weight loss maintenance. Am J Clin Nutr 2005; 82: 222S–225S.
Erdos EG . Angiotensin I converting enzyme and the changes in our concepts through the years. Lewis K. Dahl memorial lecture. Hypertension 1990; 16: 363–370.
Sayed-Tabatabaei FA, Oostra BA, Isaacs A, van Duijn CM, Witteman JC . ACE polymorphisms. Circ Res 2006; 98: 1123–1133.
Kramer H, Wu X, Kan D, Luke A, Zhu X, Adeyemo A et al. Angiotensin-converting enzyme gene polymorphisms and obesity: an examination of three black populations. Obes Res 2005; 13: 823–828.
Riera-Fortuny C, Real JT, Chaves FJ, Morales-Suarez-Varela M, Martinez-Triguero ML, Morillas-Arino C et al. The relation between obesity, abdominal fat deposit and the angiotensin-converting enzyme gene I/D polymorphism and its association with coronary heart disease. Int J Obes (Lond) 2005; 29: 78–84.
Eisenmann JC, Sarzynski MA, Glenn K, Rothschild M, Heelan KA . ACE I/D genotype, adiposity, and blood pressure in children. Cardiovasc Diabetol 2009; 8: 14.
Katzov H, Bennet AM, Kehoe P, Wiman B, Gatz M, Blennow K et al. A cladistic model of ACE sequence variation with implications for myocardial infarction, Alzheimer disease and obesity. Hum Mol Genet 2004; 13: 2647–2657.
Strazzullo P, Iacone R, Iacoviello L, Russo O, Barba G, Russo P et al. Genetic variation in the renin-angiotensin system and abdominal adiposity in men: the Olivetti Prospective Heart Study. Ann Intern Med 2003; 138: 17–23.
Wang JG, He X, Wang GL, Li Y, Zhou HF, Zhang WZ et al. Family-based associations between the angiotensin- converting enzyme insertion/deletion polymorphism and multiple cardiovascular risk factors in Chinese. J Hypertens 2004; 22: 487–491.
Moran CN, Vassilopoulos C, Tsiokanos A, Jamurtas AZ, Bailey ME, Wilson RH et al. Effects of interaction between angiotensin I-converting enzyme polymorphisms and lifestyle on adiposity in adolescent Greeks. Obes Res 2005; 13: 1499–1504.
Bienertova-Vasku J, Bienert P, Sablikova L, Slovackova L, Forejt M, Piskackova Z et al. Effect of ID ACE gene polymorphism on dietary composition and obesity-related anthropometric parameters in the Czech adult population. Genes Nutr 2009; 4: 207–213.
Wang P, Holst C, Andersen MR, Astrup A, Bouwman FG, van Otterdijk S et al. Blood profile of proteins and steroid hormones predicts weight change after weight loss with interactions of dietary protein level and glycemic index. PLoS One 2011; 6: e16773.
Larsen TM, Dalskov S, van Baak MA, Jebb S, Papadaki A, Pfeiffer AFH et al. Diets with high or low protein content and glycemic index for weight-loss maintenance. N Engl J Med 2010; 363: 2102–2113.
Power ML, Schulkin J . Sex differences in fat storage, fat metabolism, and the health risks from obesity: possible evolutionary origins. Br J Nutr 2008; 99: 931–940.
Xhyheri B, Bugiardini R . Diagnosis and treatment of heart disease: are women different from men? Prog Cardiovasc Dis 2010; 53: 227–236.
Komukai K, Mochizuki S, Yoshimura M . Gender and the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. Fundam Clin Pharmacol 2010; 24: 687–698.
Larsen TM, Dalskov S, van Baak M, Jebb S, Kafatos A, Pfeiffer A et al. The Diet, Obesity and Genes (Diogenes) Dietary Study in eight European countries - a comprehensive design for long-term intervention. Obes Rev 2010; 11: 76–91.
Kruit A, Grutters JC, Gerritsen WB, Kos S, Wodzig WK, van den Bosch JM et al. ACE I/D-corrected Z-scores to identify normal and elevated ACE activity in sarcoidosis. Respir Med 2007; 101: 510–515.
DeMets D, Halperin M . Estimation of a simple regression coefficient in samples arising from a sub-sampling procedure. Biometrics 1977; 33: 47–56.
Masuo K, Mikami H, Ogihara T, Tuck ML . Weight reduction and pharmacologic treatment in obese hypertensives. Am J Hypertens 2001; 14: 530–538.
Nagamia S, Pandian A, Cheema F, Natarajan R, Khan QA, Patel AD et al. The role of quinapril in the presence of a weight loss regimen: endothelial function and markers of obesity in patients with the metabolic syndrome. Prev Cardiol 2007; 10: 204–209.
Scholze J, Grimm E, Herrmann D, Unger T, Kintscher U . Optimal treatment of obesity-related hypertension: the hypertension-obesity-sibutramine (HOS) study. Circulation 2007; 115: 1991–1998.
Santos EL, de Picoli Souza K, Guimaraes PB, Reis FC, Silva SM, Costa-Neto CM et al. Effect of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor enalapril on body weight and composition in young rats. Int Immunopharmacol 2008; 8: 247–253.
de Kloet AD, Krause EG, Kim DH, Sakai RR, Seeley RJ, Woods SC . The effect of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition using captopril on energy balance and glucose homeostasis. Endocrinology 2009; 150: 4114–4123.
Weisinger RS, Stanley TK, Begg DP, Weisinger HS, Spark KJ, Jois M . Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibition lowers body weight and improves glucose tolerance in C57BL/6J mice maintained on a high fat diet. Physiol Behav 2009; 98: 192–197.
Velkoska E, Warner FJ, Cole TJ, Smith I, Morris MJ . Metabolic effects of low dose angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor in dietary obesity in the rat. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 2010; 20: 49–55.
Santos EL, de Picoli Souza K, da Silva ED, Batista EC, Martins PJ, D′Almeida V et al. Long term treatment with ACE inhibitor enalapril decreases body weight gain and increases life span in rats. Biochem Pharmacol 2009; 78: 951–958.
Toritsuka N, Tsukidate K, Igarashi T . Mechanism of weight gain suppressing effect of ER-40133, an angiotensin I converting enzyme inhibitor, in growing rats. J Toxicol Sci 1999; 24: 45–53.
Rigat B, Hubert C, Alhenc-Gelas F, Cambien F, Corvol P, Soubrier F . An insertion/deletion polymorphism in the angiotensin I-converting enzyme gene accounting for half the variance of serum enzyme levels. J Clin Invest 1990; 86: 1343–1346.
Kostis JB, Wilson AC, Hooper WC, Harrison KW, Philipp CS, Appel LJ et al. Association of angiotensin-converting enzyme DD genotype with blood pressure sensitivity to weight loss. Am Heart J 2002; 144: 625–629.
Suchanek P, Hubacek JA, Kralova Lesna I, Pinekerova V, Adamkova V . Actigenetic of ACE gene polymorphism in Czech obese sedentary females. Physiol Res 2009; 58 (Suppl 1): S47–S52.
Handjieva-Darlenska T, Handjiev S, Larsen TM, van Baak MA, Lindroos A, Papadaki A et al. Predictors of weight loss maintenance and attrition during a 6-month dietary intervention period: results from the DiOGenes study. Clin Obes 2011; e-pub ahead of print 5 July 2011; doi: 10.1111/j.1758-8111.2011.00010.x.
McKinley MJ, Albiston AL, Allen AM, Mathai ML, May CN, McAllen RM et al. The brain renin-angiotensin system: location and physiological roles. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 2003; 35: 901–918.
Porter JP, Potratz KR . Effect of intracerebroventricular angiotensin II on body weight and food intake in adult rats. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 2004; 287: R422–R428.
Zaman AK, Fujii S, Sawa H, Goto D, Ishimori N, Watano K et al. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition attenuates hypofibrinolysis and reduces cardiac perivascular fibrosis in genetically obese diabetic mice. Circulation 2001; 103: 3123–3128.
Brown NJ, Agirbasli M, Vaughan DE . Comparative effect of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition and angiotensin II type 1 receptor antagonism on plasma fibrinolytic balance in humans. Hypertension 1999; 34: 285–290.
Mariman EC, Wang P . Adipocyte extracellular matrix composition, dynamics and role in obesity. Cell Mol Life Sci 2010; 67: 1277–1292.
Harp JB, Henry SA, DiGirolamo M . Dietary weight loss decreases serum angiotensin-converting enzyme activity in obese adults. Obes Res 2002; 10: 985–990.
Engeli S, Bohnke J, Gorzelniak K, Janke J, Schling P, Bader M et al. Weight loss and the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. Hypertension 2005; 45: 356–362.
Proudler AJ, Ahmed AI, Crook D, Fogelman I, Rymer JM, Stevenson JC . Hormone replacement therapy and serum angiotensin-converting-enzyme activity in postmenopausal women. Lancet 1995; 346: 89–90.
Schunkert H, Danser AH, Hense HW, Derkx FH, Kurzinger S, Riegger GA . Effects of estrogen replacement therapy on the renin-angiotensin system in postmenopausal women. Circulation 1997; 95: 39–45.
Yanes LL, Reckelhoff JF . Postmenopausal hypertension. Am J Hypertens 2011; 24: 740–749.
Dratva J, Gomez Real F, Schindler C, Ackermann-Liebrich U, Gerbase MW, Probst-Hensch NM et al. Is age at menopause increasing across Europe? Results on age at menopause and determinants from two population-based studies. Menopause 2009; 16: 385–394.
Acknowledgements
This work is part of the Diogenes project, which is supported by the European Community (Contract No. FOOD-CT-2005-513946).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
A patent application concerning part of the results of this study has been filed by the University Maastricht (Application No. EP10172846). The remaining authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, P., Holst, C., Wodzig, W. et al. Circulating ACE is a predictor of weight loss maintenance not only in overweight and obese women, but also in men. Int J Obes 36, 1545–1551 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2011.278
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2011.278
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Differential mechanisms affecting weight loss and weight loss maintenance
Nature Metabolism (2023)
-
Normobaric hypoxia shows enhanced FOXO1 signaling in obese mouse gastrocnemius muscle linked to metabolism and muscle structure and neuromuscular innervation
Pflügers Archiv - European Journal of Physiology (2023)
-
Dissociation Between Long-term Weight Loss Intervention and Blood Pressure: an 18-month Randomized Controlled Trial
Journal of General Internal Medicine (2021)
-
Mechanisms of weight regain after weight loss — the role of adipose tissue
Nature Reviews Endocrinology (2019)
-
Dietary Fat Intake Modulates Effects of a Frequent ACE Gene Variant on Glucose Tolerance with association to Type 2 Diabetes
Scientific Reports (2017)