Abstract
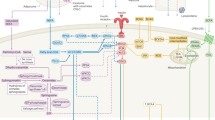
Impaired β-cell function and insufficient β-cell mass compensation are twin pathogenic features that underlie type 2 diabetes (T2D). Current therapeutic strategies continue to evolve to improve treatment outcomes in different ethnic populations and include approaches to counter insulin resistance and improve β-cell function. Although the effects of insulin secretion on metabolic organs such as liver, skeletal muscle and adipose is directly relevant for improving glucose uptake and reduce hyperglycemia, the ability of pancreatic β-cells to crosstalk with multiple non-metabolic tissues is providing novel insights into potential opportunities for improving β-cell function and/or mass that could have beneficial effects in patients with diabetes. For example, the role of the gastrointestinal system in the regulation of β-cell biology is well recognized and has been exploited clinically to develop incretin-related antidiabetic agents. The microbiome and the immune system are emerging as important players in regulating β-cell function and mass. The rich innervation of islet cells indicates it is a prime organ for regulation by the nervous system. In this review, we discuss the potential implications of signals from these organ systems as well as those from bone, placenta, kidney, thyroid, endothelial cells, reproductive organs and adrenal and pituitary glands that can directly impact β-cell biology. An added layer of complexity is the limited data regarding the relative relevance of one or more of these systems in different ethnic populations. It is evident that better understanding of this paradigm would provide clues to enhance β-cell function and/or mass in vivo in the long-term goal of treating or curing patients with diabetes.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nanditha A, Ma RC, Ramachandran A, Snehalatha C, Chan JC, Chia KS et al. Diabetes in Asia and the Pacific: implications for the Global Epidemic. Diabetes Care 2016; 39: 472–485.
Chan JC, Malik V, Jia W, Kadowaki T, Yajnik CS, Yoon KH et al. Diabetes in Asia: epidemiology, risk factors, and pathophysiology. JAMA 2009; 301: 2129–2140.
Ramachandran A, Ma RC, Snehalatha C . Diabetes in Asia. Lancet 2010; 375: 408–418.
Saisho Y, Butler AE, Manesso E, Elashoff D, Rizza RA, Butler PC . Beta-cell mass and turnover in humans: effects of obesity and aging. Diabetes Care 2013; 36: 111–117.
Yoon KH, Ko SH, Cho JH, Lee JM, Ahn YB, Song KH et al. Selective beta-cell loss and alpha-cell expansion in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Korea. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2003; 88: 2300–2308.
Rahier J, Guiot Y, Goebbels RM, Sempoux C, Henquin JC . Pancreatic beta-cell mass in European subjects with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab 2008; 10: 32–42.
Kulkarni RN, Mizrachi EB, Ocana AG, Stewart AF . Human beta-cell proliferation and intracellular signaling: driving in the dark without a road map. Diabetes 2012; 61: 2205–2213.
Bernal-Mizrachi E, Kulkarni RN, Scott DK, Mauvais-Jarvis F, Stewart AF, Garcia-Ocana A . Human beta-cell proliferation and intracellular signaling part 2: still driving in the dark without a road map. Diabetes 2014; 63: 819–831.
Stewart AF, Hussain MA, Garcia-Ocana A, Vasavada RC, Bhushan A, Bernal-Mizrachi E et al. Human beta-cell proliferation and intracellular signaling: part 3. Diabetes 2015; 64: 1872–1885.
Flier SN, Kulkarni RN, Kahn CR . Evidence for a circulating islet cell growth factor in insulin-resistant states. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2001; 98: 7475–7480.
Tilg H, Moschen AR, Roden M . NAFLD and diabetes mellitus. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2016; 14: 32–42.
Mellado-Gil J, Rosa TC, Demirci C, Gonzalez-Pertusa JA, Velazquez-Garcia S, Ernst S et al. Disruption of hepatocyte growth factor/c-Met signaling enhances pancreatic β-cell death and accelerates the onset of diabetes. Diabetes 2011; 60: 525–536.
Alvarez-Perez JC, Ernst S, Demirci C, Casinelli GP, Mellado-Gil JMD, Rausell-Palamos F et al. Hepatocyte growth factor/c-Met signaling is required for β-cell regeneration. Diabetes 2014; 63: 216–223.
El Ouaamari A, Kawamori D, Dirice E, Liew Chong W, Shadrach Jennifer L, Hu J et al. Liver-derived systemic factors drive beta cell hyperplasia in insulin-resistant states. Cell Rep 2013; 3: 401–410.
El Ouaamari A, Dirice E, Gedeon N, Hu J, Zhou J-Y, Shirakawa J et al. SerpinB1 promotes pancreatic beta cell proliferation. Cell Metab 2016; 23: 194–205.
Shirakawa J, Kulkarni RN . Novel factors modulating human beta-cell proliferation. Diabetes Obes Metab 2016; 18: 71–77.
Hussain MA, Song W-J, Wolfe A . There is kisspeptin—and then there is kisspeptin. Trends Endocrinol Metab 2015; 26: 564–572.
Song W-J, Mondal P, Wolfe A, Alonso Laura C, Stamateris R, Ong Benny WT et al. Glucagon regulates hepatic kisspeptin to impair insulin secretion. Cell Metab 2014; 19: 667–681.
Rajwani A, Ezzat V, Smith J, Yuldasheva NY, Duncan ER, Gage M et al. Increasing circulating IGFBP1 levels improves insulin sensitivity, promotes nitric oxide production, lowers blood pressure, and protects against atherosclerosis. Diabetes 2012; 61: 915–924.
Wang X, Wei W, Krzeszinski Jing Y, Wang Y, Wan Y . A liver-bone endocrine relay by IGFBP1 promotes osteoclastogenesis and mediates FGF21-induced bone resorption. Cell Metab 2015; 22: 811–824.
Lu J, Liu K-C, Schulz N, Karampelias C, Charbord J, Hilding A et al. IGFBP1 increases β-cell regeneration by promoting α- to β-cell transdifferentiation. EMBO J 2016; 35: 2026–2044.
Hussain MA, Akalestou E, Song W-j . Inter-organ communication and regulation of beta cell function. Diabetologia 2016; 59: 659–667.
Ye R, Holland WL, Gordillo R, Wang M, Wang QA, Shao M et al. Adiponectin is essential for lipid homeostasis and survival under insulin deficiency and promotes β-cell regeneration. eLife 2014; 3: e03851.
Ye R, Wang M, Wang QA, Scherer PE . Adiponectin-mediated antilipotoxic effects in regenerating pancreatic islets. Endocrinology 2015; 156: 2019–2028.
Amitani M, Asakawa A, Amitani H, Inui A . The role of leptin in the control of insulin-glucose axis. Front Neurosci 2013; 7: 51.
Kulkarni RN, Wang ZL, Wang RM, Hurley JD, Smith DM, Ghatei MA et al. Leptin rapidly suppresses insulin release from insulinoma cells, rat and human islets and, in vivo, in mice. J Clin Invest 1997; 100: 2729–2736.
Chen P-C, Kryukova YN, Shyng S-L . Leptin regulates KATP channel trafficking in pancreatic β-cells by a signaling mechanism involving amp-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA). J Biol Chem 2013; 288: 34098–34109.
Polyzos SA, Kountouras J, Mantzoros CS . Adipokines in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Metabolism 2016; 65: 1062–1079.
Lo James C, Ljubicic S, Leibiger B, Kern M, Leibiger Ingo B, Moede T et al. Adipsin is an adipokine that improves β cell function in diabetes. Cell 2014; 158: 41–53.
Wang G-X, Zhao X-Y, Lin JD . The brown fat secretome: metabolic functions beyond thermogenesis. Trends Endocrinol Metab 2015; 26: 231–237.
Whitham M, Febbraio MA . The ever-expanding myokinome: discovery challenges and therapeutic implications. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2016; 15: 719–729.
Ellingsgaard H, Hauselmann I, Schuler B, Habib AM, Baggio LL, Meier DT et al. Interleukin-6 enhances insulin secretion by increasing glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion from L cells and alpha cells. Nat Med 2011; 17: 1481–1489.
Guay C, Regazzi R . New emerging tasks for microRNAs in the control of β-cell activities. Biochim Biophys Acta 2016; 1861: 2121–2129.
Jalabert A, Vial G, Guay C, Wiklander OPB, Nordin JZ, Aswad H et al. Exosome-like vesicles released from lipid-induced insulin-resistant muscles modulate gene expression and proliferation of beta recipient cells in mice. Diabetologia 2016; 59: 1049–1058.
Jahng JWS, Song E, Sweeney G . Crosstalk between the heart and peripheral organs in heart failure. Exp Mol Med 2016; 48: e217.
Baskin Kedryn K, Winders Benjamin R, Olson Eric N . Muscle as a ‘mediator’ of systemic metabolism. Cell Metab 2015; 21: 237–248.
Hayden MR, Patel K, Habibi J, Gupta D, Tekwani SS, Whaley-Connell A et al. Attenuation of endocrine-exocrine pancreatic communication in type 2 diabetes: pancreatic extracellular matrix ultrastructural abnormalities. J Cardiometab Syndr 2008; 3: 234–243.
Peiris H, Bonder CS, Coates PTH, Keating DJ, Jessup CF . The β-cell/EC axis: how do islet cells talk to each other? Diabetes 2014; 63: 3–11.
Brissova M, Shostak A, Shiota M, Wiebe PO, Poffenberger G, Kantz J et al. Pancreatic islet production of vascular endothelial growth factor-a is essential for islet vascularization, revascularization, and function. Diabetes 2006; 55: 2974–2985.
Olerud J, Mokhtari D, Johansson M, Christoffersson G, Lawler J, Welsh N et al. Thrombospondin-1: an islet endothelial cell signal of importance for β-cell function. Diabetes 2011; 60: 1946–1954.
Cunha DA, Cito M, Carlsson P-O, Vanderwinden J-M, Molkentin JD, Bugliani M et al. Thrombospondin 1 protects pancreatic [beta]-cells from lipotoxicity via the PERK-NRF2 pathway. Cell Death Differ 2016; 23: 1995–2006.
Kulkarni RN . GIP: no longer the neglected incretin twin? Sci Transl Med 2010; 2: 49ps7.
Smith Eric P, An Z, Wagner C, Lewis Alfor G, Cohen Eric B, Li B et al. The role of β cell glucagon-like peptide-1 signaling in glucose regulation and response to diabetes drugs. Cell Metab 2014; 19: 1050–1057.
Campbell JE, Ussher JR, Mulvihill EE, Kolic J, Baggio LL, Cao X et al. TCF1 links GIPR signaling to the control of beta cell function and survival. Nat Med 2016; 22: 84–90.
Baothman OA, Zamzami MA, Taher I, Abubaker J, Abu-Farha M . The role of Gut Microbiota in the development of obesity and Diabetes. Lipids Health Dis 2016; 15: 108.
Vrieze A, Van Nood E, Holleman F, Salojärvi J, Kootte RS, Bartelsman JFWM et al. Transfer of intestinal microbiota from lean donors increases insulin sensitivity in individuals with metabolic syndrome. Gastroenterology 2012; 143: 913–6.e7.
Puddu A, Sanguineti R, Montecucco F, Viviani GL . Evidence for the gut microbiota short-chain fatty acids as key pathophysiological molecules improving diabetes. Mediators Inflamm 2014; 2014: 9.
McNelis JC, Lee YS, Mayoral R, van der Kant R, Johnson AM, Wollam J et al. GPR43 potentiates beta-cell function in obesity. Diabetes 2015; 64: 3203–3217.
Thorens B . Neural regulation of pancreatic islet cell mass and function. Diabetes Obes Metab 2014; 16: 87–95.
Lausier J, Diaz WC, Roskens V, LaRock K, Herzer K, Fong CG et al. Vagal control of pancreatic β-cell proliferation. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2010; 299: E786–E793.
Gautam D, Han SJ, Duttaroy A, Mears D, Hamdan FF, Li JH et al. Role of the M3 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor in beta-cell function and glucose homeostasis. Diabetes Obes Metab 2007; 9: 158–169.
Borden P, Houtz J, Leach SD, Kuruvilla R . Sympathetic innervation during development is necessary for pancreatic islet architecture and functional maturation. Cell Rep 2013; 4: 287–301.
Croizier S, Prevot V, Bouret SG . Leptin controls parasympathetic wiring of the pancreas during embryonic life. Cell Rep 2016; 15: 36–44.
Rodriguez-Diaz R, Abdulreda MH, Formoso AL, Gans I, Ricordi C, Berggren PO et al. Innervation patterns of autonomic axons in the human endocrine pancreas. Cell Metab 2011; 14: 45–54.
Rodriguez-Diaz R, Dando R, Jacques-Silva MC, Fachado A, Molina J, Abdulreda MH et al. Alpha cells secrete acetylcholine as a non-neuronal paracrine signal priming beta cell function in humans. Nat Med 2011; 17: 888–892.
Imai J, Katagiri H, Yamada T, Ishigaki Y, Suzuki T, Kudo H et al. Regulation of pancreatic beta cell mass by neuronal signals from the liver. Science 2008; 322: 1250–1254.
De Vos A, Heimberg H, Quartier E, Huypens P, Bouwens L, Pipeleers D et al. Human and rat beta cells differ in glucose transporter but not in glucokinase gene expression. J Clin Invest 1995; 96: 2489–2495.
McCrimmon RJ, Evans ML, Fan X, McNay EC, Chan O, Ding Y et al. Activation of ATP-sensitive K+ channels in the ventromedial hypothalamus amplifies counterregulatory hormone responses to hypoglycemia in normal and recurrently hypoglycemic rats. Diabetes 2005; 54: 3169–3174.
Thorens B, Guillam MT, Beermann F, Burcelin R, Jaquet M . Transgenic reexpression of GLUT1 or GLUT2 in pancreatic beta cells rescues GLUT2-null mice from early death and restores normal glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. J Biol Chem 2000; 275: 23751–23758.
Marty N, Dallaporta M, Foretz M, Emery M, Tarussio D, Bady I et al. Regulation of glucagon secretion by glucose transporter type 2 (glut2) and astrocyte-dependent glucose sensors. J Clin Invest 2005; 115: 3545–3553.
Ogunnowo-Bada EO, Heeley N, Brochard L, Evans ML . Brain glucose sensing, glucokinase and neural control of metabolism and islet function. Diabetes Obes Metab 2014; 16 (Suppl 1): 26–32.
Tarussio D, Metref S, Seyer P, Mounien L, Vallois D, Magnan C et al. Nervous glucose sensing regulates postnatal beta cell proliferation and glucose homeostasis. J Clin Invest 2014; 124: 413–424.
Razavi R, Chan Y, Afifiyan FN, Liu XJ, Wan X, Yantha J et al. TRPV1+ sensory neurons control beta cell stress and islet inflammation in autoimmune diabetes. Cell 2006; 127: 1123–1135.
JUN regulation of energy metabolism by the skeleton. Cell 2007; 130: 456–469.
Wei J, Hanna T, Suda N, Karsenty G, Ducy P . Osteocalcin promotes beta-cell proliferation during development and adulthood through Gprc6a. Diabetes 2014; 63: 1021–1031.
Fulzele K, Riddle RC, DiGirolamo DJ, Cao X, Wan C, Chen D et al. Insulin receptor signaling in osteoblasts regulates postnatal bone acquisition and body composition. Cell 2010; 142: 309–319.
Wei J, Ferron M, Clarke CJ, Hannun YA, Jiang H, Blaner WS et al. Bone-specific insulin resistance disrupts whole-body glucose homeostasis via decreased osteocalcin activation. J Clin Invest 2014; 124: 1–13.
Hinoi E, Gao N, Jung DY, Yadav V, Yoshizawa T, Myers MG Jr . et al. The sympathetic tone mediates leptin's inhibition of insulin secretion by modulating osteocalcin bioactivity. J Cell Biol 2008; 183: 1235–1242.
Morioka T, Asilmaz E, Hu J, Dishinger JF, Kurpad AJ, Elias CF et al. Disruption of leptin receptor expression in the pancreas directly affects beta cell growth and function in mice. J Clin Invest 2007; 117: 2860–2868.
Huang C, Snider F, Cross JC . Prolactin receptor is required for normal glucose homeostasis and modulation of beta-cell mass during pregnancy. Endocrinology 2009; 150: 1618–1626.
Karnik SK, Chen H, McLean GW, Heit JJ, Gu X, Zhang AY et al. Menin controls growth of pancreatic beta-cells in pregnant mice and promotes gestational diabetes mellitus. Science 2007; 318: 806–809.
Kim H, Toyofuku Y, Lynn FC, Chak E, Uchida T, Mizukami H et al. Serotonin regulates pancreatic beta cell mass during pregnancy. Nat Med 2010; 16: 804–808.
Demirci C, Ernst S, Alvarez-Perez JC, Rosa T, Valle S, Shridhar V et al. Loss of HGF/c-Met signaling in pancreatic beta-cells leads to incomplete maternal beta-cell adaptation and gestational diabetes mellitus. Diabetes 2012; 61: 1143–1152.
Kondegowda NG, Fenutria R, Pollack IR, Orthofer M, Garcia-Ocana A, Penninger JM et al. Osteoprotegerin and denosumab stimulate human beta cell proliferation through inhibition of the receptor activator of NF-kappaB ligand pathway. Cell Metab 2015; 22: 77–85.
De Jesus DF, Kulkarni RN . Epigenetic modifiers of islet function and mass. Trends Endocrinol Metab 2014; 25: 628–636.
Ahren B . Beta- and alpha-cell dysfunction in subjects developing impaired glucose tolerance: outcome of a 12-year prospective study in postmenopausal Caucasian women. Diabetes 2009; 58: 726–731.
Ferrara A, Karter AJ, Ackerson LM, Liu JY, Selby JV . Hormone replacement therapy is associated with better glycemic control in women with type 2 diabetes: The Northern California Kaiser Permanente Diabetes Registry. Diabetes Care 2001; 24: 1144–1150.
Tiano JP, Delghingaro-Augusto V, Le May C, Liu S, Kaw MK, Khuder SS et al. Estrogen receptor activation reduces lipid synthesis in pancreatic islets and prevents beta cell failure in rodent models of type 2 diabetes. J Clin Invest 2011; 121: 3331–3342.
Tiano JP, Mauvais-Jarvis F . Importance of oestrogen receptors to preserve functional beta-cell mass in diabetes. Nat Rev Endocrinol 2012; 8: 342–351.
Yuchi Y, Cai Y, Legein B, De Groef S, Leuckx G, Coppens V et al. Estrogen receptor alpha regulates beta-cell formation during pancreas development and following injury. Diabetes 2015; 64: 3218–3228.
Mauvais-Jarvis F . Role of sex steroids in beta cell function, growth, and survival. Trends Endocrinol Metab 2016; 27: 844–855.
Gourdy P, Bourgeois EA, Levescot A, Pham L, Riant E, Ahui ML et al. Estrogen therapy delays autoimmune diabetes and promotes the protective efficiency of natural killer T-cell activation in female nonobese diabetic mice. Endocrinology 2016; 157: 258–267.
Navarro G, Xu W, Jacobson DA, Wicksteed B, Allard C, Zhang G et al. Extranuclear actions of the androgen receptor enhance glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in the male. Cell Metab 2016; 23: 837–851.
Costrini NV, Kalkhoff RK . Relative effects of pregnancy, estradiol, and progesterone on plasma insulin and pancreatic islet insulin secretion. J Clin Invest 1971; 50: 992–999.
Picard F, Wanatabe M, Schoonjans K, Lydon J, O'Malley BW, Auwerx J . Progesterone receptor knockout mice have an improved glucose homeostasis secondary to beta -cell proliferation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2002; 99: 15644–15648.
Oda T, Taneichi H, Takahashi K, Togashi H, Hangai M, Nakagawa R et al. Positive association of free triiodothyronine with pancreatic beta-cell function in people with prediabetes. Diabet Med 2015; 32: 213–219.
Aguayo-Mazzucato C, Zavacki AM, Marinelarena A, Hollister-Lock J, El Khattabi I, Marsili A et al. Thyroid hormone promotes postnatal rat pancreatic beta-cell development and glucose-responsive insulin secretion through MAFA. Diabetes 2013; 62: 1569–1580.
Bruin JE, Saber N, O'Dwyer S, Fox JK, Mojibian M, Arora P et al. Hypothyroidism impairs human stem cell-derived pancreatic progenitor cell maturation in mice. Diabetes 2016; 65: 1297–1309.
Donath MY, Halban PA . Decreased beta-cell mass in diabetes: significance, mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Diabetologia 2004; 47: 581–589.
Eguchi K, Manabe I, Oishi-Tanaka Y, Ohsugi M, Kono N, Ogata F et al. Saturated fatty acid and TLR signaling link beta cell dysfunction and islet inflammation. Cell Metab 2012; 15: 518–533.
Ehses JA, Perren A, Eppler E, Ribaux P, Pospisilik JA, Maor-Cahn R et al. Increased number of islet-associated macrophages in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 2007; 56: 2356–2370.
Morris DL . Minireview: emerging concepts in islet macrophage biology in type 2 diabetes. Mol Endocrinol 2015; 29: 946–962.
Brissova M, Aamodt K, Brahmachary P, Prasad N, Hong JY, Dai C et al. Islet microenvironment, modulated by vascular endothelial growth factor-A signaling, promotes beta cell regeneration. Cell Metab 2014; 19: 498–511.
Dirice E, Kahraman S, Jiang W, El Ouaamari A, De Jesus DF, Teo AK et al. Soluble factors secreted by T cells promote beta-cell proliferation. Diabetes 2014; 63: 188–202.
Valdez IA, Dirice E, Gupta MK, Shirakawa J, Teo AK, Kulkarni RN . Proinflammatory cytokines induce endocrine differentiation in pancreatic ductal cells via STAT3-dependent NGN3 activation. Cell Rep 2016; 15: 460–470.
Butcher MJ, Hallinger D, Garcia E, Machida Y, Chakrabarti S, Nadler J et al. Association of proinflammatory cytokines and islet resident leucocytes with islet dysfunction in type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2014; 57: 491–501.
Jaeckle Santos LJ, Li C, Doulias PT, Ischiropoulos H, Worthen GS, Simmons RA . Neutralizing Th2 inflammation in neonatal islets prevents beta-cell failure in adult IUGR rats. Diabetes 2014; 63: 1672–1684.
Cabrera O, Berman DM, Kenyon NS, Ricordi C, Berggren PO, Caicedo A . The unique cytoarchitecture of human pancreatic islets has implications for islet cell function. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2006; 103: 2334–2339.
Fiaschi-Taesch NM, Kleinberger JW, Salim FG, Troxell R, Wills R, Tanwir M et al. Human pancreatic beta-cell G1/S molecule cell cycle atlas. Diabetes 2013; 62: 2450–2459.
Acknowledgements
This review was supported by R01 DK67536 and R01 DK103215 (to RNK). JS is supported by a Post-doctoral Fellowship for Research Abroad, the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) and the Uehara Memorial Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shirakawa, J., De Jesus, D. & Kulkarni, R. Exploring inter-organ crosstalk to uncover mechanisms that regulate β-cell function and mass. Eur J Clin Nutr 71, 896–903 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/ejcn.2017.13
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ejcn.2017.13
This article is cited by
-
Porcine models for studying complications and organ crosstalk in diabetes mellitus
Cell and Tissue Research (2020)
-
Dysregulated liver lipid metabolism and innate immunity associated with hepatic steatosis in neonatal BBdp rats and NOD mice
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
Organ crosstalk: the potent roles of inflammation and fibrotic changes in the course of organ interactions
Inflammation Research (2019)
-
Type 2 diabetes in Asia: where do we go from here?
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2017)