Abstract
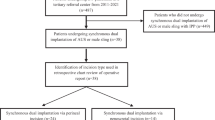
Placement of an inflatable penile prosthesis (IPP) is the most effective treatment modality for men with ED refractory to medical management. We have previously demonstrated a protocol for IPP reservoir placement within the abdominal wall musculature, which was shown to be a safer location than traditional placement in the retropubic space of Retzius. The aim of this study was to review our complications with IPP reservoir entry into the peritoneum after abdominal wall placement of the reservoir. We retrospectively reviewed our two patients with peritoneal entry of the reservoir after posterior to transversalis fascia and anterior to transversalis fascia placement during virgin and compromised IPP cases, respectively. Our goal was to assess common inherent patient and surgical factors that resulted in this complication in order to develop a management algorithm to prevent future occurrence during alternative reservoir placement. Peritoneal reservoir entry was identified in two patients. These patients were both noted to be thin (mean body mass index (BMI) 18.5 kg/m2), current or former smokers. Peritoneal entry was identified early after reservoir placement. Neither of the patients suffered bowel injury and both subsequently underwent successful reservoir removal and IPP replacement. Both are currently doing well with functional IPPs on follow-up. Peritoneal entry of the reservoir occurs very rarely and, in our series, occurred in a cohort of patients with low BMI and tobacco use history. We recommend early identification of similar patients and subsequent reservoir placement anterior to transversalis fascia with caution to prevent peritoneal entry.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 8 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $32.38 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burnett AL . Evaluation and management of erectile dysfunction. In: Wein AJ, Kavoussi LR, Novick AC, Peters CA (eds). Campbell-Walsh Urology, 10th edn, vol 4. Elsevier Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2011 pp 721–748.
Selvin E, Burnett AL, Platz EA . Prevalence and risk factors for erectile dysfunction in the US. Am J Med 2007; 120: 151–157.
Hatzimouratidis K, Amar E, Eardley I, Giuliano F, Hatzichristou D, Montorsi F et al. Guidelines on male sexual dysfunction: erectile dysfunction and premature ejaculation. Eur Urol 2010; 57: 804–814.
Montague DK, Jarow JP, Broderick GA, Dmochowski RR, Heaton JP, Lue TF et al. Erectile dysfunction guideline update panel. J Urol 2005; 174: 230–239.
Hellstrom WJ, Montague DK, Moncada I, Carson C, Minhas S, Faria G et al. Implants, mechanical devices, and vascular surgery for erectile dysfunction. J Sex Med 2010; 7: 501–523.
Wilson SK, Henry GD, Delk JR Jr, Cleves MA . The mentor alpha 1 penile prosthesis with reservoir lock-out valve: effective prevention of auto-inflation with improved capability for ectopic reservoir placement. J Urol 2002; 168: 1475–1478.
Perito PE . Ectopic reservoir placement - no longer in the space of retzius. J Sex Med 2011; 8: 2395–2398.
Perito PE, Wilson SK . Traditional (retroperitoneal) and abdominal wall (ectopic) reservoir placement. J Sex Med 2011; 8: 656–659.
Henry G, Jones L, Carrion R, Bella A, Karpman E, Christine B et al. Pertinent anatomical measurements of the retropubic space: a guide for inflatable penile prosthesis reservoirs shows that the external iliac vein is much closer than thought. J Sex Med 2014; 11: 273–278.
da Justa DG, Bianco FJ Jr, Ogle A, Dhabuwala CB . Deep venous thrombosis due to compression of external iliac vein by the penile prosthesis reservoir. Urology 2003; 61: 462.
Brison D, Ilbeigi P, Sadeghi-Nejad H . Reservoir positioning and successful thrombectomy for deep venous thrombosis secondary to compression of pelvic veins by an inflatable penile prosthesis reservoir. J Sex Med 2007; 4: 1185–1187.
Deho F, Henry GD, Marone EM, Sacca A, Chiesa R, Rigatti P et al. Severe vascular complication after implantation of a three-piece inflatable penile prosthesis. J Sex Med 2008; 5: 2956–2959.
Flanagan MJ, Krisch EB, Gerber WL . Complication of a penile prosthesis reservoir: venous compression masquerading as a deep venous thrombosis. J Urol 1991; 146: 847–848.
Eldefrawy A, Kava BR . An unusual complication during inflatable penile prosthesis implantation. Urology 2010; 76: 847.
Dupont MC, Hochman HI . Erosion of an inflatable penile prosthesis reservoir into the bladder, presenting as bladder calculi. J Urol 1988; 139: 367–368.
Brusky J, Dikranin A, Aboseif S . Retrieval of inflatable penile prosthesis reservoir from the bladder. Int J Impot Res 2005; 17: 302–303.
Fitch WP 3rd, Roddy T . Erosion of inflatable penile prosthesis reservoir into bladder. J Urol 1986; 136: 1080.
Kramer AC, Chason J, Kusakabe A . Report of two cases of bladder perforation caused by reservoir of inflatable penile prosthesis. J Sex Med 2009; 6: 2064–2067.
Jiann BP, Ou CW, Lin JT, Huang JK . Compression of ureter caused by a retained reservoir of penile prosthesis. Int J Impot Res 2006; 18: 316–317.
Hudak SJ, Mora RV . Unilateral ureteral obstruction due to a migrated inflatable penile prosthesis reservoir. J Urol 2008; 180: 336.
Sadeghi-Nehjad H, Munarriz R, Shah N . Intra-abdominal reservoir placement during penile prosthesis surgery in post-robotically assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy patients: a case report and practical considerations. J Sex Med 2011; 8: 1547–1550.
Nelson RP Jr . Small bowel obstruction secondary to migration of an inflatable penile prosthesis reservoir: recognition and prevention. J Urol 1988; 139: 1053–1054.
Godiwalla SY, Beres J, Jacobs SC . Erosion of an inflatable penile prosthesis reservoir into an ileal conduit. J Urol 1987; 137: 297–298.
Leach GE, Shapiro CE, Hadley R, Raz S . Erosion of inflatable penile prosthesis reservoir into bladder and bowel. J Urol 1984; 131: 1177–1178.
Luks FI, Huntley HN, Tula JC, Pizzi WF . Small-bowel obstruction by an inflatable penile prosthesis reservoir. Surgery 1989; 106: 101–104.
Singh I, Godec CJ . Asynchronous erosion of inflatable penile prosthesis into small and large bowel. J Urol 1992; 147: 709–710.
Stember DS, Garber BB, Perito PE . Outcomes of abdominal wall reservoir placement in inflatable penile prosthesis implantation: a safe and efficacious alternative to the space of Retzius. J Sex Med 2014; 11: 605–612.
Morey AF, Cefalu CA, Hudak SJ . High submuscular placement of urologic prosthetic balloons and reservoirs via transscrotal approach. J Sex Med 2013; 10: 603–610.
Ziegelmann MJ, Viers BR, Lomas DJ, Westerman ME, Trost LW . Ectopic penile prosthesis placement: an anatomic cadaver model of the high submuscular technique. J Sex Med 2016; 13: 1425–1431.
Karpman E, Sadeghi-Nejad H, Henry G, Khera M, Morey AF . Current opinions on alternative reservoir placement for inflatable penile prostheses among members of the Sexual Medicine Society of North America. J Sex Med 2013; 20: 2115–2120.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gross, M., Stember, D., Garber, B. et al. A retrospective analysis of risk factors for IPP reservoir entry into the peritoneum after abdominal wall placement. Int J Impot Res 29, 215–218 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/ijir.2017.26
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ijir.2017.26
This article is cited by
-
Complications and troubleshooting in primary penile prosthetic surgery—a review
International Journal of Impotence Research (2023)
-
Nuances of infrapubic incision for inflatable penile prosthesis
International Journal of Impotence Research (2022)
-
Infrapubic approach for placement of inflatable penile prosthesis: contemporary review of technique and implications
International Journal of Impotence Research (2020)
-
An outcomes analysis of penile prosthesis implantation following radical cystoprostatectomy and urinary diversion: a multicentric retrospective cohort study
International Journal of Impotence Research (2020)
-
Optimizing Outcomes in the Virgin Penile Implant Patient
Current Urology Reports (2019)