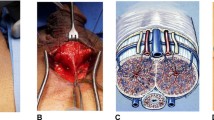
Abstract
Inflatable penile prosthesis (IPP) is an effective treatment for erectile dysfunction refractory to nonsurgical management. The infrapubic approach for IPP placement is less frequently employed than the penoscrotal approach, with only about 25% of IPPs placed via this method. Underutilization of the infrapubic method may be due to fear of injuring the penile dorsal neurovascular bundle, perceived difficulties of scrotal pump placement through a distant location, or insufficient distal corporal exposure. However, this approach appears to result in favorable operative times, faster time to device activation, equivalent postoperative satisfaction and quality of life, and similar complication rates. We provide a contemporary review of literature published before May 2019 regarding the infrapubic approach for IPP placement, technical considerations, and postoperative expectations.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 8 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $32.38 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
McCabe MP, Sharlip ID, Lewis R, Atalla E, Balon R, Fisher AD, et al. Incidence and prevalence of sexual dysfunction in women and men: a consensus statement from the fourth international consultation on sexual medicine 2015. J Sex Med. 2016;13:144–52. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1743609516000795?via%3Dihub.
Kubin M, Wagner G, Fugl-Meyer AR. Epidemiology of erectile dysfunction. Int J Impot Res. 2003;15:63–71. http://www.nature.com/articles/3900949.
Litwin MS, Nied RJ, Dhanani N. Health-related quality of life in men with erectile dysfunction. J Gen Intern Med. 1998;13:159–66. http://link.springer.com/10.1046/j.1525-1497.1998.00050.x.
Feldman HA, Goldstein I, Hatzichristou DG, Krane RJ, McKinlay JB. Impotence and its medical and psychosocial correlates: results of the Massachusetts male aging study. J Urol. 1994;151:54–61. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0022534717348711.
Balon R. Burden of sexual dysfunction. J Sex Marital Ther. 2017;43:49–55. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/0092623X.2015.1113597.
Burnett AL, Nehra A, Breau RH, Culkin DJ, Faraday MM, Hakim LS, et al. Erectile dysfunction: AUA guideline. J Urol. 2018;200:633–41. http://www.jurology.com/doi/10.1016/j.juro.2018.05.004.
Shamloul R, Ghanem H. Erectile dysfunction. Lancet. 2013;381:153–65. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0140673612605200.
Scott F, Bradley W, Timm G. Management of erectile impotence. Use of implantable inflatable prosthesis. Urol. 1973;2:80–2. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/4766860.
Rodriguez KM, Kohn TP, Davis AB, Hakky TS. Penile implants: a look into the future. Transl Androl Urol. 2017;6(Suppl 5):S860–6. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29238665.
Small MP, Carrion HM, Gordon JA. Small-Carrion penile prosthesis. New implant for management of impotence. Urol. 1975;5:479–86. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1093303.
Levine LA, Becher E, Bella A, Brant W, Kohler T, Martinez-Salamanca JI, et al. Penile prosthesis surgery: current recommendations from the International consultation on sexual medicine. J Sex Med. 2016;13:489–518. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1743609516003027?via%3Dihub.
Weinberg AC, Pagano MJ, Deibert CM, Valenzuela RJ. Sub-coronal inflatable penile prosthesis placement with modified no-touch technique: a step-by-step approach with outcomes. J Sex Med. 2016;13:270–6. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S174360951500051X.
Barrett DM, Furlow WL. Penile prosthesis implantation. In: diagnosis and treatment of erectile disturbances. Boston, MA: Springer US; 1985. 219–40. http://link.springer.com/10.1007/978-1-4615-9409-3_10.
Vollstedt A, Gross MS, Antonini G, Perito PE. The infrapubic surgical approach for inflatable penile prosthesis placement. Transl Androl Urol. 2017;6:620–7. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28904894.
Sharma N, Berookhim B, Nelson C, Jenkins L, Mulhall J. 028 contemporary practice patterns for penile prosthesis implantation. J Sex Med. 2017;14:e13–4. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1743609516309237.
Hellstrom WJG, Montague DK, Moncada I, Carson C, Minhas S, Faria G, et al. Implants, mechanical devices, and vascular surgery for erectile dysfunction. J Sex Med. 2010;7:501–23. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1743609515328587.
Ficarra V, Novara G, Rosen RC, Artibani W, Carroll PR, Costello A, et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of studies reporting urinary continence recovery after robot-assisted radical prostatectomy. Eur Urol. 2012;62:405–17. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S030228381200629X?via%3Dihub.
K Hatzimouratidis, F Giuliano, I Moncada, A Muneer, A Salonia PV. European association of urology guidelines for male sexual dysfunction. Eur Assoc Urol. 2018. https://uroweb.org/guideline/male-sexual-dysfunction/.
Trost LW, Boonjindasup AG, Hellstrom WJG. Comparison of infrapubic versus transcrotal approaches for inflatable penile prosthesis placement: a multi-institution report. Int J Impot Res. 2015;27:86–9. http://www.nature.com/articles/ijir201435.
Kramer AC, Sausville J, Schweber A. Practice patterns of urologists performing penile prosthesis surgery vary based on surgeon volume: results of a practice pattern survey. Int J Impot Res. 2010;22:262–6. http://www.nature.com/articles/ijir201013.
Karpman E, Bella A, Brant W, Christine B, Kansas B, Jones L, et al. PD26-10 outcomes of IPP placement by surgical approach, penoscrotal vs. infrapubic, results from a prospective multicenter study. J Urol. 2015;193:e569–70. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S002253471501397X.
Garber BB. Inflatable penile prosthesis: site-specific malfunction analysis. Int J Impot Res. 2003;15:22–5. http://www.nature.com/articles/3900942.
Minervini A, Ralph DJ, Pryor JP. Outcome of penile prosthesis implantation for treating erectile dysfunction: experience with 504 procedures. BJU Int. 2006;97:129–33. http://doi.wiley.com/10.1111/j.1464-410X.2005.05907.x.
Grande P, Antonini G, Cristini C, De Berardinis E, Gatto A, Di Lascio G, et al. Penoscrotal versus minimally invasive infrapubic approach for inflatable penile prosthesis placement: a single-center matched-pair analysis. World J Urol. 2018;36:1167–74. http://link.springer.com/10.1007/s00345-018-2249-z.
Antonini G, Busetto GM, De Berardinis E, Giovannone R, Vicini P, Del Giudice F, et al. Minimally invasive infrapubic inflatable penile prosthesis implant for erectile dysfunction: evaluation of efficacy, satisfaction profile and complications. Int J Impot Res. 2016;28:4–8. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26657316.
Kramer A, Chason J. Residents at the University of Maryland Medical System provide insight to learning infrapubic approach for ipp surgery: relative benefits but novel challenges exposed in first 15 cases. 2010:1298–305. https://ucill.vdxhost.com/zportal/zengine?VDXaction=GetAttachment&illno=8781157&objectno=1513785&objectseq=1&is_popup_window=true.
Montorsi F, Rigatti P, Carmignani G, Corbui C, Campo B, Ordesi G, et al. Erectile dysfunction AMS three-piece inflatable implants for erectile dysfunction: a long-term multi-institutional study in 200 consecutive patients. 2000. www.karger.com.
Tran H, Goldfarb R, Ackerman A, Valenzuela RJ. Penile lengthening, girth, and size preservation at the time of penile prosthesis insertion. Sex Med Rev. 2017;5:403–12. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28238678.
Candela JV, Hellstrom WJ. Three-piece inflatable penile prosthesis implantation: a comparison of the penoscrotal and infrapubic surgical approaches. J La State Med Soc. 1996;148:296–301. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8816024.
Palmisano F, Boeri L, Cristini C, Antonini G, Spinelli MG, Franco G, et al. Comparison of infrapubic vs. penoscrotal approaches for 3-piece inflatable penile prosthesis placement: do we have a winner? Sex Med Rev. 2018;6:631–9. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2050052118300520?via%3Dihub.
Jorissen C, De Bruyn H, Baten E, van Renterghem KMLE. 601 Clinical outcome/patient and partner satisfaction after penile implant surgery. J Sex Med. 2018;15:S353. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S174360951830780X.
Eid JF. Penile implant: review of a “No-Touch” technique. Sex Med Rev. 2016;4:294–300. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S2050052116000573.
Pineda M, Burnett AL. Penile prosthesis infections—a review of risk factors, prevention, and treatment. Sex Med Rev. 2016;4:389–98. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S2050052116300026.
O’Rourke TK, Erbella A, Zhang Y, Wosnitzer MS, Wosnitzer MS. Prevention, identification, and management of post-operative penile implant complications of infection, hematoma, and device malfunction. Transl Androl Urol. 2017;6(Suppl 5):S832–48. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29238663.
Garber BB, Marcus SM. Does surgical approach affect the incidence of inflatable penile prosthesis infection? Urol. 1998;52:291–3. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0090429598001861?via%3Dihub.
Goldstein I, Newman L, Baum N, Brooks M, Chaikin L, Goldberg K, et al. Safety and efficacy outcome of mentor alpha-1 inflatable penile prosthesis implantation for impotence treatment. J Urol. 1997;157:833–9. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9072580.
Thomalla JV, Thompson ST, Rowland RG, Mulcahy JJ. Infectious complications of penile prosthetic implants. J Urol. 1987;138:65–7. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0022534717429910.
Montague DK. Periprosthetic infections. J Urol. 1987;138:68–9. https://www.auajournals.org/doi/pdf/10.1016/S0022-5347%2817%2942992-2.
Gupta NK, Ring J, Trost L, Wilson SK, Köhler TS. The penoscrotal surgical approach for inflatable penile prosthesis placement. Transl Androl Urol. 2017;6:628–38. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28904895.
Sadeghi-Nejad H, Sharma A, Irwin RJ, Wilson SK, Delk JR. Reservoir herniation as a complication of three-piece penile prosthesis insertion. Urology. 2001;57:142–5. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0090429500008645?via%3Dihub.
Gross MS, Stember DS, Garber BB, Perito PE. A retrospective analysis of risk factors for IPP reservoir entry into the peritoneum after abdominal wall placement. Int J Impot Res. 2017;29:215–8. http://www.nature.com/doifinder/10.1038/ijir.2017.26.
Montague DK, Angermeir KW. Surgical approaches for penile prosthesis implantation: penoscrotal vs infrapubic. Int J Impot Res. 2003;15:134–5. www.nature.com/ijir.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RJ acquired data and wrote the paper. SE and JNM assisted with paper design and revision. All authors approved the final version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
RJ and SVE declare no potential conflicts of interest. JNM serves as a consultant and proctor for Boston Scientific.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jayadevan, R., Eleswarapu, S.V. & Mills, J.N. Infrapubic approach for placement of inflatable penile prosthesis: contemporary review of technique and implications. Int J Impot Res 32, 10–17 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41443-019-0193-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41443-019-0193-0
This article is cited by
-
Glans hypermobility scale (GHS): A simple grading scale and description of a modified glanspexy technique
International Journal of Impotence Research (2024)
-
50th year anniversary of penile implants: an ongoing worldwide triumph
International Journal of Impotence Research (2023)
-
The good, the bad, and the ugly about surgical approaches for inflatable penile prosthesis implantation
International Journal of Impotence Research (2022)