Synthesis
Lattice anchoring stabilizes solution-processed semiconductors
Mengxia Liu et al., Nature 570, 96-101 (2019) doi:10.1038/s41586-019-1239-7
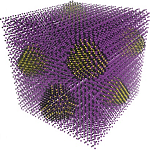
 Semiconductors that can be fabricated using simple, scalable, solution processing techniques compatible with flexible substrates are attractive for a range of next-generation optoelectronic technologies. Whilst the performance of such materials for sensing, light-emission and photovoltaics are steadily increasing, their often poor stability in air hinders their potential applications. Edward Sargent and colleagues now show that the stability of both solution-processed colloidal quantum dots and perovskites can be significantly improved by combining them into a new hybrid material. This lattice anchoring strategy, in which the colloidal quantum dots supress the formation of undesired perovskite phases, provides a route for engineering solution-processed materials for optoelectronic applications. Shareable link
Semiconductors that can be fabricated using simple, scalable, solution processing techniques compatible with flexible substrates are attractive for a range of next-generation optoelectronic technologies. Whilst the performance of such materials for sensing, light-emission and photovoltaics are steadily increasing, their often poor stability in air hinders their potential applications. Edward Sargent and colleagues now show that the stability of both solution-processed colloidal quantum dots and perovskites can be significantly improved by combining them into a new hybrid material. This lattice anchoring strategy, in which the colloidal quantum dots supress the formation of undesired perovskite phases, provides a route for engineering solution-processed materials for optoelectronic applications. Shareable link
Pb clustering and PbI2 nanofragmentation during methylammonium lead iodide perovskite degradation
Alessandra Alberti et al., Nat. Commun. 10, 2196 (2019) doi:10.1038/s41467-019-09909-0
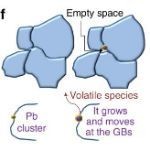 Methylammonium lead halide perovskites have great potential for optoelectronic applications but are prone to degradation. Here the authors show that degradation occurs through clustering of Pb containing defects at the grain boundaries while concurrent formation of PbI2 blocks further reactions, suggesting a strategy for passivation.
Methylammonium lead halide perovskites have great potential for optoelectronic applications but are prone to degradation. Here the authors show that degradation occurs through clustering of Pb containing defects at the grain boundaries while concurrent formation of PbI2 blocks further reactions, suggesting a strategy for passivation.
Suppressed phase separation of mixed-halide perovskites confined in endotaxial matrices
Xi Wang et al., Nat. Commun. 10, 695 (2019) doi:10.1038/s41467-019-08610-6
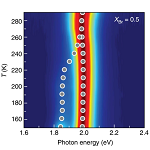
Compositional and orientational control in metal halide perovskites of reduced dimensionality
Rafael Quintero-Bermudez et al., Nat. Mater. 17, 900-907 (2018) doi:10.1038/s41563-018-0154-x
From the archive
A fluorene-terminated hole-transporting material for highly efficient and stable perovskite solar cells
Nam Joong Jeon et al., Nat. Energy 3, 682-689 (2018) doi:10.1038/s41560-018-0200-6
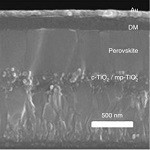 Interfacial losses between device layers play a key role in determining characteristics of solar cells. Jeon et al. address this in perovskite solar cells by synthesizing a hole-transporting layer that is better matched to the surrounding layers, and show high-efficiency and high-stability devices. Shareable link
Interfacial losses between device layers play a key role in determining characteristics of solar cells. Jeon et al. address this in perovskite solar cells by synthesizing a hole-transporting layer that is better matched to the surrounding layers, and show high-efficiency and high-stability devices. Shareable link
Shape-preserving transformation of carbonate minerals into lead halide perovskite semiconductors based on ion exchange/insertion reactions
Tim Holtus et al., Nat. Chem. 10, 740-745 (2018) doi:10.1038/s41557-018-0064-1
 Biominerals feature unique and potentially useful three-dimensional structures but are often difficult to transform into functional materials. Now, a two-step ion exchange/insertion reaction has been shown to convert synthetic carbonate salts and calcium carbonate biominerals into lead halide perovskites with tunable optoelectronic properties while preserving the shapes and microstructures of the precursors. Shareable link
Biominerals feature unique and potentially useful three-dimensional structures but are often difficult to transform into functional materials. Now, a two-step ion exchange/insertion reaction has been shown to convert synthetic carbonate salts and calcium carbonate biominerals into lead halide perovskites with tunable optoelectronic properties while preserving the shapes and microstructures of the precursors. Shareable link
Surfactant-controlled ink drying enables high-speed deposition of perovskite films for efficient photovoltaic modules
Yehao Deng et al., Nat. Energy 3, 560-566 (2018) doi:10.1038/s41560-018-0153-9
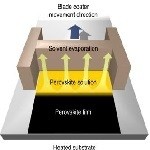 Scaling up perovskite film deposition necessitates controlling the film formation dynamics. Here, Deng et al. use amphoteric choline surfactants to blade-coat well-passivated films, reaching module efficiencies of ~15% for aperture areas up to 57 cm2. Shareable link
Scaling up perovskite film deposition necessitates controlling the film formation dynamics. Here, Deng et al. use amphoteric choline surfactants to blade-coat well-passivated films, reaching module efficiencies of ~15% for aperture areas up to 57 cm2. Shareable link
Perovskite seeding growth of formamidinium-lead-iodide-based perovskites for efficient and stable solar cells
Yicheng Zhao et al., Nat. Commun. 9, 1607 (2018) doi:10.1038/s41467-018-04029-7
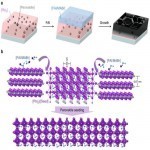 Formamidinium-lead-iodide based perovskites have a preferred bandgap below 1.55 eV for solar cell applications but suffer from the operational instability. Here Zhao et al. improve the film quality by Cesium-containing seeded growth to show high stabilized efficiency and more than 100 hours lifetime under simulated sunlight.
Formamidinium-lead-iodide based perovskites have a preferred bandgap below 1.55 eV for solar cell applications but suffer from the operational instability. Here Zhao et al. improve the film quality by Cesium-containing seeded growth to show high stabilized efficiency and more than 100 hours lifetime under simulated sunlight.
Large guanidinium cation mixed with methylammonium in lead iodide perovskites for 19% efficient solar cells
Alexander D. Jodlowski et al., Nat. Energy 2, 972-979 (2017) doi:10.1038/s41560-017-0054-3
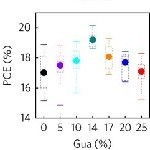 Cation engineering has been used to tune the efficiency and stability of perovskite solar cells. Here, Jodlowski et al. introduce guanidinium, a cation slightly larger than previously thought possible, mixed with the traditional methylammonium cation, into the 3D structure, improving device stability. Shareable link
Cation engineering has been used to tune the efficiency and stability of perovskite solar cells. Here, Jodlowski et al. introduce guanidinium, a cation slightly larger than previously thought possible, mixed with the traditional methylammonium cation, into the 3D structure, improving device stability. Shareable link
A solvent- and vacuum-free route to large-area perovskite films for efficient solar modules
Han Chen et al., Nature (2017) doi:10.1038/nature23877
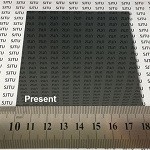 Hybrid inorganic-organic perovskite solar cells are a contender for commercialisation and to perhaps compete with silicon solar cells in the future, but issues with stability and scaling-up thin films mean that large scale production is not yet possible. Liyuan Han and colleagues have developed a new deposition method for polycrystalline thin films that does not rely on spin- or drip-coating precursors in solvent, or on vacuum deposition, and therefore is therefore more amenable to larger area films than previous techniques. The procedure uses gaseous precursors and application of pressure, and has allowed a device of 36 cm2 to be certified at 12.1% power conversion efficiency. Shareable link
Hybrid inorganic-organic perovskite solar cells are a contender for commercialisation and to perhaps compete with silicon solar cells in the future, but issues with stability and scaling-up thin films mean that large scale production is not yet possible. Liyuan Han and colleagues have developed a new deposition method for polycrystalline thin films that does not rely on spin- or drip-coating precursors in solvent, or on vacuum deposition, and therefore is therefore more amenable to larger area films than previous techniques. The procedure uses gaseous precursors and application of pressure, and has allowed a device of 36 cm2 to be certified at 12.1% power conversion efficiency. Shareable link
Rationalizing the light-induced phase separation of mixed halide organic–inorganic perovskites
Sergiu Draguta et al., Nat. Commun. 8, 200 (2017) doi:10.1038/s41467-017-00284-2
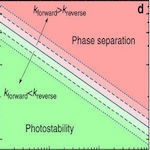 Mixed halide hybrid perovskites possess tunable band gaps, however, under illumination they undergo phase separation. Using spectroscopic measurements and theoretical modelling, Draguta and Sharia et al., quantitatively rationalize the microscopic processes that occur during phase separation.
Mixed halide hybrid perovskites possess tunable band gaps, however, under illumination they undergo phase separation. Using spectroscopic measurements and theoretical modelling, Draguta and Sharia et al., quantitatively rationalize the microscopic processes that occur during phase separation.
Wafer-scale single-crystal perovskite patterned thin films based on geometrically-confined lateral crystal growth
Lynn Lee et al., Nat. Commun. 8, 15882 (2017)
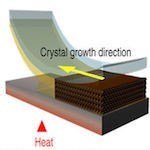 Wafer-scale deposition of uniform metal halide perovskite single-crystals is a step towards commercialisation. Using geometrically-confined lateral crystal growth, Lee et al., report patterned thin films of highly-aligned single-crystals and achieve lateral solar cells with efficiencies up to 4.83%.
Wafer-scale deposition of uniform metal halide perovskite single-crystals is a step towards commercialisation. Using geometrically-confined lateral crystal growth, Lee et al., report patterned thin films of highly-aligned single-crystals and achieve lateral solar cells with efficiencies up to 4.83%.
The effect of illumination on the formation of metal halide perovskite films
Amita Ummadisingu et al., Nature 545, 208-212 (2017) doi:10.1038/nature22072
 Solar cells that use hybrid organic–inorganic halide perovskites as the absorber material have been the fastest-improving devices in recent years in terms of power conversion efficiency. Several different methodologies have been developed to improve and control the quality of perovskite films to maximize device performance. Here, Michael Grätzel and colleagues show that light irradiation during the formation of perovskite films is an important consideration, and not just that light should be excluded as is commonly done. For two widely used fabrication techniques, they show that irradiation enhances film quality in one of them, but degrades it in the other. This is attributed to light-enhanced nucleation of perovskite crystals during film formation. Shareable link
Solar cells that use hybrid organic–inorganic halide perovskites as the absorber material have been the fastest-improving devices in recent years in terms of power conversion efficiency. Several different methodologies have been developed to improve and control the quality of perovskite films to maximize device performance. Here, Michael Grätzel and colleagues show that light irradiation during the formation of perovskite films is an important consideration, and not just that light should be excluded as is commonly done. For two widely used fabrication techniques, they show that irradiation enhances film quality in one of them, but degrades it in the other. This is attributed to light-enhanced nucleation of perovskite crystals during film formation. Shareable link
Perovskite ink with wide processing window for scalable high-efficiency solar cells
Mengjin Yang et al., Nat. Energy 2, 17038 (2017) doi:10.1038/nenergy.2017.38
 Perovskite-based solar cells are often fabricated by methods that are not industrially scalable. Here, Yang et al. develop an ink formulation which gives similar devices by spin coating, the lab-scale standard, and blade coating, which is a more scalable, industry-relevant deposition method. Shareable link
Perovskite-based solar cells are often fabricated by methods that are not industrially scalable. Here, Yang et al. develop an ink formulation which gives similar devices by spin coating, the lab-scale standard, and blade coating, which is a more scalable, industry-relevant deposition method. Shareable link
Strongly emissive perovskite nanocrystals inks for high voltage solar cells
Quinten A. Akkerman et al., Nat. Energy 2, 16194 (2016) doi:10.1038/nenergy.2016.194

Nonstoichiometric acid–base reaction as reliable synthetic route to highly stable CH3NH3PbI3 perovskite film
Mingzhu Long et al., Nat. Commun. 7, 13503 (2016) doi:10.1038/ncomms13503
 Perovskite thin-film prepared by nonstoichiometric acid–base reaction route is stable for two months with negligible PbI2-impurity under ∼65% humidity, where high quality of intermediate HPbI3 and CH3NH2 abundance play important roles.
Perovskite thin-film prepared by nonstoichiometric acid–base reaction route is stable for two months with negligible PbI2-impurity under ∼65% humidity, where high quality of intermediate HPbI3 and CH3NH2 abundance play important roles.
Polymer-templated nucleation and crystal growth of perovskite films for solar cells with efficiency greater than 21%
Dongbi Bi et al., Nat. Energy 1, 16142 (2016) doi:10.1038/nenergy.2016.142
 Controlling the crystallization process of perovskite films is crucial to obtaining high efficiency in perovskite solar cells. Bi et al. propose the use of poly(methyl methacrylate) as a template for the controlled nucleation and growth of perovskite crystals achieving efficiency of 21.6%. Shareable link
Controlling the crystallization process of perovskite films is crucial to obtaining high efficiency in perovskite solar cells. Bi et al. propose the use of poly(methyl methacrylate) as a template for the controlled nucleation and growth of perovskite crystals achieving efficiency of 21.6%. Shareable link
Quantum-dot-in-perovskite solids
Zhijun Ning et al., Nature 523, 324-328 (2015), doi: 10.1038/nature14563
Shareable Link
Organohalide perovskites and preformed colloidal quantum dots are combined in the solution phase to produce epitaxially aligned ‘dots-in-a-matrix’ crystals that have both the excellent electrical transport properties of the perovskite matrix and the high radiative efficiency of the quantum dots.
High-quality bulk hybrid perovskite single crystals within minutes by inverse temperature crystallization
Makhsud I. Saidaminov et al., Nat. Commun. 6, 7586 (2015) doi:10.1038/ncomms8586
Hybrid perovskites are a promising class of materials for photovoltaic applications. Here, addressing the need for high-quality hybrid perovskite materials, the authors achieve the rapid growth of hybrid perovskite single crystals of high quality by inverse temperature crystallization.
Ultrasmooth organic–inorganic perovskite thin-film formation and crystallization for efficient planar heterojunction solar cells
Wei Zhang et al., Nat. Commun. 6, 6142 (2015) doi:10.1038/ncomms7142
Organic-inorganic metal halide perovskites are of considerable promise for efficient, easy to manufacture solar cells. Here, the authors show that the choice of anions in the perovskite solution can considerably affect the crystal growth and performance of these solar cells.
Compositional engineering of perovskite materials for high-performance solar cells
Nam Joong Jeon et al., Nature 517, 476-480 (2015) doi:10.1038/nature14133
Shareable Link
Inorganic–organic lead halide perovskite could be efficient when used as the light-harvesting component of solar cells; here incorporation of methylammonium lead bromide into formamidinium lead iodide stabilizes the perovskite and improves the power conversion efficiency of the solar cell up to 17.9 per cent.