Abstract
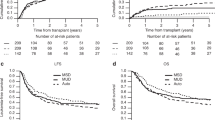
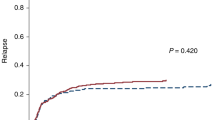
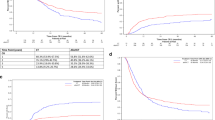
Reduced intensity conditioning regimens lead to an increasing use of allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT) in elderly patients. We retrospectively analyzed 151 patients aged ⩾60 receiving allogeneic HCT 2000–2012 at our center. Median age was 66 years. Kaplan–Meier estimated 3-year OS was 42% with a median follow-up of 38 months. Cumulative incidences of progression and non-relapse mortality after 3 years were 38 and 24%. OS was better in the group of patients >65 years with a Kaplan–Meier estimated OS of 50% vs 34%, P=0.060. We observed a significant influence of donor age (<50 years: 53% vs >50 years: 30%, P=0.017) and gender match (matched: 57% vs mismatched: 32%, P=0.007) on outcome. The use of a matched related donor was inferior compared with a matched or mismatched unrelated donor (19% vs 47%, P=0.015). On multivariate analysis there was an increased hazard ratio for a non-gender-matched HLA-matched-related donor (hazard ratio 3.23, 95% confidence interval 1.55–6.74, P=0.002). Age had no significant impact on OS (P=0.414). In conclusion, the data suggest that older age alone has no negative impact on the outcome of allogeneic HCT. Transplant decision should be tailored to disease risk and patient performance status rather than age.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xie Y, Davies SM, Xiang Y, Robison LL, Ross JA . Trends in leukemia incidence and survival in the United States (1973–1998). Cancer 2003; 97: 2229–2235.
Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A . Cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin 2012; 62: 10–29.
Buchner T, Berdel WE, Haferlach C, Haferlach T, Schnittger S, Muller-Tidow C et al. Age-related risk profile and chemotherapy dose response in acute myeloid leukemia: a study by the German Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cooperative Group. J Clin Oncol 2009; 27: 61–69.
Hasenclever D, Diehl V . A prognostic score for advanced Hodgkin's disease. International Prognostic Factors Project on Advanced Hodgkin's Disease. N Engl J Med 1998; 339: 1506–1514.
Solal-Celigny P, Roy P, Colombat P, White J, Armitage JO, Arranz-Saez R et al. Follicular lymphoma international prognostic index. Blood 2004; 104: 1258–1265.
Evens AM, Sweetenham JW, Horning SJ . Hodgkin lymphoma in older patients: an uncommon disease in need of study. Oncology (Williston Park) 2008; 22: 1369–1379.
Rowe JM . Optimal management of adults with ALL. Br J Haematol 2009; 144: 468–483.
Appelbaum FR, Gundacker H, Head DR, Slovak ML, Willman CL, Godwin JE et al. Age and acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2006; 107: 3481–3485.
Slavin S, Nagler A, Naparstek E, Kapelushnik Y, Aker M, Cividalli G et al. Nonmyeloablative stem cell transplantation and cell therapy as an alternative to conventional bone marrow transplantation with lethal cytoreduction for the treatment of malignant and nonmalignant hematologic diseases. Blood 1998; 91: 756–763.
Sorror ML, Sandmaier BM, Storer BE, Franke GN, Laport GG, Chauncey TR et al. Long-term outcomes among older patients following nonmyeloablative conditioning and allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for advanced hematologic malignancies. JAMA 2011; 306: 1874–1883.
Sorror ML, Maris MB, Storb R, Baron F, Sandmaier BM, Maloney DG et al. Hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT)-specific comorbidity index: a new tool for risk assessment before allogeneic HCT. Blood 2005; 106: 2912–2919.
Armand P, Gibson CJ, Cutler C, Ho VT, Koreth J, Alyea EP et al. A disease risk index for patients undergoing allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Blood 2012; 120: 905–913.
Brunner AM, Kim HT, Coughlin E, Alyea EP 3rd, Armand P, Ballen KK et al. Outcomes in patients age 70 or older undergoing allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for hematologic malignancies. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2013; 19: 1374–1380.
Glucksberg H, Storb R, Fefer A, Buckner CD, Neiman PE, Clift RA et al. Clinical manifestations of graft-versus-host disease in human recipients of marrow from HL-A-matched sibling donors. Transplantation 1974; 18: 295–304.
Lee SJ, Vogelsang G, Flowers ME . Chronic graft-versus-host disease. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2003; 9: 215–233.
Bacigalupo A, Ballen K, Rizzo D, Giralt S, Lazarus H, Ho V et al. Defining the intensity of conditioning regimens: working definitions. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2009; 15: 1628–1633.
Giralt S, Ballen K, Rizzo D, Bacigalupo A, Horowitz M, Pasquini M et al. Reduced-intensity conditioning regimen workshop: defining the dose spectrum. Report of a workshop convened by the center for international blood and marrow transplant research. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2009; 15: 367–369.
Bader P, Beck J, Frey A, Schlegel PG, Hebarth H, Handgretinger R et al. Serial and quantitative analysis of mixed hematopoietic chimerism by PCR in patients with acute leukemias allows the prediction of relapse after allogeneic BMT. Bone Marrow Transplant 1998; 21: 487–495.
Pepe MS, Mori M . Kaplan-Meier, marginal or conditional probability curves in summarizing competing risks failure time data? Stat Med 1993; 12: 737–751.
Koreth J, Aldridge J, Kim HT, Alyea EP III, Cutler C, Armand P et al. Reduced-intensity conditioning hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in patients over 60 years: hematologic malignancy outcomes are not impaired in advanced age. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2010; 16: 792–800.
Lim Z, Brand R, Martino R, van Biezen A, Finke J, Bacigalupo A et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation for patients 50 years or older with myelodysplastic syndromes or secondary acute myeloid leukemia. J Clin Oncol 2010; 28: 405–411.
McClune BL, Weisdorf DJ, Pedersen TL, Tunes da Silva G, Tallman MS, Sierra J et al. Effect of age on outcome of reduced-intensity hematopoietic cell transplantation for older patients with acute myeloid leukemia in first complete remission or with myelodysplastic syndrome. J Clin Oncol 2010; 28: 1878–1887.
Lim ZY, Ingram W, Brand R, Ho A, Kenyon M, Devereux S et al. Impact of pretransplant comorbidities on alemtuzumab-based reduced-intensity conditioning allogeneic hematopoietic SCT for patients with high-risk myelodysplastic syndrome and AML. Bone Marrow Transplant 2010; 45: 633–639.
Boehm A, Sperr WR, Leitner G, Worel N, Oehler L, Jaeger E et al. Comorbidity predicts survival in myelodysplastic syndromes or secondary acute myeloid leukaemia after allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Eur J Clin Invest 2008; 38: 945–952.
Hegenbart U, Niederwieser D, Sandmaier BM, Maris MB, Shizuru JA, Greinix H et al. Treatment for acute myelogenous leukemia by low-dose, total-body, irradiation-based conditioning and hematopoietic cell transplantation from related and unrelated donors. J Clin Oncol 2006; 24: 444–453.
Kroger N, Zabelina T, de Wreede L, Berger J, Alchalby H, van Biezen A et al. Allogeneic stem cell transplantation for older advanced MDS patients: improved survival with young unrelated donor in comparison with HLA-identical siblings. Leukemia 2013; 27: 604–609.
Ringden O, Horowitz MM, Gale RP, Biggs JC, Gajewski J, Rimm AA et al. Outcome after allogeneic bone marrow transplant for leukemia in older adults. JAMA 1993; 270: 57–60.
Nakai K, Kanda Y, Fukuhara S, Sakamaki H, Okamoto S, Kodera Y et al. Value of chemotherapy before allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation from an HLA-identical sibling donor for myelodysplastic syndrome. Leukemia 2005; 19: 396–401.
de Witte T, Hermans J, Vossen J, Bacigalupo A, Meloni G, Jacobsen N et al. Haematopoietic stem cell transplantation for patients with myelo-dysplastic syndromes and secondary acute myeloid leukaemias: a report on behalf of the Chronic Leukaemia Working Party of the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation (EBMT). Br J Haematol 2000; 110: 620–630.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the study nurses and staff of the transplant unit, who took part in the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Federmann, B., Faul, C., Meisner, C. et al. Influence of age on outcome after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation: a single center study in patients aged ⩾60. Bone Marrow Transplant 50, 427–431 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2014.292
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2014.292
This article is cited by
-
Retrospective comparison of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation following reduced-intensity conditioning with fludarabine/low-dose melphalan plus 4 Gy TBI versus fludarabine/ busulfan plus 4 Gy TBI
International Journal of Hematology (2022)
-
Retrospective single center analysis of outcome, risk factors and therapy in steroid refractory graft-versus-host disease after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2019)
-
Fludarabine and busulfan plus low-dose TBI as reduced intensity conditioning in older patients undergoing allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplant for myeloid malignancies
Annals of Hematology (2018)
-
FLT3 mutational status is an independent risk factor for adverse outcomes after allogeneic transplantation in AML
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2016)
-
Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation in patients ⩾70 years: which patients may benefit?
Blood Cancer Journal (2016)