Abstract
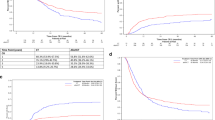
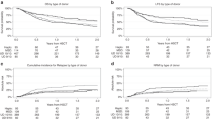
The long-term outcomes of allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT) with reduced-intensity conditioning (RIC) remain inconclusive. To address this issue, we conducted a nationwide registry-based study of patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) age 50 years or older who underwent allogeneic HCT in complete remission using RIC (n = 284) or myeloablative conditioning (MAC, n = 190) between 2002 and 2007. The median follow-up period for surviving patients was 10.1 years for RIC recipients and 10.4 years for MAC recipients. The 10-year probabilities of overall survival, relapse, and non-relapse mortality were 36.4%, 30.0%, and 35.7% for RIC recipients, and 39.8%, 26.3%, and 35.5% for MAC recipients, respectively. Multivariate analysis revealed that the conditioning intensity did not affect overall mortality (P = 0.184), relapse (P = 0.904), or non-relapse mortality (P = 0.387). For the 218 patients qualifying for propensity score-matched pairing (109 pairs), RIC was found to be associated with similar survival (P = 0.095) and relapse (P = 0.467), and significantly lower non-relapse mortality (P = 0.046) compared with MAC. Our results confirm the long-term efficacy of RIC allogeneic HCT for older patients with AML and mitigate concerns over an increase in late relapse.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yanada M. Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for acute myeloid leukemia during first complete remission: a clinical perspective. Int J Hematol. 2015;101:243–54.
Sengsayadeth S, Savani BN, Blaise D, Malard F, Nagler A, Mohty M. Reduced intensity conditioning allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for adult acute myeloid leukemia in complete remission - a review from the Acute Leukemia Working Party of the EBMT. Haematologica. 2015;100:859–69.
Aoudjhane M, Labopin M, Gorin NC, Shimoni A, Ruutu T, Kolb HJ, et al. Comparative outcome of reduced intensity and myeloablative conditioning regimen in HLA identical sibling allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplantation for patients older than 50 years of age with acute myeloblastic leukaemia: a retrospective survey from the Acute Leukemia Working Party (ALWP) of the European group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation (EBMT). Leukemia. 2005;19:2304–12.
Ringden O, Labopin M, Ehninger G, Niederwieser D, Olsson R, Basara N, et al. Reduced intensity conditioning compared with myeloablative conditioning using unrelated donor transplants in patients with acute myeloid leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:4570–7.
Luger SM, Ringden O, Zhang MJ, Perez WS, Bishop MR, Bornhauser M, et al. Similar outcomes using myeloablative vs reduced-intensity allogeneic transplant preparative regimens for AML or MDS. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2012;47:203–11.
Bornhauser M, Kienast J, Trenschel R, Burchert A, Hegenbart U, Stadler M, et al. Reduced-intensity conditioning versus standard conditioning before allogeneic haemopoietic cell transplantation in patients with acute myeloid leukaemia in first complete remission: a prospective, open-label randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012;13:1035–44.
Martino R, de Wreede L, Fiocco M, van Biezen A, von dem Borne PA, Hamladji RM, et al. Comparison of conditioning regimens of various intensities for allogeneic hematopoietic SCT using HLA-identical sibling donors in AML and MDS with <10% BM blasts: a report from EBMT. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2013;48:761–70.
Passweg JR, Labopin M, Cornelissen J, Volin L, Socie G, Huynh A, et al. Conditioning intensity in middle-aged patients with AML in first CR: no advantage for myeloablative regimens irrespective of the risk group-an observational analysis by the Acute Leukemia Working Party of the EBMT. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2015;50:1063–8.
Russell NH, Kjeldsen L, Craddock C, Pagliuca A, Yin JA, Clark RE, et al. A comparative assessment of the curative potential of reduced intensity allografts in acute myeloid leukaemia. Leukemia. 2015;29:1478–84.
Shimoni A, Labopin M, Savani B, Volin L, Ehninger G, Kuball J, et al. Long-term survival and late events after allogeneic stem cell transplantation from HLA-matched siblings for acute myeloid leukemia with myeloablative compared to reduced-intensity conditioning: a report on behalf of the acute leukemia working party of European group for blood and marrow transplantation. J Hematol Oncol. 2016;9:118.
Scott BL, Pasquini MC, Logan BR, Wu J, Devine SM, Porter DL, et al. Myeloablative versus reduced-intensity hematopoietic cell transplantation for acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndromes. J Clin Oncol. 2017;35:1154–61.
Yanada M, Kurosawa S, Kobayashi T, Ozawa Y, Kanamori H, Kobayashi N, et al. Reduced-intensity conditioning allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for younger patients with acute myeloid leukemia: a registry-based study. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2017;52:818–24.
Fasslrinner F, Schetelig J, Burchert A, Kramer M, Trenschel R, Hegenbart U, et al. Long-term efficacy of reduced-intensity versus myeloablative conditioning before allogeneic haemopoietic cell transplantation in patients with acute myeloid leukaemia in first complete remission: retrospective follow-up of an open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Haematol. 2018;5:e161–69.
Herr AL, Labopin M, Blaise D, Milpied N, Potter M, Michallet M, et al. HLA-identical sibling allogeneic peripheral blood stem cell transplantation with reduced intensity conditioning compared to autologous peripheral blood stem cell transplantation for elderly patients with de novo acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia. 2007;21:129–35.
McClune BL, Weisdorf DJ, Pedersen TL, Tunes da Silva G, Tallman MS, Sierra J, et al. Effect of age on outcome of reduced-intensity hematopoietic cell transplantation for older patients with acute myeloid leukemia in first complete remission or with myelodysplastic syndrome. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:1878–87.
Gyurkocza B, Storb R, Storer BE, Chauncey TR, Lange T, Shizuru JA, et al. Nonmyeloablative allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation in patients with acute myeloid leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:2859–67.
Baron F, Labopin M, Niederwieser D, Vigouroux S, Cornelissen JJ, Malm C, et al. Impact of graft-versus-host disease after reduced-intensity conditioning allogeneic stem cell transplantation for acute myeloid leukemia: a report from the Acute Leukemia Working Party of the European group for blood and marrow transplantation. Leukemia. 2012;26:2462–8.
Nagler A, Labopin M, Shimoni A, Mufti GJ, Cornelissen JJ, Blaise D, et al. Mobilized peripheral blood stem cells compared with bone marrow from HLA-identical siblings for reduced-intensity conditioning transplantation in acute myeloid leukemia in complete remission: a retrospective analysis from the Acute Leukemia Working Party of EBMT. Eur J Haematol. 2012;89:206–13.
Chevallier P, Labopin M, Milpied N, Cornelissen JJ, Blaise D, Petersen E, et al. Impact of cytogenetics risk on outcome after reduced intensity conditioning allo-SCT from an HLA-identical sibling for patients with AML in first CR: a report from the acute leukemia working party of EBMT. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2012;47:1442–7.
Peffault de Latour R, Brunstein CG, Porcher R, Chevallier P, Robin M, Warlick E, et al. Similar overall survival using sibling, unrelated donor, and cord blood grafts after reduced-intensity conditioning for older patients with acute myelogenous leukemia. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl. 2013;19:1355–60.
Yeshurun M, Labopin M, Blaise D, Cornelissen JJ, Sengeloev H, Vindelov L, et al. Impact of postremission consolidation chemotherapy on outcome after reduced-intensity conditioning allogeneic stem cell transplantation for patients with acute myeloid leukemia in first complete remission: a report from the Acute Leukemia Working Party of the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Cancer. 2014;120:855–63.
Warlick ED, Paulson K, Brazauskas R, Zhong X, Miller AM, Camitta BM, et al. Effect of postremission therapy before reduced-intensity conditioning allogeneic transplantation for acute myeloid leukemia in first complete remission. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl. 2014;20:202–8.
Versluis J, Labopin M, Niederwieser D, Socie G, Schlenk RF, Milpied N, et al. Prediction of non-relapse mortality in recipients of reduced intensity conditioning allogeneic stem cell transplantation with AML in first complete remission. Leukemia. 2015;29:51–7.
Aoki J, Kanamori H, Tanaka M, Yamasaki S, Fukuda T, Ogawa H, et al. Impact of age on outcomes of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation with reduced intensity conditioning in elderly patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Am J Hematol. 2016;91:302–7.
Devine SM, Owzar K, Blum W, Mulkey F, Stone RM, Hsu JW, et al. Phase II Study of Allogeneic Transplantation for older patients with acute myeloid leukemia in first complete remission using a reduced-intensity conditioning regimen: results from cancer and leukemia group B 100103 (Alliance for Clinical Trials in Oncology)/Blood and Marrow Transplant Clinical Trial Network 0502. J Clin Oncol. 2015;33:4167–75.
Yamasaki S, Hirakawa A, Aoki J, Uchida N, Fukuda T, Ogawa H, et al. Role of reduced-intensity conditioning allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation in older patients with de novo acute myeloid leukemia. Ann Hematol. 2017;96:289–97.
Atsuta Y. Introduction of transplant registry unified management program 2 (TRUMP2): scripts for TRUMP data analyses, part I (variables other than HLA-related data). Int J Hematol. 2016;103:3–10.
Yanada M, Masuko M, Mori J, Aoki J, Mizuno S, Fukuda T, et al. Patients with acute myeloid leukemia undergoing allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation: trends in survival during the past two decades. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2019;54:578–86.
Yanada M, Konuma T, Kuwatsuka Y, Kondo T, Kawata T, Takahashi S, et al. Unit selection for umbilical cord blood transplantation for adults with acute myeloid leukemia in complete remission: a Japanese experience. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2019;54:1789–98.
Oken MM, Creech RH, Tormey DC, Horton J, Davis TE, McFadden ET, et al. Toxicity and response criteria of the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group. Am J Clin Oncol. 1982;5:649–55.
Yanada M, Mori J, Aoki J, Harada K, Mizuno S, Uchida N, et al. Effect of cytogenetic risk status on outcomes for patients with acute myeloid leukemia undergoing various types of allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation: an analysis of 7812 patients. Leuk Lymphoma. 2018;59:601–09.
Przepiorka D, Weisdorf D, Martin P, Klingemann HG, Beatty P, Hows J, et al. 1994 consensus conference on acute GVHD grading. Bone Marrow Transpl. 1995;15:825–8.
Sullivan KM, Agura E, Anasetti C, Appelbaum F, Badger C, Bearman S, et al. Chronic graft-versus-host disease and other late complications of bone marrow transplantation. Semin Hematol. 1991;28:250–9.
Fine JP, Gray RJ. A proportional hazards model for the subdistribution of a competing risk. J Am Stat Assoc. 1999;94:496–509.
Holtan SG, DeFor TE, Lazaryan A, Bejanyan N, Arora M, Brunstein CG, et al. Composite end point of graft-versus-host disease-free, relapse-free survival after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Blood. 2015;125:1333–8.
Mantel N, Byar DP. Evaluation of response-time data involving transient states: an illustration using heart-transplant data. Am Stat Assoc. 1974;69:81–6.
Horowitz MM, Gale RP, Sondel PM, Goldman JM, Kersey J, Kolb HJ, et al. Graft-versus-leukemia reactions after bone marrow transplantation. Blood. 1990;75:555–62.
Weisdorf D, Zhang MJ, Arora M, Horowitz MM, Rizzo JD, Eapen M. Graft-versus-host disease induced graft-versus-leukemia effect: greater impact on relapse and disease-free survival after reduced intensity conditioning. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl. 2012;18:1727–33.
Baron F, Labopin M, Peniket A, Jindra P, Afanasyev B, Sanz MA, et al. Reduced-intensity conditioning with fludarabine and busulfan versus fludarabine and melphalan for patients with acute myeloid leukemia: a report from the Acute Leukemia Working Party of the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Cancer. 2015;121:1048–55.
Acknowledgements
We thank Yoshihiro Inamoto of the National Cancer Center Hospital for providing statistical input. This work was supported in part by a grant from the Practical Research Project for Allergic Diseases and Immunology (Research Technology of Medical Transplantation) from the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (AMED), grant number: 18ek0510023h0002, and a grant from the Aichi Cancer Research Foundation, grant number: 2019-8.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yanada, M., Fukuda, T., Tanaka, M. et al. Long-term results of reduced-intensity conditioning allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for older patients with acute myeloid leukemia: a retrospective analysis of 10-year follow-up data. Bone Marrow Transplant 55, 2008–2016 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41409-020-0868-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41409-020-0868-7
This article is cited by
-
Age and allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation outcomes in acute myeloid leukemia
International Journal of Hematology (2023)
-
Pitfalls and Successes in Trials in Older Transplant Patients with Hematologic Malignancies
Current Oncology Reports (2022)
-
Predicting non-relapse mortality following allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation during first remission of acute myeloid leukemia
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2021)