Abstract
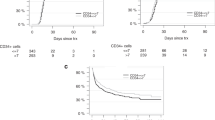
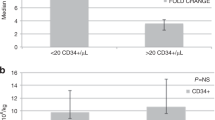
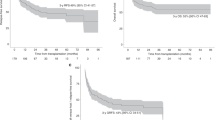
We report the long-term follow up of 49 patients (pts) enrolled on plerixafor compassionate use protocol. Thirty-seven pts (76%) had failed one previous mobilization attempt, while 12 (24%) had failed two or more previous attempts. Using the combination of plerixafor and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor, we collected⩾2.5 × 106 CD34+cells/kg in 33 pts (67%). Forty-three of the 49 pts proceeded to an auto-SCT (ASCT). The median days to WBC and platelet engraftment were 11 (range, 9–13 days) and 16 (range, 11–77 days) days post ASCT, respectively. The median WBC count, Hb and platelet counts 1 year after ASCT were 4.7 × 109/L, 12.2 g/dL and 109 × 109/L, respectively. With median follow up of 42 months (range <1–54 months), 21 pts had evidence of disease progression. Five pts developed myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS)/AML at median of 29 months post ASCT. The cumulative incidence of MDS/AML at 42 months was 17% (95% confidence interval, 6 to 32%). Development of secondary MDS/AML in pts proceeding to ASCT after plerixafor mobilization needs to be studied further in a larger cohort.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Attal M, Harousseau JL, Facon T, Guilhot F, Doyen C, Fuzibet JG et al. Single versus double autologous stem-cell transplantation for multiple myeloma. N Engl J Med 2003; 349: 2495–2502.
Philip T, Chauvin F, Armitage J, Bron D, Hagenbeek A, Biron P et al. Parma international protocol: pilot study of DHAP followed by involved-field radiotherapy and BEAC with autologous bone marrow transplantation. Blood 1991; 77: 1587–1592.
Allan DS, Keeney M, Howson-Jan K, Popma J, Weir K, Bhatia M et al. Number of viable CD34(+) cells reinfused predicts engraftment in autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 2002; 29: 967–972.
Bensinger W, DiPersio JF, McCarty JM . Improving stem cell mobilization strategies: future directions. Bone Marrow Transplant 2009; 43: 181–195.
Villalon L, Odriozola J, Larana JG, Zamora C, Perez de Oteyza J, Jodra MH et al. Autologous peripheral blood progenitor cell transplantation with <2 × 10(6) CD34(+)/kg: an analysis of variables concerning mobilisation and engraftment. Hematol J 2000; 1: 374–381.
De Clercq E . Inhibition of HIV infection by bicyclams, highly potent and specific CXCR4 antagonists. Mol Pharmacol 2000; 57: 833–839.
Hendrix CW, Flexner C, MacFarland RT, Giandomenico C, Fuchs EJ, Redpath E et al. Pharmacokinetics and safety of AMD-3100, a novel antagonist of the CXCR-4 chemokine receptor, in human volunteers. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2000; 44: 1667–1673.
Liles WC, Rodger E, Broxmeyer HE, Dehner C, Badel K, Calandra G et al. Augmented mobilization and collection of CD34+ hematopoietic cells from normal human volunteers stimulated with granulocyte-colony-stimulating factor by single-dose administration of AMD3100, a CXCR4 antagonist. Transfusion 2005; 45: 295–300.
Devine SM, Flomenberg N, Vesole DH, Liesveld J, Weisdorf D, Badel K et al. Rapid mobilization of CD34+ cells following administration of the CXCR4 antagonist AMD3100 to patients with multiple myeloma and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 2004; 22: 1095–1102.
Hubel K, Fresen MM, Salwender H, Basara N, Beier R, Theurich S et al. Plerixafor with and without chemotherapy in poor mobilizers: results from the German compassionate use program. Bone Marrow Transplant 2011; 46: 1045–1052.
Duarte RF, Shaw BE, Marin P, Kottaridis P, Ortiz M, Morante C et al. Plerixafor plus granulocyte CSF can mobilize hematopoietic stem cells from multiple myeloma and lymphoma patients failing previous mobilization attempts: EU compassionate use data. Bone Marrow Transplant 2011; 46: 52–58.
Calandra G, McCarty J, McGuirk J, Tricot G, Crocker SA, Badel K et al. AMD3100 plus G-CSF can successfully mobilize CD34+ cells from non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma, Hodgkin’s disease and multiple myeloma patients previously failing mobilization with chemotherapy and/or cytokine treatment: compassionate use data. Bone Marrow Transplant 2008; 41: 331–338.
Basak GW, Knopinska-Posluszny W, Matuszak M, Kisiel E, Hawrylecka D, Szmigielska-Kaplon A et al. Hematopoietic stem cell mobilization with the reversible CXCR4 receptor inhibitor plerixafor (AMD3100)-Polish compassionate use experience. Ann Hematol 2011; 90: 557–568.
Darrington DL, Vose JM, Anderson JR, Bierman PJ, Bishop MR, Chan WC et al. Incidence and characterization of secondary myelodysplastic syndrome and acute myelogenous leukemia following high-dose chemoradiotherapy and autologous stem-cell transplantation for lymphoid malignancies. J Clin Oncol 1994; 12: 2527–2534.
Stone RM, Neuberg D, Soiffer R, Takvorian T, Whelan M, Rabinowe SN et al. Myelodysplastic syndrome as a late complication following autologous bone marrow transplantation for non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 1994; 12: 2535–2542.
Miller JS, Arthur DC, Litz CE, Neglia JP, Miller WJ, Weisdorf DJ . Myelodysplastic syndrome after autologous bone marrow transplantation: an additional late complication of curative cancer therapy. Blood 1994; 83: 3780–3786.
Traweek ST, Slovak ML, Nademanee AP, Brynes RK, Niland JC, Forman SJ . Clonal karyotypic hematopoietic cell abnormalities occurring after autologous bone marrow transplantation for Hodgkin’s disease and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Blood 1994; 84: 957–963.
Friedberg JW, Neuberg D, Stone RM, Alyea E, Jallow H, LaCasce A et al. Outcome in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome after autologous bone marrow transplantation for non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 1999; 17: 3128–3135.
Milligan DW, Ruiz De Elvira MC, Kolb HJ, Goldstone AH, Meloni G, Rohatiner AZ et al. Secondary leukaemia and myelodysplasia after autografting for lymphoma: results from the EBMT. EBMT lymphoma and late effects working parties. European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Br J Haematol 1999; 106: 1020–1026.
Krishnan A, Bhatia S, Slovak ML, Arber DA, Niland JC, Nademanee A et al. Predictors of therapy-related leukemia and myelodysplasia following autologous transplantation for lymphoma: an assessment of risk factors. Blood 2000; 95: 1588–1593.
Micallef IN, Lillington DM, Apostolidis J, Amess JA, Neat M, Matthews J et al. Therapy-related myelodysplasia and secondary acute myelogenous leukemia after high-dose therapy with autologous hematopoietic progenitor-cell support for lymphoid malignancies. J Clin Oncol 2000; 18: 947–955.
Traweek ST, Slovak ML, Nademanee AP, Brynes RK, Niland JC, Forman SJ . Myelodysplasia and acute myeloid leukemia occurring after autologous bone marrow transplantation for lymphoma. Leuk Lymphoma 1996; 20: 365–372.
Armitage JO, Carbone PP, Connors JM, Levine A, Bennett JM, Kroll S . Treatment-related myelodysplasia and acute leukemia in non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma patients. J Clin Oncol 2003; 21: 897–906.
Li L, Li M, Sun C, Francisco L, Chakraborty S, Sabado M et al. Altered hematopoietic cell gene expression precedes development of therapy-related myelodysplasia/acute myeloid leukemia and identifies patients at risk. Cancer Cell 2011; 20: 591–605.
Chakraborty S, Sun CL, Francisco L, Sabado M, Li L, Chang KL et al. Accelerated telomere shortening precedes development of therapy-related myelodysplasia or acute myelogenous leukemia after autologous transplantation for lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 2009; 27: 791–798.
Acknowledgements
The study sponsor initially was AnorMED Inc. Vancouver, BC and subsequently Genzyme Corporation, Cambridge, MA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
MHA is on speaker bureau and received research funding from Millennium Pharmaceuticals and ZA received research funding from Genzyme Corporation. All other authors have no relevant or competing conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deol, A., Abrams, J., Masood, A. et al. Long-term follow up of patients proceeding to transplant using plerixafor mobilized stem cells and incidence of secondary myelodysplastic syndrome/AML. Bone Marrow Transplant 48, 1112–1116 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2013.10
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2013.10
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Platelet-derived circulating soluble P-selectin is sufficient to induce hematopoietic stem cell mobilization
Stem Cell Research & Therapy (2023)
-
Hematopoietic progenitor cell collection after autologous transplant for multiple myeloma: low platelet count predicts for poor collection and sole use of resulting graft enhances risk of myelodysplasia
Leukemia (2014)