Abstract
Despite widespread resistance to many important antibiotics, the factors that govern the emergence and prevalence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria are still unclear. When exposed to antibiotic gradients in soft agar plates measuring as little as 1.25 × 11 cm we found that Escherichia coli rapidly became resistant to representatives from every class of antibiotics active against Gram-negative bacteria. Evolution kinetics were independent of the frequency of spontaneous mutations that confer antibiotic resistance or antibiotic dose-response curves, and were only loosely correlated to maximal antibiotic concentrations. Instead, rapid evolution required unrealized mutations that could markedly decrease antibiotic susceptibility. When bacteria could not evolve through these “high-impact” mutations, populations frequently bottlenecked, reducing the number of cells from which mutants could arise and prolonging evolution times. This effect was independent of the antibiotic’s mechanism of action, and may affect the evolution of antibiotic resistance in clinical settings.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Antibiotic resistance is one of the greatest threats to modern medicine. Antibiotic-resistant organisms are thought to cause over 2,000,000 infections and 23,000 deaths in the United States each year1. Historically, preclinical assessment of new antibiotics has focused on measuring the rate with which resistance-conferring mutations occur in vitro2. Compounds with low or non-existent spontaneous resistance mutation rates are considered insensitive to the evolution of resistance in vivo, to the extent that some may theoretically be “evolution-proof”3,4. Unfortunately, clinical outcomes are less encouraging. The rate of spontaneous resistance development for clinical antibiotics span from 10−5 to 10−11 resistant mutations per cell per generation, and aren’t linked to the prevalence of resistance2. Rapid evolution of resistance during therapy also isn’t correlated to spontaneous resistance mutation rates; the leucyl-tRNA synthetase inhibitor GSK2251052/AN3365 recently failed a phase II clinical trial after rapid evolution of drug resistance in vivo, despite a mutation rate of 1.4 × 10−7 5,6.
The recent development of laboratory evolution chambers has enabled directed evolution of bacteria without labour-intensive sub-culturing, allowing researchers to map the genotypic pathways to antibiotic resistance following growth in etched silicon wafers, moribodostats, and MEGA plates7,8,9. The latter has also revealed exciting evolution dynamics: bacteria growing in desk-sized MEGA plates encounter wedges of geometrically-increasing antibiotic concentrations up to 20,000x the initial MIC. In this environment, resistant mutants leave behind their susceptible brethren, providing an excellent example of how competition for nutrients can drive the evolution of antibiotic resistance9.
Unfortunately, operating these devices requires a combination of specialized expertise and custom-built equipment, limiting their throughput and general utility. To make the evolution of bacteria in vitro more accessible we have designed a compact system based on Soft Agar Gradient Evolution (SAGE). SAGE plates are built from standard petri dishes or similar labware, and can be run in high-throughput without ongoing operator involvement. We validated this system by generating mutants of Escherichia coli (E. coli) individually resistant to twelve antibiotics or antibiotic mixtures, covering every major antibiotic class active against Gram-negative bacteria. We then investigated the kinetics of in vitro evolution, using the fine control over selective pressure provided by the SAGE system to determine the key factors governing the rate of antibiotic resistance. We found that successful strains often exhibited mutation rates distinct from their progenitors, and that mutation supply rates didn’t constrain evolution rates in even small bacterial populations. Instead, evolution rates appeared to be constrained by the limited availability of potential high-impact mutations, unrealized changes to the genome that could markedly increase antibiotic resistance.
Results
Evolution chamber design
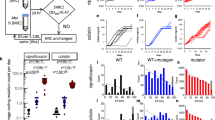
Hard agar gradient plates have been used since at least 1952 for antibiotic susceptibility testing10. They are created by sequentially pouring agar wedges of differing composition and allowing diffusion to equalize concentrations across the layers. By controlling the quantity of agar and the slope of the plate, it’s possible to create smooth gradients of arbitrary composition10,11. We found that these gradients are similarly stable at soft agar concentrations (0.2–0.75% agar w/v, Fig. 1), that allow bacteria to swim throughout the plate12. Bacteria inoculated into plates with antibiotic gradients grow until they encounter limiting concentrations of the antibiotic, at which point resistant mutants are selected for.
Evolution of antibiotic resistance. (A) Immediately after pouring the agar layers form two distinct wedges, as shown with the dye malachite green as a visual indicator. (B) After 16 hr of incubation the two layers have intermixed to create a smooth gradient of the dye. (C) A top-down schematic, showing the site of inoculation and chemical gradient. (D) Changes in minimum inhibitory concentration following antibiotic exposure, minimum of three biological replicates. Speed-selected E. coli MG1655 cells were passed through SAGE plates containing the listed antibiotics at approximately 5x the initial MIC value. Those which evolved resistance were then passed through a separate plate containing 25x the initial MIC. Individual tests are shown in Table S1. Lineages derived from the first passage were named e.g. Poly B 1, Poly B 2, etc., and lineages built by passing evolved strains through the 25x plates were correspondingly named Poly B 1-1, Poly B 1–2, etc. *Bacteria were exposed to plates containing 10x and 50x the initial MIC of ciprofloxacin, and 20x and 100x the initial MIC of rifampicin, respectively. ‡Resistance was greater than 256x the initial MIC. Cells were uniformly resistant to 8192 mg/L of streptomycin, and poor solubility limited testing at higher drug concentrations.
Movement through soft agar
To select for efficient chemotaxis, E. coli MG1655, BW25113 ΔmutL and BW25113 ΔmutS were passed three times through 0.25% agar plates, at which point they were able to traverse the plate within 20 hours of incubation at 37 °C. Adding a thin layer of mineral oil both reduced syneresis and decreased the experiment times to approximately 4 hr (Figs S1–3). Bacteria on oil-containing plates had lower densities, with growth restricted to the upper millimetre of the gel (Fig. S3). Increasing the strength of the agar decreased bacterial movement in accordance with previous work on the movement of E. coli in soft agar12, while decreasing the agar load led to gels that were too fragile to handle efficiently.
Using the antibiotic ciprofloxacin at 75 μg/L (~5x the initial bacterial minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC)), we then screened for the evolution of antibiotic resistance in SAGE plates. Circular petri dishes, square petri dishes, machined polycarbonate plates of varying widths, and rectangular 4-well nunclon-treated plates all gave similar results (Fig. S2), with resistant cells emerging after 24 hr of incubation at 37 °C. Due to the similarities in outcomes all further evolution studies were performed with 4-well nunclon-treated plates.
Time-lapse microscopy revealed that E. coli moved smoothly through the agar medium (Fig. S4), propagating in a wave of high density cells9,12. Entering agar free of other strains, mutants were able to quickly establish a buffer of discarded cells, blocking competition from faster growing but more antibiotic-susceptible cells. This is similar to what was observed around the step gradients of MEGA plates9, and greatly reduced the impact of loss-of-fitness mutations, provided that these mutations also reduce antibiotic susceptibility.
Evolution of antibiotic resistance
When challenged with a variety of antibiotics at a minimum of 5x the MIC, antibiotic resistance emerged in the three E. coli strains under investigation: speed-selected variants of E. coli MG1655 and two strains with elevated mutation rates due to defects in their mismatch repair systems; E. coli BW25113 ΔmutS and ΔmutL13. The magnitude of resistance varied by antibiotic, from 4x to 512x the initial MIC (Fig. 1D, Tables S1–3. Lower levels of resistance could in some cases be further increased by exposing mutants to a second SAGE plate containing 25x the original MIC.
Resistance evolved against every antibiotic tested as well as co-trimoxazole, a 1:19 mixture of trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole. This included representatives from every major class of antibiotics, as well as antibiotics that don’t readily evolve resistance in other in vitro systems. E.g. resistance to both doxycycline and chloramphenicol increased 32-fold following passage through their respective SAGE plates, versus a 10-fold increase in doxycycline resistance after twenty-five days of growth in a morbidostat (compared to a 870-fold increase in chloramphenicol resistance over the same time period)7. Similarly, the ease with which we developed resistance to drugs like ampicillin, doripenem, and polymyxin B is at odds with antibiotic resistance in the clinic, which often takes years to gain prevalence in bacterial pathogens14. Clinical resistance is also often linked to the transfer of plasmid-encoded inactivating proteins, which were absent in this study15. For example, resistance to beta-lactams in E. coli is largely due to the production of beta-lactamases, but we were able to readily obtain mutants resistant to ampicillin and doripenem despite the fact that E. coli MG1655 lacks an inducible beta-lactamase (though a copy of ampC is expressed at low levels)15,16,17.
Both MG1655 and the mutator strains developed resistance at similar levels (Fig. 1D, Tables S1–3). Counter to a theoretical model comparing evolution under uniform and increasing drug concentrations18, the bacterial strains rapidly evolved resistance to both ciprofloxacin and streptomycin, despite the different fitness effects of their resistance-conferring mutations. This may be because the strong founder effect of the system limits competition between naïve and resistant strains, as detailed above.
Genetic analysis
Amplification and sequencing of known proto-resistance genes identified several previously reported mutations in strains resistant to streptomycin, ciprofloxacin and trimethoprim (Tables S4 and S5). In particular, all four streptomycin-resistant lineages contained a K42R mutation in RpsL, which has been previously reported to confer near-immunity to streptomycin19,20. To evaluate broader genetic alterations we sequenced the genome of the progenitor strain of E. coli MG1655 and lineages resistant to ampicillin, gentamicin, or polymyxin B (Tables 1 and S6). The ancestral strain was found to have 78 mutations distinct from that of the previously published genome for E. coli MG165521. Some of these were likely acquired prior to this work, but there was an interesting V42A mutation in LrhA, a transcriptional repressor of bacterial motility. This mutation has not been previously reported, but mutants lacking lrhA show enhanced chemotaxis22. It’s possible that the chemotaxis screen conducted at the start of this work selected for strains with deficient or altered LrhA function.
Correcting for mutations in the ancestral strain, we found between 29 and 178 single nucleotide polymorphisms in the evolved strains (Table 1; a full list of mutations can be found in Table S6). In general, resistance appeared to be conferred not by any single genetic change but rather by the additive effects of a small series of mutations. For example, both ampicillin-resistant mutants contained a V545I mutation in penicillin-binding protein 3, FtsI. This mutation is linked to a roughly 3-fold increase in beta-lactam resistance in Salmonella spp.23, but the MIC of ampicillin rose 64-fold following passage through SAGE plates. The further increase in MIC appears to be related to missense mutations in the AcrAB efflux pump and its regulators, AcrR and MarR. Mutations in AcrR and MarR have been previously linked to a 4-fold increase in ampicillin resistance, by increasing expression of AcrAB and thereby reducing drug uptake24. Similarly, while the polymyxin B-resistant lineages contained a number of mutations in proteins involved in LPS biosynthesis or modification, they also contained mutations not previously linked to polymyxin B resistance, including in MalF, YfiM, and HofM. These proteins are found in the cell envelope, and may be involved in movement of polymyxin B across the membrane. Gentamicin and polymyxin B both traverse the outer membrane through self-promoted uptake25 and gentamicin-resistant lineages shared mutations in MalF and HofM (Table 1). Strains of E. coli deficient in malF and hofM were acquired from the Keio collection, but showed no appreciable difference in their MIC values to polymyxin B. The change in MIC conferred by these mutations may be lower than our limit of detection (one doubling of antibiotic concentration).
Mutation rate and population size
While no mutations in mismatch repair were observed during whole genome sequencing, we were concerned that passage through SAGE plates might select for mutators: strains with constitutively high mutation rates. We therefore determined the mutation rate of several strains before and after passage through SAGE plates, using the frequency of spontaneous resistance to rifampicin as a proxy measurement (Table 2)26,27. Mutation rates for all three progenitor strains (MG1655, BW25113 ΔmutL and BW25113 ΔmutS) were altered during the speed selection process, elevating the mutation rate of MG1655 while reducing the mutation rates of BW25113 ΔmutL and BW25113 ΔmutS. Subsequent passage through SAGE plates containing polymyxin B or ampicillin further altered the frequency of spontaneous resistance to rifampicin in MG1655, leading to lineages with rates both above (MG1655 Poly B 1 and 2) and below (MG1655 Poly B 1-1 and 1–2) that of the speed selected progenitor.
To gain a clearer picture of the mutation supply rate, we estimated the population size in SAGE plates. Representative samples from the growing front and stationary lawn of antibiotic-free SAGE plates were excised, and the cell counts in each sample were determined via qPCR using universal 16 S primers and a dilution standard of genomic E. coli DNA. qPCR is often used to measure populations of environmental bacteria28 and was favoured here as the bacterial cells of interest were embedded within an agar matrix. Relating our results back to the width of the excisions (~0.75 cm) and depth of the plate (0.45 cm), we found that a growing front contains approximately 1.31 × 107 cells/cm (s = 1.0 × 106), and that the density of cells behind this front is approximately 5.98 × 107 cells/cm2 (s = 3.2 × 107). Only cells in the front are under selection, and so the maximal population under selection is 3.93 × 107 cells (s = 3.0 × 106). This value is likely to be an overestimate, both due to the likely presence of a small number of dead and dormant cells, and because during antibiotic selection the front often fragments into distinct lineages, creating a number of smaller sub-populations (see Fig. 3; below).
Factors governing the evolution of antibiotic resistance
Maximal antibiotic concentration and slope
The time required for bacteria to evolve antibiotic resistance was consistent across replicate experiments for each antibiotic investigated, but varied between drugs. To determine the factors that governed the evolution of resistance we began to vary the slope and concentration of antibiotic that bacteria were exposed to.
Increasing the maximal concentration of streptomycin in the plates from 5x MIC to 40x MIC and 320x MIC decreased growth across the plate during the first two days of incubation, but had no statistically significant effect on growth at 72 hours. (Fig. 2A). Other antibiotics showed a similar pattern, though with ciprofloxacin increasing the maximal drug concentration from 75x MIC to 125x MIC actually accelerated growth. This may be due to the mutagenic effect of subinhibitory ciprofloxacin concentrations, which could potentially increase the effective mutant supply rate29. Of the antibiotics tested, only doxycycline showed a statistically significant difference in growth at 72 hr (10x MIC vs 50x MIC, s = 0.04, two-tailed, unequal variance Student’s t-test).
Passage through SAGE plates as a function of (A) antibiotic concentration and (B) slope. Averages of three biological replicates are shown. Antibiotic concentrations are given as the maximal concentration in the plate, as a function of MIC. The slope in (A) was 8 mm. (B) The likelihood that the observed differences in movement were due to chance was calculated via a two-tailed unequal variance Student’s T test.*P value < 0.05, **P value < 0.01, ***P value < 0001, ****P value < 0.00001.
Increasing the slope of the antibiotic gradients from 8 mm to 12.5 mm also gave mixed results (Fig. 2B). No significant difference in movement rate was observed with plates containing trimethoprim, but differences of varying magnitude were observed in SAGE plates laced with ampicillin, doxycycline, and polymyxin B. The effect was pronounced with the latter two antibiotics at 25x the initial MIC, with much slower movement across the 13 mm plates.
Antibiotic dose-response
In SAGE plates selective pressure is restricted to a narrow, high-density band of growing cells (Fig. S4; see above). Varying the maximal antibiotic concentration or slope may reduce the width of this band, constricting the population under selection and causing the prolonged experiment times we observed30. As changing the antibiotic concentration could also alter the mutations required for resistance we investigated the correlation between evolution time and band width through the antibiotic dose-response curve31. Compounds with steep dose-response curves will rapidly lower bacterial growth rates as the concentration of drug increases, reducing the width of the growing band. The antibiotic dose-response curve is also closely linked to the mutant selective window in other evolution systems, and is thought to contribute to the slow evolution rate of resistance against antimicrobial peptides like polymyxin B30,32.
However, we found no correlation between the dose-response curves of antibiotics and evolution rates (Table 3). Populations of fast-swimming E. coli MG1655 exposed to both doxycycline and polymyxin B required more time to traverse SAGE plates than populations exposed to ciprofloxacin or trimethoprim, though doxycycline had the shallowest measured dose-response curve and polymyxin B the steepest.
The impact of resistance-conferring mutations determines evolution rates
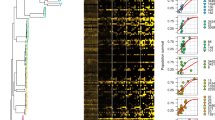
At elevated antibiotic concentrations the dynamics of growth across SAGE plates changed. While bacteria still began by growing in a band of high-density cells, movement at growth-limiting concentrations of antibiotic was slow enough that individual mutation events were visible (Figs 3 and S4). Mutants first appeared as pinpricks of high density cells, growing over time into cones as cells radiated out from their point of origin. In trimethoprim plates these cones quickly coalesced into new bands of high-density cells, which moved across the plate until the concentration of antibiotic was again growth-limiting (Fig. S4).
Visual observation of resistance to doxycycline. SAGE plates were incubated at 37 °C for seven days. Shown here is one representative lane, containing up to 25x the initial MIC of doxycycline at a slope of 12.5 mm. Nodules of resistant cells observed on day 2 are marked by arrows. With high concentrations of doxycycline, many of these mutations conferred only a small increase in MIC, leading to small populations of moderately resistant bacteria. Large bacterial populations did not reform until day 5.
Mutations were also observed in doxycycline plates, but the change in MIC provided by these mutations was much smaller. As a result, the majority of mutants didn’t form large cones, but instead stopped growing near the point of mutation, leaving behind small nodules of high-density cells (Fig. 3, arrows). Over several days the bacteria in these nodules mutated further, increasing their resistance and allowing further movement across the plate. Increasing the plate’s slope significantly compressed the nodules, reducing the population that could give rise to highly-resistant mutants. This in turn increased the amount of time required for doxycycline resistance to evolve.
Thus, the rate of evolution in SAGE plates is set by the change in antibiotic susceptibility conferred by unrealized mutations. Latent “high-impact” mutations allow strains to re-establish large populations following antibiotic challenge, ensuring that if the concentration of antibiotic once again becomes growth limiting there is a large population from which further mutants can arise. When resistance is conferred by low-impact mutations, the bacteria become trapped in population bottlenecks, reducing the likelihood of further mutations.
With this new framework, we can explain the rapid evolution of bacteria exposed to high levels of ciprofloxacin, trimethoprim, and streptomycin. Resistance to each of these antibiotics is known to occur from a small number of high-impact mutations19,33,34, several of which were observed in strains following passage through SAGE plates (Table S5). In principle, any antibiotic whose activity can be sharply curtailed by a small number of high-impact mutations will be quickly rendered ineffective by SAGE, regardless of the spontaneous resistance mutation rate or maximal antibiotic concentration.
Population mutation rates appear to vary within SAGE plates
The population bottlenecks that antibiotics create within SAGE plates may be partially alleviated by transiently increasing the mutation supply rate by rapid cell turnover35. Antibiotic stress is also known to trigger transiently elevated mutation rates through the SOS response, the stringent response, and the production of reactive oxygen species36,37,38. However, our work suggests that in SAGE plates these bacteria may also improve their mutation supply rate through the transient evolution of strains with high background mutation rates.
High mutation rates are known to help populations more easily develop antibiotic resistance37, and mutator strains are more prevalent in populations of bacterial pathogens39,40. However, we found that mutators were uncommon following exposure of speed selected E. coli MG1655 to gradients of polymyxin B, and that simple passage of E. coli BW25114 ΔmutS through antibiotic-free agar was sufficient to drop the observed mutation rate 14-fold, bringing it close to values recorded for the other strains investigated (Table 2, see above). High mutation rates can reduce fitness in the absence of stress40,41 and we hypothesize that this is leading to counter-selection later in the plate, when the bulk of the population is antibiotic resistant.
Similar behaviour has been recently observed in E. coli populations exposed to ethanol stress, where population mutation rates frequently rose and fell in response to increasing ethanol concentrations42. If this process is occurring in the SAGE system it could explain why we observed relatively small populations of both wildtype progenitor strains and progenitors with mutator phenotypes rapidly developing resistance to antibiotics with low spontaneous resistance mutation rates.
Other environments
Extending these results to bacterial evolution in other systems, access to high-impact mutations may broadly constrain the in vitro evolution of antibiotic resistance. Resistant mutants are often less fit, and in liquid environments like that of morbidostats don’t form a significant fraction of the population until the antibiotic significantly inhibits susceptible strains43. When bacteria evolve resistance through a series of low-impact mutations these in vitro systems may be unable to distinguish between the susceptibility of naïve and resistant strains. This may be the case with doxycycline resistance, which generally doesn’t exceed 10x the initial MIC following either serial passage through liquid media or growth in a morbidostat7,44. The low-level mutants we observed in SAGE plates may occur in these systems, but the concentration of doxycycline needed to inhibit the growth of susceptible strains will likely inhibit the mutants as well, preventing them from forming the majority of the population or evolving elevated levels of resistance.
Discussion
Using antibiotic gradients in soft agar we evolved mutants of E. coli resistant to representatives of every major class of antibiotic active against Gram-negative bacteria. Our findings show that in soft agar gradients evolution kinetics are constrained by the potential for high-impact mutations. When bacteria develop resistance through high-impact mutations, as with streptomycin resistance, bacteria quickly recover from population bottlenecks following selection, easing passage through future selective barriers. In contrast, factors that have been previously linked to the rate of resistance development, such as the maximal antibiotic concentration, spontaneous resistance mutation frequency, and antibiotic dose-response/mutant selection window had little influence on evolutionary success. Their limited impact in the SAGE plates appears to be in part due to the transient evolution of strains with elevated mutation rates, which increases the mutation supply rate and allows for the generation of resistant mutants from even small bacterial populations. In the absence of antibiotic stress these hypermutators appear to be rapidly replaced by strains with lower mutation rates.
Natural environments are unlikely to contain semi-solid agar gels, but will likely contain antibiotic gradients, potentially allowing for evolutionary dynamics similar to what we have observed. In particular, the human body readily creates drug gradients during both antibiotic therapy and chemotherapy, due to limited penetration into various tissues45,46,47. If these gradients accelerate the evolution of resistance in vivo, this likely explains why our current methods of evaluating potential new antibiotics are poorly correlated to clinical outcomes2. To reduce the emergence of resistance, antibiotic candidates should instead be evaluated by their potential to be nullified by a small number high-impact mutation. Those which lack such convenient resistance pathways will be less susceptible to the evolution of resistance.
Experimental Procedures
Soft agar gradient evolution plates
Sterile 4-well nunclon treated culture dishes were purchased from Thermo Scientific (cat. 167063), and used for the majority of evolution experiments. The hydrophilic surface treatment was not critical for SAGE experiments, but led to more resilient gels due to increased interactions between gel and plate.
Strains
E. coli MG1655 was a generous gift from Éric Déziel, INRS, Canada. E. coli BW25113 ∆mutS and ∆mutL were purchased from the Coli Genetic Stock Center (CGSC) and are part of the Keio Collection13.
Soft agar gradient evolution experiments
Molten 0.25% cation-adjusted Mueller-Hinton agar (MHA) was poured into 4-well plates that were raised on one side 3 mm, 8 mm, or 12.5 mm. Convenient lifters were made from P200 pipette tips, P1000 pipette tips, or a 1/2” role of labeling tape, respectively. Agar was added to half the height of the well on the lower side (0.45 cm), then left to gel at room temperature for 20 minutes. The supports were then removed and a second agar solution was added to an even depth. Plates were incubated overnight at room temperature to allow diffusion between the two layers.
To initiate experiments up to 50 µL of an overnight bacterial culture was inoculated in a line on the side of the well where the concentration of antibiotic was lowest. The wells were then covered with up to 5 mL of mineral oil to prevent desiccation and incubated at 37 °C.
After cells had grown throughout the plate mutants were harvested by sampling relevant regions of the plate via pipette. The soft agar extracted was then added to 5 mL of cation-adjusted Mueller-Hinton Broth (MHB) and incubated overnight at 37 °C. Cells were stored at −80 °C in glycerol or used for further experiments.
Minimum inhibitory concentration measurements
Populations extracted from SAGE plates were assessed following standard microdilution procedures48. In brief, 50 µL of cation-adjusted MHB containing the antibiotic of interest was mixed 1:1 with fresh media containing approximately 1 × 106 bacterial cells (verified against a freshly prepared McFarland 0.5 standard) to give a final cell density of 5 × 105 CFU. Plates were then incubated at 37 °C for 16–20 hours. Wells lacking bacteria were used as negative controls, and wells with bacteria and without antibiotic were used as positive controls. The MIC was defined as the minimum concentration of antibiotic that results in no visible growth to the naked eye.
Dose response curves and growth rate measurements
To measure the growth rate of E.coli in the presence of different concentrations of each antibiotic, bacteria were added to 96-well plates as described above. The plates were then sealed with parafilm and incubated at 30 °C in a Tecan Sunrise plate reader running Magellan V 7.1. Absorbance was measured at 595 nm every 30 seconds, with 15 seconds of shaking and two seconds of settle time prior to each measurement. Measurements were collected for 23 hours. The data was then exported to Excel. Measurements were zeroed and converted to their natural log. The steepest region of the growth curve was then determined, and a minimum of forty measurements were then fit to a linear curve. These dose response curves were then plotted against antibiotic concentration and fit to a Hill function via linear regression with the Excel Solver tool31,49:
where, g(c) is growth rate as a function of antibiotic concentration, c, g0 is the growth rate in the absence of antibiotic, and IC50 is the concentration of antibiotic where the growth rate was half g0, n is the hill co-efficient, and corresponds to how quickly growth decreases as the antibiotic concentration increases.
Mutation rates
To infer the mutation rate of evolved E. coli lineages we measured the frequency of spontaneous resistance to rifampicin26. In brief, each strain was grown in MHB media overnight. Cells were then diluted in fresh MHB and plated in triplicate onto either LB-agar or LB-agar with 100 µg/mL rifampicin. The plates were incubated for 16–20 hours at 37 °C, and the number of colonies on each was counted. The median frequency, f, of each strain was then calculated and used to determine the median mutation rate, μ, based on the formula:
where N is the total population, determined by counting cells grown on rifampicin-free agar26,50.
Whole genome sequencing
Strains of interest were grown overnight in MHB, then genomic DNA was extracted using the EZ-10 Bacterial Genomic DNA miniprep kit according to manufacturer’s specifications. Samples were sequenced by Genome Quebec on an Illumina HiSeq. 4000 PE100. Sequence data was then assembled with the A5-miseq pipeline software. Snippy was used to compare the genome assemblies to the reference genome of E. coli MG1655, U00096.3 (https://github.com/tseemann/snippy).
Population size calculations
SAGE plates free of antibiotic were inoculated with 50 μL of E. coli MG1655, then incubated at 37 °C for four hours. Agar blocks containing representative bands and bacterial lawns were then excised with a sterile spatula and heated at 98 °C for five minutes. Cells were mixed 1:10 with distilled, deionized water, heated at 98 °C for three more minutes, and then used as template for qPCR. In brief, 1 μL of template was mixed with 14.6 μL ddH2O, 4 μL 5X EvaGreen qPCR mix, 0.4 μL forward primer (0.1 μM, 16 S F27) and 0.4 μL reverse primer (0.1 μM, 16 S R1492)51. The thermal profile used was 15 min of polymerase activation at 95 °C followed by the PCR cycling stage with 40 cycles (95 °C for 45 sec, 55 °C for 30 sec, 72 °C for 1 min) and ending with a melting curve (95 °C for 15 sec, 55 °C for 15 sec, 95 °C for 15 sec). Results from a dilution series of genomic DNA were used to determine the cell copy numbers.
For cells extracted from the growing front, the reported number of cells was multiplied by 10 to account for the initial dilution, then standardized to the total volume of the excised gel band. This population was then divided by the width of the excised band (~0.75 cm) to give a cell count per cm of the growing front. Values corresponding to cells extracted from the lawn were multiplied by 10, divided 0.05 mL and multiplied by sqrt (1 cm3/0.45 cm) = 1.49 cm2 to adjust for the depth of the agar (0.45 cm). The total population of the growing front was estimated by multiplying the width of the lane (2.9 cm), the width of the growing front in the absence of antibiotic (0.3 cm) and the depth of the agar which contained cells (0.1 cm). Results are presented as the average of three independent replicates.
Data Availability
Full MIC testing results and whole-genome sequencing data are included in the supplementary information files.
References
Laxminarayan, R. et al. Antibiotic resistance-the need for global solutions. Lancet Infect. Dis. 13, 1057–1098 (2013).
Sommer, M. O. A., Munck, C., Toft-Kehler, R. V. & Andersson, D. I. Prediction of antibiotic resistance: time for a new preclinical paradigm? Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 15, 689–696 (2017).
Salipante, S. J. Determining the Limits of the Evolutionary Potential of an Antibiotic Resistance Gene. Mol. Biol. Evol. 20, 653–659 (2003).
Bell, G. & MacLean, C. The Search for ‘Evolution-Proof’ Antibiotics. Trends Microbiol., https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tim.2017.11.005 (2017).
O’Dwyer, K. et al. Bacterial Resistance to Leucyl-tRNA Synthetase Inhibitor GSK2251052 Develops during Treatment of Complicated Urinary Tract Infections. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 59, 289–298 (2015).
Monteferrante, C. G. et al. Evaluation of the characteristics of leucyl-tRNA synthetase (LeuRS) inhibitor AN3365 in combination with different antibiotic classes. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Eur. Soc. Clin. Microbiol., https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-016-2738-1 (2016).
Toprak, E. et al. Evolutionary paths to antibiotic resistance under dynamically sustained drug selection. Nat. Genet. 44, 101–105 (2011).
Zhang, Q. et al. Acceleration of Emergence of Bacterial Antibiotic Resistance in Connected Microenvironments. Science 333, 1764–1767 (2011).
Baym, M. et al. Spatiotemporal microbial evolution on antibiotic landscapes. Science 353, 1147–1151 (2016).
Szybalski, W. & Bryson, V. Genetic studies on microbial cross resistance to toxic agents I.: Cross Resistance of Escherichia coli to Fifteen Antibiotics1, 2. J. Bacteriol. 64, 489 (1952).
Curiale, M. S. & Levy, S. B. Two complementation groups mediate tetracycline resistance determined by Tn10. J. Bacteriol. 151, 209–215 (1982).
Croze, O. A., Ferguson, G. P., Cates, M. E. & Poon, W. C. K. Migration of Chemotactic Bacteria in Soft Agar: Role of Gel Concentration. Biophys. J. 101, 525–534 (2011).
Baba, T. et al. Construction of Escherichia coli K-12 in-frame, single-gene knockout mutants: the Keio collection. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2(2006), 0008 (2006).
McClure, N. S. & Day, T. A theoretical examination of the relative importance of evolution management and drug development for managing resistance. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 281, 20141861–20141861 (2014).
King, D. T., Sobhanifar, S. & Strynadka, N. C. J. One ring to rule them all: Current trends in combating bacterial resistance to the β-lactams: Structure-Based Approaches to Overcome β-Lactam Resistance. Protein Sci. 25, 787–803 (2016).
Jacoby, G. A. AmpC -Lactamases. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 22, 161–182 (2009).
Nordmann, P. & Poirel, L. The difficult-to-control spread of carbapenemase producers among Enterobacteriaceae worldwide. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 20, 821–830 (2014).
Greulich, P., Waclaw, B. & Allen, R. J. Mutational pathway determines whether drug gradients accelerate evolution of drug-resistant cells. Phys. Rev. Lett. 109, 088101 (2012).
Björkman, J., Samuelsson, P., Andersson, D. I. & Hughes, D. Novel ribosomal mutations affecting translational accuracy, antibiotic resistance and virulence of Salmonella typhimurium. Mol. Microbiol. 31, 53–58 (1999).
Sander, P. et al. Fitness Cost of Chromosomal Drug Resistance-Conferring Mutations. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 46, 1204–1211 (2002).
Blattner, F. R. et al. The complete genome sequence of Escherichia coli K-12. Science 277, 1453–1462 (1997).
Lehnen, D. et al. LrhA as a new transcriptional key regulator of flagella, motility and chemotaxis genes in Escherichia coli. Mol. Microbiol. 45, 521–532 (2002).
Sun, S., Selmer, M. & Andersson, D. I. Resistance to β-Lactam Antibiotics Conferred by Point Mutations in Penicillin-Binding Proteins PBP3, PBP4 and PBP6 in Salmonella enterica. PLOS One 9, e97202 (2014).
Okusu, H., Ma, D. & Nikaido, H. AcrAB efflux pump plays a major role in the antibiotic resistance phenotype of Escherichia coli multiple-antibiotic-resistance (Mar) mutants. J. Bacteriol. 178, 306–308 (1996).
Hancock, R. E. & Bell, A. Antibiotic uptake into gram-negative bacteria. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Eur. Soc. Clin. Microbiol. 7, 713–720 (1988).
Garibyan, L. Use of the rpoB gene to determine the specificity of base substitution mutations on the Escherichia coli chromosome. DNA Repair 2, 593–608 (2003).
Badran, A. H. & Liu, D. R. Development of potent in vivo mutagenesis plasmids with broad mutational spectra. Nat. Commun. 6, 8425 (2015).
Nadkarni, M. A., Martin, F. E., Jacques, N. A. & Hunter, N. Determination of bacterial load by real-time PCR using a broad-range (universal) probe and primers set. Microbiology 148, 257–266 (2002).
Song, L. Y. et al. Mutational Consequences of Ciprofloxacin in Escherichia coli. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 60, 6165–6172 (2016).
Hermsen, R., Deris, J. B. & Hwa, T. On the rapidity of antibiotic resistance evolution facilitated by a concentration gradient. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 109, 10775–10780 (2012).
Chevereau, G. et al. Quantifying the Determinants of Evolutionary Dynamics Leading to Drug Resistance. PLOS Biol. 13, e1002299 (2015).
Yu, G., Baeder, D. Y., Regoes, R. R. & Rolff, J. Predicting drug resistance evolution: insights from antimicrobial peptides and antibiotics. Proc. Biol. Sci. 285, (2018).
Eliopoulos, G. M. & Huovinen, P. Resistance to Trimethoprim-Sulfamethoxazole. Clin. Infect. Dis. 32, 1608–1614 (2001).
Baudry-Simner, P. J. et al. Mechanisms of reduced susceptibility to ciprofloxacin in Escherichia coli isolates from Canadian hospitals. Can. J. Infect. Dis. Med. Microbiol. 23, e60–e64 (2012).
Frenoy, A. & Bonhoeffer, S. Death and population dynamics affect mutation rate estimates and evolvability under stress in bacteria. PLOS Biol. 16, e2005056 (2018).
Laureti, L., Matic, I. & Gutierrez, A. Bacterial Responses and Genome Instability Induced by Subinhibitory Concentrations of Antibiotics. Antibiotics 2, 100–114 (2013).
Jolivet-Gougeon, A. et al. Bacterial hypermutation: clinical implications. J. Med. Microbiol. 60, 563–573 (2011).
Van Acker, H. & Coenye, T. The Role of Reactive Oxygen Species in Antibiotic-Mediated Killing of Bacteria. Trends Microbiol. 25, 456–466 (2017).
LeClerc, J. E., Li, B., Payne, W. L. & Cebula, T. A. High mutation frequencies among Escherichia coli and Salmonella pathogens. Science 274, 1208–1211 (1996).
Taddei, F. et al. Role of mutator alleles in adaptive evolution. Nature 387, 700 (1997).
Turrientes, M.-C. et al. Normal Mutation Rate Variants Arise in a Mutator (Mut S) Escherichia coli Population. PLoS ONE 8, e72963 (2013).
Swings, T. et al. Adaptive tuning of mutation rates allows fast response to lethal stress in Escherichia coli. eLife 6, e22939 (2017).
Spagnolo, F., Rinaldi, C., Sajorda, D. R. & Dykhuizen, D. E. Evolution of Resistance to Continuously Increasing Streptomycin Concentrations in Populations of Escherichia coli. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 60, 1336–1342 (2016).
Oz, T. et al. Strength of Selection Pressure Is an Important Parameter Contributing to the Complexity of Antibiotic Resistance Evolution. Mol. Biol. Evol. 31, 2387–2401 (2014).
Baquero, F. & Negri, M.-C. Challenges: Selective compartments for resistant microorganisms in antibiotic gradients. Bioessays 19, 731–736 (1997).
Fu, F., Nowak, M. A. & Bonhoeffer, S. Spatial Heterogeneity in Drug Concentrations Can Facilitate the Emergence of Resistance to Cancer Therapy. PLOS Comput. Biol. 11, e1004142 (2015).
Moreno-Gamez, S. et al. Imperfect drug penetration leads to spatial monotherapy and rapid evolution of multidrug resistance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 112, E2874–E2883 (2015).
Wiegand, I., Hilpert, K. & Hancock, R. E. W. Agar and broth dilution methods to determine the minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) of antimicrobial substances. Nat. Protoc. 3, 163–175 (2008).
Hall, B. G., Acar, H., Nandipati, A. & Barlow, M. Growth Rates Made Easy. Mol. Biol. Evol. 31, 232–238 (2014).
Drake, J. W. A constant rate of spontaneous mutation in DNA-based microbes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 88, 7160–7164 (1991).
Frank, J. A. et al. Critical Evaluation of Two Primers Commonly Used for Amplification of Bacterial 16S rRNA Genes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 74, 2461–2470 (2008).
Acknowledgements
We are indebted to L. Freeman and M. Whiteway for helpful discussions and A. Ramachandran for assistance with the qPCR experiments. Growth rates and qPCR studies were conducted with equipment from the Concordia University Centre for Structural and Functional Genomics. Genomes were assembled with the assistance of the Canadian Centre for Computational Genomics (C3G). C3G is a node of the Canadian Genomic Innovation Network and is supported by the Canadian Government through Genome Canada.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
M.H., N.G. and B.F. ran SAGE experiments. N.G. and B.F. performed MIC testing. M.H. completed mutation and growth rate measurements. B.F. conceived of and designed the experiments. All authors contributed to the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Ghaddar, N., Hashemidahaj, M. & Findlay, B.L. Access to high-impact mutations constrains the evolution of antibiotic resistance in soft agar. Sci Rep 8, 17023 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-34911-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-34911-9
Keywords
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.