Abstract
Argyle is the world’s largest source of natural diamonds, yet one of only a few economic deposits hosted in a Paleoproterozoic orogen. The geodynamic triggers responsible for its alkaline ultramafic volcanic host are unknown. Here we show, using U-Pb and (U-Th)/He geochronology of detrital apatite and detrital zircon, and U-Pb dating of hydrothermal titanite, that emplacement of the Argyle lamproite is bracketed between 1311 ± 9 Ma and 1257 ± 15 Ma (2σ), older than previously known. To form the Argyle lamproite diatreme complex, emplacement was likely driven by lithospheric extension related to the breakup of the supercontinent Nuna. Extension facilitated production of low-degree partial melts and their migration through transcrustal corridors in the Paleoproterozoic Halls Creek Orogen, a rheologically-weak rift zone adjacent to the Kimberley Craton. Diamondiferous diatreme emplacement during (super)continental breakup may be prevalent but hitherto under-recognized in rift zones at the edges of ancient continental blocks.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
The vast majority of primary economic diamond deposits are hosted in kimberlite diatremes located in Archean cratons1,2, with characteristically old and thick continental lithosphere thought to be necessary for sustained diamond growth3. However, the largest source of natural diamonds discovered to date, the Argyle mine in the Kimberley region of Western Australia, is one of only a few economic deposits found within a Paleoproterozoic orogen adjacent to cratonic regions underlain by Archean basement2,4. Moreover, Argyle is hosted in olivine lamproite, rather than kimberlite, and has yielded >90% of all pink diamonds discovered5. The discovery of Argyle in 1979 resulted in a paradigm shift that led to diamond exploration in non-Archean terranes6. Despite its importance, the geodynamic drivers responsible for the emplacement of such an unusual diamondiferous pipe complex remain unclear.
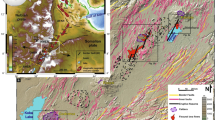
The Argyle (formally AK1) lamproite is situated in the Carr Boyd Basin, a small Meso- to Neoproterozoic intracontinental basin in the Paleoproterozoic to Paleozoic Halls Creek Orogen at the southeastern edge of the Kimberley Craton4. Argyle is situated in an intracontinental rift that formed as a result of various, discrete far-field tectonic drivers between c. 1910 and 1805 Ma, the most important of which are the c. 1870–1850 Ma Hooper and c. 1835–1805 Ma Halls Creek Orogenies7. Argyle comprises four merged, NNE-striking diatremes compartmentalised by numerous NNW-striking faults4, with the most diamond-rich diatreme (in excess of 20 carats per tonne8) towards the southern end of the deposit (Fig. 1B). Each diatreme comprises volcaniclastic olivine lamproite intruded by sparse narrow dikes of olivine lamproite. The predominant volcaniclastic lithologies are quartz-rich lapilli tuffs and coarse-grained ash tuffs (‘sandy tuff’), comprising olivine lamproite lapilli mixed with variable amounts of quartz grains and country rock fragments. These lithologies formed by phreatomagmatic eruptions of the lamproite magma through unconsolidated water-rich sands and silts of the Carr Boyd Group in a maar-diatreme complex4,9. The northernmost diatreme is infilled with olivine lamproite tuffs free of detrital quartz grains (‘non-sandy tuff’). The phreatomagmatic eruptions involving extensive interaction with water-saturated sediments were syn-eruptively accompanied by subsidence of the tephra, and by concomitant and pervasive hydrothermal alteration of the pipe4,10. Following emplacement, deformation of the Argyle pipe resulted in gentle tilting of the diatreme complex to the north4. Exhumation to its present depth likely occurred in the Early Cretaceous as inferred from apatite fission track analysis on samples proximal to Argyle11.
The age of emplacement of the Argyle lamproite has been estimated from whole-rock and altered phlogopite K-Ar and Rb-Sr dates, ranging from 1240 to 1110 Ma (see Supplementary Table 112,13,14). However, K-Ar and Rb-Sr systematics can easily be modified by alteration15, with previous workers recognising that the K contents of dated phlogopite in the main diatreme complex were “anomalously low” and indicative of partial chloritization12. The extensive alteration of K-bearing minerals means they are likely unsuitable as geochronometers for Argyle16. Although there is relatively fresh phlogopite in some of the lamproite dykes17, dating it with high-precision 40Ar/39Ar has proved challenging due to the presence of excess radiogenic Ar. Moreover, whilst the excess radiogenic Ar issue may be obviated with in situ Rb-Sr dating18,19, minor alteration of the phlogopite and uncertainty around whether the dykes are coeval with the diatreme still make dating these phlogopite grains problematic.
Here, we provide a combination of petrographic observations, U-Pb geochronology of titanite, and U-Pb and (U-Th)/He dating of zircon and apatite separated from a sample of high grade drill core of the Argyle lamproite to resolve the age of the Argyle deposit and provide an explanation for when and why Argyle formed.
Results
Petrography of the Argyle lamproite
A representative drill core sample was provided by Rio Tinto from the high-grade mineralised diatreme (AK1-Lh01), with two thin sections prepared from this material. AK1-Lh01 comprises ~45% lamproite clasts (chiefly chlorite and serpentine after original olivine and phlogopite), ~40% quartz clasts, ~10% calcite cement, and 4% late-stage titanite that rims combined quartz–lamproite clusters (Fig. 2, all vol. %; Supplementary Table 2 and Supplementary Fig. 1). Except for the largest clasts, quartz clasts are well rounded with no evidence of authigenic quartz overgrowths, indicative of a detrital origin with minimal diagenetic overprint. Titanite forms a quasi-connected network surrounding combined lamproite-detritus clasts (Fig. 2B). Titanite is anhedral and contains inclusions of the lamproite clasts (chlorite and serpentine), detrital matrix (quartz, zircon and apatite) and calcite cement (Fig. 2D). This petrographic evidence indicates that titanite post-dates emplacement of the lamproite and carbonate alteration (Fig. 2B–D). The titanite was likely formed by dissolving original perovskite from the lamproite with the addition of silica from the surrounding maar-derived meteoric waters17, implying that the titanite was a product of deuteric alteration and only very shortly post-dates lamproite emplacement, well within uncertainty of any radiometric technique. Trace rounded zircon and subangular apatite are also present within the detrital matrix. Although not present in thin section, diamonds were also found through disaggregation of the core sample (e.g., ~1 mm dodecahedral diamond fragment; Supplementary Fig. 2).
A Automated mineral analysis map of major and minor minerals. B Backscattered electron map of A but showing Ti Kα peak overlain in red, the vast majority of which corresponds to titanite. C Expanded view of B, showing late-stage titanite rimming a cluster of lamproite, detrital quartz and calcite. D Expanded view of C, showing inclusions of zircon, quartz and calcite within titanite. For additional petrographic images, see Supplementary Table 2 and Supplementary Fig. 1.
Age for the Argyle (AK1) lamproite diamond deposit
Three minerals—detrital zircon and detrital apatite, and hydrothermal titanite—were dated using U-Pb laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS) to provide a maximum depositional age (apatite, zircon) and a minimum age of hydrothermal alteration (titanite), which together bracket emplacement of the Argyle lamproite (see Supplementary Fig. 3 and Supplementary Data 1–2). Selected titanite were re-dated using U-Pb isotope dilution thermal ionisation mass spectrometry (ID-TIMS) to aid in improving the precision. Detrital zircon and apatite were also dated using (U-Th)/He to understand the low-temperature history at Argyle, and to test whether hydrothermal titanite formed after exhumation.
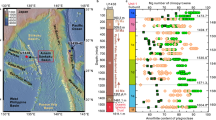
Detrital apatite yields a slightly overdispersed (p < 0.05) spread of 207Pb-corrected dates centred at c. 1900–1820 Ma (Fig. 3A, B). Coupled with the angular nature of the apatite grains (Supplementary Fig. 3), slight dispersion in the data can be explained by the apatite detritus originating from erosion of proximal rocks formed during the c. 1870–1850 Ma Hooper and c. 1835–1805 Ma Halls Creek orogenies, with a few older grains (Fig. 3A). As none of the apatite analyses is concordant, individual 207Pb-corrected dates are model ages, dependent on an assumed common-Pb composition and closed system behaviour. The youngest coherent group of detrital apatite 207Pb-corrected dates yields a weighted mean of 1828 ± 6 Ma (MSWD = 1.01, p = 0.40) that, whilst providing a maximum emplacement age of the Argyle lamproite, is significantly older than the Meso- to Neoproterozoic Carr Boyd Group in which Argyle is hosted. Importantly, the U-Pb system in these apatite grains was not thermally reset (i.e., heated above ~450 °C, which is the closure temperature to Pb in apatite20), as after the c. 1835–1805 Ma Halls Creek Orogeny there is no known local tectonothermal event of sufficient magnitude to cause open system behaviour.
A Detrital apatite concordia plot; inset shows the weighted mean of youngest grains. B Probability density plot of detrital zircon and apatite, including published zircon data from two proximal samples from elsewhere in the Carr Boyd Basin21,22. C Detrital zircon, with inset showing cathodoluminescence images of the two youngest grains. D Hydrothermal titanite concordia plot.
Detrital zircon analyses define a major peak at c. 1870 Ma, implying derivation from rocks formed during the c. 1870–1850 Ma Hooper Orogeny, as well as minor peaks at c. 2.5 Ga, 2.0 Ga, c. 1.8 Ga and c. 1.6 Ga (amongst even rarer age components; Fig. 3B, C). This age spectrum is similar to other detrital zircon age spectra from the Carr Boyd Group sedimentary rocks into which Argyle was emplaced, although the published data have a higher proportion of c. 1835–1805 Ma detritus derived from rocks crystallised during the Halls Creek Orogeny (Fig. 3B21,22). The most important subordinate detrital zircon ages are three analyses younger than 1360 Ma, with the youngest two of these yielding a 206Pb/238U weighted mean age of 1311 ± 9 Ma (MSWD = 1.02, p = 0.31; Fig. 3C), providing a robust maximum emplacement age for the Argyle lamproite (see Supplementary Fig. 4 for evaluation of data quality).
Titanite from Argyle is small (<50 µm, necessitating a small laser spot size of 30 µm), low in U (5–25 ppm) and rich in common Pb (38–78%), consistent with a hydrothermal origin23, but meaning that only low-precision dates can be obtained using LA-ICP-MS. Free-regression through all titanite data collected using LA-ICP-MS yields a robust but imprecise lower concordia intercept of 1268 ± 40 Ma (MSWD = 1.3, p = 0.09, n = 58, Fig. 3D). Ten selected grains were re-dated using ID-TIMS, which broadly show similar trends as LA-ICP-MS data but with excess scatter to the right of the discordia. Potential causes for this scatter include recent Pb-loss through alteration or ancient Pb-loss during a subsequent tectonothermal event. Using only the six analyses that broadly overlap with the LA-ICP-MS data yields a free-regressed lower concordia intercept of 1271 ± 40 Ma (MSWD = 0.75, p = 0.56, n = 6 of 10, Fig. 3D), very similar in both precision and accuracy due to the higher precision of individual analyses but a lower spread along discordia. Harnessing both the spread of the LA-ICP-MS data and the precision of the ID-TIMS data, we compute a combined free-regressed age of 1257 ± 15 Ma (MSWD = 1.2, p = 0.13, n = 64 of 68, Fig. 3D). Importantly, as titanite has a higher closure temperature to Pb (~650 °C24) than apatite (~450 °C20), this c. 1260 Ma age cannot reflect a discrete heating and cooling event, as detrital apatite would also be reset. Thus, the age of 1257 ± 15 Ma reflects the pervasive hydrothermal alteration of the combined lamproite–detritus clasts. Given that there is mild scatter on the ID-TIMS and that this may be present but masked by the higher uncertainties in the LA-ICP-MS, the age of 1257 ± 15 Ma records in a most conservative sense a minimum emplacement age for the Argyle diatreme complex.
If exhumation occurred prior to hydrothermal titanite formation, apatite and zircon (U-Th)/He (with closure temperatures to He of ~75 °C and ~180 °C, respectively25) could provide better age constraints on lamproite eruption. Seven of eight detrital apatite grains yielded a corrected (U-Th)/He weighted mean age of 121 ± 10 Ma (MSWD = 1.4, p = 0.21; Supplementary Fig. 5), which can be readily linked to Cretaceous exhumation of the Kimberley Craton11. Detrital zircon crystals yielded overdispersed (U-Th)/He dates ranging from c. 1150 to 185 Ma, which could relate to passage through the partial He retention zone. The oldest dates provide a minimum age for the lamproite (Supplementary Fig. 5), although this postdates hydrothermal titanite formation.
In summary, the best age constraints for emplacement of the Argyle lamproite are provided by a maximum depositional zircon age of 1311 ± 9 Ma and a minimum hydrothermal titanite alteration age of 1257 ± 15 Ma.
Discussion
At c. 1300 Ma, the supercontinent Nuna was on the cusp of breakup26. At the time, most plate tectonic reconstructions place Argyle at the periphery of the McArthur-Yanliao Gulf (Fig. 4), an intercontinental Mesoproterozoic basin between proto-Australia, North China, Siberia and Laurentia27,28,29,30,31,32 (and in some reconstructions also including India29,31 and/or South China28,29). Temporally-constrained paleomagnetic and geological evidence indicates that Nuna was together at c. 1320 but dispersed by c. 1220 Ma, with scarce high-quality paleomagnetic data in the intervening 100 Myr making it difficult to be more precise on the exact timing of breakup28.
A At 1330 Ma. B At 1300 Ma. C At 1270 Ma. The paleogeographic reconstruction is made using GPlates 2.3 open-source software (https://www.gplates.org/) with the full-plate model of Li et al.30. The potential extent of plume head that caused the Derim Derim-Galiwinku-Yanliao LIP is also shown, with its dimension elongated along rift zones28, 34.
At c. 1330–1295 Ma, dyke swarms and related volcanism emplaced around the periphery of the McArthur-Yanliao Gulf, covering part of the North China Craton (Yanliao rift zone, including the Yanliao sills and Datong dykes33) and the North Australian Craton (Derim Derim-Galiwinku dyke swarms34), which are collectively termed the Derim Derim-Galiwinku-Yanliao large igneous province (Fig. 434). Given the paucity of known c. 1310 Ma source rocks in the vicinity of the Kimberley Craton, it is likely that these rare, young zircon grains found in Argyle were derived from the eroded portions of the Derim Derim-Galiwinku-Yanliao large igneous province. Such an interpretation is consistent with plate reconstructions28, which would favour a sedimentary transport pathway from the centre of the McArthur-Yanliao Gulf towards a circum-Nuna ocean towards the northeast, draining past the Kimberley Craton and perhaps into the Halls Creek Orogen (Fig. 4).
Argyle is situated in the Halls Creek Orogen, a rheologically-weak rift zone with thinner lithosphere that is prone to reactivation7. Additional heat from the Derim Derim-Galiwinku-Yanliao large igneous province and/or mechanical extension from the breakup of Nuna could have reactivated mantle-to-crust pathways to facilitate rapid ascent of low-degree volatile-rich partial melts (e.g., lamproites) to the surface. The two mechanisms may also be intimately inter-related, with large igneous provinces commonly heralding continental breakup35 and thermal weakening lowering the extensional forces required to initiate continental breakup36,37. Although the precise timing of the onset of Nuna breakup is not yet known, paleomagnetic constraints indicate that the West–North Australian cratons, North China Craton and Laurentia were separated sometime between 1320 and 1220 Ma28, coincident with emplacement of the Argyle lamproite.
Lithospheric extension in, or adjacent to, Archean cratons during continental rifting has previously been recognized as a mechanism for emplacement of kimberlites, lamproites and other related volatile- and incompatible element-enriched ultramafic diatremes38,39,40,41,42. Examples include the East European Platform during Nuna breakup (c. 1250–1230 Ma43), the Kimberley Craton during attempted Rodinia breakup (c. 840–800 Ma44) and the Kaapvaal Craton during Gondwana/Pangea breakup (c. 200–120 Ma45,46), amongst many others. However, the role of (super)continental breakup has only recently begun to be significantly appreciated for kimberlite emplacement during periods of continental breakup2,38,42. In all breakup-related cases, diatreme emplacement appears to be contemporaneous with breakup, but with a peak production of volatile-rich ultramafic rocks lagging behind the breakup period41,42. The same applies to Argyle and Nuna breakup. Whilst Argyle appears to be coincident with the onset of Nuna breakup, together with temporally near-coincident magmatism at Helpmekaar in South Africa41 and kimberlites in the East European platform43, it is not until 1200–1100 Ma that diatreme emplacement peaked worldwide, coincident with accelerated plate velocities30. Thus, there appears to be a first-order control of continental extension and plate velocities on (diamondiferous) kimberlite and related volatile-rich ultramafic diatreme production41.
The global volatile-rich ultramafic diatreme record is undoubtedly affected by preservation bias, particularly for pre-Pangean diatremes, but it is second order to continental rifting processes. Continental amalgamation and associated post-orogenic relaxation/extension is known to be better at preserving the geological record47,48. Thus, one might expect that preservation would be higher at c. 1800–1600 Ma (Nuna assembly), 1100–900 Ma (Rodinia assembly), 650–500 Ma (Gondwana assembly) and 250–200 Ma (Pangea assembly)30. With the exception of Gondwana assembly, periods of continental breakup after supercontinent assembly are marked by significantly more kimberlite and related volatile-rich ultramafic production38,49, further supporting the notion that crustal extension is a first order control that is not erased by preservation bias. The implication is that continental extension is one of the dominant driving forces in ensuring that volatiles are destabilised in the deep mantle and propagated towards the surface. That being said, there was still likely significant erosion of breakup-related diatremes, and it is perhaps for this reason that diatremes concomitant with initial continental breakup are rare in the geological record. One only has to look at Argyle to appreciate the fortuity involved in preserving a diamond-bearing diatreme. It was buried to >5–6 km (>180 °C, zircon [U-Th]/He) and exhumed to <2 km by the Early Cretaceous, to only be partly eroded and at mineable depth at the present.
Methods
Thin section petrographic methods and preparation
Two polished thin sections were prepared from one sample, AK1-Lh01a and AK1-Lh01b, by Adelaide Petrographic Laboratories. Entire thin sections were imaged using an Axio Imager II in the School of Earth and Planetary Sciences, Curtin University, in transmitted plane-polarised, transmitted cross-polarised and reflected plane-polarised light to provide clear petrographic overviews.
The thin section was subsequently carbon coated and analysed using a Tescan Integrated Mineral Analyser (TIMA) in the John de Laeter Centre (JdLC), Curtin University, to aid in mineral identification, particularly with respect to identifying dateable minerals50,51,52. A TIMA is a field emission gun scanning electron microscope (FEG-SEM), equipped with four electron dispersive X-ray spectrometers (EDS), and capable of recording 420k X-ray counts per second. Thin sections were analysed in ‘dot-mapping’ mode with a rectangular mesh at a step-size of 3 µm for backscattered electron (BSE) imaging. One thousand EDS counts are collected every 9th step (i.e., 27 µm) or when the BSE contrast changes (i.e., a change in mineral phase). For a given mineral grain, EDS counts are integrated across the entire grain. TIMA analyses used an accelerating voltage of 25 kV, a probe current of 5.5 nA, a spot size of 80 nm and a nominal working distance of 15 mm. After imaging and EDS collection, BSE signals and EDS peaks are referenced to a mineral library for automatic mineral classification.
Detailed backscattered electron (BSE) and cathodoluminescence (CL) imaging were undertaken on a Clara FEG-SEM in the JdLC using an accelerating voltage of 20 kV (BSE) or 12 kV (CL), a nominal working distance of 10.0 mm (BSE) or 16.5 mm (CL), and a beam intensity of 1 nA for both.
A full compendium of optical and scanning electron images for thin sections may be found in Supplementary Fig. 1.
Geochronological processing and grain imaging analysis
Approximately 2 kg of sample AK1-Lh01 was cut into ~2–3 cm cubes and disaggregated using a SelFrag high-voltage pulse fragmentation system in the JdLC, Curtin University, to liberate constituent minerals. Resultant slurries were run through a Jasper Canyon Research concentrating shaker table for initial concentration of heavy minerals and subsequently through lithium heteropolytungstate (LST) heavy liquids at 2.9 g cm−3 and through methylene iodide at 3.3 g cm−3. Magnetic minerals were removed from the >3.3 g cm−3 and 2.9–3.3 g cm−3 fractions using a hand magnet and a Frantz isodynamic magnetic separator to concentrate zircon, apatite and titanite. Both sets of concentrates were subsequently dump-mounted in 25 mm epoxy rounds. All mounts were polished to half-grain thickness to expose grain interiors. Mounted grains were imaged with transmitted and reflected light on an optical microscope and, subsequently, CL imaged (zircon) and BSE imaged (titanite and apatite). Transmitted and reflected light images were used to assess grain shape and transparency. CL and BSE images were used to document internal zonation patterns (e.g. oscillatory, sector), recognise inclusions and identify growth and recrystallisation textures53. A full compendium of CL and BSE images may be found in Supplementary Fig. 3. U-Pb spots were not pre-selected to mitigate bias in detrital populations54.
We also note that, during a short examination of the coarse (>425 µm) mineral fraction under a binocular microscope, one subhedral diamond was discovered in AK1-Lh01 (Supplementary Fig. 2).
Detrital apatite U-Pb dating via laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS)
Apatite U-Pb isotope measurements were collected at the GeoHistory Facility, JdLC, Curtin University. An excimer laser (Resonetics S-155-SE 193 nm) was used at a spot size of 50 µm, on-sample fluence of 2.2 J cm−2 and repetition rate of 6 Hz. Ablations on reference materials and unknowns were undertaken over 30 s with 40 s of background capture. All analyses were preceded by two cleaning pulses. The sample cell was flushed by ultrahigh purity He (0.32 L min−1) and N2 (1.2 mL min−1).
Apatite U-Pb data were collected on an Agilent 8900 triple quadrupole mass spectrometer with high-purity Ar as the carrier gas for both sessions (flow rate 0.98 L min−1). Analyses of ~20 unknowns were bracketed by analysis of a standard block containing the primary apatite reference material Mount McClure (523.5 ± 1.5 Ma; ref. 55), which was used to monitor and correct for mass fractionation and instrumental drift. The standard block also contained a range of secondary apatite standards, including Durango (31.44 ± 0.18 Ma; ref. 56), MAD2 (474.25 ± 0.41 Ma; ref. 57) and AS3/FC-Duluth (1099.1 ± 1.2 Ma; ref. 58), which were used to monitor data accuracy and precision. The secondary standards and unknowns were reduced against Mount McClure using regressions anchored to contemporaneous common 207Pb/206Pb values from the reference material. During the analytical session, Durango, MAD2 and FC-Duluth yielded statistically-reliable (p > 0.05) regressed ages of 29 ± 7 Ma, 476 ± 13 and 1091 ± 40 Ma (all uncertainties at 2 s.d.), respectively, all of which are within uncertainty of the published age (see Supplementary Data 1 for full U-Pb reference material compilation).
Data were reduced using the VizualAge UComPbine data reduction scheme in Iolite459,60. Uncertainties on analyses of primary reference materials were propagated in quadrature to the unknowns and secondary apatite reference materials. For the unknowns, some analyses ablated across inadvertent inclusions; these inclusion-related signals were cropped from the integrations; although this maintains the accuracy of the cropped analyses, the U-Pb precision is significantly reduced due to the shorter integration times51,61. If inclusions were too large or numerous, the integrations were deleted. No corrections were applied for common Pb because almost all analyses have appreciable amounts of common Pb (Supplementary Data 2). Age calculations and plots were made using Isoplot 4.1562. 207Pb-corrected 206Pb/238U model dates were computed for each individual grain using the 207Pb/206Pb(i) of a free-regressed line through the data. However, we caution that, due to slight excess scatter (MSWD = 2.5) and potential unrecognised Pb loss or incorporated common Pb of alternative 207Pb/206Pb ratios, these 207Pb-corrected 206Pb/238U dates should strictly be treated as model ages. All spot analyses are presented at 2σ and weighted mean analyses are presented at 95% confidence.
Full isotopic data for the reference materials and samples are given in Supplementary Data 1 and 2, respectively.
Detrital zircon U-Pb dating via LA-ICP-MS
Zircon U-Pb measurements were collected across two sessions at the GeoHistory Facility, JdLC, Curtin University. The second session was necessitated as only a single analysis at c. 1310 Ma was recognized in the first session. For both sessions, a RESOlution SE 193 nm ArF with a Lauren Technic S155 cell was used. The beam diameter was 30 µm, on-sample energy was 3.2 J cm−2 with a repetition rate of 6 Hz for 25 s of analysis time and ~45 s of background capture. All analyses were preceded by two cleaning pulses. The sample cell was flushed by ultrahigh purity He (0.32 L min−1) and N2 (1.2 mL min−1).
Zircon U-Pb isotope data were collected on an Agilent 8900 triple quadrupole mass spectrometer for all sessions with high purity Ar as the carrier gas (flow rate 0.98 L min−1). Analyses of ~20 unknowns were bracketed by analysis of a standard block containing the primary zircon reference materials GJ-1 (601.95 ± 0.40 Ma; refs. 63,64) and, for the second session, OG1 (3465.4 ± 0.6 Ma; ref. 65), which were used to monitor and correct for mass fractionation and instrumental drift. The standard block also contained the Phanerozoic to Archean reference materials Rak-17 (first session only, 295.56 ± 0.21 Ma; International Association of Geoanalysts, pers. comms. 2019), Plešovice (337.13 ± 0.37 Ma; ref. 66), 91500 (1063.78 ± 0.65 Ma; refs. 64,67), R33 first session only, 418.9 ± 0.4 Ma; ref. 68), FC-1 (first session only, 1099.0 ± 0.6 Ma; ref. 69) and Maniitsoq (3008.70 ± 0.72 Ma; ref. 70; all uncertainties at 2σ), which were used to monitor data accuracy and precision. During the analytical sessions, when reduced against a matrix-matched reference material, Rak-17, Plešovice, R33, 91500, FC-1 and Maniitsoq yielded statistically-reliable (p > 0.05) weighted mean ages of 293 ± 6 Ma, 340.1 ± 3.8 Ma to 340.5 ± 3.4 Ma, 417 ± 7 Ma, 1059 ± 11 Ma to 1063 ± 14, 1101 ± 13, and 3010 ± 36 to 3013 ± 17 Ma (all uncertainties at 2 s.d.), respectively, all of which are within the published age (see Supplementary Data 1 for full reference material compilation).
U-Pb isotopic data were reduced in Iolite459. Uncertainties on analyses of primary reference materials were propagated in quadrature to the unknowns and secondary zircon reference materials. For the unknowns, some analyses ablated across inadvertent inclusions; these inclusion-relates signals were cropped from the integrations or, if too large or numerous, integrations deleted; whilst the accuracy of the cropped analyses is maintained, the precision of the U-Pb data is significantly reduced due to the shorter integration times71,72,73. No corrections were applied for common Pb because common Pb was below detection limits for almost all concordant analyses (f206, Supplementary Data 2). Zircon analyses are considered concordant where the error ellipses at 2σ generated by the 207Pb/206Pb and 206Pb/238U ratios overlap the inverse concordia curve, excluding uncertainties on the decay constant. Age calculations and plots were made using Isoplot 4.1562. All zircon dates >1.5 Ga are presented as 207Pb/206Pb ages and those <1.5 Ga are presented as 206Pb/238U ages for optimum precision74. All spot analyses are presented at 2σ and weighted mean analyses are presented at 95% confidence.
Full isotopic data for the reference materials and samples are given in Supplementary Data 1 and 2, respectively.
Hydrothermal titanite U-Pb dating via LA-ICP-MS
Titanite U–Pb isotope data were collected at the GeoHistory Facility, JdLC, Curtin University. An excimer laser (Resonetics S-155-SE 193 nm) was used with a spot size of 30 µm, an on-sample fluence of 2.2 J cm−2 and repetition rate of 5 Hz for ~25 s of total analysis time and 40 s of background capture. All analyses were preceded by two cleaning pulses. The sample cell was flushed by ultrahigh purity He (0.32 L min−1) and N2 (1.2 mL min−1).
U–Pb data were collected on an Agilent 8900 triple quadrupole mass spectrometer with high purity Ar as the carrier gas for both sessions (flow rate 0.98 L min−1). Analyses of ~20 unknowns were bracketed by analysis of a standard block containing the primary titanite reference materials MKED 1 (1517.32 ± 0.32 Ma; ref. 75), which was used to monitor and correct for mass fractionation and instrumental drift. The standard block also contained the Phanerozoic to Proterozoic reference materials Khan (522.2 ± 2.2 Ma; ref. 76) and BLR-1 (1047.1 ± 0.4 Ma; ref. 77), which were used to monitor data accuracy and precision. The secondary standards and unknowns were reduced against MKED1 using regressions anchored to contemporaneous common 207Pb/206Pb values from the reference material. During the analytical session, Khan and BLR-1 yielded statistically-reliable (p > 0.05) regressed ages of 529 ± 8 Ma and 1050 ± 16 Ma (all uncertainties at 2 s.d.), both of which are within uncertainty of the published age (see Supplementary Data 1 for full compilation of results for U-Pb reference materials).
Data were reduced using U-Pb geochronology in Iolite459,60. Uncertainties on the primary reference materials were propagated in quadrature to the unknowns and secondary titanite reference materials. For the unknowns, some analyses inadvertently ablated through inclusions represented by short time duration spikes in characteristic isotopes (e.g., 232Th for monazite); these were cropped from the sample integration or, if too large or numerous, that sample integration was deleted. While the accuracy of the cropped analyses is maintained, the precision of the U-Pb is significantly reduced due to the shorter integration time23,78,79. No corrections were applied for common-Pb was not corrected because almost all analyses have appreciable amounts of common Pb (Supplementary Data 2). Age calculations and plots were made using Isoplot 4.1562. 207Pb-corrected 206Pb/238U model dates were computed for each individual grain using the 207Pb/206Pb(i) of a free-regressed line through the data. All spot analyses are presented at 2σ and weighted mean analyses are presented at 95% confidence.
Full isotopic data for the reference materials and samples are given in Supplementary Data 1 and 2, respectively.
Hydrothermal titanite U-Pb dating via ID-TIMS
Selected titanite crystals that had previously been ablated and analysed with ICP-MS were extracted from a resin mount at the British Geological Survey, UK. Ten grains were plucked from the mount used for LA-ICP-MS. Eight of these grains came from one area of the mount, with the other two grains selected based on different ratios of radiogenic to common Pb (as per the LA-ICP-MS discordia in Fig. 3D). All of the analysed titanite crystals were ultrasonically cleaned for an hour before being placed on a hotplate for 30 min, and rinsed in ultrapure acetone. After rinsing, titanite fractions were transferred to 300 μl Teflon PFA microcapsules, and leached in ~ 120 μl of 29 M HF with a trace amount of 4 M HNO3 for 12 h at 180 °C. The acid solution was then removed, and titanite crystals were rinsed again in 4 M HNO3 and 6 M HCl before spiking with mixed EARTHTIME 233U–235U–205Pb tracer (ET53580,81), placed in Parr vessels at ~220 °C for 60 h, dried to fluorides and then converted to chlorides by mixing in 3 M HCl at ~180 °C overnight. U and Pb were separated using standard HBr and HNO3-based anion-exchange chromatographic procedures on 0.05 ml PRFE columns. Isotopic ratios were measured at the British Geological Survey using a Thermo Scientific Triton Thermal Ionisation Mass-Spectrometer (TIMS). Pb and U were loaded separately on single Re filaments in a silica-gel/phosphoric acid mixture. Pb and U were measured by peak hopping on a single SEM detector, with Pb isotopes corrected for mass bias using a fractionation factor of 0.12 ± 0.04%/amu (1σ) and U mass fractionation was calculated in real time based on the isotopic composition of the ET535 tracer. Oxide correction was based on an 18O/16O ratio of 0.00205 ± 0.00004, and the sample 238U/235U ratio was assumed to be 137.818 ± 0.04582. Data reduction was based upon the algorithms of Schmitz and Schoene83.
Apatite and zircon (U-Th)/He dating
(U-Th)/He dating of apatite and zircon was conducted at the Western Australia ThermoChronology Hub Facility, JdLC, Curtin University, and followed the procedures detailed in Danišík, Štěpančíková84, Danišík, McInnes85, and Danišík, Lowe86. Single crystals of apatite and zircon were hand-picked following strict selection criteria with regard to their morphology, clarity, and presence of inclusions, then photographed and measured for physical dimensions in order to calculate alpha-ejection correction factors87. Selected crystals were loaded in Pt (apatite) or Nb (zircon) tubes and loaded into an Alphachron II instrument for He extraction. Together with other gases, 4He was extracted at ~960 °C (apatite) or ~1250 °C (zircon) under ultra-high vacuum using a diode laser, cleaned on Ti-Zr getters, and spiked with 99.9% pure 3He gas. The volume of 4He was measured by isotope dilution on a QMG 220 M1 Pfeiffer Prisma Plus mass spectrometer. A ‘re-extract’ was run after each analysis to verify complete outgassing of the crystal. Helium gas signals were corrected for blank, determined by analysing empty Nb or Pt microtubes interspersed between the unknowns using the same gas extraction procedure.
After the He measurements, microtubes containing the crystals were retrieved from the Alphachron, spiked with 235U and 230Th, and dissolved. Apatite was dissolved in HNO3 at room temperature using ultrasonication; zircon was dissolved in Parr acid digestion vessels in two cycles of HF, HNO3 (cycle 1), and HCl acids (cycle 2) following the procedures described in Evans, Byrne88. Sample, blank, and spiked standard solutions were then diluted by Milli-Q water and analysed by isotope dilution for 238U and 232Th, and by external calibration for 147Sm on an Element XR™ High Resolution ICP-MS. The total analytical uncertainty (TAU) was calculated by addition in quadrature on He and weighted uncertainties on U, Th, and Sm measurements. The (U–Th)/He ages were corrected for α-ejection (Ft correction) after Farley, Wolf87, whereby a homogeneous distribution of U, Th, and Sm was assumed for the crystals. Accuracy of the (U–Th)/He dating procedure was monitored by replicate analyses of Fish Canyon Tuff zircon (n = 3) and Durango apatite (n = 4) measured over the period of this study as internal standards, yielding mean (U–Th)/He ages of 28.5 ± 3.1 Ma and 31.5 ± 1.9 Ma, respectively (2 s.d.). These ages are in good agreement with the reference material ages of 28.3 ± 1.3 Ma (Fish Canyon Tuff89) and 31.13 ± 1.01 Ma (Durango56).
References
Pearson, D. G. et al. Deep continental roots and cratons. Nature 596, 199–210 (2021).
Kjarsgaard, B. A. et al. A review of the geology of global diamond mines and deposits. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 88, 1–117 (2022).
Stachel, T. & Luth, R. W. Diamond formation—Where, when and how? Lithos 220, 200–220 (2015).
Rayner, M. J. et al. The geology of the Argyle (AK1) diamond deposit, Western Australia. In: Geoscience and Exploration of the Argyle, Bunder, Diavik, and Murowa Diamond Deposits (eds Davy A. T., Smith C. B., Helmstaedt H. H., Jaques A. L., Gurney J. J.) (Society of Economic Geologists, 2018).
Bulanova, G. P. et al. The unique nature of argyle fancy diamonds: internal structure, paragenesis, and reasons for color. In: Geoscience and Exploration of the Argyle, Bunder, Diavik, and Murowa Diamond Deposits) (Society of Economic Geologists, 2018).
Smith, C. B., Atkinson, W. J., Tyler, E. W. J., Hall, A. E. & Macdonald, I. The discovery of the Argyle pipe, Western Australia: the world’s first lamproite-hosted diamond mine. Soc. Econ. Geol. Spec. Publ. 20, 49–64 (2018).
Maidment, D. W. et al. Geochronology of metasedimentary and igneous rocks in the Lamboo Province, Kimberley region: reassessing collisional geodynamic models. Geol. Surv. West. Aust. 215, 1–82 (2022).
Roffey, S., Rayner, M. J., Davy, A. T. & Platell, R. W. Evaluation of the AK1 deposit at argyle diamond. Mine. Soc. Econ. Geol. Spec. Publ. 20, 65–87 (2018).
Rayner, M. J. et al. New insights into volcanic processes from deep mining of the southern diatreme within the Argyle lamproite pipe, Western Australia. Mineral. Petrol. 112, 351–363 (2018).
Jaques, A. L., Sun, S.-S. & Chappell, B. W. Geochemistry of the Argyle (AK1) lamproite pipe, Western Australia. Geol. Soc. Aust. Spec. Publ. 14, e188 (1989).
Kohn, B. P. et al. Shaping the Australian crust over the last 300 million years: insights from fission track thermotectonic imaging and denudation studies of key terranes. Aust. J. Earth Sci. 49, 697–717 (2002).
Pidgeon, R. T., Smith, C. B. & Fanning, C. M. Kimberlite and lamproite emplacement ages in Western Australia. Kimberl. Relat. Rocks 1, 382–391 (1989).
Skinner, E. M. W., Bristow, J. W., Smith, C. B., Scott Smith, B. H. & Dawson, J. B. Proterozoic kimberlites and lamproites and a preliminary age for the Argyle lamproite pipe, Western Australia. Trans. Geol. Soc. S. Afr. 88, 335–340 (1985).
Sun, S.-S., Jaques, A. L. & McCulloch, M. T. Isotopic evolution of the Kimberley block, Western Australia. Int. Kimberl. Conf. 4, 346–348 (1986).
Baksi, A. K. A quantitative tool for detecting alteration in undisturbed rocks and minerals—I: Water, chemical weathering, and atmospheric argon. Geol. Soc. Am. Spec. Pap. 430, 285–303 (2007).
Jiang, Q. et al. 40Ar/39Ar dating of basaltic rocks and the pitfalls of plagioclase alteration. Geochim. et. Cosmochim. Acta 314, 334–357 (2021).
Jaques, A. L., Haggerty, S. E., Lucas, H. & Boxer, G. L. Mineralogy and petrology of the Argyle (AK1) lamproite pipe, Western Australia. Geol. Soc. Aust. Spec. Publ. 14, 153–170 (1989).
Hogmalm, K. J., Zack, T., Karlsson, A. K. O., Sjöqvist, A. S. L. & Garbe-Schönberg, D. In situ Rb–Sr and K–Ca dating by LA-ICP-MS/MS: an evaluation of N 2 O and SF 6 as reaction gases. J. Anal. Spectrom. 32, 305–313 (2017).
Olierook, H. K. H. et al. Resolving multiple geological events using in situ Rb–Sr geochronology: implications for metallogenesis at Tropicana, Western Australia. Geochronology 2, 283–303 (2020).
Cherniak, D. J., Lanford, W. A. & Ryerson, F. J. Lead diffusion in apatite and zircon using ion implantation and Rutherford Backscattering techniques. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 55, 1663–1673 (1991).
Lu Y., Wingate M. T. D., Phillips C. 226411: siltstone, Sam South mine. Geochronology Record 1702, Geological Survey of Western Australia, 1-7 (2020).
Lu Y., Wingate M. T. D., Phillips C. 226410: lithic sandstone, Tony East mine. Geochronology Record 1701, Geological Survey of Western Australia, 1-7 (2020).
Olierook, H. K. H. et al. Unravelling complex geologic histories using U–Pb and trace element systematics of titanite. Chem. Geol. 504, 105–122 (2019).
Pidgeon, R. T., Bosch, D. & Bruguier, O. Inherited zircon and titanite U▯Pb systems in an Archaean syenite from southwestern Australia: implications for U▯Pb stability of titanite. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 141, 187–198 (1996).
Reiners, P. W., Spell, T. L., Nicolescu, S. & Zanetti, K. A. Zircon (U-Th)/He thermochronometry: he diffusion and comparisons with 40Ar/39Ar dating. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 68, 1857–1887 (2004).
Evans, D. A. D., Li, Z.-X. & Murphy, J. B. Four-dimensional context of Earth’s supercontinents. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 424, 1–14 (2016).
Pisarevsky, S. A., Elming, S.-Å., Pesonen, L. J. & Li, Z.-X. Mesoproterozoic paleogeography: supercontinent and beyond. Precambrian Res. 244, 207–225 (2014).
Kirscher, U. et al. Paleomagnetic constraints on the duration of the Australia-Laurentia connection in the core of the Nuna supercontinent. Geology 49, 174–179 (2021).
Pehrsson S. J., Eglington B. M., Evans D. A. D., Huston D., Reddy S. M. Metallogeny and its link to orogenic style during the Nuna supercontinent cycle. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec.Publ. 424, 83-94 (2016).
Li Z-X, Liu Y., Ernst R. A dynamic 2000–540 Ma Earth history: from cratonic amalgamation to the age of supercontinent cycle. Earth-Sci. Rev. 238, 104336 (2023).
Liu, Y., Mitchell, R. N., Brown, M., Johnson, T. E. & Pisarevsky, S. Linking metamorphism and plate boundaries over the past 2 billion years. Geology 50, 631–635 (2022).
Evans, D. A. D. & Mitchell, R. N. Assembly and breakup of the core of Paleoproterozoic–Mesoproterozoic supercontinent Nuna. Geology 39, 443–446 (2011).
Zhang, S.-H., Zhao, Y., Li, X.-H., Ernst, R. E. & Yang, Z.-Y. The 1.33–1.30 Ga Yanliao large igneous province in the North China Craton: Implications for reconstruction of the Nuna (Columbia) supercontinent, and specifically with the North Australian Craton. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 465, 112–125 (2017).
Nixon, A. L. et al. Inter-cratonic geochronological and geochemical correlations of the Derim Derim–Galiwinku/Yanliao reconstructed Large Igneous Province across the North Australian and North China cratons. Gondwana Res. 103, 473–486 (2022).
Coffin, M. F. & Eldholm, O. Volcanism and continental break-up: a global compilation of large igneous provinces. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 68, 17–30 (1992).
Geoffroy, L., Burov, E. B. & Werner, P. Volcanic passive margins: another way to break up continents. Sci. Rep. 5, 14828 (2015).
Dang, Z. et al. Weak orogenic lithosphere guides the pattern of plume-triggered supercontinent break-up. Commun. Earth Environ. 1, 51 (2020).
Heaman, L. M., Phillips, D. & Pearson, G. Dating kimberlites: methods and emplacement patterns through time. Elements 15, 399–404 (2019).
Heaman, L. M., Kjarsgaard, B. A. & Creaser, R. A. The timing of kimberlite magmatism in North America: implications for global kimberlite genesis and diamond exploration. Lithos 71, 153–184 (2003).
Heaman, L. M., Kjarsgaard, B. A. & Creaser, R. A. The temporal evolution of North American kimberlites. Lithos 76, 377–397 (2004).
Tappe, S., Smart, K., Torsvik, T., Massuyeau, M. & de Wit, M. Geodynamics of kimberlites on a cooling Earth: clues to plate tectonic evolution and deep volatile cycles. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 484, 1–14 (2018).
Gernon, T. M. et al. Rift-induced disruption of cratonic keels drives kimberlite volcanism. Nature 620, 344–350 (2023).
Bogatikov, O. A., Kononova, V. A., Nosova, A. A. & Kondrashov, I. A. Kimberlites and lamproites of the East European Platform: petrology and geochemistry. Petrology 15, 315–334 (2007).
Downes, P. J. et al. Perovskite geochronology and petrogenesis of the Neoproterozoic Mad Gap Yards ultramafic lamprophyre dykes, East Kimberley region, Western Australia. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 178, 21 (2023).
Field, M., Stiefenhofer, J., Robey, J. & Kurszlaukis, S. Kimberlite-hosted diamond deposits of southern Africa: a review. Ore Geol. Rev. 34, 33–75 (2008).
Tappe, S., Shaikh, A. M., Wilson, A. H. & Stracke, A. Evolution of ultrapotassic volcanism on the Kaapvaal craton: deepening the orangeite versus lamproite debate. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 513, 17–44 (2022).
Spencer, C. J., Roberts, N. M. W. & Santosh, M. Growth, destruction, and preservation of Earth’s continental crust. Earth-Sci. Rev. 172, 87–106 (2017).
Hawkesworth, C., Cawood, P., Kemp, T., Storey, C. & Dhuime, B. A matter of preservation. Science 323, 49–50 (2009).
Pandey, A. & Rao, N. V. C. Supercontinent transition as a trigger for ~1.1 Gyr diamondiferous kimberlites and related magmatism in India. Lithos 370-371, 105620 (2020).
Olierook, H. K. H. et al. Xenotime reveals Caledonian hydrothermal overprint on Neoproterozoic Cu mineralization, East Greenland. J. Geol. Soc., 180, jgs2022-2141 (In Press).
Olierook, H. K. H. et al. Terminal tectono-magmatic phase of the New England Orogen driven by lithospheric delamination. Gondwana Res. 106, 105–125 (2022).
Olierook, H. K. H. et al. Mineralization proximal to the final Nuna suture in northeastern Australia. Gondwana Res. 92, 54–71 (2021).
Corfu, F., Hanchar, J. M., Hoskin, P. W. O. & Kinny, P. Atlas of zircon textures. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 53, 469–500 (2003).
Dröllner, M., Barham, M., Kirkland, C. L. & Ware, B. Every zircon deserves a date: selection bias in detrital geochronology. Geol. Mag. 158, 1135–1142 (2021).
Schoene, B. & Bowring, S. A. U–Pb systematics of the McClure Mountain syenite: thermochronological constraints on the age of the 40Ar/39Ar standard MMhb. Contributions Mineral. Petrol. 151, 615 (2006).
McDowell, F. W., McIntosh, W. C. & Farley, K. A. A precise 40Ar–39Ar reference age for the Durango apatite (U–Th)/He and fission-track dating standard. Chem. Geol. 214, 249–263 (2005).
Thomson S. N., Gehrels G. E., Ruiz J., Buchwaldt R. Routine low-damage apatite U-Pb dating using laser ablation–multicollector–ICPMS. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 13, Q0AA21 (2012).
Schmitz, M. D., Bowring, S. A. & Ireland, T. R. Evaluation of Duluth Complex anorthositic series (AS3) zircon as a U-Pb geochronological standard: new high-precision isotope dilution thermal ionization mass spectrometry results. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 67, 3665–3672 (2003).
Paton, C., Hellstrom, J., Paul, B., Woodhead, J. & Hergt, J. Iolite: Freeware for the visualisation and processing of mass spectrometric data. J. Anal. Spectrom. 26, 2508–2518 (2011).
Chew, D. M., Petrus, J. A. & Kamber, B. S. U–Pb LA–ICPMS dating using accessory mineral standards with variable common Pb. Chem. Geol. 363, 185–199 (2014).
Olierook, H. K. H. et al. Mafic intrusions in southwestern Australia related to supercontinent assembly or breakup? Aust. J. Earth Sci. 69, 200–222 (2022).
Ludwig K. User’s manual for Isoplot version 3.75–4.15: a geochronological toolkit for Microsoft. Excel Berkley Geochronological Center Special Publication (2012).
Jackson, S. E., Pearson, N. J., Griffin, W. L. & Belousova, E. A. The application of laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry to in situ U–Pb zircon geochronology. Chem. Geol. 211, 47–69 (2004).
Horstwood, M. S. A. et al. Community-derived standards for LA-ICP-MS U-(Th-)Pb geochronology – uncertainty propagation, age interpretation and data reporting. Geostand. Geoanal. Res. 40, 311–332 (2016).
Stern, R. A., Bodorkos, S., Kamo, S. L., Hickman, A. H. & Corfu, F. Measurement of SIMS Instrumental Mass Fractionation of Pb Isotopes During Zircon Dating. Geostand. Geoanal. Res. 33, 145–168 (2009).
Sláma, J. et al. Plešovice zircon — a new natural reference material for U–Pb and Hf isotopic microanalysis. Chem. Geol. 249, 1–35 (2008).
Wiedenbeck, M. et al. Three natural zircon standards For U-Th-Pb, Lu-Hf, trace element And REE analyses. Geostand. Newsl. 19, 1–23 (1995).
Black, L. P. et al. Improved 206Pb/238U microprobe geochronology by the monitoring of a trace-element-related matrix effect; SHRIMP, ID–TIMS, ELA–ICP–MS and oxygen isotope documentation for a series of zircon standards. Chem. Geol. 205, 115–140 (2004).
Paces, J. B. & Miller, J. D. Precise U‐Pb ages of Duluth complex and related mafic intrusions, northeastern Minnesota: Geochronological insights to physical, petrogenetic, paleomagnetic, and tectonomagmatic processes associated with the 1.1 Ga midcontinent rift system. J. Geophys. Res.: Solid Earth 98, 13997–14013 (1993).
Marsh J. H., Jørgensen T. R. C., Petrus J. A., Hamilton M. A., Mole D. R. U-Pb, trace element, and hafnium isotope composition of the Maniitsoq zircon: A potential new Archean zircon reference material. Goldschmidt. Abstract Details (2019).
Olierook, H. K. H. et al. Differentiating between inherited and autocrystic zircon in granitoids. J. Petrol. 61, egaa081 (2020).
Olierook, H. K. H. et al. Extracting meaningful U-Pb ages from core–rim mixtures. Gondwana Res. 92, 102–112 (2021).
Olierook, H. K. H. et al. Regional zircon U-Pb geochronology for the Maniitsoq region, southwest Greenland. Sci. Data 8, 139 (2021).
Spencer, C. J., Kirkland, C. L. & Taylor, R. J. M. Strategies towards statistically robust interpretations of in situ U–Pb zircon geochronology. Geosci. Front. 7, 581–589 (2016).
Spandler, C. et al. MKED1: A new titanite standard for in situ analysis of Sm–Nd isotopes and U–Pb geochronology. Chem. Geol. 425, 110–126 (2016).
Heaman, L. M. The application of U–Pb geochronology to mafic, ultramafic and alkaline rocks: an evaluation of three mineral standards. Chem. Geol. 261, 43–52 (2009).
Aleinikoff, J. N. et al. Ages and origins of rocks of the Killingworth dome, south-central Connecticut: Implications for the tectonic evolution of southern New England. Am. J. Sci. 307, 63–118 (2007).
Kirkland, C. L. et al. Titanite petrochronology linked to phase equilibrium modelling constrains tectono-thermal events in the Akia Terrane, West Greenland. Chem. Geol. 536, 119467 (2020).
Wang, S. et al. Two-stage exhumation of deeply subducted continental crust: Insight from zircon, titanite, and apatite petrochronology, Sulu belt of eastern China. GSA Bull. 135, 48–66 (2023).
Condon, D. J., Schoene, B., McLean, N. M., Bowring, S. A. & Parrish, R. R. Metrology and traceability of U–Pb isotope dilution geochronology (EARTHTIME Tracer Calibration Part I). Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 164, 464–480 (2015).
McLean, N. M., Condon, D. J., Schoene, B. & Bowring, S. A. Evaluating uncertainties in the calibration of isotopic reference materials and multi-element isotopic tracers (EARTHTIME Tracer Calibration Part II). Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 164, 481–501 (2015).
Hiess, J., Condon, D. J., McLean, N. & Noble, S. R. 238U/235U systematics in terrestrial uranium-bearing minerals. Science 335, 1610–1614 (2012).
Schmitz M. D., Schoene B. Derivation of isotope ratios, errors, and error correlations for U‐Pb geochronology using 205Pb‐235U‐(233U)‐spiked isotope dilution thermal ionization mass spectrometric data. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 8, Q08006 (2007).
Danišík M., Štěpančíková P., Evans N. J. Constraining long‐term denudation and faulting history in intraplate regions by multisystem thermochronology: An example of the Sudetic Marginal Fault (Bohemian Massif, central Europe). Tectonics 31, TC2003 (2012).
Danišík, M. et al. Seeing is believing: visualization of He distribution in zircon and implications for thermal history reconstruction on single crystals. Sci. Adv. 3, e1601121 (2017).
Danišík, M. et al. Sub-millennial eruptive recurrence in the silicic Mangaone Subgroup tephra sequence, New Zealand, from Bayesian modelling of zircon double-dating and radiocarbon ages. Quat. Sci. Rev. 246, 106517 (2020).
Farley, K. A., Wolf, R. A. & Silver, L. T. The effects of long alpha-stopping distances on (U‐Th)/He ages. Geochim. cosmochim. Acta 60, 4223–4229 (1996).
Evans, N. J., Byrne, J. P., Keegan, J. T. & Dotter, L. E. Determination of uranium and thorium in zircon, apatite, and fluorite: application to laser (U-Th)/He thermochronology. J. Anal. Chem. 60, 1159–1165 (2005).
Reiners P. W. Thermochronology (eds Reiners P. W., Ehlers T. A.). (Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 2005).
Acknowledgements
Funding was provided by the Geological Survey of Western Australia (GSWA) to D. F. and the open fund of State Key Laboratory of Geological Processes and Mineral Resources, China University of Geosciences, Wuhan (Project No. GPMR202201) to L. S. D. Rio Tinto Group are thanked for providing samples to D. F. The John de Laeter Centre acknowledges operational funding for the GeoHistory Facility from AuScope (auscope.org.au) and the Australian Government via the National Collaborative Research Infrastructure Strategy (NCRIS). The Australian Research Council is thanked for funding the Tescan Clara FESEM (ARC LE190100176), Tescan Integrated Mineral Analyser (ARC LE1400100150), the Selfrag HV pulse fragmentor (ARC LE130100219) and Laureate Fellowship grant to Z. X. L. (ARC FL150100133). M. T. D. W. publishes with permission of the Executive Director of GSWA. This is a contribution to IGCP 648: Supercontinent and Global Geodynamics.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
H.K.H.O. interpreted all analyses and led the drafting of the paper. D.F. and L.S.D. obtained funding and samples. Y.L. made the plate reconstructions. M.J.R. supplied the samples. M.D., D.J.C., N.J.E. and B.J.M. carried out the geochronological analyses. C.M. picked and imaged the diamond. B.I.A.M., A.L.J., Z.X.L., C.L.K. and M.T.D.W. supervised the work and provided geological and technical expertise. All authors contributed to editing of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
M.J.R. is an employee at Rio Tinto Group. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Communications thanks Bruce Kjarsgaard and N.V. Chalapathi Rao for their contribution to the peer review of this work. A peer review file is available.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Olierook, H.K.H., Fougerouse, D., Doucet, L.S. et al. Emplacement of the Argyle diamond deposit into an ancient rift zone triggered by supercontinent breakup. Nat Commun 14, 5274 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-40904-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-40904-8
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.