Abstract
Background
The use of home enteral nutrition (HEN) has increased enormously. HEN has been shown to decrease length of stays, improve clinical outcomes, and increase quality of life. Literature on HEN epidemiology has also sprouted recently. Nevertheless, studies on Chinese HEN users are hardly seen. The objective of this study was thus to describe the epidemiological characteristics of HEN users from a Chinese tertiary hospital in 2018.
Methods
Data were retrospectively analyzed using the personal patient profiles we created upon each HEN initiation. In the year of 2018, 2007 patients and a cumulative total of 3375 episodes were recorded.
Results
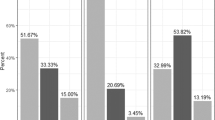
The median age was 61 (IQR 46–75) years, and 63 (IQR 49–75) for males and 55 (IQR 43–72) for females. The most frequent indication for HEN implementation was oncological diseases (35.8%), followed by digestive diseases (13.4%), and neurological diseases (9.0%). Overall, 90.0% of the episodes were prescribed for oral nutrition supplement (ONS) and 9.5% for tube feeding (TF). Majority (70.8%) of the episodes comprised standard commercial formula.
Conclusions
Our study revealed some fundamental epidemiological characteristics of Chinese HEN patients. This preliminary single-center study has multiple limitations but still possesses revelatory and referential significance for other Chinese practitioners in the field of HEN. In future, multicenter studies and qualified HEN registries are widely needed in China.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bischoff SC, Austin P, Boeykens K, Chourdakis M, Cuerda C, Jonkers-Schuitema C, et al. ESPEN guideline on home enteral nutrition. Clin Nutr. 2020;39:5–22.
Wong A, Goh G, Banks MD, Bauer JD. A systematic review of the cost and economic outcomes of home enteral nutrition. Clin Nutr. 2018;37:429–42.
Maeda M, Fukuda H, Shimizu S, Ishizaki T. A comparative analysis of treatment costs for home-based care and hospital-based care in enteral nutrition patients: a retrospective analysis of claims data. Health Policy. 2019;123:367–72.
Klek S, Hermanowicz A, Dziwiszek G, Matysiak K, Szczepanek K, Szybinski P, et al. Home enteral nutrition reduces complications, length of stay, and health care costs: results from a multicenter study. Am J Clin Nutr. 2014;100:609–15.
Klek S, Szybinski P, Sierzega M, Szczepanek K, Sumlet M, Kupiec M, et al. Commercial enteral formulas and nutrition support teams improve the outcome of home enteral tube feeding. J Parenter Enter Nutr. 2011;35:380–5.
Mazur CE, Zago RCC, Schieferdecker MEM, Maluf E. Home enteral nutrition: clinical-nutritional analysis and outcomes of 10 years of public policy. Nutr Hosp. 2019;36:758–63.
Mundi MS, Pattinson A, McMahon MT, Davidson J, Hurt RT. Prevalence of home parenteral and enteral nutrition in the United States. Nutr Clin Pract. 2017;32:799–805.
Pironi L, Candusso M, Biondo A, Bosco A, Castaldi P, Contaldo F, et al. Prevalence of home artificial nutrition in Italy in 2005: a survey by the Italian Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition (SINPE). Clin Nutr. 2007;26:123–32.
Cuerda C, Planas M, Gomez Candela C, Luengo LM, group N-S. Trends in home enteral nutrition in Spain: analysis of the NADYA registry 1992-2007. Nutr Hosp. 2009;24:347–53.
Howard L, Ament M, Fleming CR, Shike M, Steiger E. Current use and clinical outcome of home parenteral and enteral nutrition therapies in the United States. Gastroenterology. 1995;109:355–65.
Hebuterne X, Bozzetti F, Moreno Villares JM, Pertkiewicz M, Shaffer J, Staun M, et al. Home enteral nutrition in adults: a European multicentre survey. Clin Nutr. 2003;22:261–6.
Wanden-Berghe C, Matia Martin P, Luengo Perez LM, Cuerda Compes C, Burgos Pelaez R, Alvarez Hernandez J, et al. Home enteral nutrition in Spain; NADYA registry 2011-2012. Nutr Hosp. 2014;29:1339–44.
Wanden-Berghe C, Puiggros JC, Calanas A, Cuerda C, Garcia-Luna PP, Rabassa-Soler A, et al. The Spanish Home Enteral Nutrition registry of the year 2009: from the NADYA-SENPE group. Nutr Hosp. 2010;25:959–63.
Wanden-Berghe Lozano C, Campos C, Burgos Pelaez R, Alvarez J, Frias Soriano L, Matia Martin MP, et al. Spanish home enteral nutrition registry of the year 2016 and 2017 from the NADYA-SENPE Group. Nutr Hosp. 2019;36:233–7.
Song G, Liu H. Effect of Hospital to Home nutrition management model on postoperative clinical outcomes of patients with laryngeal carcinoma. Oncol Lett. 2017;14:4059–64.
De Luis DA, Izaola O, Cuellar LA, Terroba MC, Cabezas G, De La Fuente B. Experience over 12 years with home enteral nutrition in a healthcare area of Spain. J Hum Nutr Diet. 2013;26:39–44.
Villar Taibo R, Martinez Olmos MA, Bellido Guerrero D, Vidal Casariego A, Peino Garcia R, Martis Sueiro A, et al. Epidemiology of home enteral nutrition: an approximation to reality. Nutr Hosp. 2018;35:511–8.
de Luis DA, Aller R, Izaola O, Terroba MC, Cabezas G, Cuellar LA. Experience of 6 years with home enteral nutrition in an area of Spain. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2006;60:553–7.
Cawsey SI, Soo J, Gramlich LM. Home enteral nutrition: outcomes relative to indication. Nutr Clin Pract. 2010;25:296–300.
de Luis Roman D, Aller de la Puente R, de Luis Roman J, Cuellar Olmedo LA, Terroba Larumbe MC, Izaola Jauregui O. Home enteral nutrition: analysis of efficiency in a Health District. Rev Clin Esp. 2003;203:317–20.
Wanden-Berghe C, Alvarez Hernandez J, Burgos Pelaez R, Cuerda Compes C, Matia Martin P, Luengo Perez LM, et al. A home enteral nutrition (HEN); spanish registry of NADYA-SENPE group; for the year 2013. Nutr Hosp. 2015;31:2518–22.
Campos-Martin C, Garcia-Torres MD, Castillo-Martin C, Dominguez-Rabadan R, Rabat-Restrepo JM. Patients discharged with home enteral nutrition from a third-level hospital in 2018. Nutrients. 2019;11:1–6.
Puiggros C, Lecha M, Rodriguez T, Perez-Portabella C, Planas M. Karnosfsky index as a mortality predicting factor in patients on home-based enteral nutrition. Nutr Hosp.2009;24:156–60.
Kwok T, Twinn S, Yan E. The attitudes of Chinese family caregivers of older people with dementia towards life sustaining treatments. J Adv Nurs. 2007;58:256–62.
King PC, Barrimore SE, Pulle RC, Bell JJ. “I Wouldn’t Ever Want It”: a qualitative evaluation of patient and caregiver perceptions toward enteral tube feeding in hip fracture inpatients. JPEN J Parenter Enter Nutr. 2019;43:526–33.
The Lancet Protecting Chinese doctors. Lancet. 2020;395:90.
Fan L, Li J, Xiang M, Yuan L, Zhang Y, Feng G, et al. Attitudes of radiation oncologists to percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy in patients with head and neck cancer and eating difficulties: a survey in China. J Int Med Res. 2018;46:1709–16.
Klek S, Chourdakis M, Bischoff S, Dubrov S, Forbes A, Galas A, et al. Economy matters to fight against malnutrition: results from a multicenter survey. Clin Nutr. 2017;36:162–9.
Li X, Zhou J, Chu C, You Q, Zhong R, Rao Z, et al. Home enteral nutrition may prevent myelosuppression of patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma treated by concurrent chemoradiotherapy. Head Neck. 2019;41:3525–34.
Wong A, Banks MD, Bauer JD. A Survey of Home Enteral Nutrition Practices and Reimbursement in the Asia Pacific Region. Nutrients. 2018;10.
Santarpia L, Pagano MC, Pasanisi F, Contaldo F. Home artificial nutrition: an update seven years after the regional regulation. Clin Nutr 2014;33:872–8.
Gossum AV. Home enteral nutrition. epidemiology and legislation in Europe. Nestle Nutr Workshop Ser Clin Perform Program. 2005;10:59–71.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
You, Q., Li, X., Ma, Y. et al. A retrospective analysis on epidemiological characteristics of home enteral nutrition: results from a Chinese tertiary hospital in 2018. Eur J Clin Nutr 75, 473–479 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41430-020-00755-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41430-020-00755-8