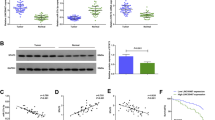
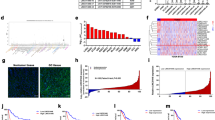
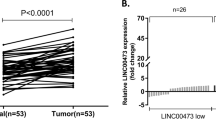
Abstract
Gastric cancer (GC) is a common cancer and a leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide. Recent studies have supported the important role of long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) in GC progression. This study identified functional significance of X inactive specific transcript (XIST) in GC. The expression of XIST and EPHA1 in GC tissues and cells was measured. Then, dual luciferase reporter gene assay, RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP) assay and Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assay were performed to explore the interaction among XIST, EPHA1 and HNF4A. The effects of XIST on GG progression were evaluated by determining expression of proliferation- and invasion-related proteins (Ki67, PCNA, MMP-2, and MMP-9). Further, the functional role of XIST in GC with the involvement of NFκB pathway was also analyzed. Subsequently, the tumor growth in nude mice was evaluated. High expression of XIST and EPHA1 was observed in GC. XIST elevated EPHA1 expression by recruiting HNF4A. In addition, silencing of XIST inhibited GC progression in vitro and in vivo. Overexpressed XIST and EPHA1 yielded a reversed effect on cell proliferation and invasion. SN50 treatment (inhibitor of NFκB pathway) counteracted the promotive effect on GC cell proliferation and invasion mediated by XIST. The present study unveils that XIST increases the enrichment of HNF4A in the promoter region of EPHA1, thus promoting the deterioration of GC.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated/analyzed during the current study are available.
Change history
12 September 2023
This article has been retracted. Please see the Retraction Notice for more detail: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41417-023-00667-2
References
Van Cutsem E, Sagaert X, Topal B, Haustermans K, Prenen H. Gastric cancer. Lancet. 2016;388:2654–64.
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:394–424.
Thrumurthy SG, Chaudry MA, Chau I, Allum W. Does surgery have a role in managing incurable gastric cancer? Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2015;12:676–82.
Yamaoka Y. How to eliminate gastric cancer-related death worldwide? Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2018;15:407–08.
Allum WH, Blazeby JM, Griffin SM, Cunningham D, Jankowski JA, Wong R, et al. Guidelines for the management of oesophageal and gastric cancer. Gut. 2011;60:1449–72.
Li F, Huang C, Li Q, Wu X. Construction and comprehensive analysis for dysregulated long non-coding RNA (lncRNA)-associated competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) network in gastric cancer. Med Sci Monit. 2018;24:37–49.
Qi D, Wang Q, Wu M, Zhang X. Comprehensive bioinformatics analysis of lncRNAs in gastric cancer. Oncol Lett. 2019;17:1279–91.
Zhang Y, Han T, Li J, Cai H, Xu J, Chen L, et al. Comprehensive analysis of the regulatory network of differentially expressed mRNAs, lncRNAs and circRNAs in gastric cancer. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;122:109686.
Zhang Q, Chen B, Liu P, Yang J. XIST promotes gastric cancer (GC) progression through TGF-beta1 via targeting miR-185. J Cell Biochem. 2018;119:2787–96.
Arya VB, Rahman S, Senniappan S, Flanagan SE, Ellard S, Hussain K. HNF4A mutation: switch from hyperinsulinaemic hypoglycaemia to maturity-onset diabetes of the young, and incretin response. Diabet Med. 2014;31:e11–5.
Taniguchi H, Fujimoto A, Kono H, Furuta M, Fujita M, Nakagawa H. Loss-of-function mutations in Zn-finger DNA-binding domain of HNF4A cause aberrant transcriptional regulation in liver cancer. Oncotarget. 2018;9:26144–56.
Moore BD, Khurana SS, Huh WJ, Mills JC. Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4alpha is required for cell differentiation and homeostasis in the adult mouse gastric epithelium. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2016;311:G267–75.
Saberi Anvar M, Minuchehr Z, Shahlaei M, Kheitan S. Gastric cancer biomarkers; a systems biology approach. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2018;13:141–46.
Shi J, Dai R, Chen Y, Guo H, Han Y, Zhang Y. LncRNA LINP1 regulates acute myeloid leukemia progression via HNF4alpha/AMPK/WNT5A signaling pathway. Hematol Oncol. 2019;37:474–82.
Wu BO, Jiang WG, Zhou D, Cui YX. Knockdown of EPHA1 by CRISPR/CAS9 promotes adhesion and motility of HRT18 colorectal carcinoma cells. Anticancer Res. 2016;36:1211–9.
Inokuchi M, Nakagawa M, Baogok N, Takagi Y, Tanioka T, Gokita K, et al. Prognostic significance of high EphA1-4 expression levels in locally advanced gastric cancer. Anticancer Res. 2018;38:1685–93.
Nakagawa M, Inokuchi M, Takagi Y, Kato K, Sugita H, Otsuki S, et al. Erythropoietin-producing hepatocellular A1 is an independent prognostic factor for gastric cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2015;22:2329–35.
Xia L, Tan S, Zhou Y, Lin J, Wang H, Oyang L, et al. Role of the NFkappaB-signaling pathway in cancer. Onco Targets Ther. 2018;11:2063–73.
Fu J, Yu L, Luo J, Huo R, Zhu B. Paeonol induces the apoptosis of the SGC7901 gastric cancer cell line by downregulating ERBB2 and inhibiting the NFkappaB signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med. 2018;42:1473–83.
Carpenter TC, Schroeder W, Stenmark KR, Schmidt EP. Eph-A2 promotes permeability and inflammatory responses to bleomycin-induced lung injury. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2012;46:40–7.
Chia NY, Tan P. Molecular classification of gastric cancer. Ann Oncol. 2016;27:763–9.
Corso S, Giordano S. How can gastric cancer molecular profiling guide future therapies? Trends Mol Med. 2016;22:534–44.
Gu Y, Chen T, Li G, Yu X, Lu Y, Wang H, et al. LncRNAs: emerging biomarkers in gastric cancer. Future Oncol. 2015;11:2427–41.
Zhang K, Shi H, Xi H, Wu X, Cui J, Gao Y, et al. Genome-wide lncRNA microarray profiling identifies novel circulating lncRNAs for detection of gastric cancer. Theranostics. 2017;7:213–27.
Chen DL, Ju HQ, Lu YX, Chen LZ, Zeng ZL, Zhang DS, et al. Long non-coding RNA XIST regulates gastric cancer progression by acting as a molecular sponge of miR-101 to modulate EZH2 expression. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2016;35:142.
Ma L, Zhou Y, Luo X, Gao H, Deng X, Jiang Y. Long non-coding RNA XIST promotes cell growth and invasion through regulating miR-497/MACC1 axis in gastric cancer. Oncotarget 2017;8:4125–35.
Yang C, Zhang J, Ding M, Xu K, Li L, Mao L, et al. Ki67 targeted strategies for cancer therapy. Clin Transl Oncol. 2018;20:570–75.
Shemesh A, Kundu K, Peleg R, Yossef R, Kaplanov I, Ghosh S, et al. NKp44-derived peptide binds proliferating cell nuclear antigen and mediates tumor cell death. Front Immunol. 2018;9:1114.
Nguyen PH, Giraud J, Staedel C, Chambonnier L, Dubus P, Chevret E, et al. All-trans retinoic acid targets gastric cancer stem cells and inhibits patient-derived gastric carcinoma tumor growth. Oncogene. 2016;35:5619–28.
Majumder A, Ray S, Banerji A. Epidermal growth factor receptor-mediated regulation of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and matrix metalloproteinase-9 in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 2019;452:111–21.
Wu YJ, Lin SH, Din ZH, Su JH, Liu CI. Sinulariolide inhibits gastric cancer cell migration and invasion through downregulation of the EMT process and suppression of FAK/PI3K/AKT/mTOR and MAPKs signaling pathways. Mar Drugs. 2019;17:
Chang HR, Nam S, Kook MC, Kim KT, Liu X, Yao H, et al. HNF4alpha is a therapeutic target that links AMPK to WNT signalling in early-stage gastric cancer. Gut. 2016;65:19–32.
Cui Y, Wu BO, Flamini V, Evans BAJ, Zhou D, Jiang WG. Knockdown of EPHA1 Using CRISPR/CAS9 suppresses aggressive properties of ovarian cancer cells. Anticancer Res. 2017;37:4415–24.
Jiao Y, Yang H, Qian J, Gong Y, Liu H, Wu S, et al. miR36645P suppresses the proliferation and metastasis of gastric cancer by attenuating the NFkappaB signaling pathway through targeting MTDH. Int J Oncol. 2019;54:845–58.
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge and appreciate our colleagues for their valuable efforts and comments on this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ping Li, LW, Pengfe Li, FH, YC, and DT participated in the conception and design of the study. Ping Li, LW, Pengfe Li, GY, DW, and HL performed the analysis and interpretation of data. Ping Li, LW, GY, DW, and HL contributed to drafting the article. FH, YC, GY, and DW revised it critically for important intellectual content. HL is the GUARANTOR for the article who accepts full responsibility for the work and/or the conduct of the study, had access to the data, and oversaw the decision to publish.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The current study was performed with the approval of the ethical committee of Jiangdu People’s Hospital of Yangzhou and written informed consent was obtained from each participant. Animal experiments were conducted in strict accordance with recommendations in the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals of the National Institutes of Health.
Informed consent
Consent for publication was obtained from the participants.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article has been retracted. Please see the retraction notice for more detail: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41417-023-00667-2
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, P., Wang, L., Li, P. et al. RETRACTED ARTICLE: Silencing of long non-coding RNA XIST represses gastric cancer progression through blocking NFκB pathway via inhibiting HNF4A-mediated transcription of EPHA1. Cancer Gene Ther 28, 307–320 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41417-020-00220-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41417-020-00220-5
This article is cited by
-
Potential roles of lncRNA-XIST/miRNAs/mRNAs in human cancer cells
Clinical and Translational Oncology (2023)
-
Long non-coding RNA XIST: a novel oncogene in multiple cancers
Molecular Medicine (2021)