Abstract
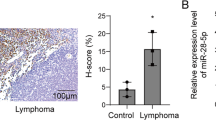
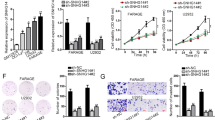
Understanding the molecular mechanisms for the development of non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) will improve our ability to cure the patients. qRT-PCR was applied for the examination of the efficiency of shRNA for DNMT1, the expression of suppressor genes, miRNA-152. The MTT analysis, cell cycle analysis, clonal formation, and apoptotic analysis were used to examine the functions of DNMT1 and miR-152 in lymphoma cells. Methylation-specific polymerase chain reaction (MSP) was used to examine the methylation of tumor suppressor genes. The dual luciferase assay and western blot were used to validate if DNMT1 is the target of miR-152. For the in vivo experiments, the lymphoma cells were injected into the nude mice for quantification of the tumor growth after transfection of miR-152 mimics. Knockdown of DNMT1 by shRNA (sh-DNMT1) in OCI-Ly10 and Granta-159 cells significantly upregulated the expression of tumor suppressor genes (SOCS3, BCL2L10, p16, p14, and SHP-1) via decreasing their methylation level. At the cellular level, we found sh-DNMT1 inhibited the proliferation, clonal formation and cell cycle progression and induced the cell apoptosis of lymphoma cells. Furthermore, we found miR-152 can downregulates the expression of DNMT1 via directly targeting the gene. Overexpression of miR-152 also increased the expression of tumor suppressor genes SOCS3 and SHP-1. And miR-152 also can inhibit the cell proliferation and induce the cell apoptosis. Moreover, we found overexpression of miR-152 significantly repressed the tumor growth with decreased DNMT1 expression and increased expression of tumor suppressor genes in vivo. Our study demonstrates that miR-152 can inhibit lymphoma growth via suppressing DNMT1-mediated silencing of SOCS3 and SHP-1. These data demonstrate a new mechanism for the development of NHL and this may provide a new therapeutic target for NHL.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shankland KR, Armitage JO, Hancock BW. Non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Lancet. 2012;380:848–57.
Armitage JO, Gascoyne RD, Lunning MA, Cavalli F. Non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Lancet. 2017;390:298–310.
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66:7–30.
Wilson WH, Jung SH, Porcu P, Hurd D, Johnson J, et al. A Cancer and Leukemia Group B multi-center study of DA-EPOCH-rituximab in untreated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma with analysis of outcome by molecular subtype. Haematologica. 2012;97:758–65.
Otto SP, Walbot V. DNA methylation in eukaryotes: kinetics of demethylation and de novo methylation during the life cycle. Genetics. 1990;124:429–37.
Amara K, Ziadi S, Hachana M, Soltani N, Korbi S, et al. DNA methyltransferase DNMT3b protein overexpression as a prognostic factor in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphomas. Cancer Sci. 2010;101:1722–30.
Bogdanovic O, Veenstra GJ. DNA methylation and methyl-CpG binding proteins: developmental requirements and function. Chromosoma. 2009;118:549–65.
Wang X, Li B. DNMT1 regulates human endometrial carcinoma cell proliferation. Onco Targets Ther. 2017;10:1865–73.
Jones PA, Baylin SB. The fundamental role of epigenetic events in cancer. Nat Rev Genet. 2002;3:415–28.
Bestor TH. The DNA methyltransferases of mammals. Hum Mol Genet. 2000;9:2395–402.
Alkebsi L, Handa H, Sasaki Y, Osaki Y, Yanagisawa K, et al. DNMT3B7 expression related to MENT expression and its promoter methylation in human lymphomas. Leuk Res. 2013;37:1662–7.
Pradhan S, Talbot D, Sha M, Benner J, Hornstra L, et al. Baculovirus-mediated expression and characterization of the full-length murine DNA methyltransferase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997;25:4666–73.
Robertson KD. DNA methylation, methyltransferases, and cancer. Oncogene. 2001;20:3139–55.
Suzuki M, Sunaga N, Shames DS, Toyooka S, Gazdar AF, et al. RNA interference-mediated knockdown of DNA methyltransferase 1 leads to promoter demethylation and gene re-expression in human lung and breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2004;64:3137–43.
Sengupta D, Deb M, Rath SK, Kar S, Parbin S, et al. DNA methylation and not H3K4 trimethylation dictates the expression status of miR-152 gene which inhibits migration of breast cancer cells via DNMT1/CDH1 loop. Exp Cell Res. 2016;346:176–87.
Li Y, Liu X, Guo X, Liu X, Luo J. DNA methyltransferase 1 mediated aberrant methylation and silencing of SHP-1 gene in chronic myelogenous leukemia cells. Leuk Res. 2017;58:9–13.
Capello D, Gloghini A, Baldanzi G, Martini M, Deambrogi C, Lucioni M, et al. Alterations of negative regulators of cytokine signalling in immunodeficiency-related non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Hematol Oncol. 2013;31:22–8.
Koyama M, Oka T, Ouchida M, Nakatani Y, Nishiuchi R, Yoshino T, et al. Activated proliferation of B-cell lymphomas/leukemias with the SHP1 gene silencing by aberrant CpG methylation. Lab Invest. 2003;83:1849–58.
Takino H, Li C, Hu S, Kuo TT, Geissinger E, Muller-Hermelink HK, et al. Primary cutaneous marginal zone B-cell lymphoma: a molecular and clinicopathological study of cases from Asia, Germany, and the United States. Mod Pathol. 2008;21:1517–26.
Fabiani E, Leone G, Giachelia M, D’alo’ F, Greco M, Criscuolo M, et al. Analysis of genome-wide methylation and gene expression induced by 5-aza-2’-deoxycytidine identifies BCL2L10 as a frequent methylation target in acute myeloid leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma. 2010;51:2275–84.
Boosani CS, Dhar K, Agrawal DK. Down-regulation of hsa-miR-1264 contributes to DNMT1-mediated silencing of SOCS3. Mol Biol Rep. 2015;42:1365–76.
Zhang Q, Wang HY, Marzec M, Raghunath PN, Nagasawa T, Wasik MA. STAT3- and DNA methyltransferase 1-mediated epigenetic silencing of SHP-1 tyrosine phosphatase tumor suppressor gene in malignant T lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005;102:6948–53.
Burri N, Shaw P, Bouzourene H, Sordat I, Sordat B, Gillet M, et al. Methylation silencing and mutations of the p14ARF and p16INK4a genes in colon cancer. Lab Invest. 2001;81:217–29.
Zhou W, Chen H, Hong X, Niu X, Lu Q. Knockdown of DNA methyltransferase-1 inhibits proliferation and derepresses tumor suppressor genes in myeloma cells. Oncol Lett. 2014;8:2130–4.
Maduri S. Applicability of RNA interference in cancer therapy: current status. Indian J Cancer. 2015;52:11–21.
Seo JH, Jeong ES, Choi YK. Therapeutic effects of lentivirus-mediated shRNA targeting of cyclin D1 in human gastric cancer. BMC Cancer. 2014;14:175.
Grimm D, Kay MA. RNAi and gene therapy: a mutual attraction. Hematol Am Soc Hematol Educ Progr. 2007;1:473-81.
Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–97.
Chen J, Odenike O, Rowley JD. Leukaemogenesis: more than mutant genes. Nat Rev Cancer. 2010;10:23–36.
Wang YS, Chou WW, Chen KC, Cheng HY, Lin RT, Juo SH. MicroRNA-152 mediates DNMT1-regulated DNA methylation in the estrogen receptor alpha gene. PLoS One. 2012;7:e30635.
Mingozzi F, High KA. Immune responses to AAV vectors: overcoming barriers to successful gene therapy. Blood. 2013;122:23–36.
Rothe M, Modlich U, Schambach A. Biosafety challenges for use of lentiviral vectors in gene therapy. Curr Gene Ther. 2013;13:453–68.
Barrington SF, Mikhaeel NG, Kostakoglu L, Meignan M, Hutchings M, Müeller SP, et al. Role of imaging in the staging and response assessment of lymphoma: consensus of the International Conference on Malignant Lymphomas Imaging Working Group. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32:3048–58.
Meltzer PS. Cancer genomics: small RNAs with big impacts. Nature. 2005;435:745–6.
Jang JY, Choi Y, Jeon YK, Kim CW. Suppression of adenine nucleotide translocase-2 by vector-based siRNA in human breast cancer cells induces apoptosis and inhibits tumor growth in vitro and in vivo. Breast Cancer Res. 2008;10:R11.
Li M, Zhang Y, Bharadwaj U, Zhai QJ, Ahern CH, Fisher WE, et al. Down-regulation of ZIP4 by RNA interference inhibits pancreatic cancer growth and increases the survival of nude mice with pancreatic cancer xenografts. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15:5993–6001.
Tummalapalli P, Gondi CS, Dinh DH, Gujrati M, Rao JS. RNA interference-mediated targeting of urokinase plasminogen activator receptor and matrix metalloproteinase-9 gene expression in the IOMM-lee malignant meningioma cell line inhibits tumor growth, tumor cell invasion and angiogenesis. Int J Oncol. 2007;31:5–17.
Zufferey R, Nagy D, Mandel RJ, Naldini L, Trono D. Multiply attenuated lentiviral vector achieves efficient gene delivery in vivo. Nat Biotechnol. 1997;15:871–5.
Moffat J, Grueneberg DA, Yang X, Kim SY, Kloepfer AM, Hinkle G, et al. A lentiviral RNAi library for human and mouse genes applied to an arrayed viral high-content screen. Cell. 2006;124:1283–98.
Juliano R, Bauman J, Kang H, Ming X. Biological barriers to therapy with antisense and siRNA oligonucleotides. Mol Pharm. 2009;6:686–95.
Scaggiante B, Dapas B, Farra R, Grassi M, Pozzato G, Giansante C, et al. Improving siRNA bio-distribution and minimizing side effects. Curr Drug Metab. 2011;12:11–23.
Jackson AL, Bartz SR, Schelter J, Kobayashi SV, Burchard J, Mao M, et al. Expression profiling reveals off-target gene regulation by RNAi. Nat Biotechnol. 2003;21:635–7.
Chen Y, Gao DY, Huang L. In vivo delivery of miRNAs for cancer therapy: challenges and strategies. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2015;81:128–41.
Si ML, Zhu S, Wu H, Lu Z, Wu F, Mo YY. miR-21-mediated tumor growth. Oncogene. 2007;26:2799–803.
Ji Q, Hao X, Zhang M, Tang W, Yang M, Li L. MicroRNA miR-34 inhibits human pancreatic cancer tumor-initiating cells. PLoS One. 2009;4:e6816.
Xu Q, Jiang Y, Yin Y, Li Q, He J, Jing Y, et al. A regulatory circuit of miR-148a/152 and DNMT1 in modulating cell transformation and tumor angiogenesis through IGF-IR and IRS1. J Mol Cell Biol. 2013;5:3–13.
Acknowledgements
We would like to give our sincere gratitude to the reviewers for their constructive comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, QM., Lian, GY., Song, Y. et al. Downregulation of miR-152 contributes to DNMT1-mediated silencing of SOCS3/SHP-1 in non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Cancer Gene Ther 26, 195–207 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41417-018-0057-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41417-018-0057-7
This article is cited by
-
Epigenetic alterations and advancement of lymphoma treatment
Annals of Hematology (2023)
-
Regulation of DNA methylation machinery by epi-miRNAs in human cancer: emerging new targets in cancer therapy
Cancer Gene Therapy (2021)
-
Overcoming biological barriers to improve solid tumor immunotherapy
Drug Delivery and Translational Research (2021)