Abstract
Objective
To assess the association of volume, size, the availability of highly-specialized professionals and nutrition management of NICUs with treatment quality among VLBW infants.
Study design
A prospective multicenter study of 923 VLBW infants in 66 German NICUs, born between May and October 2013. Using multilevel modeling, we examined the association between the aforementioned organizational characteristics and treatment quality, measured via major morbidities (severe IVH, PVL, BPD, NEC, FIP, ROP, and discharge without severe complications) and medical process measures of VLBW infants.
Results
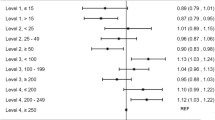
After risk-adjustment and accounting for other NICU characteristics, infants in low-volume NICUs were at higher risk of IVH, ROP and PVL. However, the initial effect of volume on process measures (growth velocity, administration of antenatal steroids) disappeared.
Conclusion
Volume can only partially explain differences in the treatment quality of VLBWs. The underlying organizational mechanisms should be considered to improve the quality of care.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Phibbs CS, Baker LC, Caughey AB, Danielsen B, Schmitt SK, Phibbs RH. Level and volume of neonatal intensive care and mortality in very-low-birth-weight infants. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:2165–75.
Chung JH, Phibbs CS, Boscardin WJ, Kominski GF, Ortega AN, Needleman J. The effect of neonatal intensive care level and hospital volume on mortality of very low birth weight infants. Med Care. 2010;48:635–44.
Jensen EA, Lorch SA. Effects of a birth hospital´s neonatal intensive care unit level and annual volume of very-low-birth-weight infant deliveries on morbidity and mortality. JAMA Pediatr. 2015;169:e151906 https://doi.org/10.1001/jamapediatrics.2015.1906.
Bartels DB, Wypij D, Wenzlaff P, Dammann O, Poets CF. Hospital volume and neonatal mortality among very low birth weight infants. Pediatrics. 2006;117:2206–14.
Eichenwald EC, Stark AR. Management and outcomes of very low birth weight. N Engl J Med. 2008;358:1700–11.
Pollack MM, Koch MA. Association of outcomes with organizational characteristics of neonatal intensive care units. Crit Care Med. 2003;32:1620–8.
Nembhard IM, Edmondson AC. Making it safe: The effects of leader inclusiveness and professional status on psychological safety and improvement efforts in health care teams. J Org Behav. 2006;27:941–66.
Pick V, Halstenberg K, Demel A, Kirchenberger V, Riedel R, Schlößer R, et al. Staff and parents are discriminators for outcomes in neonatal intensive care units. Acta Paediatr. 2014;103:e475–483.
Kusuda S, Fujimura M, Sakuma I, Aotani H, Kabe K, Itani Y, et al. Morbidity and mortality of infants with very low birth weight in japan: center variation. Pediatrics. 2006;118:e1130–8.
Alleman BW, Bell EF, Li L, Dagle JM, Smith PB, Ambalavanan N, et al. Individual and center-level factors affecting mortality among extremely low birth weight infants. Pediatrics. 2013;132:e175–84.
Rysavy MA, Li L, Bell EF, Das A, Hintz SR, Stoll BJ, et al. Between-hospital variation in treatment and outcomes in extremely preterm infants. N Engl J Med. 2015;372:1801–11.
Profit J, Zupancic JAF, Gould JB, Pietz K, Kowalkowski MA, Draper D, et al. Correlation of neonatal intensive care units performance across multiple measures of quality of care. JAMA Pediatr. 2013;167:47–54.
Profit J, Kowalkowski MA, Zupancic JAF, Pietz K, Richardson P, Draper D, et al. Baby-MONITOR: a composite indicator of NICU quality. Pediatrics. 2014;134:74–82.
Shah PS, Mirea L, Ng E, Solimano A, Lee SK. Association of unit size, resource utilization and occupancy with outcomes of preterm infants. J Perinatol. 2015;35:522–9.
Synnes AR, McNab YC, Qiu Z, Ohlsson A, Gustafson P, Dean CB, et al. Neonatal intensive care unit characteristics affect the incidence of severe intraventricular hemorrhage. Med Care. 2006;44:754–9.
Tucker J, UK Neonatal Staffing Study Group. Patient volume, staffing, and workload in relation to risk-adjusted outcomes in a random stratified sample of UK neonatal intensive care units: a prospective evaluation. Lancet. 2002;359:99–107.
Spiegler J, Preuß M, Gebauer C, Bendiks M, Herting E, Göpel W. Does breastmilk influence the development of bronchopulmonary dysplasia? J Pediatr. 2016;169:76–80.
Hair AB, Peluso AM, Hawthorne KM, Perez J, Smith DP, Khan JY, et al. Beyond necrotizing enterocolitis prevention: improving outcomes with an exclusive human milk–based diet. Breastfeed Med. 2016;11:70–4.
Patel AL, Johnson TJ, Engstrom JL, Fogg LF, Jegier BJ, Bigger HR, et al. Impact of early human milk on sepsis and health care costs in very low birth weight infants. J Perinatol. 2013;33:514–9.
Rogowski JA, Horbar JD, Staiger DO, Kenny M, Carpenter J, Geppert J. Indirect vs. direct hospital quality indicators for very-low-birth-weight infants. JAMA. 2004;291:202–9.
Wehby GL, Ullrich F, Xie Y. Very low birth weight hospital volume and mortality—an instrumental variables approach. Med Care. 2012;50:714–21.
Papile LA, Burstein J, Burstein R, Koffler H. Incidence and evolution of subependymal and intraventricular hemorrhage: a study of infants with birth weights less than 1500 g. J Pediatr. 1978;92:529–34.
Göpel W. Komplikationen bei Frühgeborenen. Mon Kinderheilkd. 2016;164:668–72.
Jobe AH, Bancalari E. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Am J Resp Crit Care Med. 2001;163:1723–9.
Patel AL, Engstrom JL, Meier PP, Kimura RE. Accuracy of methods for calculating postnatal growth velocity for extremely low birth weight infants. Pediatrics. 2015;116:1466–73.
Voigt M, Fusch C, Olbertz D, Schneider KTM. Analysis of the neonatal collective in the Federal Republic of Germany. 12th Report: presentation of detailed percentiles for the body measurement of newborns. Geburtsh Frau. 2006;66:956–70.
Parry G, Tucker J, Tarnow-Mordi W. Crib II: An update of the clinical risk index for babies score. Lancet. 2003;361:1789–91.
Institute for applied quality improvement and research in health care. Quality Report 2013. Göttingen; 2014.
Profit J, Gould JB, Bennett M, Goldstein BA, Draper D, Phibbs CS, et al. The association of level of care with NICU quality. Pediatrics. 2016;137:e20144210. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2014-4210.
Esser M, Lack N, Riedel C, Mansmann U, von Kries R. Relevance of hospital characteristics as performance indicators for treatment of very-low-birth-weight neonates. Eur J Public Health. 2014;24:739–44.
Kusuda S, Fujimura M, Uchiyama A, Nakanishi H, Totsu S. Identification of practices and morbidities affecting the mortality of very low birth weight infants using a multilevel logistic analysis: clinical trial or standardization? BMJ Open. 2013;3:e003317. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2013-003317.
Acknowledgements
The study was funded by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (Grant No.: 01GY1152), participating hospitals received financial allowance. The following hospitals and investigators participated in the study (in alphabetical order): Department of Neonatology, Klinikum Frankfurt (Oder): Cornelia Ast, MD; Department of Neonatology, Children’s Hospital, Marienhospital Bottrop gGmbH: Sezgin Ata, MD; Children’s Hospital, St. Vincenz-Krankenhaus GmbH: Björn Beckers, MD; Department of Neonatology and Pediatric Intensive Care, University Medical Center Greifswald: Anke Beyersdorff, MD; Department of Neonatology, Charité University Medical Center Berlin: Christoph Bührer, MD; Children’s Hospital, Klinikum Oberberg GmbH: Salem El-Hamid, MD; Children’s University Hospital, Johannes Wesling Klinikum Minden: Bernhard Erdlenbruch, MD; Department of Neonatology, GFO Kliniken Bonn: St. Marien Hospital: Werner Garbe, MD; Department of Neonatology, Dr. von Hauner Kinderspital, Klinikum der Universität München: O. Genzel-Boroviczény, MD; Department of Neonatology, Christophorus-Kliniken Coesfeld: Hubert Gerleve, MD; Department of Neonatology and Pediatric Intensive Care, Children’s Hospital, Marienhospital Witten: Baham Gharavi, MD; Department of Neonatology, Children’s Hospital Lübeck, University Hospital Schleswig-Holstein: Wolfgang Göpel, MD; Department of Neonatology, St. Marien- und St. Annastiftskrankenhaus: Birgit Görtz, MD; Department of Neonatology and Pediatric Intensive Care, University Hospital Halle, Martin Luther University Halle: Roland Haase, MD; Department of Neonatology, Children’s Hospital, Diakoniekrankenhaus Bad Kreuznach: Edmondo Hammond, MD; Department of Neonatology and Pediatric Intensive Care, Children’s Hospital, Helios Klinikum Krefeld: Peter Heister, MD; Department of Neonatology, Children’s Hospital, University of Witten/Herdecke, Helios University Hospital Wuppertal: Michael Heldmann, MD; Department of Neonatology and Pediatric Intensive Care, Children’s Hospital, University Hospital of Freiburg: Roland Hentschel, MD; Department of Neonatology, Children’s Hospital St. Marien, Landshut: Reinhard Herterich, MD; Department of Neonatology, Children’s Hospital, Krankenhaus St. Elisabeth und St. Barbara Halle (Saale) GmbH: Claudia Heß, MD; Department of Neonatology and Pediatric Intensive Care, Children’s Hospital, Klinikum Itzehoe: Georg Hillebrand, MD; Children’s Hospital, Gesundheitszentrum Rheine, Mathias-Spital: Hans-Georg Hoffmann, MD; Children’s Hospital, Evangelisches Krankenhaus Lippstadt: Thomas Hofmann, MD; Department of Neonatology, Heinrich-Heine-University Düsseldorf: Thomas Höhn, MD; Children’s Hospital, Klinikum Leverkusen gGmbH: Peter Jahn, MD; Children’s Hospital, Evangelisches Waldkrankenhaus Spandau, Berlin: Frank Jochum, MD; Children’s Hospital, OVGU University Magdeburg: Gerhard Jorch, MD; Department of Neonatology Ostbayern, Children’s Hospital, Kliniken Dritter Orden gGmbh Passau: Matthias Keller, MD; Children’s Hospital, Bethlehem Gesundheitszentrum Stolberg gGmbH: Heiner Kentrup, MD; Department of Neonatology, University of Regensburg, Klinik St. Hedwig, Krankenhaus Barmherzige Brüder: Jochen Kittel, MD; Children’s Hospital, Helios Dr. Horst Schmidt Kliniken Wiesbaden: Markus Knuf, MD; Department of Neonatology and Pediatric Intensive Care, Children’s Hospital, Klinikum Links der Weser gGmbH: Hans Thorsten Körner, MD; Department of Neonatology, Städtisches Klinikum Karlsruhe gGmbH: Alexander Krauth, MD; Department of Neonatology, Children’s Hospital, University Hospital of Cologne: Angela Kribs, MD; Department of Neonatology, University Children’s Hospital Göttingen: Helmut Küster, MD; Department of Neonatology, Children’s Hospital, DRK Kliniken Berlin Westend: Arpad von Moers, MD; Department of Neonatology and Pediatric Intensive Care, University Hospital of Bonn: Andreas Müller, MD; Children’s Hospital, Klinikum Kassel: Dirk Müller, MD; Department of Neonatology, Children’s Hospital, Klinikum Memmingen: Ralf Pallacks, MD; Department of Neonatology and Pediatric Intensive Care, DRK Kinderklinik Siegen: Markus Pingel, MD; Department of Neonatology, Children's Hospital, Klinikum Fulda: Reinald Repp, MD; Children’s Hospital, Vivantes Klinikum Neukölln: Rainer Rossi, MD; Department of Neonatology, Children’s Hospital, Katholisches Karl-Leisner-Klinikum gGmbH, St.-Antonius-Hospital, Kleve: Jochen Rübo, MD; Children’s University Hospital, Paracelsius Medizinische Privatuniversität, Klinikum Nürnberg Süd: Stefan Schäfer, MD; Children’s Hospital, St. Joseph-KH Berlin: Antje Schlesinger, MD; Department of Neonatology, Children’s Hospital, University Hospital of Frankfurt: Rolf L. Schlößer, MD; Children’s Hospital, Städtisches Klinikum Dresden/Neustadt: Stefan Schmidt, MD; Department of Neonatology, Children’s Hospital, Klinikum Esslingen GmbH: Christian von Schnakenburg, MD; Department of Neonatology Nordostbayern, St. Marien, Amberg: Alexander Schnelke, MD; Children’s Hospital, Stauferklinikum Schwäbisch Gmünd: Birgit Schwander, MD; Department of Neonatology and Pediatric Intensive Care, Children’s Hospital, Klinikum Worms gGmbH: Heino Skopnik, MD; Children’s Hospital, Harzklinikum Dorothea Christiane Erxleben: Dieter Sontheimer, MD; Department of Neonatology, Children’s Hospital, Klinikum Herford: Uwe Spille, MD; Children’s Hospital, Klinikum Mutterhaus der Borromäerinnen: Wolfgang Thomas, MD; Children’s Hospital, University of Erlangen-Nürnberg: Hans Georg Topf, MD; Department of Neonatology, Children’s Hospital, Klinikum Singen: Andreas Trotter, MD; Department of Neonatology and Pediatric Intensive Care Medicine, Asklepios Klinik Sankt Augustin: Beatrix Wiebe, MD; Department of Neonatology and Pediatric Intensive Care Medicine, Klinikum Aschaffenburg: Christian Wieg, MD; Children’s Hospital, Caritas Hospital Bad Mergentheim: Christian Willaschek, MD; Department of Neonatology, DONAUISAR Klinikum Deggendorf: Michael Welsch, MD; Department of Neonatology and Pediatric Intensive Care, Altonaer Kinderkrankenhaus gGmbH: Axel von der Wense, MD; Department of Neonatology, Children’s Hospital, Carl-Thiem-Klinikum Cottbus gGmbH: Ulrike Wetzel, MD; Department of Neonatology, Main-Kinzig-Kliniken: Manuel Wilhelm, MD; Department of Neonatology, Children’s Hospital Bamberg: Alfons Wolf, MD; Department of General Pediatrics and Neonatology, University Hospital Saarland: Caroline Wollny.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miedaner, F., Langhammer, K., Enke, C. et al. Volume, size, professionals' specialization and nutrition management of NICUs and their association with treatment quality in VLBW infants. J Perinatol 38, 402–410 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41372-017-0036-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41372-017-0036-0