Abstract
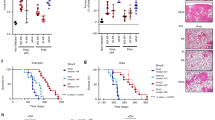
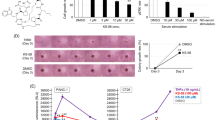
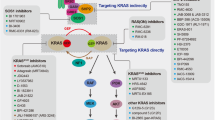
KRAS is one of the most frequently mutated oncogenes in human non-small cell lung cancers (NSCLCs). RAS proteins trigger multiple effector signalling pathways including the highly conserved RAF-MAPK pathway. CRAF, a direct RAS effector protein, is required for KRAS-mediated tumourigenesis. Thus, the molecular mechanisms driving the activation of CRAF are intensively studied. Prohibitin 1 (PHB1) is an evolutionarily conserved adaptor protein and interaction of CRAF with PHB1 at the plasma membrane is essential for CRAF activation. Here, we demonstrate that PHB1 is highly expressed in NSCLC patients and correlates with poor survival. Targeting of PHB1 with two chemical ligands (rocaglamide and fluorizoline) inhibits epidermal growth factor (EGF)/RAS-induced CRAF activation. Consistently, treatment with rocaglamide inhibited proliferation, migration and anchorage-independent growth of KRAS-mutated lung carcinoma cell lines. Surprisingly, rocaglamide treatment inhibited Ras-GTP loading in KRAS-mutated cells as well as in EGF-stimulated cells. Rocaglamide treatment further prevented the oncogenic growth of KRAS-driven lung cancer allografts and xenografts in mouse models. Our results suggest rocaglamide as a RAS inhibitor and that targeting plasma membrane-associated PHB1 with chemical ligands would be a viable therapeutic strategy to combat KRAS-mediated NSCLCs.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Downward J . Targeting RAS signalling pathways in cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 2003; 3: 11–22.
Vasan N, Boyer JL, Herbst RS . A RAS renaissance: emerging targeted therapies for KRAS-mutated non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2014; 20: 3921–3930.
Hopkins AL, Groom CR . The druggable genome. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2002; 1: 727–730.
Mitin N, Rossman KL, Der CJ . Signaling interplay in Ras superfamily function. Curr Biol 2005; 15: R563–R574.
Dhillon AS, Hagan S, Rath O, Kolch W . MAP kinase signalling pathways in cancer. Oncogene 2007; 26: 3279–3290.
Wellbrock C, Karasarides M, Marais R . The RAF proteins take centre stage. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2004; 5: 875–885.
Raman M, Chen W, Cobb MH . Differential regulation and properties of MAPKs. Oncogene 2007; 26: 3100–3112.
Davies H, Bignell GR, Cox C, Stephens P, Edkins S, Clegg S et al. Mutations of the BRAF gene in human cancer. Nature 2002; 417: 949–954.
Rajakulendran T, Sahmi M, Lefrancois M, Sicheri F, Therrien M . A dimerization-dependent mechanism drives RAF catalytic activation. Nature 2009; 461: 542–545.
Downward J . Targeting RAF: trials and tribulations. Nat Med 2011; 17: 286–288.
Fleuren ED, Zhang L, Wu J, Daly RJ . The kinome 'at large' in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2016; 16: 83–98.
Blasco RB, Francoz S, Santamaria D, Canamero M, Dubus P, Charron J et al. c-Raf, but not B-Raf, is essential for development of K-Ras oncogene-driven non-small cell lung carcinoma. Cancer Cell 2011; 19: 652–663.
Dumaz N, Hayward R, Martin J, Ogilvie L, Hedley D, Curtin JA et al. In melanoma, RAS mutations are accompanied by switching signaling from BRAF to CRAF and disrupted cyclic AMP signaling. Cancer Res 2006; 66: 9483–9491.
Rajalingam K, Wunder C, Brinkmann V, Churin Y, Hekman M, Sievers C et al. Prohibitin is required for Ras-induced Raf-MEK-ERK activation and epithelial cell migration. Nat Cell Biol 2005; 7: 837–843.
Fischer A, Baljuls A, Reinders J, Nekhoroshkova E, Sibilski C, Metz R et al. Regulation of RAF activity by 14-3-3 proteins: RAF kinases associate functionally with both homo- and heterodimeric forms of 14-3-3 proteins. J Biol Chem 2009; 284: 3183–3194.
Chiu CF, Ho MY, Peng JM, Hung SW, Lee WH, Liang CM et al. Raf activation by Ras and promotion of cellular metastasis require phosphorylation of prohibitin in the raft domain of the plasma membrane. Oncogene 2013; 32: 777–787.
Mishra S, Ande SR, Nyomba BL . The role of prohibitin in cell signaling. FEBS J 2010; 277: 3937–3946.
Merkwirth C, Dargazanli S, Tatsuta T, Geimer S, Lower B, Wunderlich FT et al. Prohibitins control cell proliferation and apoptosis by regulating OPA1-dependent cristae morphogenesis in mitochondria. Genes Dev 2008; 22: 476–488.
Merkwirth C, Langer T . Prohibitin function within mitochondria: essential roles for cell proliferation and cristae morphogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta 2009; 1793: 27–32.
Polier G, Neumann J, Thuaud F, Ribeiro N, Gelhaus C, Schmidt H et al. The natural anticancer compounds rocaglamides inhibit the Raf-MEK-ERK pathway by targeting prohibitin 1 and 2. Chem Biol 2012; 19: 1093–1104.
Lovly CM, Shaw AT . Molecular pathways: resistance to kinase inhibitors and implications for therapeutic strategies. Clin Cancer Res 2014; 20: 2249–2256.
Lito P, Saborowski A, Yue J, Solomon M, Joseph E, Gadal S et al. Disruption of CRAF-mediated MEK activation is required for effective MEK inhibition in KRAS mutant tumors. Cancer Cell 2014; 25: 697–710.
Luan Z, He Y, Alattar M, Chen Z, He F . Targeting the prohibitin scaffold-CRAF kinase interaction in RAS-ERK-driven pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Mol Cancer 2014; 13: 38.
Rajalingam K, Schreck R, Rapp UR, Albert S . Ras oncogenes and their downstream targets. Biochim Biophys Acta 2007; 1773: 1177–1195.
Niault T, Baccarini M . Targets of Raf in tumorigenesis. Carcinogenesis 2010; 31: 1165–1174.
Manzano JL, Layos L, Buges C, de Los Llanos Gil M, Vila L, Martinez-Balibrea E et al. Resistant mechanisms to BRAF inhibitors in melanoma. Ann Transl Med 2016; 4: 237.
Freeman AK, Ritt DA, Morrison DK . Effects of Raf dimerization and its inhibition on normal and disease-associated Raf signaling. Mol Cell 2013; 49: 751–758.
Weber CK, Slupsky JR, Kalmes HA, Rapp UR . Active Ras induces heterodimerization of cRaf and BRaf. Cancer Res 2001; 61: 3595–3598.
Leevers SJ, Paterson HF, Marshall CJ . Requirement for Ras in Raf activation is overcome by targeting Raf to the plasma membrane. Nature 1994; 369: 411–414.
Sharma A, Qadri A . Vi polysaccharide of Salmonella typhi targets the prohibitin family of molecules in intestinal epithelial cells and suppresses early inflammatory responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004; 101: 17492–17497.
Yurugi H, Tanida S, Ishida A, Akita K, Toda M, Inoue M et al. Expression of prohibitins on the surface of activated T cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2012; 420: 275–280.
Yurugi H, Tanida S, Akita K, Ishida A, Toda M, Nakada H . Prohibitins function as endogenous ligands for Siglec-9 and negatively regulate TCR signaling upon ligation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2013; 434: 376–381.
Ande SR, Mishra S . Palmitoylation of prohibitin at cysteine 69 facilitates its membrane translocation and interaction with Eps 15 homology domain protein 2 (EHD2). Biochem Cell Biol 2010; 88: 553–558.
Doudican NA, Orlow SJ . Inhibition of the CRAF/prohibitin interaction reverses CRAF-dependent resistance to vemurafenib. Oncogene 2016; 36: 423–428.
Becker MS, Schmezer P, Breuer R, Haas SF, Essers MA, Krammer PH et al. The traditional Chinese medical compound Rocaglamide protects nonmalignant primary cells from DNA damage-induced toxicity by inhibition of p53 expression. Cell Death Dis 2014; 5: e1000.
Perez-Perarnau A, Preciado S, Palmeri CM, Moncunill-Massaguer C, Iglesias-Serret D, Gonzalez-Girones DM et al. A trifluorinated thiazoline scaffold leading to pro-apoptotic agents targeting prohibitins. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 2014; 53: 10150–10154.
McCarty Jr KS, Miller LS, Cox EB, Konrath J, McCarty KS Sr . Estrogen receptor analyses. Correlation of biochemical and immunohistochemical methods using monoclonal antireceptor antibodies. Arch Pathol Lab Med 1985; 109: 716–721.
Acknowledgements
We thank Alexandra Dimitrijevic for the excellent technical assistance, and Dr Melzer for her help and advice with the animal experiments. We thank Professors Tyler Jacks, Susan Horwitz, Scott Randell, Channing Der and Ulf Rapp for contributing several constructs and cell lines that are employed in this study. We thank Professor Hartmut Juhl and Dr Bernd Gromoll (Indivumed GmbH) for assistance with the analyses of the NSCLC tissue microarrays. This work is supported through a BIS–PLUS3 fellowship of the Boehringer Ingelheim Stiftuing to KR. KR is a Heisenberg Professor of the DFG (RA1739/4-1) and a GFK fellow. A generous financial support for this work was provided by the ‘Association pour la Recherche sur le Cancer’ to LD. We are also grateful to AAREC Filia Research and the ‘Association Nationale de la Recherche et de la Technologie’ (ANRT) for fellowships to QZ.
Author contributions
HY conceived, designed and performed most of the experiments, analysed, interpreted the data and wrote the manuscript. FM and HB contributed to bioinformatics analyses. CW contributed to the staining and analyses of NSCLC tissue microarray. KD contributed to the design and analysis. QZ and LD contributed to the synthesis of fluorizoline. KR contributed to the conception, design, analysis, interpretation of the data, and wrote the manuscript with input from all the authors and supervised the project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yurugi, H., Marini, F., Weber, C. et al. Targeting prohibitins with chemical ligands inhibits KRAS-mediated lung tumours. Oncogene 36, 4778–4789 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2017.93
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2017.93