Abstract
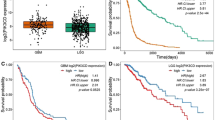
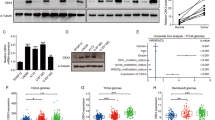
Glioblastoma (GBM) is the most common primary brain tumor and has a dismal prognosis. Amplification of chromosome 12q13-q15 (Cyclin-dependent kinase 4 (CDK4) amplicon) is frequently observed in numerous human cancers including GBM. Phosphoinositide 3-kinase enhancer (PIKE) is a group of GTP-binding proteins that belong to the subgroup of centaurin GTPase family, encoded by CENTG1 located in CDK4 amplicon. However, the pathological significance of CDK4 amplicon in GBM formation remains incompletely understood. In the current study, we show that co-expression of PIKE-A and CDK4 in TP53/PTEN double knockout GBM mouse model additively shortens the latency of glioma onset and survival compared to overexpression of these genes alone. Consequently, p-mTOR, p-Akt and p-ERK pathways are highly upregulated in the brain tumors, in alignment with their oncogenic activities by CDK4 and PIKE-A stably transfected in GBM cell lines. Hence, our findings support that PIKE amplification or overexpression coordinately acts with CDK4 to drive GBM tumorigenesis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. Comprehensive genomic characterization defines human glioblastoma genes and core pathways. Nature 2008; 455: 1061–1068.
Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med 2005; 352: 987–996.
Grzmil M, Hemmings BA . Deregulated signalling networks in human brain tumours. Biochim Biophys Acta 2010; 1804: 476–483.
Khatib ZA, Matsushime H, Valentine M, Shapiro DN, Sherr CJ, Look AT . Coamplification of the CDK4 gene with MDM2 and GLI in human sarcomas. Cancer Res 1993; 53: 5535–5541.
Reifenberger G, Ichimura K, Reifenberger J, Elkahloun AG, Meltzer PS, Collins VP . Refined mapping of 12q13-q15 amplicons in human malignant gliomas suggests CDK4/SAS and MDM2 as independent amplification targets. Cancer Res 1996; 56: 5141–5145.
Wikman H, Nymark P, Vayrynen A, Jarmalaite S, Kallioniemi A, Salmenkivi K et al. CDK4 is a probable target gene in a novel amplicon at 12q13.3-q14.1 in lung cancer. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2005; 42: 193–199.
Muthusamy V, Hobbs C, Nogueira C, Cordon-Cardo C, McKee PH, Chin L et al. Amplification of CDK4 and MDM2 in malignant melanoma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2006; 45: 447–454.
Sherr CJ, Roberts JM . Living with or without cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases. Genes Dev 2004; 18: 2699–2711.
Ye K, Snyder SH . PIKE GTPase: a novel mediator of phosphoinositide signaling. J Cell Sci 2004; 117 (Pt 2): 155–161.
Ahn JY, Hu Y, Kroll TG, Allard P, Ye K . PIKE-A is amplified in human cancers and prevents apoptosis by up-regulating Akt. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004; 101: 6993–6998.
Ahn JY, Rong R, Kroll TG, Van Meir EG, Snyder SH, Ye K . PIKE (phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase enhancer)-A GTPase stimulates Akt activity and mediates cellular invasion. The Journal of biological chemistry 2004; 279: 16441–16451.
Liu X, Hu Y, Hao C, Rempel SA, Ye K . PIKE-A is a proto-oncogene promoting cell growth, transformation and invasion. Oncogene 2007; 26: 4918–4927.
Cerami E, Demir E, Schultz N, Taylor BS, Sander C . Automated network analysis identifies core pathways in glioblastoma. PloS one 2010; 5: e8918.
Kim H, Huang W, Jiang X, Pennicooke B, Park PJ, Johnson MD . Integrative genome analysis reveals an oncomir/oncogene cluster regulating glioblastoma survivorship. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2010; 107: 2183–2188.
Wells JA, McClendon CL . Reaching for high-hanging fruit in drug discovery at protein-protein interfaces. Nature 2007; 450: 1001–1009.
Ivanov AA, Khuri FR, Fu H . Targeting protein-protein interactions as an anticancer strategy. Trends Pharmacol Sci 2013; 34: 393–400.
Qi Q, He K, Liu X, Pham C, Meyerkord C, Fu H et al. Disrupting the PIKE-A/Akt interaction inhibits glioblastoma cell survival, migration, invasion and colony formation. Oncogene 2013; 32: 1030–1040.
Chow LM, Endersby R, Zhu X, Rankin S, Qu C, Zhang J et al. Cooperativity within and among Pten, p53, and Rb pathways induces high-grade astrocytoma in adult brain. Cancer Cell 2011; 19: 305–316.
Marumoto T, Tashiro A, Friedmann-Morvinski D, Scadeng M, Soda Y, Gage FH et al. Development of a novel mouse glioma model using lentiviral vectors. Nat Med 2009; 15: 110–116.
Ye K, Hurt KJ, Wu FY, Fang M, Luo HR, Hong JJ et al. Pike. A nuclear gtpase that enhances PI3kinase activity and is regulated by protein 4.1 N. Cell 2000; 103: 919–930.
Uras N, Oguz SS, Zergeroglu S, Akdag A, Polat B, Dizdar EA et al. CD31 and Factor VIII in angiogenesis of normal and pre-eclamptic human placentas. J Obstet Gynaecol 2012; 32: 533–536.
Proescholdt MA, Merrill MJ, Stoerr EM, Lohmeier A, Pohl F, Brawanski A . Function of carbonic anhydrase IX in glioblastoma multiforme. Neurooncology 2012; 14: 1357–1366.
Lang FF, Miller DC, Pisharody S, Koslow M, Newcomb EW . High frequency of p53 protein accumulation without p53 gene mutation in human juvenile pilocytic, low grade and anaplastic astrocytomas. Oncogene 1994; 9: 949–954.
Zhu H, Acquaviva J, Ramachandran P, Boskovitz A, Woolfenden S, Pfannl R et al. Oncogenic EGFR signaling cooperates with loss of tumor suppressor gene functions in gliomagenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2009; 106: 2712–2716.
Network TC. Corrigendum: Comprehensive genomic characterization defines human glioblastoma genes and core pathways. Nature 2013; 494: 506.
Ma Z, Liu X, Li F, Wang Y, Xu Y, Zhang M et al. Perfluorooctanoic acid induces human Ishikawa endometrial cancer cell migration and invasion through activation of ERK/mTOR signaling. Oncotarget 2016; 7: 66558–66568.
Pathak P, Kumar A, Jha P, Purkait S, Faruq M, Suri A et al. Genetic alterations related to BRAF-FGFR genes and dysregulated MAPK/ERK/mTOR signaling in adult pilocytic astrocytoma. Brain Pathol 2016.
Muranen T, Selfors LM, Hwang J, Gallegos LL, Coloff JL, Thoreen CC et al. ERK and p38 MAPK Activities Determine Sensitivity to PI3K/mTOR Inhibition via Regulation of MYC and YAP. Cancer research 2016; 76: 7168–7180.
Feng C, He K, Zhang C, Su S, Li B, Li Y et al. JNK contributes to the tumorigenic potential of human cholangiocarcinoma cells through the mTOR pathway regulated GRP78 induction. PLoS ONE 2014; 9: e90388.
Liu R, Tian B, Gearing M, Hunter S, Ye K, Mao Z . Cdk5-mediated regulation of the PIKE-A-Akt pathway and glioblastoma cell invasion. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2008; 105: 7570–7575.
He K, Qi Q, Chan CB, Xiao G, Liu X, Tucker-Burden C et al. Blockade of glioma proliferation through allosteric inhibition of JAK2. Sci Signal 2013; 6: ra55.
Zhang S, Qi Q, Chan CB, Zhou W, Chen J, Luo HR et al. Fyn-phosphorylated PIKE-A binds and inhibits AMPK signaling, blocking its tumor suppressive activity. Cell Death Differ 2016; 23: 52–63.
Acknowledgements
This work has been funded in part with Federal funds from National Cancer Institute (NCI), National Institutes of Health (NIH), under the NCI Chemical Biology Consortium Contract HHSN261200800001E (HF; KY), NIH grant RO1 CA186918 (KY), U01 CA168449 (HF), SBTF Foundation (KY), National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.81672781). We are thankful to Dr Suzanne J. Baker for the PTEN/P53 loxP/loxP mice and to the Winship Cancer Institute of Emory University Cancer Center Support Grant P30-CA138292.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qi, Q., Kang, S., Zhang, S. et al. Co-amplification of phosphoinositide 3-kinase enhancer A and cyclin-dependent kinase 4 triggers glioblastoma progression. Oncogene 36, 4562–4572 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2017.67
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2017.67
This article is cited by
-
HMGA1 augments palbociclib efficacy via PI3K/mTOR signaling in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma
Biomarker Research (2023)
-
Familial/inherited cancer syndrome: a focus on the highly consanguineous Arab population
npj Genomic Medicine (2020)
-
SP1 and RARα regulate AGAP2 expression in cancer
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
Cellular energy stress induces AMPK-mediated regulation of glioblastoma cell proliferation by PIKE-A phosphorylation
Cell Death & Disease (2019)