Abstract
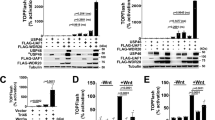
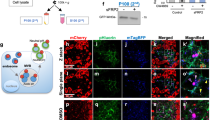
The Wnt pathway has essential roles in cell proliferation, cell fate determination and tumorigenesis by regulating the expression of a wide range of target genes. As a core signaling cascade, the canonical Wnt pathway is regulated at different levels by numerous proteins. We have previously shown that carboxypeptidase E (CPE) is a novel regulator of the canonical Wnt signaling pathway. Here, we show that CPE and the Wnt3a ligand are co-secreted from cells. We show that although the C'-terminal Lys residue of Wnt3a is critical for its activity and is important for the effect of CPE on the Wnt pathway, CPE does not execute its effect by removing this Wnt3a residue. Interestingly, CPE through its N'-terminal sequence, forms aggregates with Wnt3a and possible endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress leading to its loss of function. Together, our current results provide a mechanistic insight into the way CPE regulates the canonical Wnt signaling pathway.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Clevers H . Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in development and disease. Cell 2006; 127: 469–480.
Polakis P . Wnt signaling and cancer. Genes Dev 2000; 14: 1837–1851.
MacDonald BT, Tamai K, He X . Wnt/beta-catenin signaling: components, mechanisms, and diseases. Dev Cell 2009; 17: 9–26.
Cool DR, Normant E, Shen F, Chen HC, Pannell L, Zhang Y et al. Carboxypeptidase E is a regulated secretory pathway sorting receptor: genetic obliteration leads to endocrine disorders in Cpe(fat) mice. Cell 1997; 88: 73–83.
Fricker LD, Snyder SH . Purification and characterization of enkephalin convertase, an enkephalin-synthesizing carboxypeptidase. J Biol Chem 1983; 258: 10950–10955.
Skalka N, Caspi M, Caspi E, Loh YP, Rosin-Arbesfeld R . Carboxypeptidase E: a negative regulator of the canonical Wnt signaling pathway. Oncogene 2013; 32: 2836–2847.
Park JJ, Cawley NX, Loh YP . Carboxypeptidase E cytoplasmic tail-driven vesicle transport is key for activity-dependent secretion of peptide hormones. Mol Endocrinol 2008; 22: 989–1005.
Cawley NX, Wetsel WC, Murthy SR, Park JJ, Pacak K, Loh YP . New roles of carboxypeptidase E in endocrine and neural function and cancer. Endocr Rev 2012; 33: 216–253.
Du C, Zhang C, Li Z, Biswas MH, Balaji KC . Beta-catenin phosphorylated at threonine 120 antagonizes generation of active beta-catenin by spatial localization in trans-Golgi network. PLoS One 2012; 7: e33830.
Reznik SE, Fricker LD . Carboxypeptidases from A to z: implications in embryonic development and Wnt binding. Cell Mol Life Sci 2001; 58: 1790–1804.
Wang L, Shao YY, Ballock RT . Carboxypeptidase Z (CPZ) links thyroid hormone and Wnt signaling pathways in growth plate chondrocytes. J Bone Miner Res 2009; 24: 265–273.
Moeller C, Swindell EC, Kispert A, Eichele G . Carboxypeptidase Z (CPZ) modulates Wnt signaling and regulates the development of skeletal elements in the chicken. Development 2003; 130: 5103–5111.
Shintani T, Klionsky DJ . Autophagy in health and disease: a double-edged sword. Science 2004; 306: 990–995.
Naggert JK, Fricker LD, Varlamov O, Nishina PM, Rouille Y, Steiner DF et al. Hyperproinsulinaemia in obese fat/fat mice associated with a carboxypeptidase E mutation which reduces enzyme activity. Nat Genet 1995; 10: 135–142.
Qian Y, Varlamov O, Fricker LD . Glu300 of rat carboxypeptidase E is essential for enzymatic activity but not substrate binding or routing to the regulated secretory pathway. J Biol Chem 1999; 274: 11582–11586.
Varlamov O, Leiter EH, Fricker L . Induced and spontaneous mutations at Ser202 of carboxypeptidase E. Effect on enzyme expression, activity, and intracellular routing. J Biol Chem 1996; 271: 13981–13986.
Rawlings ND, Barrett AJ . Evolutionary families of metallopeptidases. Methods Enzymol 1995; 248: 183–228.
Liu A, Shao C, Jin G, Liu R, Hao J, Shao Z et al. Downregulation of CPE regulates cell proliferation and chemosensitivity in pancreatic cancer. Tumour Biol 2014; 35: 12459–12465.
Liang XH, Li LL, Wu GG, Xie YC, Zhang GX, Chen W et al. Upregulation of CPE promotes cell proliferation and tumorigenicity in colorectal cancer. BMC Cancer 2013; 13: 412.
Murthy SR, Dupart E, Al-Sweel N, Chen A, Cawley NX, Loh YP . Carboxypeptidase E promotes cancer cell survival, but inhibits migration and invasion. Cancer Lett 2013; 341: 204–213.
Zhou K, Liang H, Liu Y, Yang C, Liu P, Jiang X . Overexpression of CPE-DeltaN predicts poor prognosis in colorectal cancer patients. Tumour Biol 2013; 34: 3691–3699.
Selvaraj P, Huang JS, Chen A, Skalka N, Rosin-Arbesfeld R, Loh YP . Neurotrophic factor-alpha1 modulates NGF-induced neurite outgrowth through interaction with Wnt-3a and Wnt-5a in PC12 cells and cortical neurons. Mol Cell Neurosci 2015; 68: 222–233.
Thouennon E, Cheng Y, Falahatian V, Cawley NX, Loh YP . Rosiglitazone-activated PPARgamma induces neurotrophic factor-alpha1 transcription contributing to neuroprotection. J Neurochem 2015; 134: 463–470.
Qin XY, Cheng Y, Murthy SR, Selvaraj P, Loh YP . carboxypeptidase E-DeltaN, a neuroprotein transiently expressed during development protects embryonic neurons against glutamate neurotoxicity. PLoS One 2014; 9: e112996.
Cheng Y, Cawley NX, Loh YP . Carboxypeptidase E (NF-alpha1): a new trophic factor in neuroprotection. Neurosci Bull 2014; 30: 692–696.
Murthy SR, Thouennon E, Li WS, Cheng Y, Bhupatkar J, Cawley NX et al. Carboxypeptidase E protects hippocampal neurons during stress in male mice by up-regulating prosurvival BCL2 protein expression. Endocrinology 2013; 154: 3284–3293.
Kim HJ, Hong J, Yoon HJ, Yoon YR, Kim SY . Carboxypeptidase E is a novel modulator of RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation. Mol Cells 2014; 37: 685–690.
Bar F, Foh B, Pagel R, Schroder T, Schlichting H, Hirose M et al. Carboxypeptidase E modulates intestinal immune homeostasis and protects against experimental colitis in mice. PLoS One 2014; 9: e102347.
Willert K, Nusse R . Wnt proteins. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2012; 4: a007864.
Holzer T, Liffers K, Rahm K, Trageser B, Ozbek S, Gradl D . Live imaging of active fluorophore labelled Wnt proteins. FEBS Lett 2012; 586: 1638–1644.
Kunz M, Herrmann M, Wedlich D, Gradl D . Autoregulation of canonical Wnt signaling controls midbrain development. Dev Biol 2004; 273: 390–401.
Wallkamm V, Dorlich R, Rahm K, Klessing T, Nienhaus GU, Wedlich D et al. Live imaging of Xwnt5A-ROR2 complexes. PLoS One 2014; 9: e109428.
Rhinn M, Lun K, Luz M, Werner M, Brand M . Positioning of the midbrain-hindbrain boundary organizer through global posteriorization of the neuroectoderm mediated by Wnt8 signaling. Development 2005; 132: 1261–1272.
Sharma K, Ishaq M, Sharma G, Khan MA, Dutta RK, Majumdar S . Pentoxifylline triggers autophagy via ER stress response that interferes with Pentoxifylline induced apoptosis in human melanoma cells. Biochem Pharmacol 2016; 103: 17–28.
Zhang J, Yi M, Zha L, Chen S, Li Z, Li C et al. Sodium butyrate induces endoplasmic reticulum stress and autophagy in colorectal cells: implications for apoptosis. PLoS One 2016; 11: e0147218.
Li X, Wang Y, Wang H, Huang C, Huang Y, Li J . Endoplasmic reticulum stress is the crossroads of autophagy, inflammation, and apoptosis signaling pathways and participates in liver fibrosis. Inflamm Res 2015; 64: 1–7.
He P, Varticovski L, Bowman ED, Fukuoka J, Welsh JA, Miura K et al. Identification of carboxypeptidase E and gamma-glutamyl hydrolase as biomarkers for pulmonary neuroendocrine tumors by cDNA microarray. Hum Pathol 2004; 35: 1196–1209.
Horing E, Harter PN, Seznec J, Schittenhelm J, Buhring HJ, Bhattacharyya S et al. The ‘go or grow’ potential of gliomas is linked to the neuropeptide processing enzyme carboxypeptidase E and mediated by metabolic stress. Acta Neuropathol 2012; 124: 83–97.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Rising Tide Foundation for Clinical Cancer Research, by the Gateway for Cancer Research Foundation and by the Israel Science Foundation (Grant no. 20120016).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Skalka, N., Caspi, M., Lahav-Ariel, L. et al. Carboxypeptidase E (CPE) inhibits the secretion and activity of Wnt3a. Oncogene 35, 6416–6428 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2016.173
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2016.173