Abstract
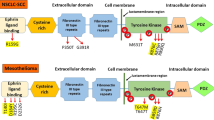
Mesothelioma is an asbestos-associated and notoriously chemotherapy-resistant neoplasm. Activation of the receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs), epidermal growth factor receptor and MET, has been described in subsets of mesothelioma, suggesting that TKs might represent therapeutic targets in this highly lethal disease. We employed proteomic screening by phosphotyrosine immunoaffinity purification and tandem mass spectrometry to characterize RTK activation in mesothelioma cell lines. These assays demonstrated expression and activation of the AXL protein, which is an RTK with known oncogenic properties in non-mesothelial cancer types. AXL was expressed and activated strongly in 8 of 9 mesothelioma cell lines and 6 of 12 mesothelioma biopsies, including each of 12 mesotheliomas with spindle-cell histology. Somatic AXL mutations were not found, but all mesotheliomas expressed an alternatively spliced AXL transcript with in-frame deletion of exon 10, and six of seven mesothelioma cell lines expressed the AXL ligand, growth arrest-specific 6 (GAS6). GAS6 expression appeared to be functionally relevant, as indicated by modulation of AXL tyrosine phosphorylation by knockdown of endogeneous GAS6, and by administration of exogenous GAS6. AXL silencing by lentivirus-mediated short hairpin RNA suppressed mesothelioma migration and cellular proliferation due to G1 arrest. The AXL inhibitor DP-3975 inhibited cell migration and proliferation in mesotheliomas with strong AXL activation. DP-3975 response in these tumors was characterized by inhibition of PI3-K/AKT/mTOR and RAF/MAPK signaling. AXL inhibition suppressed mesothelioma anchorage-independent growth, with reduction in colony numbers and size. These studies suggest that AXL inhibitors warrant clinical evaluation in mesothelioma.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burchert A, Attar EC, McCloskey P, Fridell YW, Liu ET . (1998). Determinants for transformation induced by the Axl receptor tyrosine kinase. Oncogene 16: 3177–3187.
Carbone M, Pass HI, Rizzo P, Marinetti M, Di Muzio M, Mew DJ et al. (1994). Simian virus 40-like DNA sequences in human pleural mesothelioma. Oncogene 9: 1781–1790.
Catalano A, Romano M, Martinotti S, Procopio A . (2002). Enhanced expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) plays a critical role in the tumor progression potential induced by simian virus 40 large T antigen. Oncogene 21: 2896–2900.
Craighead JE, Mossman BT . (1982). The pathogenesis of asbestos-associated diseases. N Engl J Med 306: 1446–1455.
Craven RJ, Xu LH, Weiner TM, Fridell YW, Dent GA, Srivastava S et al. (1995). Receptor tyrosine kinases expressed in metastatic colon cancer. Int J Cancer 60: 791–797.
Demetri GD, Zenzie BW, Rheinwald JG, Griffin JD . (1989). Expression of colony-stimulating factor genes by normal human mesothelial cells and human malignant mesothelioma cells lines in vitro. Blood 74: 940–946.
Faber AC, Li D, Song Y, Liang MC, Yeap BY, Bronson RT et al. (2009). Differential induction of apoptosis in HER2 and EGFR addicted cancers following PI3K inhibition. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106: 19503–19508.
Gschwind A, Fischer OM, Ullrich A . (2004). The discovery of receptor tyrosine kinases: targets for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 4: 361–370.
Harir N, Boudot C, Friedbichler K, Sonneck K, Kondo R, Martin-Lanneree S et al. (2008). Oncogenic Kit controls neoplastic mast cell growth through a Stat5/PI3-kinase signaling cascade. Blood 112: 2463–2473.
Heinrich MC, Corless CL, Duensing A, McGreevey L, Chen CJ, Joseph N et al. (2003). PDGFRA activating mutations in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Science 299: 708–710.
Holland SJ, Powell MJ, Franci C, Chan EW, Friera AM, Atchison RE et al. (2005). Multiple roles for the receptor tyrosine kinase axl in tumor formation. Cancer Res 65: 9294–9303.
Ito T, Ito M, Naito S, Ohtsuru A, Nagayama Y, Kanematsu T et al. (1999). Expression of the Axl receptor tyrosine kinase in human thyroid carcinoma. Thyroid 9: 563–567.
Jacob AN, Kalapurakal J, Davidson WR, Kandpal G, Dunson N, Prashar Y et al. (1999). A receptor tyrosine kinase, UFO/Axl, and other genes isolated by a modified differential display PCR are overexpressed in metastatic prostatic carcinoma cell line DU145. Cancer Detect Prev 23: 325–332.
Jagadeeswaran R, Ma PC, Seiwert TY, Jagadeeswaran S, Zumba O, Nallasura V et al. (2006). Functional analysis of c-Met/hepatocyte growth factor pathway in malignant pleural mesothelioma. Cancer Res 66: 352–361.
Janne PA, Taffaro ML, Salgia R, Johnson BE . (2002). Inhibition of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling in malignant pleural mesothelioma. Cancer Res 62: 5242–5247.
Janssen JW, Schulz AS, Steenvoorden AC, Schmidberger M, Strehl S, Ambros PF et al. (1991). A novel putative tyrosine kinase receptor with oncogenic potential. Oncogene 6: 2113–2120.
Klominek J, Baskin B, Liu Z, Hauzenberger D. . (1998). Hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor stimulates chemotaxis and growth of malignant mesothelioma cells through c-met receptor. Int J Cancer 76: 240–249.
Lay JD, Hong CC, Huang JS, Yang YY, Pao CY, Liu CH et al. (2007). Sulfasalazine suppresses drug resistance and invasiveness of lung adenocarcinoma cells expressing AXL. Cancer Res 67: 3878–3887.
Lee TC, Zhang Y, Aston C, Hintz R, Jagirdar J, Perle MA et al. (1993). Normal human mesothelial cells and mesothelioma cell lines express insulin-like growth factor I and associated molecules. Cancer Res 53: 2858–2864.
Li Y, Ye X, Tan C, Hongo JA, Zha J, Liu J et al. (2009). Axl as a potential therapeutic target in cancer: role of Axl in tumor growth, metastasis and angiogenesis. Oncogene 28: 3442–3455.
Mahadevan D, Cooke L, Riley C, Swart R, Simons B, Della CK et al. (2007). A novel tyrosine kinase switch is a mechanism of imatinib resistance in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Oncogene 26: 3909–3919.
Meric F, Lee WP, Sahin A, Zhang H, Kung HJ, Hung MC . (2002). Expression profile of tyrosine kinases in breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 8: 361–367.
Mukohara T, Civiello G, Davis IJ, Taffaro ML, Christensen J, Fisher DE et al. (2005). Inhibition of the met receptor in mesothelioma. Clin Cancer Res 11: 8122–8130.
O'Bryan JP, Frye RA, Cogswell PC, Neubauer A, Kitch B, Prokop C et al. (1991). axl, a transforming gene isolated from primary human myeloid leukemia cells, encodes a novel receptor tyrosine kinase. Mol Cell Biol 11: 5016–5031.
Ohta Y, Shridhar V, Bright RK, Kalemkerian GP, Du W, Carbone M et al. (1999). VEGF and VEGF type C play an important role in angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis in human malignant mesothelioma tumours. Br J Cancer 81: 54–61.
Pache JC, Janssen YM, Walsh ES, Quinlan TR, Zanella CL, Low RB et al. (1998). Increased epidermal growth factor-receptor protein in a human mesothelial cell line in response to long asbestos fibers. Am J Pathol 152: 333–340.
Pass HI, Liu Z, Wali A, Bueno R, Land S, Lott D et al. (2004). Gene expression profiles predict survival and progression of pleural mesothelioma. Clin Cancer Res 10: 849–859.
Pass HI, Mew DJ, Carbone M, Matthews WA, Donington JS, Baserga R et al. (1996). Inhibition of hamster mesothelioma tumorigenesis by an antisense expression plasmid to the insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor. Cancer Res 56: 4044–4048.
Quong RY, Bickford ST, Ing YL, Terman B, Herlyn M, Lassam NJ . (1994). Protein kinases in normal and transformed melanocytes. Melanoma Res 4: 313–319.
Rubin BP, Singer S, Tsao C, Duensing A, Lux ML, Ruiz R et al. (2001). KIT activation is a ubiquitous feature of gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Cancer Res 61: 8118–8121.
Shaw RJ, Paez JG, Curto M, Yaktine A, Pruitt WM, Saotome I et al. (2001). The Nf2 tumor suppressor, merlin, functions in Rac-dependent signaling. Dev Cell 1: 63–72.
Shieh YS, Lai CY, Kao YR, Shiah SG, Chu YW, Lee HS et al. (2005). Expression of axl in lung adenocarcinoma and correlation with tumor progression. Neoplasia 7: 1058–1064.
Sordella R, Bell DW, Haber DA, Settleman J . (2004). Gefitinib-sensitizing EGFR mutations in lung cancer activate anti-apoptotic pathways. Science 305: 1163–1167.
Stitt TN, Conn G, Gore M, Lai C, Bruno J, Radziejewski C et al. (1995). The anticoagulation factor protein S and its relative, Gas6, are ligands for the Tyro 3/Axl family of receptor tyrosine kinases. Cell 80: 661–670.
Stommel JM, Kimmelman AC, Ying H, Nabioullin R, Ponugoti AH, Wiedemeyer R et al. (2007). Coactivation of receptor tyrosine kinases affects the response of tumor cells to targeted therapies. Science 318: 287–290.
Strizzi L, Catalano A, Vianale G, Orecchia S, Casalini A, Tassi G et al. (2001). Vascular endothelial growth factor is an autocrine growth factor in human malignant mesothelioma. J Pathol 193: 468–475.
Tai KY, Shieh YS, Lee CS, Shiah SG, Wu CW . (2008). Axl promotes cell invasion by inducing MMP-9 activity through activation of NF-kappaB and Brg-1. Oncogene 27: 4044–4055.
Tolnay E, Kuhnen C, Wiethege T, Konig JE, Voss B, Muller KM . (1998). Hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor and its receptor c-Met are overexpressed and associated with an increased microvessel density in malignant pleural mesothelioma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 124: 291–296.
Tsao AS, He D, Saigal B, Liu S, Lee JJ, Bakkannagari S et al. (2007). Inhibition of c-Src expression and activation in malignant pleural mesothelioma tissues leads to apoptosis, cell cycle arrest, and decreased migration and invasion. Mol Cancer Ther 6: 1962–1972.
Varnum BC, Young C, Elliott G, Garcia A, Bartley TD, Fridell YW et al. (1995). Axl receptor tyrosine kinase stimulated by the vitamin K-dependent protein encoded by growth-arrest-specific gene 6. Nature 373: 623–626.
Wimmel A, Glitz D, Kraus A, Roeder J, Schuermann M . (2001). Axl receptor tyrosine kinase expression in human lung cancer cell lines correlates with cellular adhesion. Eur J Cancer 37: 2264–2274.
Xia G, Kumar SR, Masood R, Koss M, Templeman C, Quinn D et al. (2005). Up-regulation of EphB4 in mesothelioma and its biological significance. Clin Cancer Res 11: 4305–4315.
Yang MH, Chang SY, Chiou SH, Liu CJ, Chi CW, Chen PM et al. (2007). Overexpression of NBS1 induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition and co-expression of NBS1 and Snail predicts metastasis of head and neck cancer. Oncogene 26: 1459–1467.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by funding from the International Mesothelioma Program at Brigham and Women's Hospital.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
Dr Flynn is an employee of Deciphera Pharmaceuticals, LLC and has an equity position in Deciphera Pharmaceuticals, LLC. Dr Wise and Dr Lu are employees of Deciphera Pharmaceuticals, LLC. The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ou, WB., Corson, J., Flynn, D. et al. AXL regulates mesothelioma proliferation and invasiveness. Oncogene 30, 1643–1652 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.555
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.555