Abstract
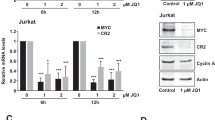
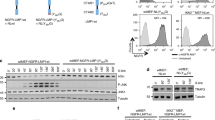
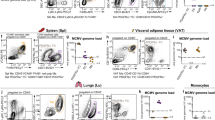
v-Rel is the acutely oncogenic member of the NF-κB family of transcription factors. Infection with retroviruses expressing v-Rel rapidly induces fatal lymphomas in birds and transforms primary lymphocytes and fibroblasts in vitro. We have previously shown that AP-1 transcriptional activity contributes to v-Rel-mediated transformation. Although v-Rel increases the expression of these factors, their activity may also be induced through phosphorylation by the mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs). The expression of v-Rel results in the strong and sustained activation of the ERK and JNK MAPK pathways. This induction is critical for the v-Rel-transformed phenotype, as suppression of MAPK activity with chemical inhibitors or small interfering RNA severely impairs colony formation of v-Rel-transformed lymphoid cell lines. However, signaling must be maintained within an optimal range in these cells, as strong additional activation of either pathway beyond the levels induced by v-Rel through the expression of constitutively active MAPK proteins attenuates the transformed phenotype. MAPK signaling also has an important role in the initial transformation of primary spleen cells by v-Rel, although distinct requirements for MAPK activity at different stages of v-Rel-mediated transformation were identified. We also show that the ability of v-Rel to induce MAPK signaling more strongly than c-Rel contributes to its greater oncogenicity.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Basseres DS, Baldwin AS . (2006). Nuclear factor-κB and inhibitor of κB kinase pathways in oncogenic initiation and progression. Oncogene 25: 6817–6830.
Blume-Jensen P, Hunter T . (2001). Oncogenic kinase signalling. Nature 411: 355–365.
Bode AM, Dong Z . (2007). The functional contrariety of JNK. Mol Carcinog 46: 591–598.
Bonizzi G, Karin M . (2004). The two NF-κB activation pathways and their role in innate and adaptive immunity. Trends Immunol 25: 280–288.
Bost F, McKay R, Bost M, Potapova O, Dean NM, Mercola D . (1999). The Jun kinase 2 isoform is preferentially required for epidermal growth factor-induced transformation of human A549 lung carcinoma cells. Mol Cell Biol 19: 1938–1949.
Bubendorf L, Kononen J, Koivisto P, Schraml P, Moch H, Gasser TC et al. (1999). Survey of gene amplifications during prostate cancer progression by high-throughout fluorescence in situ hybridization on tissue microarrays. Cancer Res 59: 803–806.
Bunting K, Rao S, Hardy K, Woltring D, Denyer GS, Wang J et al. (2007). Genome-wide analysis of gene expression in T cells to identify targets of the NF-κB transcription factor c-Rel. J Immunol 178: 7097–7109.
Chen N, Nomura M, She QB, Ma WY, Bode AM, Wang L et al. (2001). Suppression of skin tumorigenesis in c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase-2-deficient mice. Cancer Res 61: 3908–3912.
Corzo C, Corominas JM, Tusquets I, Salido M, Bellet M, Fabregat X et al. (2006). The MYC oncogene in breast cancer progression: from benign epithelium to invasive carcinoma. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 165: 151–156.
Courtois-Cox S, Jones SL, Cichowski K . (2008). Many roads lead to oncogene-induced senescence. Oncogene 27: 2801–2809.
Dhillon AS, Hagan S, Rath O, Kolch W . (2007). MAP kinase signalling pathways in cancer. Oncogene 26: 3279–3290.
Dutta J, Fan Y, Gupta N, Fan G, Gelinas C . (2006). Current insights into the regulation of programmed cell death by NF-κB. Oncogene 25: 6800–6816.
Fujii M, Minamino T, Nomura M, Miyamoto KI, Tanaka J, Seiki M . (1996). Selective activation of the proto-oncogene c-jun promoter by the transforming protein v-Rel. Oncogene 12: 2193–2202.
Gilmore TD . (1999). Multiple mutations contribute to the oncogenicity of the retroviral oncoprotein v-Rel. Oncogene 18: 6925–6937.
Gilmore TD, Kalaitzidis D, Liang MC, Starczynowski DT . (2004). The c-Rel transcription factor and B-cell proliferation: a deal with the devil. Oncogene 23: 2275–2286.
Gupta N, Delrow J, Drawid A, Sengupta AM, Fan G, Gelinas C . (2008). Repression of B-cell linker (BLNK) and B-cell adaptor for phosphoinositide 3-kinase (BCAP) is important for lymphocyte transformation by rel proteins. Cancer Res 68: 808–814.
Hayden MS, Ghosh S . (2004). Signaling to NF-κB. Genes Dev 18: 2195–2224.
Holtmann H, Winzen R, Holland P, Eickemeier S, Hoffmann E, Wallach D et al. (1999). Induction of interleukin-8 synthesis integrates effects on transcription and mRNA degradation from at least three different cytokine- or stress-activated signal transduction pathways. Mol Cell Biol 19: 6742–6753.
Houben R, Vetter-Kauczok CS, Ortmann S, Rapp UR, Broecker EB, Becker JC . (2008). Phospho-ERK staining is a poor indicator of the mutational status of BRAF and NRAS in human melanoma. J Invest Dermatol 128: 2003–2012.
Karakosta A, Golias C, Charalabopoulos A, Peschos D, Batistatou A, Charalabopoulos K . (2005). Genetic models of human cancer as a multistep process. Paradigm models of colorectal cancer, breast cancer, and chronic myelogenous and acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 24: 505–514.
Karin M . (2006). Nuclear factor-κB in cancer development and progression. Nature 441: 431–436.
Kennedy NJ, Sluss HK, Jones SN, Bar-Sagi D, Flavell RA, Davis RJ . (2003). Suppression of Ras-stimulated transformation by the JNK signal transduction pathway. Genes Dev 17: 629–637.
Kralova J, Liss AS, Bargmann W, Bose Jr HR . (1998). AP-1 factors play an important role in transformation induced by the v-rel oncogene. Mol Cell Biol 18: 2997–3009.
Kralova J, Schatzle JD, Liss AS, Bargmann W, Bose Jr HR . (1996). Synergistic stimulation of avian IκBα transcription by rel and fos/jun factors. Oncogene 12: 2595–2604.
Lin A . (2003). Activation of the JNK signaling pathway: breaking the brake on apoptosis. Bioessays 25: 17–24.
Liss AS, Tiwari R, Kralova J, Bose Jr HR . (2010). Cell transformation by v-Rel reveals distinct roles of AP-1 family members in Rel/NF-κB oncogenesis. Oncogene 29: 4925–4937.
Majid SM, Liss AS, You M, Bose Jr HR . (2006). The suppression of SH3BGRL is important for v-Rel-mediated transformation. Oncogene 25: 756–768.
Mansour SJ, Matten WT, Hermann AS, Candia JM, Rong S, Fukasawa K et al. (1994). Transformation of mammalian cells by constitutively active MAP kinase kinase. Science 265: 966–970.
McCubrey JA, Steelman LS, Chappell WH, Abrams SL, Wong EW, Chang F et al. (2007). Roles of the Raf/MEK/ERK pathway in cell growth, malignant transformation and drug resistance. Biochim Biophys Acta 1773: 1263–1284.
Murphy LO, Blenis J . (2006). MAPK signal specificity: the right place at the right time. Trends Biochem Sci 31: 268–275.
Nehyba J, Hrdlicková R, Bose Jr HR . (1997). Differences in κB DNA-binding properties of v-Rel and c-Rel are the result of oncogenic mutations in three distinct functional regions of the Rel protein. Oncogene 14: 2881–2897.
Nelson DM, Wahlfors JJ, Chen L, Onodera M, Morgan RA . (1998). Characterization of diverse viral vector preparations, using a simple and rapid whole-virion dot-blot method. Hum Gene Ther 9: 2401–2405.
Nielsen C, Thastrup J, Bottzauw T, Jaattela M, Kallunki T . (2007). c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase 2 is required for Ras transformation independently of activator protein 1. Cancer Res 67: 178–185.
Okuno H, Suzuki T, Yoshida T, Hashimoto Y, Curran T, Iba H . (1991). Inhibition of jun transformation by a mutated fos gene: design of an anti-oncogene. Oncogene 6: 1491–1497.
Oleinik NV, Krupenko NI, Krupenko SA . (2007). Cooperation between JNK1 and JNK2 in activation of p53 apoptotic pathway. Oncogene 26: 7222–7230.
Potapova O, Anisimov SV, Gorospe M, Dougherty RH, Gaarde WA, Boheler KR et al. (2002). Targets of c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase 2-mediated tumor growth regulation revealed by serial analysis of gene expression. Cancer Res 62: 3257–3263.
Pratilas CA, Taylor BS, Ye Q, Viale A, Sander C, Solit DB et al. (2009). (V600E)BRAF is associated with disabled feedback inhibition of RAF-MEK signaling and elevated transcriptional output of the pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106: 4519–4524.
Raman M, Chen W, Cobb MH . (2007). Differential regulation and properties of MAPKs. Oncogene 26: 3100–3112.
Robinson MJ, Stippec SA, Goldsmith E, White MA, Cobb MH . (1998). A constitutively active and nuclear form of the MAP kinase ERK2 is sufficient for neurite outgrowth and cell transformation. Curr Biol 8: 1141–1150.
Sewing A, Wiseman B, Lloyd AC, Land H . (1997). High-intensity Raf signal causes cell cycle arrest mediated by p21Cip1. Mol Cell Biol 17: 5588–5597.
Shaulian E, Karin M . (2002). AP-1 as a regulator of cell life and death. Nat Cell Biol 4: E131–E136.
Skarpen E, Flinder LI, Rosseland CM, Orstavik S, Wierød L, Oksvold MP et al. (2008). MEK1 and MEK2 regulate distinct functions by sorting ERK2 to different intracellular compartments. FASEB J 22: 466–476.
Suzukawa K, Weber TJ, Colburn NH . (2002). AP-1, NF-κB, and ERK activation thresholds for promotion of neoplastic transformation in the mouse epidermal JB6 model. Environ Health Perspect 110: 865–870.
Tsavachidou D, Coleman ML, Athanasiadis G, Li S, Licht JD, Olson MF et al. (2004). SPRY2 is an inhibitor of the ras/extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway in melanocytes and melanoma cells with wild-type BRAF but not with the V599E mutant. Cancer Res 64: 5556–5559.
Ussar S, Voss T . (2004). MEK1 and MEK2, different regulators of the G1/S transition. J Biol Chem 279: 43861–43869.
Whitmarsh AJ, Davis RJ . (2007). Role of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 4 in cancer. Oncogene 26: 3172–3184.
Woods D, Parry D, Cherwinski H, Bosch E, Lees E, McMahon M . (1997). Raf-induced proliferation or cell cycle arrest is determined by the level of Raf activity with arrest mediated by p21Cip1. Mol Cell Biol 17: 5598–5611.
Yang YM, Bost F, Charbono W, Dean N, McKay R, Rhim JS et al. (2003). c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase mediates proliferation and tumor growth of human prostate carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 9: 391–401.
Yoon S, Seger R . (2006). The extracellular signal-regulated kinase: multiple substrates regulate diverse cellular functions. Growth Factors 24: 21–44.
Zheng C, Xiang J, Hunter T, Lin A . (1999). The JNKK2-JNK1 fusion protein acts as a constitutively active c-Jun kinase that stimulates c-Jun transcription activity. J Biol Chem 274: 28966–28971.
Acknowledgements
We thank the laboratories of Natalie Ahn and Aming Lin for generously providing the CA MKK constructs. This work was supported by Public Health Service grants CA33192 and CA098151 from the National Cancer Institute. Jarmila Kralova was supported, in part, by grant KAN200200651 from the Grant Agency of the Academy of Sciences of the Czech Republic. We also thank R Hrdlicková and J Nehyba for their critical reading of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kralova, J., Sheely, J., Liss, A. et al. ERK and JNK activation is essential for oncogenic transformation by v-Rel. Oncogene 29, 6267–6279 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.359
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.359