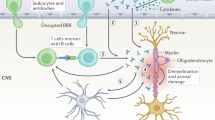
Abstract
Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIDP) is the most common chronic autoimmune neuropathy. Despite clinical challenges in diagnosis—owing in part to the existence of disease variants, and different views on how many electrophysiological abnormalities are needed to document demyelination—consensus criteria seem to have been reached for research or clinical practice. Current standard of care involves corticosteroids, intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIg) and/or plasmapheresis, which provide short-term benefits. Maintenance therapy with IVIg can induce sustained remission, increase quality of life and prevent further axonal loss, but caution is needed to avoid overtreatment. Commonly used immunosuppressive drugs offer minimal benefit, necessitating the development of new therapies for treatment-refractory patients. Advances in our understanding of the underlying immunopathology in CIDP have identified new targets for future therapeutic efforts, including T cells, B cells, and transmigration and transduction molecules. New biomarkers and scoring systems represent emerging tools with the potential to predict therapeutic responses and identify patients with active disease for enrollment into clinical trials. This Review highlights the recent advances in diagnosing CIDP, provides an update on the immunopathology including new target antigens, and discusses current treatments, ongoing challenges and future therapeutic directions.
Key Points
-
Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIDP) is the most common acquired chronic autoimmune neuropathy
-
Despite disease heterogeneity, recently revised diagnostic criteria provide an optimal balance between sensitivity and specificity
-
Molecules within the non-compact myelin and points of Schwann cell–axon interaction, rather than within compact myelin, seem to be the putative target antigens
-
Corticosteroids, intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIg) and plasmapheresis provide short-term benefits; IVIg is used for long-term maintenance
-
Potential new therapeutic approaches involve targeting key factors in the immunopathogenesis of CIDP, including T cells, B cells and complement
-
Progress in clinical trial design is focused on clinically meaningful tools to define therapeutic responses, enrolling only patients with active disease and exploring biomarkers that predict response to therapies
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Austin, J. H. Recurrent polyneuropathies and their corticosteroid treatment. Brain 81, 11–192 (1958).
Dyck, P. J. et al. Chronic inflammatory polyradiculoneuropathy. Mayo Clin. Proc. 50, 621–637 (1975).
Prineas, J. W. & McLeod, J. G. Chronic relapsing polyneuritis J. Neurol. Sci. 27, 427–458 (1976).
Dalakas, M. C. in Clinical Immunology: Principles and Practice 3rd edn (eds Rich, R. R. et al.) 977–994 (Mosby Elsevier, Philadelphia, 2008).
Koller, H., Kieseier, B. C., Jander, S. & Hartung, H. P. Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 352, 1343–1356 (2005).
Lauria, G. et al. European Federation of Neurological Societies/Peripheral Nerve Society Guideline on the use of skin biopsy in the diagnosis of small fiber neuropathy. Report of a joint task force of the European Federation of Neurological Societies and the Peripheral Nerve Society. Eur. J. Neurol. 17, 903–912 (2010).
Dalakas, M. C. & Engel, W. K. Chronic relapsing (dysimmune) polyneuropathy: pathogenesis and treatment. Ann. Neurol. 10, 134–145 (1981).
Hughes, R. A. C., Allen, D., Makowska, A. & Gregson, N. A. Pathogenesis of chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy. J. Periph. Nerv. Syst. 11, 30–46 (2006).
Vallat, J. M., Sommer, C. & Magy, L. Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy: diagnostic and therapeutic challenges for a treatable condition. Lancet Neurol. 9, 402–412 (2010).
Said, G. Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. Neuromuscul. Disord. 16, 293–303 (2006).
Dalakas, M. C., Teravinen, H. & Engel, W. K. Tremor as a feature of chronic relapsing and dysgammaglobulinemic polyneuropathies: incidence and management. Arch. Neurol. 41, 711–714 (1984).
Ryan, M. M., Grattan-Smith, P. J., Procopis, P. G., Morgan, G. & Ouvrier, R. A. Childhood chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy: clinical course and long-term outcome. Neuromuscul. Disord. 10, 398–406 (2000).
Nevo, Y. et al. Childhood chronic inflammatory demyelinating neuropathies: clinical course and long-term follow-up. Neurology 47, 98–102 (1996).
Sladky, J. T. & Teasley, J. E. What is the best initial treatment for childhood CIDP: corticosteroids or IVIg? Muscle Nerve 38, 1638–1643 (2008).
Saperstein, D. S. et al. Multifocal acquired demyelinating sensory and motor neuropathy: the Lewis–Sumner syndrome. Muscle Nerve 22, 560–566 (1999).
Lewis, R. A., Sumner, A. J., Brown, M. J. & Asbury, A. K. Multifocal demyelinating neuropathy with persistent conduction block. Neurology 32, 958–964 (1982).
Sabatelli, M. et al. Pure motor chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. J. Neurol. 248, 772–777 (2001).
Oh, S. J., Joy, J. L. & Kuruoglu, R. “Chronic sensory demyelinating neuropathy”: chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy presenting as a pure sensory neuropathy. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 55, 677–680 (1992).
Sinnreich, M. et al. Chronic immune sensory polyradiculopathy: a possibly treatable sensory ataxia. Neurology 63, 1662–1669 (2004).
Katz, J. S., Saperstein, D. S., Gronseth, G., Amato, A. A. & Barohn, R. J. Distal acquired demyelinating symmetric neuropathy. Neurology 54, 615–620 (2000).
Lunn, M. P., Manji, H., Choudhary, P. P., Hughes, R. A. & Thomas, P. K. Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy: a prevalence study in south east England. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 66, 677–680 (1999).
Laughlin, R. S., Dyck, P. J., Melton, L. J. 3rd, Leibson, C. & Ransom, J. Incidence and prevalence of CIDP and the association of diabetes mellitus. Neurology 73, 39–45 (2009).
Mygland, A. & Monstad, P. Chronic polyneuropathies in Vest-Agder, Norway. Eur. J. Neurol. 8, 157–165 (2001).
Iijima, M. et al. Prevalence and incidence rates of chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy in the Japanese population. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 79, 1040–1043 (2008).
Rajabally, Y. A., Simpson, B. S., Beri, S., Bankart, J. & Gosalakkal, J. A. Epidemiologic variability of chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy with different diagnostic criteria: study of a UK population. Muscle Nerve 39, 432–438 (2009).
Chiò, A. et al. Idiopathic chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy: an epidemiological study in Italy. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 78, 1349–1353 (2007).
Uncini, A. et al. Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy in diabetics: motor conductions are important in the differential diagnosis with diabetic polyneuropathy. Clin. Neurophysiol. 110, 705–711 (1999).
Chiò, A. et al. Comorbidity between CIDP and diabetes mellitus: only a matter of chance? Eur. J. Neurol. 16, 752–754 (2009).
Sharma, K. R. et al. Demyelinating neuropathy in diabetes mellitus. Arch. Neurol. 59, 758–765 (2002).
Rotta, F. T. et al. The spectrum of chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. J. Neurol. Sci. 173, 129–139 (2000).
Mendell, J. R. et al. Evidence for central nervous system demyelination in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy. Neurology 37, 1291–1294 (1987).
Sharma, K. R. et al. Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy associated with multiple sclerosis. J. Clin. Neuromuscul. Dis. 9, 385–396 (2008).
Dyck, P. J., Swanson, C. J., Low, P. A., Bartleson, J. D. & Lambert, E. H. Prednisone-responsive hereditary motor and sensory neuropathy. Mayo Clin. Proc. 57, 239–246 (1982).
Notturno, F. et al. Susceptibility to chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy is associated to polymorphic GA repeat in the SH2D2A gene. J. Neuroimmunol. 197, 124–127 (2008).
American Academy of Neurology AIDS Task Force. Research criteria for diagnosis of chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIDP). Neurology 41, 617–618 (1991).
Odaka, M., Yuki, N. & Hirata, K. Patients with chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy initially diagnosed as Guillain–Barré syndrome. J. Neurol. 250, 913–916 (2003).
Ruts, L., van Koningsveld, R. & van Doorn, P. A. Distinguishing acute-onset CIDP from Guillain–Barré syndrome with treatment related fluctuations. Neurology 65, 138–140 (2005).
Ruts, L., Drenthen, J., Jacobs, B. C. & van Doorn, P. A; Dutch GBS Study Group. Distinguishing acute-onset CIDP from fluctuating Guillain–Barré syndrome: a prospective study. Neurology 74, 1680–1686 (2010).
Alshekhlee, A., Basiri, K., Miles, J. D., Ahmad, S. A. & Katirji, B. Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy associated with tumor necrosis factor-α antagonists. Muscle Nerve 41, 723–727 (2010).
Bromberg, M. B. Review of the evolution of electrodiagnostic criteria for CIDP. Muscle Nerve 43, 780–794 (2011).
Brannagan, T. H. 3rd. The current diagnosis of CIDP: the need for biomarkers. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 16, 3–13 (2011).
Lewis, R. A. & Sumner, A. J. The electrodiagnostic distinctions between chronic familial and acquired demyelinative neuropathies. Neurology 32, 592–596 (1982).
Sommer, C. et al. Macrophage clustering as a diagnostic marker in sural nerve biopsies of patients with CIDP. Neurology 65, 1924–1929 (2005).
Vital, C. et al. Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy: immunopathological and ultrastructural study of peripheral nerve biopsy in 42 cases. Ultrastruct. Pathol. 24, 363–369 (2000).
Adachi, Y. et al. Brachial and lumbar plexuses in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy: MRI assessment including apparent diffusion coefficient. Neuroradiology 53, 3–11 (2011).
Nicolas, G. et al. Proposed revised electrophysiological criteria for chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy. Muscle Nerve 25, 26–30 (2002).
Van den Bergh, P. Y. & Pieret, F. Electrodiagnostic criteria for acute and chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy. Muscle Nerve 29, 565–574 (2004).
Magda, P. et al. Comparison of electrodiagnostic abnormalities and criteria in a cohort of patients with CIDP. Arch. Neurol. 60, 1755–1759 (2003).
Chan, Y. C. et al. Predicting response to treatment in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 77, 114–116 (2006).
Haq, R. U. et al. Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy—a study of proposed electrodiagnostic and histologic criteria. Arch. Neurol. 57, 1745–1750 (2000).
Thaisetthawatkul, P., Logigian, E. L. & Herrmann, D. N. Dispersion of the distal compound muscle action potential as a diagnostic criterion for chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. Neurology 59, 1526–1532 (2002).
De Sousa, E. A, Chin, R. L., Sander, H. W., Ltob, N. & Brannagean, T. H. 3rd. Demyelinating findings in typical and atypical CIDP: sensitivity and specificity. J. Clin. Neuromusc. Dis. 10, 163–169 (2009).
Rajabally, Y. A. et al. Validity of diagnostic criteria for chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy: a multicentre European study. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry. 80, 1364–1368 (2009).
Koski, C. L. et al. Derivation and validation of diagnostic criteria for chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. J. Neurol. Sci. 277, 1–8 (2009).
Bird, S. J., Brown, M. J., Shy, M. E. & Scherer, S. S. Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy associated with malignant melanoma. Neurology 46, 822–824 (1996).
Tsuchida, T., Saxton, R. E., Morton, D. L. & Irie, R. F. Gangliosides of human melanoma. Cancer 63, 1166–1174 (1989).
Weiss, M. D. et al. Molecular mimicry in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy and melanoma. Neurology 51, 1738–1741 (1998).
Kiefer, R. et al. Enhanced B7 costimulatory molecule expression in inflammatory human sural nerve biopsies. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 69, 362–368 (2000).
Murata, K. & Dalakas, M. C. Expression of the co-stimulatory molecule BB-1, the ligands CTLA-4 and CD28 and their mRNAs in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. Brain 123, 1660–1666 (2000).
Hu, W. et al. Expression of CD28-related costimulatory molecule and its ligand in inflammatory neuropathies. Neurology 68, 277–282 (2007).
Salomon, B. et al. Development of spontaneous autoimmune peripheral polyneuropathy in B7-2-deficient NOD mice. J. Exp. Med. 194, 677–684 (2001).
Chi, L. J. et al. Distribution of Th17 cells and Th1 cells in peripheral blood and cerebrospinal fluid in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 15, 345–356 (2010).
Chi, L. J., Wang, H. B. & Wang, W. Z. Impairment of circulating CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells in patients with chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 13, 54–63 (2008).
Sanvito, L., Makowska, A., Gregson, N., Nemni, R. & Hughes, R. A. Circulating subsets and CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cell function in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy. Autoimmunity 42, 667–677 (2009).
Hartung, H. P., Reiners, K., Schmidt, B., Stoll, G. & Toyka, K. V. Serum interleukin-2 concentrations in Guillain–Barré syndrome and chronic idiopathic demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy: comparison with other neurological diseases of presumed immunopathogenesis. Ann. Neurol. 30, 48–53 (1991).
Kieseier, B. C. et al. Chemokines and chemokine receptors in inflammatory demyelinating neuropathies: a central role for IP-10. Brain 125, 823–834 (2002).
Mahad, D. J., Howell, S. J. & Woodroofe, M. N. Expression of chemokines in cerebrospinal fluid and serum of patients with chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 73, 320–323 (2002).
Maimone, D., Annunziata, P., Simone, I. L., Livrea, P. & Guazzi, G. C. Interleukin-6 levels in the cerebrospinal fluid and serum of patients with Guillain–Barré syndrome and chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy. J. Neuroimmunol. 47, 55–61 (1993).
Oka, N. et al. Expression of endothelial leukocyte adhesion molecule-1 (ELAM-1) in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. Neurology 44, 946–950 (1994).
Renaud, S. et al. Gene expression profiling in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. J. Neuroimmunol. 159, 203–214 (2005).
Lee, G., Xiang, Z., Brannagan, T. H. 3rd, Chin, R. L. & Latov, N. Differential gene expression in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIDP) skin biopsies. J. Neurol. Sci. 290, 115–122 (2010).
Yan, W. X., Taylor, J., Andrias-Kauba, S. & Pollard, J. D. Passive transfer of demyelination by serum or IgG from chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy patients. Ann. Neurol. 47, 765–775 (2000).
Dalakas, M. C. & Engel, W. K. Immunoglobulin and complement deposits in nerves of patients with chronic relapsing polyneuropathy. Arch. Neurol. 37, 637–640 (1980).
Ilyas, A. A., Mitchen, F. A., Dalakas, M. C., Chen, Z. W. & Cook, S. D. Antibodies to acidic glycolipids in Guillain–Barré syndrome and chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. J. Neurol. Sci. 107, 1111–1121 (1992).
Tagawa, Y., Yuki, N. & Hirata, K. Anti-SGPG antibody in CIDP: a nosological position of IgM anti-MAG/SGPG antibody-associated neuropathy. Muscle Nerve 23, 895–899 (2000).
Yan, W. X., Archelos, J. J., Hartung, H. P. & Pollard, J. D. P0 protein is a target antigen in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy. Ann. Neurol. 50, 286–292 (2001).
Dalakas, M., Houff, S. A., Engel, W. K., Madden, D. L. & Sever, J. L. CSF monoclonal bands in chronic relapsing polyneuropathy. Neurology 30, 864–867 (1980).
Tackenberg, B. et al. Impaired inhibitory Fcγ receptor IIB expression on B cells in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 106, 4788–4792 (2009).
Cifuentes-Diaz, C. et al. Nodes of Ranvier and paranodes in chronic acquired neuropathies. PLoS ONE 6, e14533 (2011).
Lonigro, A. & Devaux, J. J. Disruption of neurofascin and gliomedin at nodes of Ranvier precedes demyelination in experimental allergic neuritis. Brain 132, 260–273 (2009).
Pollard, J. D. & Armati, P. J. CIDP—the relevance of recent advances in Schwann cell/axonal neurobiology J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 16, 15–23 (2011).
Yan, W. X., Mathey, E., Yiannikas, C. & Pollard, J. Antineurofascin antibodies are present in patients with peripheral demyelinating neuropathies and mediate changes in nerve conduction in animals. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 15, 288–289 (2010).
Iijima, M. et al. Single nucleotide polymorphism of TAG-1 influences IVIg responsiveness of Japanese patients with CIDP. Neurology 73, 1348–1352 (2009).
Dyck, P. J. et al. Prednisone improves chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy more than no treatment. Ann. Neurol. 11, 136–141 (1982).
Hughes, R. et al. Randomized controlled trial of intravenous immunoglobulin versus oral prednisolone in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy. Ann. Neurol. 50, 195–201 (2001).
Muley, S. A., Kelkar, P. & Parry, G. J. Treatment of chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy with pulsed oral steroids. Arch. Neurol. 65, 1460–1464 (2008).
van Schaik, I. N. et al. Pulsed high-dose dexamethasone versus standard prednisolone treatment for chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy (PREDICT study): a double-blind, randomised, controlled trial. Lancet Neurol. 9, 245–253 (2010).
Lopate, G., Pestronk, A. & Al-Lozi, M. Treatment of chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy with high-dose intermittent intravenous methylprednisolone. Arch. Neurol. 62, 249–254 (2005).
Mendell, J. R. et al. Randomized controlled trial of IVIg in untreated chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy. Neurology 56, 445–449 (2001).
Hahn, A. F. Treatment of chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy with intravenous immunoglobulin. Neurology 51 (6 Suppl. 5), S16–S21 (1998).
Vermeulen, M. et al. Intravenous immunoglobulin treatment in patients with chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy: a double blind, placebo controlled study. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 56, 36–39 (1993).
Dyck, P. J. et al. A plasma exchange versus immune globulin infusion trial in chronic inflamatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy. Ann. Neurol. 36, 838–845 (1994).
van Doorn, P. A., Brand, A., Strengers, P. F., Meulstee, J. & Vermeulen, M. High-dose intravenous immunoglobulin treatment in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy: a double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover study. Neurology 40, 209–212 (1990).
Hughes, R. A. C. et al. Intravenous immune globulin (10% caprylate-chromatography purified) for the treatment of chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy (ICE study): a randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Neurol. 7, 136–144 (2008).
Merkies, I. S. et al. Health-related quality-of-life improvements in CIDP with immune globulin IV 10%: the ICE Study. Neurology 72, 1337–1344 (2009).
Bril, V. et al. Electrophysiologic correlations with clinical outcomes in CIDP. Muscle Nerve 42, 492–497 (2010).
Latov, N. et al. Timing and course of clinical response to intravenous immunoglobulin in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy. Arch. Neurol. 67, 802–807 (2010).
Lee, D. H. et al. Subcutaneous immunoglobulin infusion: a new therapeutic option in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. Muscle Nerve 37, 406–409 (2008).
Dyck, P. J. et al. Plasma exchange in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 314, 461–465 (1986).
Hahn, A. F. et al. Plasma-exchange therapy in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. A double blind, sham-controlled, cross-over study. Brain 119, 1055–1066 (1996).
Hughes, R., Swan, A. & Doorn, P. Cytotoxic drugs and interferons for chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, Issue 1. Art. No.: CD003280. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003280 (2003).
Mahdi-Rodgers, M., Swan, A. V., van Doorn, P. A. & Hughes, R. A. C. Immunomodulatory treatment other than corticosteroids, immunoglobulin and plasma exchange for CIDP. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, Issue 11. Art. No.: CD003280. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003280.pub3 (2010).
Dyck, P. J., O'Brien, P., Swanson, C., Low, P. & Daube, J. Combined azathioprine and prednisone in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. Neurology 35, 1173–1176 (1985).
Brannagan, T. H. 3rd et al. High-dose cyclophosphamide without stem-cell rescue for refractory CIDP. Neurology 58, 1856–1858 (2002).
Gladstone, D. E., Prestrud, A. A. & Brannagan, T. H. High-dose cyclophosphamide results in long-term disease remission with restoration of a normal quality of life in patients with severe refractory chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 10, 11–16 (2005).
Good, J. L., Chehrenama, M., Mayer, R. F. & Koski, C. L. Pulse cyclophosphamide therapy in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. Neurology 51, 1735–1738 (1998).
Gorson, K. C., Amato, A. A. & Ropper, A. H. Efficacy of mycophenolate mofetil in patients with chronic immune demyelinating polyneuropathy. Neurology 63, 715–717 (2004).
Radziwill, A. J., Schweikert, K., Kuntzer, T., Fuhr, P. & Steck, A. J. Mycophenolate mofetil for chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy: an open-label study. Eur. Neurol. 56, 37–38 (2006).
Barnett, M. H., Pollard, J. D., Davies, L. & McLeod, J. G. Cyclosporin A in resistant chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy. Muscle Nerve 21, 454–460 (1998).
Hughes, R. A. et al. Intramuscular interferon beta-1a in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy. Neurology 74, 651–657 (2010).
RMC Trial Group. Randomised controlled trial of methotrexate for chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy (RMC trial): a pilot, multicentre study. Lancet Neurol. 8, 158–164 (2009).
Dalakas, M. C. Therapeutic targets in patients with inflammatory myopathies: present approaches and a look to the future. Neuromuscul. Disord. 16, 223–236 (2006).
Vermeulen, M. & Van Oers, M. H. Successful autologous stem cell transplantation in a patient with chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 72, 127–128 (2002).
Kazmi, M. A., Mahdi-Rogers, M. & Sanvito, L. Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy: a role for haematopoietic stem cell transplantation? Autoimmunity 41, 611–615 (2008).
Marsh, E. A. et al. Alemtuzumab in the treatment of IVIG-dependent chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. J. Neurol. 257, 913–919 (2010).
Dalakas, M. C. B cells as therapeutic targets in autoimmune neurological disorders. Nat. Clin. Pract. Neurol. 4, 557–567 (2008).
Dalakas, M. C. Inhibition of B cell functions: implications for neurology. Neurology 70, 2252–2260 (2008).
Benedetti, L. et al. Rituximab in patients with chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy: a report of 13 cases and review of the literature. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 82, 306–308 (2011).
Münch, C., Anagnostou, P., Meyer, R. & Haas, J. Rituximab in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy associated with diabetes mellitus J. Neurol. Sci. 256, 100–102 (2007).
Briani, C. et al. Rituximab-responsive CIDP. Eur. J. Neurol. 11, 788 (2004).
Kosmidis, M. & Dalakas, M. C. Practical considerations on the use of rituximab in autoimmune neurological disorders. Ther. Adv. Neurol. Disord. 3, 93–105 (2010).
Fitzpatrick, A. M. et al. An open label clinical trial of complement inhibition in multifocal motor neuropathy. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 16, 84–91 (2011).
Wolf, C. et al. Natalizumab treatment in a patient with chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. Arch. Neurol. 67, 881–883 (2010).
Dalakas, M. C. Advances in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy: disease variants and inflammatory response mediators and modifiers. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 12, 403–409 (1999).
Dalakas, M. C. Potential biomarkers for monitoring therapeutic responses to IVIg and other therapies in CIDP. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 16, 63–67 (2011).
Comi, C. et al. Fas-mediated T-cell apoptosis is impaired in patients with chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 11, 53–60 (2006).
Tanighuchi, J. et al. Inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy sera inhibit axonal growth of mouse dorsal root ganglion neurons by activation of Rho-kinase. Ann. Neurol. 66, 694–697 (2009).
Gorson, K. C. et al. Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy disease activity status: recommendations for clinical research standards and use in clinical practice. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 15, 326–333 (2010).
Hartung, H. P., Lehmann, H. C. & Willison, H. G. Establishing common clinical research standards for CIDP. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 7, 250–251 (2011).
Acknowledgements
L. Barclay, freelance writer and reviewer, is the author of and is solely responsible for the content of the learning objectives, questions and answers of the Medscape, LLC-accredited continuing medical education activity associated with this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The author has received speaking honoraria or consulting fees for serving on the steering committees of the following companies: Biogen, Novartis, Octapharma, Talecris/Grifol.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dalakas, M. Advances in the diagnosis, pathogenesis and treatment of CIDP. Nat Rev Neurol 7, 507–517 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneurol.2011.121
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneurol.2011.121
This article is cited by
-
How I Treat Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy Podcast
Neurology and Therapy (2023)
-
Protocol of comparison of the effects of single plasma exchange and double filtration plasmapheresis on peripheral lymphocyte phenotypes in patients with Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyradiculoneuropathy: a monocentric prospective study with single-case experimental design
BMC Neurology (2022)
-
The Role of the Complement System in Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy: Implications for Complement-Targeted Therapies
Neurotherapeutics (2022)
-
Evolution of Anti-B Cell Therapeutics in Autoimmune Neurological Diseases
Neurotherapeutics (2022)
-
Corneal inflammatory cell infiltration predicts disease activity in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy
Scientific Reports (2021)