Abstract
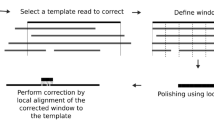
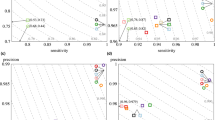
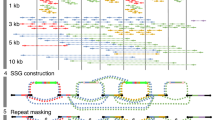
We present a tool that combines fast mapping, error correction, and de novo assembly (MECAT; accessible at https://github.com/xiaochuanle/MECAT) for processing single-molecule sequencing (SMS) reads. MECAT's computing efficiency is superior to that of current tools, while the results MECAT produces are comparable or improved. MECAT enables reference mapping or de novo assembly of large genomes using SMS reads on a single computer.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$29.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
References
Schadt, E.E., Turner, S. & Kasarskis, A. Hum. Mol. Genet. 19, R227–R240 (2010).
Eid, J. et al. Science 323, 133–138 (2009).
Chin, C.S. et al. Nat. Methods 10, 563–569 (2013).
Jain, M. et al. Nat. Methods 12, 351–356 (2015).
Sović, I. et al. Nat. Commun. 7, 11307 (2016).
Loman, N.J., Quick, J. & Simpson, J.T. Nat. Methods 12, 733–735 (2015).
Koren, S. et al. Nat. Biotechnol. 30, 693–700 (2012).
Seo, J.S. et al. Nature 538, 243–247 (2016).
Shi, L. et al. Nat. Commun. 7, 12065 (2016).
Gordon, D. et al. Science 352, aae0344 (2016).
Berlin, K. et al. Nat. Biotechnol. 33, 623–630 (2015).
Chin, C.S. et al. Nat. Methods 13, 1050–1054 (2016).
Koch, P., Platzer, M. & Downie, B.R. Nucleic Acids Res. 42, e80 (2014).
Koren, S., Walenz, B.P., Berlin, K., Miller, J.R. & Phillippy, A.M. Genome Res. 27, 722–736 (2017).
Chaisson, M.J. & Tesler, G. BMC Bioinformatics 13, 238 (2012).
Myers, E.W. Algorithmica 1, 251–266 (1986).
Myers, G. Algorithms in Bioinformatics, 52–67 (2014).
Li, H. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/1303.3997 (2013).
Langmead, B. & Salzberg, S.L. Nat. Methods 9, 357–359 (2012).
Acknowledgements
We thank D.P. Wang for supplying the Chinese human data set. We thank the NCBI assembly group for the Han-1 Chinese annotation. This work was collectively supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31471232, 31471789 and 31600667), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (15ykjc23d), the Guangdong Natural Science Foundation (2015A030313127), the Joint Research Fund for the Overseas Natural Science of China (3030901001222), infrastructure support from Center for Precision Medicine (Sun Yat-sen University), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2017M612798), and the National Institute of Food and Agriculture (NIFA), USA (2017-70016-26051).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
C.-L.X. conceived and designed this project. Y.C. and C.-L.X. implemented the algorithms. S.-Q.X., C.L.-X., and Y.C. performed the test experiments. K.-N.C., Y.W., and Y.H. coordinated the data release and assisted with executing the pipeline. F.L. provided theoretical analysis of the algorithms. C.-L.X., F.L., Z.X., Y.C., and S.-Q.X. wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Integrated supplementary information
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–2, Supplementary Notes 1–11 and Supplementary Tables 1, 2, 3, 5 and 6.
Supplementary Table 4
The read coverage of human reference genome alignment by BLASR and MECAT around regions with large structural variants
Supplementary Table 7
Comparison of Read Coverage of Reference Genome Alignment at Large Structural Variants
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, CL., Chen, Y., Xie, SQ. et al. MECAT: fast mapping, error correction, and de novo assembly for single-molecule sequencing reads. Nat Methods 14, 1072–1074 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.4432
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.4432
This article is cited by
-
High-quality genome resource of Lasiodiplodia pseudotheobromae associated with die-back on Eucalyptus trees
BMC Genomic Data (2024)
-
A high heterozygosity genome assembly of Aedes albopictus enables the discovery of the association of PGANT3 with blood-feeding behavior
BMC Genomics (2024)
-
Genome assembly in the telomere-to-telomere era
Nature Reviews Genetics (2024)
-
Technology-enabled great leap in deciphering plant genomes
Nature Plants (2024)
-
De novo diploid genome assembly using long noisy reads
Nature Communications (2024)