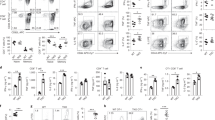
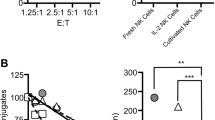
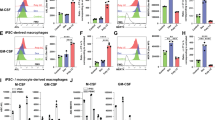
Abstract
Inflammation is a critical component of the immune response. However, acute or chronic inflammation can be highly destructive. Uncontrolled inflammation forms the basis for allergy, asthma and various autoimmune disorders. Here we identified a signaling pathway that was exclusively responsible for the production of inflammatory cytokines but not for cytotoxicity. Recognition of tumor cells expressing the NK cell–activatory ligands H60 or CD137L by mouse natural killer (NK) cells led to efficient cytotoxicity and the production of inflammatory cytokines. Both of those effector functions required the kinases Lck, Fyn and PI(3)K (subunits p85α and p110δ) and the signaling protein PLC-γ2. However, a complex of Fyn and the adaptor ADAP exclusively regulated the production of inflammatory cytokines but not cytotoxicity in NK cells. That unique function of ADAP required a Carma1–Bcl-10–MAP3K7 signaling axis. Our results have identified molecules that can be targeted to regulate inflammation without compromising NK cell cytotoxicity.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
23 September 2013
In the version of this article initially published online, the affiliation of author Bart Vanhaesebroeck was incorrect. The correct affiliation is as follows: Center for Cell Signaling, Barts Cancer Institute, Queen Mary University of London, London, UK. The error has been corrected for the print, PDF and HTML versions of this article.
References
Billadeau, D.D., Upshaw, J.L., Schoon, R.A., Dick, C.J. & Leibson, P.J. NKG2D–DAP10 triggers human NK cell-mediated killing via a Syk-independent regulatory pathway. Nat. Immunol. 4, 557–564 (2003).
Wu, J., Cherwinski, H., Spies, T., Phillips, J.H. & Lanier, L.L. DAP10 and DAP12 form distinct, but functionally cooperative, receptor complexes in natural killer cells. J. Exp. Med. 192, 1059–1068 (2000).
Zompi, S. et al. NKG2D triggers cytotoxicity in mouse NK cells lacking DAP12 or Syk family kinases. Nat. Immunol. 4, 565–572 (2003).
Myers, L.M. & Vella, A.T. Interfacing T-cell effector and regulatory function through CD137 (4–1BB) co-stimulation. Trends Immunol. 26, 440–446 (2005).
Wilcox, R.A., Tamada, K., Strome, S.E. & Chen, L. Signaling through NK cell-associated CD137 promotes both helper function for CD8+ cytolytic T cells and responsiveness to IL-2 but not cytolytic activity. J. Immunol. 169, 4230–4236 (2002).
Kim, Y.J. et al. Novel T cell antigen 4–1BB associates with the protein tyrosine kinase p56lck1. J. Immunol. 151, 1255–1262 (1993).
Sabbagh, L., Pulle, G., Liu, Y., Tsitsikov, E.N. & Watts, T.H. ERK-dependent Bim modulation downstream of the 4–1BB-TRAF1 signaling axis is a critical mediator of CD8 T cell survival in vivo. J. Immunol. 180, 8093–8101 (2008).
Cannons, J.L., Choi, Y. & Watts, T.H. Role of TNF receptor-associated factor 2 and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase activation during 4–1BB-dependent immune response. J. Immunol. 165, 6193–6204 (2000).
Regunathan, J., Chen, Y., Wang, D. & Malarkannan, S. NKG2D receptor-mediated NK cell function is regulated by inhibitory Ly49 receptors. Blood 105, 233–240 (2005).
Suzuki, I. & Fink, P.J. Maximal proliferation of cytotoxic T lymphocytes requires reverse signaling through Fas ligand. J. Exp. Med. 187, 123–128 (1998).
Filipp, D. et al. Regulation of Fyn through translocation of activated Lck into lipid rafts. J. Exp. Med. 197, 1221–1227 (2003).
Kapeller, R. et al. Identification of two SH3-binding motifs in the regulatory subunit of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 269, 1927–1933 (1994).
Vanhaesebroeck, B. et al. P110δ, a novel phosphoinositide 3-kinase in leukocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94, 4330–4335 (1997).
Min, L., Joseph, R.E., Fulton, D.B. & Andreotti, A.H. Itk tyrosine kinase substrate docking is mediated by a nonclassical SH2 domain surface of PLCγ1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 106, 21143–21148 (2009).
Medeiros, R.B. et al. Regulation of NF-κB activation in T cells via association of the adapter proteins ADAP and CARMA1. Science 316, 754–758 (2007).
Peterson, E.J. et al. Coupling of the TCR to integrin activation by Slap-130/Fyb. Science 293, 2263–2265 (2001).
May, R.M. et al. Murine natural killer immunoreceptors use distinct proximal signaling complexes to direct cell function. Blood 121, 3135–3146 (2013).
Newton, K. & Dixit, V.M. Mice lacking the CARD of CARMA1 exhibit defective B lymphocyte development and impaired proliferation of their B and T lymphocytes. Curr. Biol. 13, 1247–1251 (2003).
Sato, S. et al. Essential function for the kinase TAK1 in innate and adaptive immune responses. Nat. Immunol. 6, 1087–1095 (2005).
Baessler, T. et al. CD137 ligand mediates opposite effects in human and mouse NK cells and impairs NK-cell reactivity against human acute myeloid leukemia cells. Blood 115, 3058–3069 (2010).
Filipp, D. et al. Lck-dependent Fyn activation requires C terminus-dependent targeting of kinase-active Lck to lipid rafts. J. Biol. Chem. 283, 26409–26422 (2008).
Dong, Z. et al. The adaptor SAP controls NK cell activation by regulating the enzymes Vav-1 and SHIP-1 and by enhancing conjugates with target cells. Immunity 36, 974–985 (2012).
Manciulea, M. et al. Divergent phosphotyrosine signaling via FcγRIIIA on human NK cells. Cell. Immunol. 167, 63–71 (1996).
Biondi, A. et al. Expression of lineage-restricted protein tyrosine kinase genes in human natural killer cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 21, 843–846 (1991).
Kudlacz, E.M. et al. Genetic ablation of the src kinase p59fynT exacerbates pulmonary inflammation in an allergic mouse model. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 24, 469–474 (2001).
Mason, L.H., Willette-Brown, J., Taylor, L.S. & McVicar, D.W. Regulation of Ly49D/DAP12 signal transduction by Src-family kinases and CD45. J. Immunol. 176, 6615–6623 (2006).
Wu, J. et al. An activating immunoreceptor complex formed by NKG2D and DAP10. Science 285, 730–732 (1999).
Susa, M., Rohner, D. & Bichsel, S. Differences in binding of PI 3-kinase to the src-homology domains 2 and 3 of p56 lck and p59 fyn tyrosine kinases. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 220, 729–734 (1996).
Prasad, K.V. et al. Src-homology 3 domain of protein kinase p59fyn mediates binding to phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in T cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90, 7366–7370 (1993).
Karnitz, L.M., Sutor, S.L. & Abraham, R.T. The Src-family kinase, Fyn, regulates the activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in an interleukin 2-responsive T cell line. J. Exp. Med. 179, 1799–1808 (1994).
Guo, H., Samarakoon, A., Vanhaesebroeck, B. & Malarkannan, S. The p110δ of PI3K plays a critical role in NK cell terminal maturation and cytokine/chemokine generation. J. Exp. Med. 205, 2419–2435 (2008).
Kim, N. et al. The p110δ catalytic isoform of PI3K is a key player in NK-cell development and cytokine secretion. Blood 110, 3202–3208 (2007).
Lee, K.Y., D'Acquisto, F., Hayden, M.S., Shim, J.H. & Ghosh, S. PDK1 nucleates T cell receptor-induced signaling complex for NF-κB activation. Science 308, 114–118 (2005).
Regunathan, J. et al. Differential and nonredundant roles of phospholipase Cγ2 and phospholipase Cγ1 in the terminal maturation of NK cells. J. Immunol. 177, 5365–5376 (2006).
Liu, J. et al. FYB (FYN binding protein) serves as a binding partner for lymphoid protein and FYN kinase substrate SKAP55 and a SKAP55-related protein in T cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 8779–8784 (1998).
Srivastava, R., Burbach, B.J. & Shimizu, Y. NF-kappaB activation in T cells requires discrete control of IκB kinase α/β (IKKα/β) phosphorylation and IKKγ ubiquitination by the ADAP adapter protein. J. Biol. Chem. 285, 11100–11105 (2010).
Fostel, L.V., Dluzniewska, J., Shimizu, Y., Burbach, B.J. & Peterson, E.J. ADAP is dispensable for NK cell development and function. Int. Immunol. 18, 1305–1314 (2006).
Chen, X., Trivedi, P.P., Ge, B., Krzewski, K. & Strominger, J.L. Many NK cell receptors activate ERK2 and JNK1 to trigger microtubule organizing center and granule polarization and cytotoxicity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 104, 6329–6334 (2007).
Li, C. et al. JNK MAP kinase activation is required for MTOC and granule polarization in NKG2D-mediated NK cell cytotoxicity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 105, 3017–3022 (2008).
Colucci, F. et al. Functional dichotomy in natural killer cell signaling: Vav1-dependent and -independent mechanisms. J. Exp. Med. 193, 1413–1424 (2001).
Gaide, O. et al. CARMA1 is a critical lipid raft-associated regulator of TCR-induced NF-kappa B activation. Nat. Immunol. 3, 836–843 (2002).
Rajasekaran, K. et al. Transforming growth factor-β-activated kinase 1 regulates natural killer cell-mediated cytotoxicity and cytokine production. J. Biol. Chem. 286, 31213–31224 (2011).
Blonska, M. et al. The CARMA1-Bcl10 signaling complex selectively regulates JNK2 kinase in the T cell receptor-signaling pathway. Immunity 26, 55–66 (2007).
Murphy, L.O., Smith, S., Chen, R.H., Fingar, D.C. & Blenis, J. Molecular interpretation of ERK signal duration by immediate early gene products. Nat. Cell Biol. 4, 556–564 (2002).
Wang, W., Zhou, G., Hu, M.C., Yao, Z. & Tan, T.H. Activation of the hematopoietic progenitor kinase-1 (HPK1)-dependent, stress-activated c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) pathway by transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β)-activated kinase (TAK1), a kinase mediator of TGF β signal transduction. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 22771–22775 (1997).
Okkenhaug, K. et al. The p110δ isoform of phosphoinositide 3-kinase controls clonal expansion and differentiation of Th cells. J. Immunol. 177, 5122–5128 (2006).
Egawa, T. et al. Requirement for CARMA1 in antigen receptor-induced NF-κB activation and lymphocyte proliferation. Curr. Biol. 13, 1252–1258 (2003).
Tang, M. et al. TAK1 is required for the survival of hematopoietic cells and hepatocytes in mice. J. Exp. Med. 205, 1611–1619 (2008).
Mason, L.H. et al. The Ly-49D receptor activates murine natural killer cells. J. Exp. Med. 184, 2119–2128 (1996).
Malarkannan, S. et al. Differences that matter: major cytotoxic T cell-stimulating minor histocompatibility antigens. Immunity 13, 333–344 (2000).
Acknowledgements
We thank L. Sammarco and her Lulu's Lemonade Stand for support through Blood Center's Research Foundation, inspiration and motivation; K.E. Nichols (Children's Hospital, Philadelphia) for Adap−/− mice; D.R. Littman (New York University) for Carma1−/− mice; J. Zhang and Y. Xiao (Loyola University Chicago Stritch School of Medicine) for Map3k7fl/fl and Map3k7fl/flMx1-Cre spleens; Y. Chen and B. Ren (Blood Research Institute, Milwaukee) for wild-type and Fyn−/− spleens; V. Arumugam and T. Foster for technical help; and T. Heil, L. Savatski, P.J. Newman and Q. Shi for critical reading. Supported by the US National Institutes of Health (R01 A1064828 and R01 AI102893 to S.M.), the American Cancer Society (S.M. and M.S.T.), Midwest Athletes Against Childhood Cancer Fund (M.S.T. and S.M.) and Hyundai Hope on Wheels (M.S.T.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
K.R. designed and executed analysis of the cytotoxic potential and production of inflammatory cytokines of Fyn−/−, p110δ(D910A), Adap−/−, Carma1−/− and Carma1(ΔCARD) NK cells (freshly isolated or cultured with IL-2), did various NK cell–activation assays, prepared cell lysates, did immunoblot analysis and immunoprecipitation assays, purified human primary NK cells and used them for siRNA treatment and functional analyses, and helped in revising the manuscript; P.K. designed siRNA and knocked down various mouse signaling proteins; K.M.S. maintained various animal colonies and prepared NK cells (freshly isolated or cultured with IL-2) for studies; V.D. provided Carma1(ΔCARD) mice; E.J.P. provided Adap−/− spleens and discussed the data; B.V. provided p110δ(D910A) mice; E.J.P. and B.V. helped in the final editing of the manuscript; M.S.T. helped in the preparation of the manuscript; and S.M. conceived of the study, designed experiments, analyzed the data and wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–8 (PDF 1580 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rajasekaran, K., Kumar, P., Schuldt, K. et al. Signaling by Fyn-ADAP via the Carma1–Bcl-10–MAP3K7 signalosome exclusively regulates inflammatory cytokine production in NK cells. Nat Immunol 14, 1127–1136 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.2708
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.2708
This article is cited by
-
Redox regulation of the immune response
Cellular & Molecular Immunology (2022)
-
The biological function and clinical significance of SF3B1 mutations in cancer
Biomarker Research (2020)
-
Fyn depletion ameliorates tauP301L-induced neuropathology
Acta Neuropathologica Communications (2020)
-
MicroRNA-125a-3p participates in odontoblastic differentiation of dental pulp stem cells by targeting Fyn
Cytotechnology (2020)
-
Effects of rapamycin on social interaction deficits and gene expression in mice exposed to valproic acid in utero
Molecular Brain (2019)