Abstract
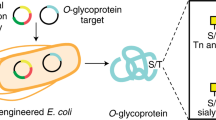
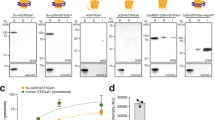
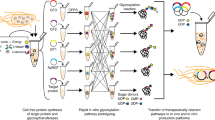
We performed bottom-up engineering of a synthetic pathway in Escherichia coli for the production of eukaryotic trimannosyl chitobiose glycans and the transfer of these glycans to specific asparagine residues in target proteins. The glycan biosynthesis was enabled by four eukaryotic glycosyltransferases, including the yeast uridine diphosphate-N-acetylglucosamine transferases Alg13 and Alg14 and the mannosyltransferases Alg1 and Alg2. By including the bacterial oligosaccharyltransferase PglB from Campylobacter jejuni, we successfully transferred glycans to eukaryotic proteins.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Helenius, A. & Aebi, M. Science 291, 2364–2369 (2001).
Szymanski, C.M., Yao, R., Ewing, C.P., Trust, T.J. & Guerry, P. Mol. Microbiol. 32, 1022–1030 (1999).
Wacker, M. et al. Science 298, 1790–1793 (2002).
Kowarik, M. et al. EMBO J. 25, 1957–1966 (2006).
Schwarz, F. et al. Glycobiology 21, 45–54 (2011).
Ielmini, M.V. & Feldman, M.F. Glycobiology 21, 734–742 (2011).
Weerapana, E. & Imperiali, B. Glycobiology 16, 91R–101R (2006).
Feldman, M.F. et al. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102, 3016–3021 (2005).
Ihssen, J. et al. Microb. Cell Fact. 9, 61 (2010).
Schwarz, F. et al. Nat. Chem. Biol. 6, 264–266 (2010).
Pandhal, J. & Wright, P.C. Biotechnol. Lett. 32, 1189–1198 (2010).
Van Patten, S.M. et al. Glycobiology 17, 467–478 (2007).
O'Reilly, M.K., Zhang, G. & Imperiali, B. Biochemistry 45, 9593–9603 (2006).
Couto, J.R., Huffaker, T.C. & Robbins, P.W. J. Biol. Chem. 259, 378–382 (1984).
Wang, X., Weldeghiorghis, T., Zhang, G., Imperiali, B. & Prestegard, J.H. Structure 16, 965–975 (2008).
Ilg, K., Yavuz, E., Maffioli, C., Priem, B. & Aebi, M. Glycobiology 20, 1289–1297 (2010).
Fisher, A.C. et al. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 77, 871–881 (2011).
Alaimo, C. et al. EMBO J. 25, 967–976 (2006).
Cipollo, J.F., Trimble, R.B., Chi, J.H., Yan, Q. & Dean, N. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 21828–21840 (2001).
Lizak, C., Gerber, S., Numao, S., Aebi, M. & Locher, K.P. Nature 474, 350–355 (2011).
Liu, X. et al. Anal. Chem. 78, 6081–6087 (2006).
Kowarik, M. et al. Science 314, 1148–1150 (2006).
Çelik, E., Fisher, A.C., Guarino, C., Mansell, T.J. & DeLisa, M.P. Protein Sci. 19, 2006–2013 (2010).
Dürr, C., Nothaft, H., Lizak, C., Glockshuber, R. & Aebi, M. Glycobiology 20, 1366–1372 (2010).
Nasab, F.P., Schulz, B.L., Gamarro, F., Parodi, A.J. & Aebi, M. Mol. Biol. Cell 19, 3758–3768 (2008).
Acknowledgements
We thank B. Imperiali (Massachusetts Institute of Technology) for plasmid pBAD(ALG2)-DEST49, G. O'Toole (Dartmouth College) for plasmid pMQ70, T. Mansell for helpful discussions regarding RNaseA glycosylation, C. Hong for helpful discussions regarding glycan synthesis and individuals from the Functional Genomic Center Zürich for input and instrument support. This work was supported by the National Science Foundation Career Award CBET-0449080 (to M.P.D.), the New York State Office of Science, Technology and Academic Research Distinguished Faculty Award (to M.P.D.), the National Institutes of Health Small Business Innovation Research grants R43 GM087766 and R43 GM086965 (to A.C.F.), the National Institutes of Health National Center for Research Resources grant 1 P41 RR018502-01 (to the Complex Carbohydrate Research Center) and a graduate fellowship from LASPAU and the Universidad Antonio Nariño (to J.D.V.-R.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J.D.V.-R. and A.C.F. designed research, performed research, analyzed data and wrote the paper. J.H.M. designed research and performed research. Y.-Y.F. performed MS analysis and analyzed data. C.A.R. and K.C. performed research. C.H. and P.A. performed NMR analysis and analyzed data. M.A. designed research and analyzed data. M.P.D. designed research, analyzed data and wrote the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
A.C.F., J.H.M. and C.A.R. are employees of Glycobia, Inc.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Methods and Supplementary Results (PDF 11274 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Valderrama-Rincon, J., Fisher, A., Merritt, J. et al. An engineered eukaryotic protein glycosylation pathway in Escherichia coli. Nat Chem Biol 8, 434–436 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.921
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.921
This article is cited by
-
Rapid biosynthesis of glycoprotein therapeutics and vaccines from freeze-dried bacterial cell lysates
Nature Protocols (2023)
-
Progress towards a glycoconjugate vaccine against Group A Streptococcus
npj Vaccines (2023)
-
Strategies for efficient production of recombinant proteins in Escherichia coli: alleviating the host burden and enhancing protein activity
Microbial Cell Factories (2022)
-
A universal glycoenzyme biosynthesis pipeline that enables efficient cell-free remodeling of glycans
Nature Communications (2022)
-
Bioactive VEGF-C from E. coli
Scientific Reports (2022)