Abstract
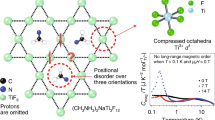
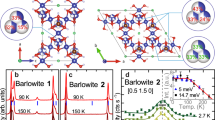
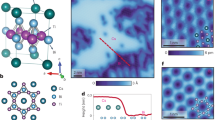
Frustrated magnetic lattices offer the possibility of many exotic ground states that are of great fundamental importance. Of particular significance is the hunt for frustrated spin-1/2 networks as candidates for quantum spin liquids, which would have exciting and unusual magnetic properties at low temperatures. The few reported candidate materials have all been based on d9 ions. Here, we report the ionothermal synthesis of [NH4]2[C7H14N][V7O6F18], an inorganic–organic hybrid solid that contains a S = 1/2 kagome network of d1 V4+ ions. The compound exhibits a high degree of magnetic frustration, with significant antiferromagnetic interactions but no long-range magnetic order or spin-freezing above 2 K, and appears to be an excellent candidate for realizing a quantum spin liquid ground state in a spin-1/2 kagome network.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Harrison, A. First catch your hare: the design and synthesis of frustrated magnets. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 16, S553–S572 (2004).
Ramirez, A. P. Strongly geometrically frustrated magnets. Annu. Rev. Mater. Sci. 24, 453–480 (1994).
Balents, L. Spin liquids in frustrated magnets. Nature 464, 199–208 (2010).
Colman, R. H. et al. Spin dynamics in the S = 1/2 kagome compound vesignieite, Cu3Ba(VO5H)2 . Phys. Rev. B 83, 180416(R) (2011).
Shores, M. P., Nytko, E. A., Bartlett, B. M. & Nocera, D. G. A structurally perfect S = 1/2 kagome antiferromagnet. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127, 13462–13463 (2005).
Mendels, P. et al. Quantum magnetism in the paratacamite family: towards an ideal kagome lattice. Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 077204 (2007).
Lee, S. H. et al. Quantum-spin-liquid states in the two-dimensional kagome antiferromagnets ZnxCu4–x(OD)6Cl2 . Nature Mater. 6, 853–857 (2007).
Poilblanc, D. & Ralko, A. Impurity-doped kagome antiferromagnet: a quantum dimer model approach. Phys. Rev. B 82, 174424 (2010).
Helton, J. S. et al. Spin dynamics of the spin-1/2 kagome lattice antiferromagnet ZnCu3(OH)6Cl2 . Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 107204 (2007).
Freedman, D. E. et al. Site specific X-ray anomalous dispersion of the geometrically frustrated kagome magnet, herbertsmithite, ZnCu3(OH)6Cl2 . J. Am. Chem. Soc. 132, 16185–16190 (2010).
de Vries, M. A. & Harrison, A. Model's reputation restored. Nature 468, 908–909 (2010).
Marcipar, L. et al. Muon-spin spectroscopy of the organometallic spin-1/2 kagome-lattice compound Cu(1,3-benzenedicarboxylate). Phys. Rev. B 80, 132402 (2009).
Matan, K. et al. Pinwheel valence-bond solid and triplet excitations in the two-dimensional deformed kagome lattice. Nature Phys. 6, 865–869 (2010).
Papoutsakis, D., Grohol, D. & Nocera, D. G. Magnetic properties of a homologous series of vanadium jarosite compounds. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 124, 2647–2656 (2002).
Miller, W. et al. A kagome compound based on vanadium(III) with a highly frustrated ground state. Chem. Mater. 23, 1315–1322 (2011).
Ballou, R., Canals, B., Elhajal, M., Lacroix, C. & Wills, A. S. Models for ordering in the jarosites kagome systems. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 262, 465–471 (2003).
Aldous, D. W., Stephens, N. F. & Lightfoot, P. The role of temperature in the solvothermal synthesis of hybrid vanadium oxyfluorides. Dalton Trans. 4207–4213 (2007).
Adil, K., Leblanc, M., Maisonneuve, V. & Lightfoot, P. Structural chemistry of organically-templated metal fluorides. Dalton Trans. 39, 5983–5993 (2010).
Morris, R. E. Ionothermal synthesis—ionic liquids as functional solvents in the preparation of crystalline materials. Chem. Commun. 2990–2998 (2009).
Parnham, E. R. & Morris, R. E. Ionothermal synthesis of zeolites, metal–organic frameworks, and inorganic–organic hybrids. Acc. Chem. Res. 40, 1005–1013 (2007).
Cooper, E. R. et al. Ionic liquids and eutectic mixtures as solvent and template in synthesis of zeolite analogues. Nature 430, 1012–1016 (2004).
Drylie, E. A. et al. Ionothermal synthesis of unusual choline-templated cobalt aluminophosphates. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 46, 7839–7843 (2007).
Wei, Y. et al. Ionothermal synthesis of an aluminophosphate molecular sieve with 20-ring pore openings. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 49, 5367–5370 (2010).
Lin, Z. J., Li, Y., Slawin, A. M. Z. & Morris, R. E. Hydrogen-bond-directing effect in the ionothermal synthesis of metal coordination polymers. Dalton Trans. 3989–3994 (2008).
Lin, Z. J., Wragg, D. S., Warren, J. E. & Morris, R. E. Anion control in the ionothermal synthesis of coordination polymers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 129, 10334–10335 (2007).
Kuhn, P., Antonietti, M. & Thomas, A. Porous, covalent triazine-based frameworks prepared by ionothermal synthesis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 47, 3450–3453 (2008).
DeBurgomaster, P. et al. Solvatothermal chemistry of organically templated vanadium fluorides and oxyfluorides. Inorg. Chim. Acta 363, 1102–1113 (2010).
Himeur, F. et al. Increasing the dimensionality of hybrid vanadium oxyfluorides using ionothermal synthesis. Dalton Trans. 39, 6018–6020 (2010).
Parnham, E. R., Drylie, E. A., Wheatley, P. S., Slawin, A. M. Z. & Morris, R. E. Ionothermal materials synthesis using unstable deep-eutectic solvents as template-delivery agents. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 45, 4962–4966 (2006).
Kidder, T., Fenner, L. A., Dee, A. A., Terasaki, I., Hagiwara, M. & Wills, A. S. The giant anomalous Hall effect in the ferromagnet Fe3Sn2—a frustrated kagome metal. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 23, 112205 (2011).
Mutka, H. et al. Low-temperature relaxation in kagome bilayer antiferromagnets. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 19, 145254 (2007).
Pati, S. K. & Rao, C. N. R. Kagome network compounds and their novel magnetic properties. Chem. Commun. 4683–4693 (2008).
Ferey, G. & Parmentier, J. The pyrochlore–HTB–ReO3 successive phase-transitions of FeF3 . Eur. J. Solid State Inorg. Chem. 31, 697–704 (1994).
Ono, T. et al. Magnetic susceptibilities in a family of S = 1/2 kagome antiferromagnets. Phys. Rev. B 79, 174407 (2009).
Yamabe, Y., Ono, T., Suto, T. & Tanaka, H. S = 1/2 kagome antiferromagnets Cs2Cu3MF12 with M = Zr and Hf. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 19, 145253 (2007).
Englich, U., Frommen, C. & Massa, W. Jahn–Teller ordering in Kagome-type layers of compounds A2A′Mn3F12 (A = Rb, Cs; A′ = Li, Na, K). J. Alloys Compd. 246, 155–165 (1997).
Wasserscheid, P. & Keim, W. Ionic liquids—new ‘solutions’ for transition metal catalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 39, 3772–3789 (2000).
Bonhote, P., Dias, A. P., Papageorgiou, N., Kalyanasundaram, K. & Gratzel, M. Hydrophobic, highly conductive ambient-temperature molten salts. Inorg. Chem. 35, 1168–1178 (1996).
Morris, R. E. & Bu, X. H. Induction of chiral porous solids containing only achiral building blocks. Nature Chem. 2, 353–361 (2010).
Lin, Z. J., Slawin, A. M. Z. & Morris, R. E. Chiral induction in the ionothermal synthesis of a 3-D coordination polymer. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 129, 4880–4881 (2007).
Villaescusa, L. A., Wheatley, P. S., Bull, I., Lightfoot, P. & Morris, R. E. The location and ordering of fluoride ions in pure silica zeolites with framework types IFR and STF; implications for the mechanism of zeolite synthesis in fluoride media. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 123, 8797–8805 (2001).
Aidoudi, F. H. et al. Ionic liquids and deep eutectic mixtures as new solvents for the synthesis of vanadium fluorides and oxyfluorides. Dalton Trans. 40, 4324–4331 (2011).
Aldous, D. W., Goff, R. J., Attfield, J. P. & Lightfoot, P. Novel vanadium(IV) oxyfluorides with ‘spin-ladder’-like structures, and their relationship to (VO)2P2O7 . Inorg. Chem. 46, 1277–1282 (2007).
Aldous, D. W., Slawin, A. M. Z. & Lightfoot, P. An unusual hybrid fluoride featuring a [V7F27]6− chain motif based on a pyrochlore-like building unit. J. Solid State Chem. 181, 3033–3036 (2008).
Acknowledgements
The authors thank L. Downie, L. Clark and A. Kusmartseva for help with the magnetic measurements, and C. Tang and D. Allan for assistance with synchrotron X-ray diffraction. The authors acknowledge the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC) and Science and Technology Facilities Council (STFC) for funding. Thanks also go to A. Harrison for helpful discussions. R.E.M. is a Royal Society Industry Fellow.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
F.H.A. and D.W.A. carried out the synthetic chemistry. F.H.A. solved the crystal structure, with the assistance of A.M.Z.S. F.H.A. and R.J.G. analysed the magnetic data, under the guidance of J.P.A. P.L. and R.E.M. initiated the research and co-wrote the paper. P.L. coordinated the project.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information
Supplementary information (PDF 644 kb)
Supplementary information
Crystallographic data for compound 1 (CIF 11 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aidoudi, F., Aldous, D., Goff, R. et al. An ionothermally prepared S = 1/2 vanadium oxyfluoride kagome lattice. Nature Chem 3, 801–806 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/nchem.1129
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nchem.1129
This article is cited by
-
A three-dimensional uranium-fluorine spin-frustrated CaB6-type lattice as potential conductive and quantum spin liquid candidate
Ionics (2023)
-
Muon spin spectroscopy
Nature Reviews Methods Primers (2022)
-
Synthesis of a d1-titanium fluoride kagome lattice antiferromagnet
Nature Chemistry (2020)
-
Taking titanium for a spin
Nature Chemistry (2020)
-
Spin liquid mediated RKKY interaction
Scientific Reports (2019)