Abstract
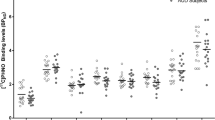
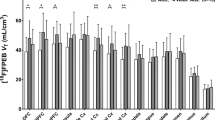
Brain cannabinoid CB1 receptors contribute to alcohol-related behaviors in experimental animals, but their potential role in humans with alcohol dependence is poorly understood. We measured CB1 receptors in alcohol dependent patients in early and protracted abstinence, and in comparison with control subjects without alcohol use disorders, using positron emission tomography and [18F]FMPEP-d2, a radioligand for CB1 receptors. We scanned 18 male in-patients with alcohol dependence twice, within 3–7 days of admission from ongoing drinking, and after 2–4 weeks of supervised abstinence. Imaging data were compared with those from 19 age-matched healthy male control subjects. Data were also analyzed for potential influence of a common functional variation (rs2023239) in the CB1 receptor gene (CNR1) that may moderate CB1 receptor density. On the first scan, CB1 receptor binding was 20–30% lower in patients with alcohol dependence than in control subjects in all brain regions and was negatively correlated with years of alcohol abuse. After 2–4 weeks of abstinence, CB1 receptor binding remained similarly reduced in these patients. Irrespective of the diagnostic status, C allele carriers at rs2023239 had higher CB1 receptor binding compared with non-carriers. Alcohol dependence is associated with a widespread reduction of cannabinoid CB1 receptor binding in the human brain and this reduction persists at least 2–4 weeks into abstinence. The correlation of reduced binding with years of alcohol abuse suggests an involvement of CB1 receptors in alcohol dependence in humans.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Maccioni P, Colombo G, Carai MA . Blockade of the cannabinoid CB1 receptor and alcohol dependence: preclinical evidence and preliminary clinical data. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 2010; 9: 55–59.
Mechoulam R, Parker L . Cannabis and alcohol – a close friendship. Trends Pharmacol Sci 2003; 24: 266–268.
Basavarajappa BS . The endocannabinoid signaling system: a potential target for next-generation therapeutics for alcoholism. Mini Rev Med Chem 2007; 7: 769–779.
Herkenham M, Lynn AB, Little MD, Johnson MR, Melvin LS, de Costa BR et al. Cannabinoid Receptor Localization in Brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci 1990; 87: 1932–1936.
Glass M, Dragunow M, Faull RL . Cannabinoid receptors in the human brain: a detailed anatomical and quantitative autoradiographic study in the fetal, neonatal and adult human brain. Neuroscience 1997; 77: 299–318.
Howlett AC, Barth F, Bonner TI, Cabral G, Casellas P, Devane WA et al. International Union of Pharmacology. XXVII. Classification of cannabinoid receptors. Pharmacol Rev 2002; 54: 161–202.
Wilson RI, Nicoll RA . Endocannabinoid signaling in the brain. Science 2002; 296: 678–682.
Colombo G, Serra S, Vacca G, Carai M, Gessa G . Endocannabinoid system and alcohol addiction: pharmacological studies. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 2005; 81: 369–380.
Hungund BL, Szakall I, Adam A, Basavarajappa BS, Vadasz C . Cannabinoid CB1 receptor knockout mice exhibit markedly reduced voluntary alcohol consumption and lack alcohol-induced dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens. J Neurochem 2003; 84: 698–704.
Wang L, Liu J, Harvey-White J, Zimmer A, Kunos G . Endocannabinoid signaling via cannabinoid receptor 1 is involved in ethanol preference and its age-dependent decline in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci 2003; 100: 1393–1398.
Racz I, Bilkei-Gorzo A, Toth ZE, Michel K, Palkovits M, Zimmer A . A critical role for the cannabinoid CB1 receptors in alcohol dependence and stress-stimulated ethanol drinking. J Neurosci 2003; 23: 2453–2458.
Rodriguez de Fonseca F, Roberts AJ, Bilbao A, Koob GF, Navarro M . Cannabinoid receptor antagonist SR141716A decreases operant ethanol self administration in rats exposed to ethanol-vapor chambers. Zhongguo Yao Li Xue Bao 1999; 20: 1109–1114.
Arnone M, Maruani J, Chaperon F, Thiebot MH, Poncelet M, Soubrie P et al. Selective inhibition of sucrose and ethanol intake by SR 141716, an antagonist of central cannabinoid (CB1) receptors. Psychopharmacology 1997; 132: 104–106.
Colombo G, Agabio R, Fa M, Guano L, Lobina C, Loche A et al. Reduction of voluntary ethanol intake in ethanol-preferring sP rats by the cannabinoid antagonist SR-141716. Alcohol Alcohol 1998; 33: 126–130.
Basavarajappa BS, Cooper TB, Hungund BL . Chronic ethanol administration down-regulates cannabinoid receptors in mouse brain synaptic plasma membrane. Brain Res 1998; 793: 212–218.
Vinod K, Yalamanchili R, Xie S, Cooper T, Hungund B . Effect of chronic ethanol exposure and its withdrawal on the endocannabinoid system. Neurochem Int 2006; 49: 619–625.
Mitrirattanakul S, López-Valdés HE, Liang J, Matsuka Y, Mackie K, Faull KF et al. Bidirectional alterations of hippocampal cannabinoid 1 receptors and their endogenous ligands in a rat model of alcohol withdrawal and dependence. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 2007; 31: 855–867.
Vinod KY, Kassir SA, Hungund BL, Cooper TB, Mann JJ, Arango V . Selective alterations of the CB1 receptors and the fatty acid amide hydrolase in the ventral striatum of alcoholics and suicides. J Psychiatric Res 2010; 44: 591–597.
Zhang PW, Ishiguro H, Ohtsuki T, Hess J, Carillo F, Walther D et al. Human cannabinoid receptor 1: 5′ exons, candidate regulatory regions, polymorphisms, haplotypes and association with polysubstance abuse. Mol Psychiatry 2004; 9: 916–931.
Hutchison KE, Haughey H, Niculescu M, Schacht J, Kaiser A, Stitzel J et al. The incentive salience of alcohol: translating the effects of genetic variant in CNR1. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2008; 65: 841–850.
Terry GE, Hirvonen J, Liow JS, Zoghbi SS, Gladding R, Tauscher JT et al. Imaging and quantitation of cannabinoid CB1 receptors in human and monkey brains using (18)F-labeled inverse agonist radioligands. J Nucl Med 2010; 51: 112–120.
Donohue SR, Krushinski JH, Pike VW, Chernet E, Phebus L, Chesterfield AK et al. Synthesis, ex vivo evaluation, and radiolabeling of potent 1,5-diphenylpyrrolidin-2-one cannabinoid subtype-1 receptor ligands as candidates for in vivo imaging. J Med Chem 2008; 51: 5833–5842.
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders 4th edn., text revision. American Psychiatric Association: Washington, DC, 2000.
First MB, Spitzer RL, Gibbon M, Williams JBW . Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-IV Axis I Disorders, Clinician Version (SCID-CV). American Psychiatric Press: Washington, DC, 1996.
Skinner HA, Allen BA . Alcohol dependence syndrome: measurement and validation. J Abnorm Psychol 1982; 91: 199–209.
Sobell LC, Sobell MB . Timeline follow-back: a technique for assessing self-reported ethanol consumption, In: Measuring Alcohol Consumption: Psychosocial and Biochemical Methods, Allen, J, Litten, R (eds). 41–72. Humana Press, Totowa, NJ, 1992.
Flannery BA, Volpicelli JR, Pettinati HM . Psychometric properties of the Penn Alcohol Craving Scale. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 1999; 23: 1289–1295.
Svanborg P . State and Trait Measures in the Affective Disorders. Karolinska Institute, Department of Clinical Neuroscience, Psychiatry Institute: Stockholm, 1999.
Sullivan JT, Sykora K, Schneiderman J, Naranjo CA, Sellers EM . Assessment of alcohol withdrawal: the revised clinical institute withdrawal assessment for alcohol scale (CIWA-Ar). Br J Addict 1989; 84: 1353–1357.
Hirvonen J, Goodwin RS, Li CT, Terry GE, Zoghbi SS, Morse C et al. Reversible and regionally selective downregulation of brain cannabinoid CB(1) receptors in chronic daily cannabis smokers. Mol Psychiatry 2012; 17: 642–649.
Gandelman MS, Baldwin RM, Zoghbi SS, Zea-Ponce Y, Innis RB . Evaluation of ultrafiltration for the free-fraction determination of single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) radiotracers: beta-CIT, IBF, and iomazenil. J Pharm Sci 1994; 83: 1014–1019.
Zoghbi SS, Shetty HU, Ichise M, Fujita M, Imaizumi M, Liow JS et al. PET imaging of the dopamine transporter with 18F-FECNT: a polar radiometabolite confounds brain radioligand measurements. J Nucl Med 2006; 47: 520–527.
Tzourio-Mazoyer N, Landeau B, Papathanassiou D, Crivello F, Etard O, Delcroix N et al. Automated anatomical labeling of activations in SPM using a macroscopic anatomical parcellation of the MNI MRI single-subject brain. Neuroimage 2002; 15: 273–289.
Burger C, Mikolajczyk K, Grodzki M, Rudnicki P, Szabatin M, Buck A . Java tools for quantitative post-processing of brain PET data. J Nucl Med 1998; 39: 277p–278p.
Friston KJ, Holmes AP, Worsley KJ, Poline JP, Frith C, Frackowiak RSJ . Statistical parametric maps in functional imaging: a general linear approach. Hum Brain Mapp 1995; 2: 189–210.
Innis RB, Cunningham VJ, Delforge J, Fujita M, Gjedde A, Gunn RN et al. Consensus nomenclature for in vivo imaging of reversibly binding radioligands. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2007; 27: 1533–1539.
Quarantelli M, Berkouk K, Prinster A, Landeau B, Svarer C, Balkay L et al. Integrated software for the analysis of brain PET/SPECT studies with partial-volume-effect correction. J Nucl Med 2004; 45: 192–201.
Terry G, Liow J, Chernet E, Zoghbi S, Phebus L, Felder C et al. Positron emission tomography imaging using an inverse agonist radioligand to assess cannabinoid CB1 receptors in rodents. Neuroimage 2008; 41: 690–698.
Caille S, Alvarez-Jaimes L, Polis I, Stouffer DG, Parsons LH . Specific Alterations of extracellular endocannabinoid levels in the nucleus accumbens by ethanol, heroin, and cocaine self-administration. J Neurosci 2007; 27: 3695–3702.
Gonzalez S, Fernandez-Ruiz J, Sparpaglione V, Parolaro D, Ramos JA . Chronic exposure to morphine, cocaine or ethanol in rats produced different effects in brain cannabinoid CB(1) receptor binding and mRNA levels. Drug Alcohol Depend 2002; 66: 77–84.
Koob GF, Le Moal M . Addiction and the brain antireward system. Annu Rev Psychol 2008; 59: 29–53.
Koob GF . A role for brain stress systems in addiction. Neuron 2008; 59: 11–34.
Hill MN, Patel S, Campolongo P, Tasker JG, Wotjak CT, Bains JS . Functional interactions between stress and the endocannabinoid system: from synaptic signaling to behavioral output. J Neurosci 2010; 30: 14980–14986.
Hill MN, McEwen BS . Involvement of the endocannabinoid system in the neurobehavioural effects of stress and glucocorticoids. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 2010; 34: 791–797.
Soyka M, Koller G, Schmidt P, Lesch O-M, Leweke M, Fehr C et al. Cannabinoid Receptor 1 Blocker Rimonabant (SR 141716) for Treatment of Alcohol Dependence. J Clin Psychopharmacol 2008; 28: 317–324.
George DT, Herion DW, Jones CL, Phillips MJ, Hersh J, Hill D et al. Rimonabant (SR141716) has no effect on alcohol self-administration or endocrine measures in nontreatment-seeking heavy alcohol drinkers. Psychopharmacology 2009; 208: 37–44.
Cippitelli A, Cannella N, Braconi S, Duranti A, Tontini A, Bilbao A et al. Increase of brain endocannabinoid anandamide levels by FAAH inhibition and alcohol abuse behaviours in the rat. Psychopharmacology 2008; 198: 449–460.
Umhau JC, Momenan R, Schwandt ML, Singley E, Lifshitz M, Doty L et al. Effect of acamprosate on magnetic resonance spectroscopy measures of central glutamate in detoxified alcohol-dependent individuals: a randomized controlled experimental medicine study. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2010; 67: 1069–1077.
Rubio M, Villain H, Docagne F, Roussel BD, Ramos JA, Vivien D et al. Pharmacological activation/inhibition of the cannabinoid system affects alcohol withdrawal-induced neuronal hypersensitivity to excitotoxic insults. PloS one 2011; 6: e23690.
Acknowledgements
We thank Kimberly Jenko, Kacey Anderson and David Clark for assisting in the measurements of radioligand in plasma; Maria D Ferraris Araneta, Gerald Hodges, William C Kreisl and Barbara Scepura as well as Chris Geyer and the NIAAA nursing staff for subject recruitment and care; the NIH PET Department for imaging; and the PMOD Technologies for providing its image analysis and modeling software. This research was supported by the Intramural Programs of NIMH and NIAAA. Jussi Hirvonen was supported by personal grants from The Academy of Finland; The Finnish Cultural Foundation; The Finnish Foundation for Alcohol Studies; The Finnish Medical Foundation; The Instrumentarium Foundation; The Jalmari and Rauha Ahokas Foundation; The Paulo Foundation; The Research Foundation of Orion Corporation; and The Yrjö Jahnsson Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Molecular Psychiatry website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hirvonen, J., Zanotti-Fregonara, P., Umhau, J. et al. Reduced cannabinoid CB1 receptor binding in alcohol dependence measured with positron emission tomography. Mol Psychiatry 18, 916–921 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2012.100
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2012.100