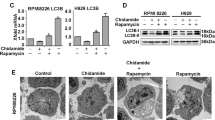
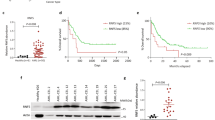
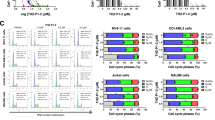
Abstract
Histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors (HDACis) are well-characterized anti-cancer agents with promising results in clinical trials. However, mechanistically little is known regarding their selectivity in killing malignant cells while sparing normal cells. Gene expression-based chemical genomics identified HDACis as being particularly potent against Down syndrome-associated myeloid leukemia (DS-AMKL) blasts. Investigating the antileukemic function of HDACis revealed their transcriptional and post-translational regulation of key autophagic proteins, including ATG7. This leads to suppression of autophagy, a lysosomal degradation process that can protect cells against damaged or unnecessary organelles and protein aggregates. DS-AMKL cells exhibit low baseline autophagy due to mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) activation. Consequently, HDAC inhibition repressed autophagy below a critical threshold, which resulted in accumulation of mitochondria, production of reactive oxygen species, DNA damage and apoptosis. Those HDACi-mediated effects could be reverted upon autophagy activation or aggravated upon further pharmacological or genetic inhibition. Our findings were further extended to other major acute myeloid leukemia subgroups with low basal level autophagy. The constitutive suppression of autophagy due to mTOR activation represents an inherent difference between cancer and normal cells. Thus, via autophagy suppression, HDACis deprive cells of an essential pro-survival mechanism, which translates into an attractive strategy to specifically target cancer cells.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
References
Klusmann JH, Creutzig U, Zimmermann M, Dworzak M, Jorch N, Langebrake C et al. Treatment and prognostic impact of transient leukemia in neonates with Down syndrome. Blood 2008; 111: 2991–2998.
Creutzig U, Reinhardt D, Diekamp S, Dworzak M, Stary J, Zimmermann M . AML patients with Down syndrome have a high cure rate with AML-BFM therapy with reduced dose intensity. Leukemia 2005; 19: 1355–1360.
O'Brien MM, Cao X, Pounds S, Dahl GV, Raimondi SC, Lacayo NJ et al. Prognostic features in acute megakaryoblastic leukemia in children without Down syndrome: a report from the AML02 multicenter trial and the Children's Oncology Group study POG 9421. Leukemia 2013; 27: 731–734.
Klusmann JH, Godinho FJ, Heitmann K, Maroz A, Koch ML, Reinhardt D et al. Developmental stage-specific interplay of GATA1 and IGF signaling in fetal megakaryopoiesis and leukemogenesis. Genes Dev 2010; 24: 1659–1672.
Blink M, Buitenkamp TD, van den Heuvel-Eibrink MM, Danen-van Oorschot AA, de Haas V, Reinhardt D et al. Frequency and prognostic implications of JAK 1-3 aberrations in Down syndrome acute lymphoblastic and myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 2011; 25: 1365–1368.
Klusmann JH, Reinhardt D, Hasle H, Kaspers GJ, Creutzig U, Hahlen K et al. Janus kinase mutations in the development of acute megakaryoblastic leukemia in children with and without Down's syndrome. Leukemia 2007; 21: 1584–1587.
Barbetti V, Gozzini A, Cheloni G, Marzi I, Fabiani E, Santini V et al. Time- and residue-specific differences in histone acetylation induced by VPA and SAHA in AML1/ETO-positive leukemia cells. Epigenetics 2013; 8: 210–219.
Minucci S, Pelicci PG . Histone deacetylase inhibitors and the promise of epigenetic (and more) treatments for cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2006; 6: 38–51.
Ungewickell A, Medeiros BC . Novel agents in acute myeloid leukemia. Int J Hematol 2012; 96: 178–185.
He LZ, Tolentino T, Grayson P, Zhong S, Warrell RP Jr, Rifkind RA et al. Histone deacetylase inhibitors induce remission in transgenic models of therapy-resistant acute promyelocytic leukemia. J Clin Invest 2001; 108: 1321–1330.
Trus MR, Yang L, Suarez SF, Bordeleau L, Jurisica I, Minden MD . The histone deacetylase inhibitor valproic acid alters sensitivity towards all trans retinoic acid in acute myeloblastic leukemia cells. Leukemia 2005; 19: 1161–1168.
Chuang DM, Leng Y, Marinova Z, Kim HJ, Chiu CT . Multiple roles of HDAC inhibition in neurodegenerative conditions. Trends Neurosci 2009; 32: 591–601.
Garcia-Manero G . Can we improve outcomes in patients with acute myelogenous leukemia? incorporating HDAC inhibitors into front-line therapy. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol 2012; 25: 427–435.
Quintas-Cardama A, Santos FP, Garcia-Manero G . Histone deacetylase inhibitors for the treatment of myelodysplastic syndrome and acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 2011; 25: 226–235.
Roy S, Packman K, Jeffrey R, Tenniswood M . Histone deacetylase inhibitors differentially stabilize acetylated p53 and induce cell cycle arrest or apoptosis in prostate cancer cells. Cell Death Differ 2005; 12: 482–491.
McCormack E, Haaland I, Venas G, Forthun RB, Huseby S, Gausdal G et al. Synergistic induction of p53 mediated apoptosis by valproic acid and nutlin-3 in acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 2012; 26: 910–917.
Youle RJ, Narendra DP . Mechanisms of mitophagy. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2011; 12: 9–14.
Insinga A, Monestiroli S, Ronzoni S, Gelmetti V, Marchesi F, Viale A et al. Inhibitors of histone deacetylases induce tumor-selective apoptosis through activation of the death receptor pathway. Nat Med 2005; 11: 71–76.
Robert T, Vanoli F, Chiolo I, Shubassi G, Bernstein KA, Rothstein R et al. HDACs link the DNA damage response, processing of double-strand breaks and autophagy. Nature 2011; 471: 74–79.
Carew JS, Nawrocki ST, Kahue CN, Zhang H, Yang C, Chung L et al. Targeting autophagy augments the anticancer activity of the histone deacetylase inhibitor SAHA to overcome Bcr-Abl-mediated drug resistance. Blood 2007; 110: 313–322.
Carew JS, Medina EC, Esquivel JA, Mahalingam D, Swords R, Kelly K et al. Autophagy inhibition enhances vorinostat-induced apoptosis via ubiquitinated protein accumulation. J Cell Mol Med 2010; 14: 2448–2459.
Gammoh N, Lam D, Puente C, Ganley I, Marks PA, Jiang X . Role of autophagy in histone deacetylase inhibitor-induced apoptotic and nonapoptotic cell death. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2012; 109: 6561–6565.
Klusmann JH, Li Z, Bohmer K, Maroz A, Koch ML, Emmrich S et al. miR-125b-2 is a potential oncomiR on human chromosome 21 in megakaryoblastic leukemia. Genes Dev 2010; 24: 478–490.
Li C, Wong WH . Model-based analysis of oligonucleotide arrays: expression index computation and outlier detection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2001; 98: 31–36.
Subramanian A, Tamayo P, Mootha VK, Mukherjee S, Ebert BL, Gillette MA et al. Gene set enrichment analysis: a knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2005; 102: 15545–15550.
Lamb J, Crawford ED, Peck D, Modell JW, Blat IC, Wrobel MJ et al. The Connectivity Map: using gene-expression signatures to connect small molecules, genes, and disease. Science 2006; 313: 1929–1935.
Bourquin JP, Subramanian A, Langebrake C, Reinhardt D, Bernard O, Ballerini P et al. Identification of distinct molecular phenotypes in acute megakaryoblastic leukemia by gene expression profiling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2006; 103: 3339–3344.
Tonelli R, Sartini R, Fronza R, Freccero F, Franzoni M, Dongiovanni D et al. G1 cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis by histone deacetylase inhibition in MLL-AF9 acute myeloid leukemia cells is p21 dependent and MLL-AF9 independent. Leukemia 2006; 20: 1307–1310.
Kiyoi H, Yamaji S, Kojima S, Naoe T . JAK3 mutations occur in acute megakaryoblastic leukemia both in Down syndrome children and non-Down syndrome adults. Leukemia 2007; 21: 574–576.
Lucas DM, Davis ME, Parthun MR, Mone AP, Kitada S, Cunningham KD et al. The histone deacetylase inhibitor MS-275 induces caspase-dependent apoptosis in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells. Leukemia 2004; 18: 1207–1214.
Balasubramanian S, Ramos J, Luo W, Sirisawad M, Verner E, Buggy JJ . A novel histone deacetylase 8 (HDAC8)-specific inhibitor PCI-34051 induces apoptosis in T-cell lymphomas. Leukemia 2008; 22: 1026–1034.
Behrends C, Sowa ME, Gygi SP, Harper JW . Network organization of the human autophagy system. Nature 2010; 466: 68–76.
Mizushima N, Yoshimori T, Levine B . Methods in mammalian autophagy research. Cell 2010; 140: 313–326.
Mizushima N . Autophagy: process and function. Genes Dev 2007; 21: 2861–2873.
Lee IH, Cao L, Mostoslavsky R, Lombard DB, Liu J, Bruns NE et al. A role for the NAD-dependent deacetylase Sirt1 in the regulation of autophagy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2008; 105: 3374–3379.
Lee IH, Finkel T . Regulation of autophagy by the p300 acetyltransferase. J Biol Chem 2009; 284: 6322–6328.
Choudhary C, Kumar C, Gnad F, Nielsen ML, Rehman M, Walther TC et al. Lysine acetylation targets protein complexes and co-regulates major cellular functions. Science 2009; 325: 834–840.
Dalby KN, Tekedereli I, Lopez-Berestein G, Ozpolat B . Targeting the prodeath and prosurvival functions of autophagy as novel therapeutic strategies in cancer. Autophagy 2010; 6: 322–329.
Chan LL, Shen D, Wilkinson AR, Patton W, Lai N, Chan E et al. A novel image-based cytometry method for autophagy detection in living cells. Autophagy 2012; 8: 1371–1382.
Nakahira K, Haspel JA, Rathinam VA, Lee SJ, Dolinay T, Lam HC et al. Autophagy proteins regulate innate immune responses by inhibiting the release of mitochondrial DNA mediated by the NALP3 inflammasome. Nat Immunol 2011; 12: 222–230.
Zhang Y, Qi H, Taylor R, Xu W, Liu LF, Jin S . The role of autophagy in mitochondria maintenance: characterization of mitochondrial functions in autophagy-deficient S. cerevisiae strains. Autophagy 2007; 3: 337–346.
White E . Deconvoluting the context-dependent role for autophagy in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2012; 12: 401–410.
Janes MR, Limon JJ, So L, Chen J, Lim RJ, Chavez MA et al. Effective and selective targeting of leukemia cells using a TORC1/2 kinase inhibitor. Nat Med 2010; 16: 205–213.
Aronson LI, Davenport EL, Mirabella F, Morgan GJ, Davies FE . Understanding the interplay between the proteasome pathway and autophagy in response to dual PI3K/mTOR inhibition in myeloma cells is essential for their effective clinical application. Leukemia 2013; 27: 2397–2403.
Kojima K, Shimanuki M, Shikami M, Samudio IJ, Ruvolo V, Corn P et al. The dual PI3 kinase/mTOR inhibitor PI-103 prevents p53 induction by Mdm2 inhibition but enhances p53-mediated mitochondrial apoptosis in p53 wild-type AML. Leukemia 2008; 22: 1728–1736.
Wullschleger S, Loewith R, Hall MN . TOR signaling in growth and metabolism. Cell 2006; 124: 471–484.
Maiso P, Colado E, Ocio EM, Garayoa M, Martin J, Atadja P et al. The synergy of panobinostat plus doxorubicin in acute myeloid leukemia suggests a role for HDAC inhibitors in the control of DNA repair. Leukemia 2009; 23: 2265–2274.
Rosato RR, Almenara JA, Yu C, Grant S . Evidence of a functional role for p21WAF1/CIP1 down-regulation in synergistic antileukemic interactions between the histone deacetylase inhibitor sodium butyrate and flavopiridol. Mol Pharmacol 2004; 65: 571–581.
Ungerstedt JS, Sowa Y, Xu WS, Shao Y, Dokmanovic M, Perez G et al. Role of thioredoxin in the response of normal and transformed cells to histone deacetylase inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2005; 102: 673–678.
Batty N, Malouf GG, Issa JP . Histone deacetylase inhibitors as anti-neoplastic agents. Cancer Lett 2009; 280: 192–200.
Fullgrabe J, Lynch-Day MA, Heldring N, Li W, Struijk RB, Ma Q et al. The histone H4 lysine 16 acetyltransferase hMOF regulates the outcome of autophagy. Nature 2013; 500: 468–471.
Mizushima N . The role of the Atg1/ULK1 complex in autophagy regulation. Curr Opin Cell Biol 2010; 22: 132–139.
Mathew R, Karantza-Wadsworth V, White E . Role of autophagy in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2007; 7: 961–967.
Oehme I, Linke JP, Bock BC, Milde T, Lodrini M, Hartenstein B et al. Histone deacetylase 10 promotes autophagy-mediated cell survival. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2013; 110: E2592–E2601.
Cao DJ, Wang ZV, Battiprolu PK, Jiang N, Morales CR, Kong Y et al. Histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors attenuate cardiac hypertrophy by suppressing autophagy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2011; 108: 4123–4128.
Moresi V, Carrer M, Grueter CE, Rifki OF, Shelton JM, Richardson JA et al. Histone deacetylases 1 and 2 regulate autophagy flux and skeletal muscle homeostasis in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2012; 109: 1649–1654.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Bradner for sharing the reagents, the Mizushima and Levine laboratories for valuable methodological advice, and C Reimer and L Queißer for technical assistance. This work was supported by a grant to JHK and DR from the Wilhelm Sander-Foundation (2011.057.1), the German Research Foundation (DFG; KL-2374/1-1) and to SHO from the NIH. JHK is a fellow of the Emmy Noether-Programme from the DFG (KL-2374/2-1). SHO is an Investigator of the Howard Hughes Medical Institute. GMNB and MVS were supported by the DFG (BE-2089/2-1 and EXC62/1), NS by the SFB/TR77, ML by the DFG (LE-953/8-1 and LE-953/6-1) and the Mildred-Scheel-Stiftung (#109891) and KH by the Hannover Biomedical Research School. ZL was a Fellow of the Leukemia & Lymphoma Society and is supported by NIH grant R01 HL107663.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
JHK, MVS and ME-K designed and performed the experiments, analyzed the data and wrote the manuscript. GMNB, SHO and ZL designed the experiments, interpreted the data and wrote the manuscript. KH, NS, MEK and DPD designed and performed the experiments, analyzed the data and revised the manuscript. BT designed the experiments and revised the manuscript. JS performed and analyzed the experiments. JPB performed gene expression-based chemical genomics screening. DR, KW and ML provided materials/reagents and revised the manuscript.
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Leukemia website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stankov, M., El Khatib, M., Kumar Thakur, B. et al. Histone deacetylase inhibitors induce apoptosis in myeloid leukemia by suppressing autophagy. Leukemia 28, 577–588 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2013.264
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2013.264
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The inhibition of FKBP5 protects β-cell survival under inflammation stress via AKT/FOXO1 signaling
Cell Death Discovery (2023)
-
Expression Changes of SIRT1 and FOXO3a Significantly Correlate with Oxidative Stress Resistance Genes in AML Patients
Indian Journal of Hematology and Blood Transfusion (2023)
-
Inhibition of PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway and modulation of histone deacetylase enzymes reduce the growth of acute myeloid leukemia cells
Medical Oncology (2023)
-
Detoxified pneumolysin derivative ΔA146Ply inhibits autophagy and induces apoptosis in acute myeloid leukemia cells by activating mTOR signaling
Experimental & Molecular Medicine (2022)
-
Autophagy inhibition impairs leukemia stem cell function in FLT3-ITD AML but has antagonistic interactions with tyrosine kinase inhibition
Leukemia (2022)