Abstract
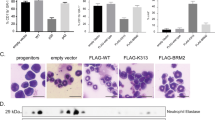
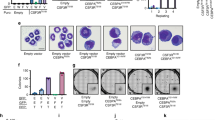
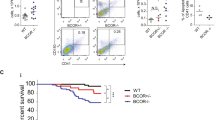
CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein-α (C/EBPα/CEBPA) is mutated in approximately 8% of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) in both familial and sporadic AML and, with FLT3 and NPM1, has received most attention as a predictive marker of outcome in patients with normal karyotype disease. Mutations clustering to either the N- or C-terminal (N- and C-ter) portions of the protein have different consequences on the protein function. In familial cases, the N-ter form is inherited with patients exhibiting long latency period before the onset of overt disease, typically with the acquisition of a C-ter mutation. Despite the essential insights murine models provide the functional consequences of wild-type C/EBPα in human hematopoiesis and how different mutations are involved in AML development have received less attention. Our data underline the critical role of C/EBPα in human hematopoiesis and demonstrate that C/EBPα mutations (alone or in combination) are insufficient to convert normal human hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells into leukemic-initiating cells, although individually each altered normal hematopoiesis. It provides the first insight into the effects of N- and C-ter mutations acting alone and to the combined effects of N/C double mutants. Our results mimicked closely what happens in CEBPA mutated patients.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Passegue E, Jamieson CH, Ailles LE, Weissman IL . Normal and leukemic hematopoiesis: are leukemias a stem cell disorder or a reacquisition of stem cell characteristics? Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2003; 100 (Suppl 1): 11842–11849.
Jordan CT, Guzman ML . Mechanisms controlling pathogenesis and survival of leukemic stem cells. Oncogene 2004; 23: 7178–7187.
Warner JK, Wang JC, Hope KJ, Jin L, Dick JE . Concepts of human leukemic development. Oncogene 2004; 23: 7164–7177.
Gililand G, Tallman MS . Focus on acute leukemias. Cancer Cell 2002; 1: 417–420.
Pabst T, Mueller BU . Transcriptional dysregulation during myeloid transformation in AML. Oncogene 2007; 26: 6829–6837.
Friedman AD . Runx1, c-Myb, and C/EBPalpha couple differentiation to proliferation or growth arrest during hematopoiesis. J Cell Biochem 2002; 86: 624–629.
Friedman AD . C/EBPalpha induces PU.1 and interacts with AP-1 and NF-kappaB to regulate myeloid development. Blood Cells Mol Dis 2007; 39: 340–343.
Friedman AD . Transcriptional control of granulocyte and monocyte development. Oncogene 2007; 26: 6816–6828.
Zhang P, Iwasaki-Arai J, Iwasaki H, Fenyus ML, Dayaram T, Owens BM et al. Enhancement of hematopoietic stem cell repopulating capacity and self-renewal in the absence of the transcription factor C/EBP alpha. Immunity 2004; 21: 853–863.
Nerlov C . The C/EBP family of transcription factors: a paradigm for interaction between gene expression and proliferation control. Trends Cell Biol 2007; 17: 318–324.
Nerlov C . C/EBPalpha mutations in acute myeloid leukaemias. Nat Rev Cancer 2004; 4: 394–400.
Koschmieder S, Halmos B, Levantini E, Tenen DG . Dysregulation of the C/EBPalpha differentiation pathway in human cancer. J Clin Oncol 2009; 27: 619–628.
Calkhoven CF, Muller C, Leutz A . Translational control of C/EBPalpha and C/EBPbeta isoform expression. Genes Dev 2000; 14: 1920–1932.
D’Alo F, Johansen LM, Nelson EA, Radomska HS, Evans EK, Zhang P et al. The amino terminal and E2F interaction domains are critical for C/EBP alpha-mediated induction of granulopoietic development of hematopoietic cells. Blood 2003; 102: 3163–3171.
Johansen LM, Iwama A, Lodie TA, Sasaki K, Felsher DW, Golub TR et al. c-Myc is a critical target for c/EBPalpha in granulopoiesis. Mol Cell Biol 2001; 21: 3789–3806.
Timchenko NA, Harris TE, Wilde M, Bilyeu TA, Burgess-Beusse BL, Finegold MJ et al. CCAAT/enhancer binding protein alpha regulates p21 protein and hepatocyte proliferation in newborn mice. Mol Cell Biol 1997; 17: 7353–7361.
Timchenko NA, Wilde M, Nakanishi M, Smith JR, Darlington GJ . CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha (C/EBP alpha) inhibits cell proliferation through the p21 (WAF-1/CIP-1/SDI-1) protein. Genes Dev 1996; 10: 804–815.
Wang H, Iakova P, Wilde M, Welm A, Goode T, Roesler WJ et al. C/EBPalpha arrests cell proliferation through direct inhibition of Cdk2 and Cdk4. Mol Cell 2001; 8: 817–828.
Porse BT, Pedersen TA, Xu X, Lindberg B, Wewer UM, Friis-Hansen L et al. E2F repression by C/EBPalpha is required for adipogenesis and granulopoiesis in vivo. Cell 2001; 107: 247–258.
Porse BT, Bryder D, Theilgaard-Monch K, Hasemann MS, Anderson K, Damgaard I et al. Loss of C/EBP alpha cell cycle control increases myeloid progenitor proliferation and transforms the neutrophil granulocyte lineage. J Exp Med 2005; 202: 85–96.
McNagny KM, Sieweke MH, Doderlein G, Graf T, Nerlov C . Regulation of eosinophil-specific gene expression by a C/EBP-Ets complex and GATA-1. EMBO J 1998; 17: 3669–3680.
Kummalue T, Friedman AD . Cross-talk between regulators of myeloid development: C/EBPalpha binds activates the promoter of the PU1 gene. J Leukoc Biol 2003; 74: 464–470.
Tenen DG, Hromas R, Licht JD, Zhang DE . Transcription factors, normal myeloid development, and leukemia. Blood 1997; 90: 489–519.
Kovacs KA, Steinmann M, Magistretti PJ, Halfon O, Cardinaux JR . CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein family members recruit the coactivator CREB-binding protein and trigger its phosphorylation. J Biol Chem 2003; 278: 36959–36965.
Nerlov C, Ziff EB . CCAAT/enhancer binding protein-alpha amino acid motifs with dual TBP and TFIIB binding ability co-operate to activate transcription in both yeast and mammalian cells. EMBO J 1995; 14: 4318–4328.
Muller C, Calkhoven CF, Sha X, Leutz A . The CCAAT enhancer-binding protein alpha (C/EBPalpha) requires a SWI/SNF complex for proliferation arrest. J Biol Chem 2004; 279: 7353–7358.
Pedersen TA, Kowenz-Leutz E, Leutz A, Nerlov C . Cooperation between C/EBPalpha TBP/TFIIB and SWI/SNF recruiting domains is required for adipocyte differentiation. Genes Dev 2001; 15: 3208–3216.
Barjesteh van Waalwijk van Doorn-Khosrovani S, Erpelinck C, Meijer J, van Oosterhoud S, van Putten WL, Valk PJ et al. Biallelic mutations in the C/EBPA gene and low C/EBPA expression levels as prognostic markers in intermediate-risk AML. Hematol J 2003; 4: 31–40.
Bienz M, Ludwig M, Leibundgut EO, Mueller BU, Ratschiller D, Solenthaler M et al. Risk assessment in patients with acute myeloid leukemia and a normal karyotype. Clin Cancer Res 2005; 11: 1416–1424.
Frohling S, Dohner H . Disruption of C/EBPalpha function in acute myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med 2004; 351: 2370–2372.
Gombart AF, Hofmann WK, Kawano S, Takeuchi S, Krug U, Kwok SH et al. Mutations in the gene encoding the transcription factor CCAAT/enhancer binding protein alpha in myelodysplastic syndromes and acute myeloid leukemias. Blood 2002; 99: 1332–1340.
Leroy H, Roumier C, Huyghe P, Biggio V, Fenaux P, Preudhomme C . C/EBPA point mutations in hematological malignancies. Leukemia 2005; 19: 329–334.
Lin LI, Chen CY, Lin DT, Tsay W, Tang JL, Yeh YC et al. Characterization of C/EBPA mutations in acute myeloid leukemia: most patients with C/EBPA mutations have biallelic mutations and show a distinct immunophenotype of the leukemic cells. Clin Cancer Res 2005; 11: 1372–1379.
Mueller BU, Pabst T . C/EBPalpha and the pathophysiology of acute myeloid leukemia. Curr Opin Hematol 2006; 13: 7–14.
Pabst T, Mueller BU, Zhang P, Radomska HS, Narravula S, Schnittger S et al. Dominant-negative mutations of C/EBPA, encoding CCAAT/enhancer binding protein-alpha (C/EBPalpha), in acute myeloid leukemia. Nat Genet 2001; 27: 263–270.
Pabst T, Eyholzer M, Haefliger S, Schardt J, Mueller BU . Somatic C/EBPA mutations are a frequent second event in families with germline C/EBPA mutations and familial acute myeloid leukemia. J Clin Oncol 2008; 26: 5088–5093.
Preudhomme C, Sagot C, Boissel N, Cayuela JM, Tigaud I, de Botton S et al. Favorable prognostic significance of C/EBPA mutations in patients with de novo acute myeloid leukemia: a study from the Acute Leukemia French Association (ALFA). Blood 2002; 100: 2717–2723.
Snaddon J, Smith ML, Neat M, Cambal-Parrales M, Dixon-McIver A, Arch R et al. Mutations of C/EBPA in acute myeloid leukemia FAB types M1 and M2. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2003; 37: 72–78.
Wouters BJ, Lowenberg B, Erpelinck-Verschueren CA, van Putten WL, Valk PJ, Delwel R . Double C/EBPA mutations, but not single C/EBPA mutations, define a subgroup of acute myeloid leukemia with a distinctive gene expression profile that is uniquely associated with a favorable outcome. Blood 2009; 113: 3088–3091.
Fitzgibbon J, Smith LL, Raghavan M, Smith ML, Debernardi S, Skoulakis S et al. Association between acquired uniparental disomy and homozygous gene mutation in acute myeloid leukemias. Cancer Res 2005; 65: 9152–9154.
Hou HA, Lin LI, Tien HF . Reply to ‘heterogeneity within AML with CEBPA mutations; only CEBPA double mutations, but not single CEBPA mutations are associated with favorable prognosis’. Br J Cancer 2009; 100: 1–3.
Pabst T, Eyholzer M, Fos C, Mueller BU . Heterogeneity within AML with CEBPA mutations; only CEBPA double mutations, but not single CEBPA mutations are associated with favourable prognosis. Br J Cancer 2009; 100: 1343–1346.
Smith ML, Cavenagh JD, Lister TA, Fitzgibbon J . Mutation of C/EBPA in familial acute myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med 2004; 351: 2403–2407.
Schlenk RF, Döhner K, Krauter J, Fröhling S, Corbacioglu A, Bullinger L et al. Mutations and treatment outcome in cytogenetically normal acute myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med 2008; 358: 1909–1918.
Renneville A, Mialou V, Philippe N, Kagialis-Girard S, Biggio V, Zabot MT et al. Another pedigree with familial acute myeloid leukemia and germline C/EBPA mutation. Leukemia 2009; 23: 804–806.
Kirstetter P, Schuster MB, Bereshchenko O, Moore S, Dvinge H, Kurz E et al. Modeling of C/EBPalpha mutant acute myeloid leukemia reveals a common expression signature of committed myeloid leukemia-initiating cells. Cancer Cell 2008; 13: 299–310.
Bereshchenko O, Mancini E, Moore S, Bilbao D, Mansson R, Luc S et al. Hematopoietic stem cell expansion precedes the generation of committed myeloid leukemia-initiating cells in C/EBPalpha mutant AML. Cancer Cell 2009; 16: 390–400.
Kato N, Kitaura J, Komeno Y, Watanabe-Okochi N, Togami K, Nakahara F et al. Two types of C/EBPα mutations play distinct but collaborative roles in leukemogenesis: lessons from clinical data and BMT models. Blood 2011; 117: 221–233.
Barabe F, Kennedy JA, Hope KJ, Dick JE . Modeling the initiation and progression of human acute leukemia in mice. Science 2007; 316: 600–604.
Wei J, Wunderlich M, Fox C, Alvarez S, Cigudosa JC, Wilhelm JS et al. Microenvironment determines lineage fate in a human model of MLL-AF9 leukemia. Cancer Cell 2008; 13: 483–495.
Cammenga J, Mulloy JC, MacGrogan D, Viale A, Nimer SD . Induction of CEBPalpha activity alters gene expression and differentiation of human CD34+ cells. Blood 2003; 101: 2206–2214.
Almarza E, Rio P, Meza NW, Aldea M, Agirre X, Guenechea G et al. Characteristics of lentiviral vectors harboring the proximal promoter of the vav proto-oncogene: a weak and efficient promoter for gene therapy. Mol Ther 2007; 15: 1487–1494.
Paz-Priel I, Ghosal AK, Kowalski J, Friedman AD . C/EBPalpha or C/EBPalpha oncoproteins regulate the intrinsic and extrinsic apoptotic pathways by direct interaction with NF-kappaB p50 bound to the bcl-2 and FLIP gene promoters. Leukemia 2009; 23: 365–374.
Niebuhr B, Iwanski GB, Schwieger M, Roscher S, Stocking C, Cammenga J . Investigation of C/EBPalpha function in human (versus murine) myelopoiesis provides novel insight into the impact of C/EBPA mutations in acute myelogenous leukemia (AML). Leukemia 2009; 23: 978–983.
Chapiro E, Russell L, Radford-Weiss I, Bastard C, Lessard M, Struski S et al. Overexpression of CEBPA resulting from the translocation t(14;19)(q32;q13) of human precursor B acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 2006; 108: 3560–3563.
Akasaka T, Balasas T, Russell LJ, Sugimoto K, Majid A, Walewska R et al. Five members of the CEBP transcription factor family are targeted by recurrent IGH translocation in B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia (BCP-ALL). Blood 2007; 109: 3451–3461.
Wouters BJ, Jorda MA, Keeshan K, Louwers I, Erpelinck-Verschueren CA, Tielemans D et al. Distinct gene expression profiles of acute myeloid/T-lymphoid leukemia with silenced C/EBPA and mutations in NOTCH1. Blood 2007; 110: 3706–3714.
Geletu M, Balkhi MY, Peer Zada AA, Christopeit M, Pulikkan JA, Trivedi AK et al. Target proteins of C/EBPalphap30 in AML: C/EBPalphap30 enhances sumoylation of C/EBPalphap42 via up-regulation of Ubc9. Blood 2007; 110: 3301–3309.
Shih LY, Liang DC, Huang CF, Wu JH, Lin TL, Wang PN et al. AML patients with C/EBPalpha mutations mostly retain identical mutant patterns but frequently change in allelic distribution at relapse: a comparative analysis on paired diagnosis and relapse samples. Leukemia 2006; 20: 604–609.
Sellick GS, Spendlove HE, Catovsky D, Pritchard-Jones K, Houlston RS . Further evidence that germline C/EBPA mutations cause dominant inheritance of acute myeloid leukaemia. Leukemia 2005; 19: 1276–1278.
Delhommeau F, Dupont S, Della Valle V, James C, Trannoy S, Massé A et al. Mutations in TET2 in myeloid cancers. N Engl J Med 2009; 360: 2289–2301.
Greaves MF, Wiemels J . Origins of chromosome translocations in childhood leukaemia. Nat Rev Cancer 2003; 3: 639–649.
Hong D, Gupta R, Ancliff P, Atzberger A, Brown J, Soneji S et al. Initiating and cancer-propagating cells in TEL-AML1-associated childhood leukemia. Science 2008; 319: 336–339.
Acknowledgements
We thank the members of FACS service and animal facilities for their help. We are grateful to Dr Oscar Escribano from Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Faculty of Pharmacy, Complutense University of Madrid, Madrid, Spain for his technical advice in performing the western blot analysis. This project was supported by Cancer Research UK and by European grant (contract no: 037632) to DB. OQ-B was supported by CRUK, LRI fellowship.
Author Contributions
OQ-B designed and performed research, analyzed and interpreted data, performed statistical analysis and wrote paper. SL-LS, EG, YR and JV performed part of the research experiments, TAL provided vital materials and JF interpreted data and wrote paper, DB designed research and analyzed and interpreted data and wrote paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Leukemia website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Quintana-Bustamante, O., Smith, SL., Griessinger, E. et al. Overexpression of wild-type or mutants forms of CEBPA alter normal human hematopoiesis. Leukemia 26, 1537–1546 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2012.38
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2012.38
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Role of microRNAs and their downstream target transcription factors in zebrafish thrombopoiesis
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
The 5th edition of the World Health Organization Classification of Haematolymphoid Tumours: Myeloid and Histiocytic/Dendritic Neoplasms
Leukemia (2022)
-
The molecular landscape of pediatric acute myeloid leukemia reveals recurrent structural alterations and age-specific mutational interactions
Nature Medicine (2018)
-
The presence of C/EBPα and its degradation are both required for TRIB2-mediated leukaemia
Oncogene (2016)
-
Positional cloning and next-generation sequencing identified a TGM6 mutation in a large Chinese pedigree with acute myeloid leukaemia
European Journal of Human Genetics (2015)