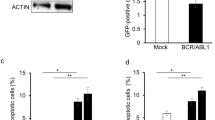
Abstract
Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) results from the expression of the BCR/ABL oncogene in a primitive hematopoietic cell. However, BCR/ABL-activated signaling mechanisms are dependent on the cellular context in which it is expressed, and mechanisms underlying primitive human hematopoietic cell transformation by BCR–ABL are not well understood. Our previous studies have shown that BCR/ABL-Y177 has an essential role in Ras activation and human hematopoietic progenitor transformation in CML. The adapter protein growth factor receptor-binding protein-2 (Grb2) can bind phosphorylated BCR/ABL-Y177, induce Grb2-SoS complex formation and activate Ras signaling. We investigated the role of Grb2 in CML progenitor transformation by cotransducing human CD34+ cells with lentivirus vectors expressing short hairpin RNA to Grb2 and retrovirus vectors expressing BCR/ABL. We show that Grb2 knockdown significantly inhibits proliferation and survival of BCR–ABL-expressing CD34+ cells, but not control CD34+ cells. Grb2 knockdown reduced mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) activity in BCR–ABL-expressing hematopoietic cells. We conclude that inhibition of Grb2 expression demonstrates an important role in BCR–ABL-mediated MAPK activation and transformation of primary human hematopoietic cells.These results support further investigation of downstream effectors of Grb2-mediated signals and targeting of Grb2 interactions in the treatment of CML.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rowley JD . Letter: a new consistent chromosomal abnormality in chronic myelogenous leukaemia identified by quinacrine fluorescence and Giemsa staining. Nature 1973; 243: 290–293.
de Klein A, van Kessel AG, Grosveld G, Bartram CR, Hagemeijer A, Bootsma D et al. A cellular oncogene is translocated to the Philadelphia chromosome in chronic myelocytic leukaemia. Nature 1982; 300: 765–767.
Lugo TG, Pendergast AM, Muller AJ, Witte ON . Tyrosine kinase activity and transformation potency of BCR-ABL oncogene products. Science 1990; 247: 1079–1082.
Zhang X, Ren R . Bcr-Abl efficiently induces a myeloproliferative disease and production of excess interleukin-3 and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor in mice: a novel model for chronic myelogenous leukemia. Blood 1998; 92: 3829–3840.
Deininger MW, Druker BJ . Specific targeted therapy of chronic myelogenous leukemia with imatinib. Pharmacol Rev 2003; 55: 401–423.
Druker BJ, Guilhot F, O’Brien SG, Gathmann I, Kantarjian H, Gattermann N et al. Five-year follow-up of patients receiving imatinib for chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med 2006; 355: 2408–2417.
Talpaz M, Silver RT, Druker BJ, Goldman JM, Gambacorti-Passerini C, Guilhot F et al. Imatinib induces durable hematologic and cytogenetic responses in patients with accelerated phase chronic myeloid leukemia: results of a phase 2 study. Blood 2002; 99: 1928–1937.
Holtz MS, Slovak ML, Zhang F, Sawyers CL, Forman SJ, Bhatia R . Imatinib mesylate (STI571) inhibits growth of primitive malignant progenitors in chronic myelogenous leukemia through reversal of abnormally increased proliferation. Blood 2002; 99: 3792–3800.
Bhatia R, Holtz M, Niu N, Gray R, Snyder DS, Sawyers CL et al. Persistence of malignant hematopoietic progenitors in chronic myelogenous leukemia patients in complete cytogenetic remission following imatinib mesylate treatment. Blood 2003; 101: 4701–4707.
Holtz MS, Forman SJ, Bhatia R . Nonproliferating CML CD34+ progenitors are resistant to apoptosis induced by a wide range of proapoptotic stimuli. Leukemia 2005; 19: 1034–1041.
Rousselot P, Huguet F, Rea D, Legros L, Cayuela JM, Maarek O et al. Imatinib mesylate discontinuation in patients with chronic myelogenous leukemia in complete molecular remission for more than 2 years. Blood 2007; 109: 58–60.
Ramaraj P, Singh H, Niu N, Chu S, Holtz M, Yee JK et al. Effect of mutational inactivation of tyrosine kinase activity on BCR/ABL-induced abnormalities in cell growth and adhesion in human hematopoietic progenitors. Cancer Res 2004; 64: 5322–5331.
Chu S, Li L, Singh H, Bhatia R . BCR-tyrosine 177 plays an essential role in Ras and Akt activation and in human hematopoietic progenitor transformation in chronic myelogenous leukemia. Cancer Res 2007; 67: 7045–7053.
Puil L, Liu J, Gish G, Mbamalu G, Bowtell D, Pelicci PG et al. Bcr-Abl oncoproteins bind directly to activators of the Ras signalling pathway. EMBO J 1994; 13: 764–773.
Sattler M, Mohi MG, Pride YB, Quinnan LR, Malouf NA, Podar K et al. Critical role for Gab2 in transformation by BCR/ABL. Cancer Cell 2002; 1: 479–492.
Million RP, Harakawa N, Roumiantsev S, Varticovski L, Van Etten RA . A direct binding site for Grb2 contributes to transformation and leukemogenesis by the Tel-Abl (ETV6-Abl) tyrosine kinase. Mol Cell Biol 2004; 24: 4685–4695.
Yam PY, Li S, Wu J, Hu J, Zaia JA, Yee JK . Design of HIV vectors for efficient gene delivery into human hematopoietic cells. Mol Ther 2002; 5: 479–484.
Ramezani A, Hawley TS, Hawley RG . Lentiviral vectors for enhanced gene expression in human hematopoietic cells. Mol Ther 2000; 2: 458–469.
Baum C, Hegewisch-Becker S, Eckert HG, Stocking C, Ostertag W . Novel retroviral vectors for efficient expression of the multidrug resistance (mdr-1) gene in early hematopoietic cells. J Virol 1995; 69: 7541–7547.
Modi H, McDonald T, Chu S, Yee JK, Forman SJ, Bhatia R . Role of BCR/ABL gene-expression levels in determining the phenotype and imatinib sensitivity of transformed human hematopoietic cells. Blood 2007; 109: 5411–5421.
Jiang Y, Zhao RC, Verfaillie CM . Abnormal integrin-mediated regulation of chronic myelogenous leukemia CD34+ cell proliferation: BCR/ABL up-regulates the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor, p27Kip, which is relocated to the cell cytoplasm and incapable of regulating cdk2 activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2000; 97: 10538–10543.
Gupta P, McCarthy JB, Verfaillie CM . Stromal fibroblast heparan sulfate is required for cytokine-mediated ex vivo maintenance of human long-term culture-initiating cells. Blood 1996; 87: 3229–3236.
Bhatia R, McGlave PB, Dewald GW, Blazar BR, Verfaillie CM . Abnormal function of the bone marrow microenvironment in chronic myelogenous leukemia: role of malignant stromal macrophages. Blood 1995; 85: 3636–3645.
Pendergast AM, Quilliam LA, Cripe LD, Bassing CH, Dai Z, Li N et al. BCR-ABL-induced oncogenesis is mediated by direct interaction with the SH2 domain of the GRB-2 adaptor protein. Cell 1993; 75: 175–185.
Zhang X, Subrahmanyam R, Wong R, Gross AW, Ren R . The NH(2)-terminal coiled-coil domain and tyrosine 177 play important roles in induction of a myeloproliferative disease in mice by Bcr-Abl. Mol Cell Biol 2001; 21: 840–853.
Ma G, Lu D, Wu Y, Liu J, Arlinghaus RB . Bcr phosphorylated on tyrosine 177 binds Grb2. Oncogene 1997; 14: 2367–2372.
Gishizky ML, Cortez D, Pendergast AM . Mutant forms of growth factor-binding protein-2 reverse BCR-ABL-induced transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1995; 92: 10889–10893.
Kolch W . Coordinating ERK/MAPK signalling through scaffolds and inhibitors. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2005; 6: 827–837.
Kardinal C, Konkol B, Lin H, Eulitz M, Schmidt EK, Estrov Z et al. Chronic myelogenous leukemia blast cell proliferation is inhibited by peptides that disrupt Grb2-SoS complexes. Blood 2001; 98: 1773–1781.
Cheng AM, Saxton TM, Sakai R, Kulkarni S, Mbamalu G, Vogel W et al. Mammalian Grb2 regulates multiple steps in embryonic development and malignant transformation. Cell 1998; 95: 793–803.
Feller SM, Tuchscherer G, Voss J . High affinity molecules disrupting GRB2 protein complexes as a therapeutic strategy for chronic myelogenous leukaemia. Leuk Lymphoma 2003; 44: 411–427.
Acknowledgements
This study is supported by the NIH grant R01 HL77847 and R01CA095684 to Ravi Bhatia. We acknowledge the support of the COHNMC Analytical Cytometry and Sequencing cores. We are grateful to StemCyte for their generous gift of cord blood samples.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Leukemia website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Modi, H., Li, L., Chu, S. et al. Inhibition of Grb2 expression demonstrates an important role in BCR–ABL-mediated MAPK activation and transformation of primary human hematopoietic cells. Leukemia 25, 305–312 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2010.257
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2010.257
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
DYRK2 controls a key regulatory network in chronic myeloid leukemia stem cells
Experimental & Molecular Medicine (2020)
-
miR-1827 inhibits osteogenic differentiation by targeting IGF1 in MSMSCs
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
Platinum pyrithione induces apoptosis in chronic myeloid leukemia cells resistant to imatinib via DUB inhibition-dependent caspase activation and Bcr-Abl downregulation
Cell Death & Disease (2017)
-
Nickel pyrithione induces apoptosis in chronic myeloid leukemia cells resistant to imatinib via both Bcr/Abl-dependent and Bcr/Abl-independent mechanisms
Journal of Hematology & Oncology (2016)
-
Gab2 signaling in chronic myeloid leukemia cells confers resistance to multiple Bcr-Abl inhibitors
Leukemia (2013)