EVENTS
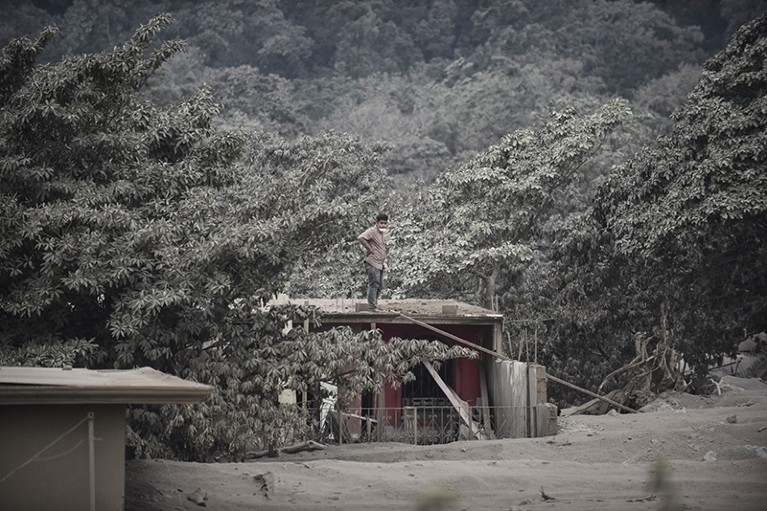
Guatemala volcano wreaks havoc The Fuego volcano in Guatemala erupted on 3 June, sending a superheated avalanche of rock and gas downhill that has killed at least 69 people. It was the deadliest eruption in Guatemala in more than a century. Volcanic ash rose some 6 kilometres into the air, and fell on Guatemala City about 40 kilometres away. Rain falling on the ash created mudflows that destroyed at least one bridge. Fuego is one of Latin America’s most active volcanoes.

Credit: Johan Ordonez/AFP/Getty
Hurricane toll Nearly 5,000 people in Puerto Rico may have died as a result of Hurricane Maria, which hit the island late in 2017 — more than 70 times the official government estimate. In a study published on 29 May, researchers surveyed a random selection of 3,300 homes, and found that 38 people had died between 20 September — the date that Hurricane Maria reached Puerto Rico — and 31 December (N. Kishore et al. N. Engl. J. Med. http://doi.org/cqgr; 2018). When they extrapolated to account for Puerto Rico’s population, they concluded that the national death rate was probably 62% higher than for the same period in 2016. The researchers say this figure is likely to be an underestimate, although it dwarfs the Puerto Rican government’s official record of 64 deaths related to Maria. The researchers believe that many of the deaths were a result of disrupted medical services.
SPACE
Closer look at Ceres On 31 May, NASA’s Dawn spacecraft began moving into its closest orbit yet around the dwarf planet Ceres. Dawn fired its ion thrusters to nudge itself into a trajectory that will take it as close as 35 kilometres above the planet’s surface. The spacecraft will target features such as the Occator Crater — in which nestle bright patches of salt deposits — to study the geology. Scientists also plan to use the new orbit to collect images of Ceres and to investigate its composition. The fly-by will take Dawn ten times closer to the dwarf planet, which is also the Solar System’s largest asteroid, than it has ever been.
RESEARCH
Saltwater rice Chinese scientists have started large field trials of rice designed to grow in salty environments. If the experiments are successful, the hybrid rice could boost the country’s crop yield. On 28 May, a team led by rice breeder Yuan Longping from the China National Hybrid Rice Research and Development Center in Changsha started planting 176 varieties of hybrid rice at sites across China. The varieties have been bred to grow in tidal flats and other salt-rich environments. The team hopes to find a strain that can be planted on the roughly 7 million hectares of land that is too salty for current strains of rice. But some scientists are sceptical about whether the ‘saltwater’ rice will be able to grow in these conditions.
Cancer-drug boom More than 1,100 cancer drugs and vaccines are in clinical trials or up for evaluation by the US Food and Drug Administration, according to a report by the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA). This is up from roughly 830 such therapies in 2015. The report, released by the lobbying organization on 30 May, highlights the intense activity in the sector (see go.nature.com/2j2gzg9). US pharmaceutical companies are testing hundreds of drugs and vaccines aimed at leukaemia, lymphoma and lung cancers alone, and more than 200 others target breast cancer, brain tumours and skin cancers.
POLICY
Student boost The European Commission has proposed opening up Erasmus+, the European Union’s student-exchange programme, to all countries. Erasmus+ enables university students, including PhD researchers, to study abroad. The plan would allow the United Kingdom to participate in the programme after Brexit, as well as researchers worldwide to gain experience at a university in Europe. The commission’s proposal, published on 30 May, also recommends doubling the Erasmus+ budget to €30 billion (US$35.2 billion) for the programme’s next instalment, which will run from 2021 to 2027. The boost would fund the participation of around 12 million people, up from 4 million in the current round. The plan must now be approved by the European Parliament and the EU Council of Ministers.
ENVIRONMENT
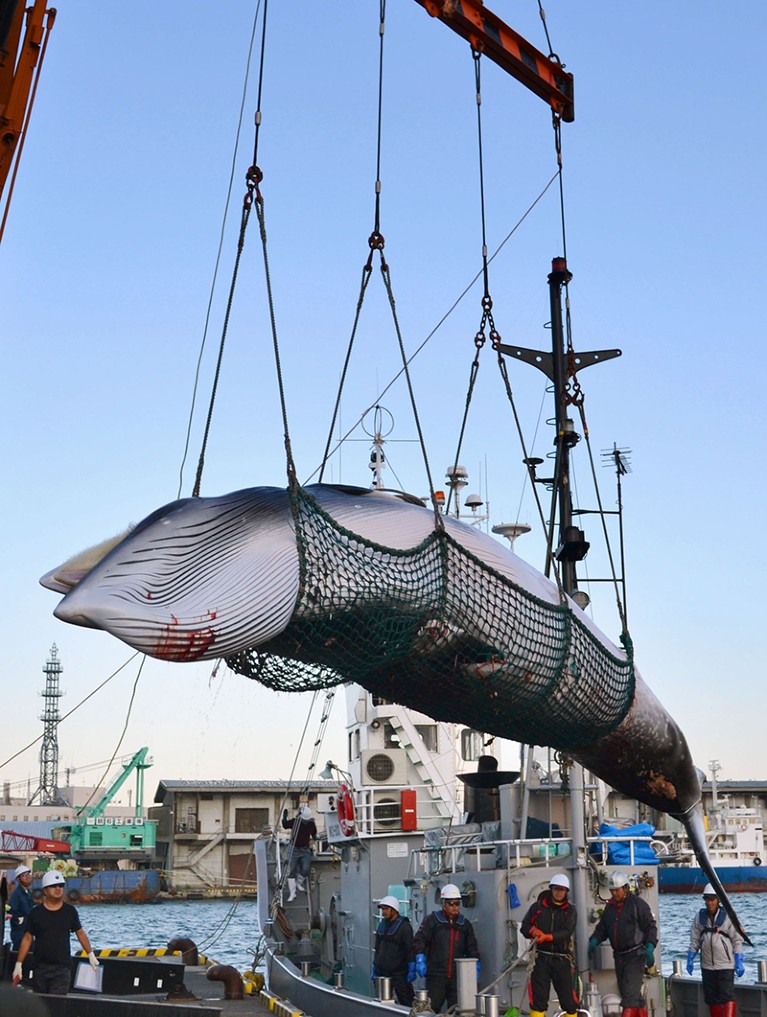
Whale hunt Japan’s latest annual Antarctic whale hunt — which the country says is for scientific purposes — killed 333 minke whales between 8 December 2017 and 28 February 2018. The International Whaling Commission reported the figures last month. The captured whales included 181 females, 95% of which were pregnant. In one area of the hunt, more than half of the animals of both sexes were juveniles. The International Court of Justice temporarily banned Japan from whaling in the Southern Ocean in 2014 (pictured, a whale captured by a Japanese whaling vessel), after deciding its hunts were not for scientific purposes as claimed. The nation launched a new whaling programme in 2015, called NEWREP-A.

Credit: Kyodo News via Getty
Forest fines Brazil’s environmental-protection agency has fined several agricultural companies for purchasing soya beans that were produced on illegally cleared land. Dubbed Operation Soy Sauce, the investigation by the Brazilian Institute of Environment and Renewable Natural Resources resulted in a total of 105.7 million reais (US$28 million) in fines against five companies, including agricultural giants Cargill in Wayzata, Minnesota, and Bunge in White Plains, New York. The investigation identified illegal agricultural operations on 77 properties in the Brazilian Cerrado, a stretch of savannah that borders the Amazon region. Authorities have seized more than 5,000 tonnes of soya beans.
BUSINESS
Fossil-power policy US President Donald Trump has directed the Department of Energy (DOE) to take immediate steps to prevent utility companies from shutting down “fuel-secure” coal and nuclear power plants, the White House said on 1 June. Administration officials argue that impending retirements of such power plants for economic reasons are endangering national security, despite assurances from electricity-grid operators that there is no threat. In January, federal regulators rejected a DOE plan to subsidize the coal and nuclear industries, but the agency is now exploring legal strategies to compel grid operators to purchase electricity from troubled facilities, according to a leaked memo dated 29 May.
Pipeline purchase The Canadian government will buy an oil pipeline owned by Texas-based company Kinder Morgan to ensure the project’s expansion. The controversial Trans Mountain pipeline would connect oil reserves in the province of Alberta to a port in British Columbia, on Canada’s Pacific coast. The country’s finance minister, Bill Morneau, announced on 29 May that the government will spend Can$4.5 billion (US$3.5 billion) to purchase the project. Environmentalists, indigenous groups and the government of British Columbia oppose the expansion, which would triple the pipeline’s capacity. They cite concerns over the environmental impact of extracting more fossil fuels from Alberta’s oil sands and the possibility of tanker spills along the coast.
POLITICS
Minister resigns Physicist Wu Maw-kuen resigned as Taiwan’s education minister — who has responsibility for universities — on 29 May, after only 41 days in the position. In a statement to Nature, Wu said that he was stepping down because Taiwan’s opposition party had made “false accusations” against him that were interfering with the work of the education ministry. At a press conference in April, Hung Meng-kai of the nationalist Kuomintang (KMT) party alleged that Wu stole patented technology while he was president of Dong Hwa University between 2012 and 2016. In a statement to the media, Wu denied the allegation. On 25 May, KMT politician Ko Chih-en also alleged that when Wu was head of the National Science Council, he attended a conference in Hangzhou in 2005 without the government’s permission, which is required of public servants. Wu told Nature that although he had attended the conference, he believes he had approval to do so.
Italian government Two populist parties — the right-wing League party and the anti-establishment Five Star Movement — have formed a coalition government in Italy, ending months of political deadlock after an inconclusive election result in March. On 31 May, Italy’s president, Sergio Mattarella, appointed Marco Bussetti, a former physical-education teacher, as education and science minister. Science and research were not major issues in the election campaign, but there are already clues to the government’s leanings on some issues. The new health minister, physician Giulia Grillo, had campaigned to reverse a 2017 decree that made vaccinations compulsory for schoolchildren, but she announced on 4 June that the government would not immediately reverse it. The environment minister, Sergio Costa, a former general with the environmental arm of the military police, is known for his successful investigations of illegal toxic-waste dumping in the Naples region.
TREND WATCH
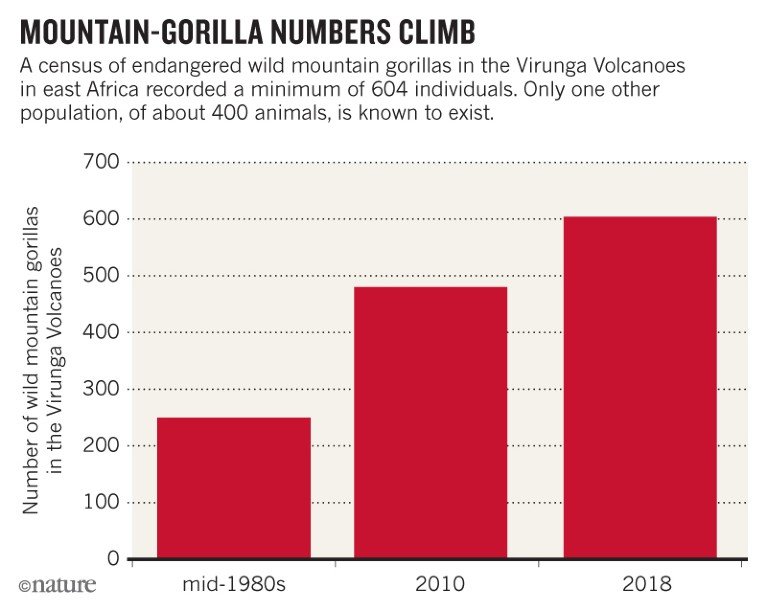
The global population of critically endangered mountain gorillas (Gorilla beringei beringei) has hit 1,000. A 2-year survey, published on 31 May, found at least 604 individuals around the Virunga Volcanoes in east Africa. The only other place where mountain gorillas are known to survive is in Uganda’s Bwindi Impenetrable National Park, where a 2012 census found about 400. The May finding represents a 26% increase over 6 years in total individuals, thanks to both population growth and improved survey methods.
Source: go.nature.com/2m2x62o