Abstract
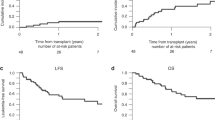
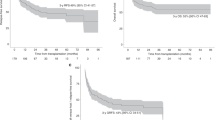
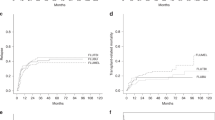
TBI-based preparative regimens are considered as standard conditioning therapy for allogeneic stem cell transplantation (AHSC) in patients with ALL. We investigated toxicity and efficacy of a non-TBI-based regimen consisting of treosulfan, etoposide and cyclophosphamide for ALL within a prospective study. Major inclusion criteria were CR and non-eligibility for TBI. Fifty patients with a median age of 46.5 years (range, 18–64) were included. Donors were HLA-identical sibling (n=8), matched (n=42) or mismatched (n=10) unrelated. The toxicity was moderate, resulting in a cumulative incidence of non-relapse mortality (NRM) at 1 year of 8% (90% confidence interval: 2–15%). Acute GvHD grade II–IV and grade III/IV was noted in 53% and 14%, respectively. Chronic GvHD at one year was seen in 41%. After a median follow-up of 24 months the cumulative incidence of relapse was 36% (90% confidence interval: 24–48) and 51% (90% confidence interval: 37–65) at 1 and 2 years, respectively. The estimated 2-year disease-free and overall survivals were 36 and 48%, respectively. Treosulfan, etoposide and cyclophosphamide followed by AHSC has a favorable toxicity profile with low NRM and therefore represents a potential alternative regimen for ALL in 1. CR (NCT00682305).
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rowe JM . Prognostic factors in adult acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Br J Haematol 2010; 150: 389–405.
Ram R, Gafter-Gvili A, Vidal L, Paul M, Ben-Bassat I, Shpilberg O et al. Management of adult patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia in first complete remission: systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer 2010; 116: 3447–3457.
Bassan R, Hoelzer D . Modern therapy of acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Clin Oncol 2011; 29: 532–543.
Storb R, Bryant JI, Buckner CD, Clift RA, Fefer A, Fialkow PJ et al. Allogeneic marrow grafting for acute lymphoblastic leukemia: leukemic relapse. Transplant Proc 1973; 5: 923–926.
Weiden PL, Flournoy N, Thomas ED, Prentice R, Fefer A, Buckner CD et al. Antileukemic effect of graft-versus-host disease in human recipients of allogeneic-marrow grafts. N Engl J Med 1979; 300: 1068–1073.
Yanada M, Matsuo K, Suzuki T, Naoe T . Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation as part of postremission therapy improves survival for adult patients with high-risk acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a metaanalysis. Cancer 2006; 106: 2657–2663.
Thiebaut A, Vernant JP, Degos L, Huguet FR, Reiffers J, Sebban C et al. Adult acute lymphocytic leukemia study testing chemotherapy and autologous and allogeneic transplantation. A follow-up report of the French protocol LALA 87. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am 2000; 14: 1353–1366.
International Bone Marrow Transplant Registry, 2002, Internet Communication.
Kiehl MG, Kraut L, Schwerdtfeger R, Hertenstein B, Remberger M, Kroeger N et al. Outcome of allogeneic hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation in adult patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: no difference in related compared with unrelated transplant in first complete remission. J Clin Oncol 2004; 22: 2816–2825.
Dahlke J, Kröger N, Zabelina T, Ayuk F, Fehse N, Wolschke C et al. Comparable results in patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia after related and unrelated stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 2006; 37: 155–163.
Blume KG, Forman SJ, O'Donnell MR, Doroshow JH, Krance RA, Nademanee AP et al. Total body irradiation and high-dose etoposide: a new preparatory regimen for bone marrow transplantation in patients with advanced hematologic malignancies. Blood 1987; 69: 1015–1020.
Tutschka PJ, Copelan EA, Klein JP . Bone marrow transplantation for leukemia following a new busulfan and cyclophosphamide regimen. Blood 1987; 70: 1382–1388.
Davies SM, Ramsay NK, Klein JP, Weisdorf DJ, Bolwell B, Cahn JY et al. Comparison of preparative regimens in transplants for children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Clin Oncol 2000; 18: 340–347.
Fichtner I, Becker M, Baumgart J . Antileukaemic activity of treosulfan in xenografted human acute lymphoblastic leukaemias (ALL). Eur J Cancer 2003; 39: 801–807.
Westerhof GR, Ploemacher RE, Boudewijn A, Blokland I, Dillingh JH, McGown AT et al. Comparison of different busulfan analogues for depletion of hematopoietic stem cells and promotion of donor-type chimerism in murine bone marrow transplant recipients. Cancer Res 2000; 60: 5470–5478.
Ploemacher RE, Westerhof GR, Blokland I, Baumgart J, Down JD . Treosulfan as an alternative conditioning agent in bone marrow transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 2000; 25: P421 (abstract).
Casper J, Knauf W, Kiefer T, Wolff D, Steiner B, Hammer U et al. Treosulfan and fludarabine: a new toxicity-reduced conditioning regimen for allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Blood 2004; 103: 725–731.
Kröger N, Shimoni A, Zabelina T, Schieder H, Panse J, Ayuk F et al. Reduced-toxicity conditioning with treosulfan, fludarabine and ATG as preparative regimen for allogeneic stem cell transplantation (alloSCT) in elderly patients with secondary acute myeloid leukemia (sAML) or myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS). Bone Marrow Transplant 2006; 37: 339–344.
Beelen DW, Trenschel R, Casper J, Freund M, Hilger RA, Scheulen ME et al. Dose-escalated treosulphan in combination with cyclophosphamide as a new preparative regimen for allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplantation in patients with an increased risk for regimen-related complications. Bone Marrow Transplant 2005; 35: 233–241.
Kako S, Morita S, Sakamaki H, Ogawa H, Fukuda T, Takahashi S et al. A decision analysis of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in adult patients with Philadelphia chromosome-negative acute lymphoblastic leukemia in first remission who have an HLA-matched sibling donor. Leukemia 2011; 25: 259–265.
Cornelissen JJ, van der Holt B, Verhoef GE, van't Veer MB, van Oers MH, Schouten HC et alDutch-Belgian HOVON Cooperative Group. Myeloablative allogeneic versus autologous stem cell transplantation in adult patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia in first remission: a prospective sibling donor versus no-donor comparison. Blood 2009; 113: 1375–1382.
Goldstone AH, Richards SM, Lazarus HM, Tallman MS, Buck G, Fielding AK et al. In adults with standard-risk acute lymphoblastic leukemia, the greatest benefit is achieved from a matched sibling allogeneic transplantation in first complete remission, and an autologous transplantation is less effective than conventional consolidation/maintenance chemotherapy in all patients: final results of the International ALL Trial (MRC UKALL XII/ECOG E2993). Blood 2008; 111: 1827–1833.
Ribera JM, Oriol A, Bethencourt C, Parody R, Hernández-Rivas JM, Moreno MJ et al. PETHEMA Group, Spain. Comparison of intensive chemotherapy, allogeneic or autologous stem cell transplantation as post-remission treatment for adult patients with high-risk acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Results of the PETHEMA ALL-93 trial. Haematologica 2005; 90: 1346–1356.
Friedman DL, Rovo A, Leisenring W, Locasciulli A, Flowers ME, Tichelli A et al. FHCRC; EBMT-Late Effect Working Party. Increased risk of breast cancer among survivors of allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation: a report from the FHCRC and the EBMT-Late Effect Working Party. Blood 2008; 111: 939–944.
Marks DI, Wang T, Pérez WS, Antin JH, Copelan E, Gale RP et al. The outcome of full-intensity and reduced-intensity conditioning matched sibling or unrelated donor transplantation in adults with Philadelphia chromosome-negative acute lymphoblastic leukemia in first and second complete remission. Blood 2010; 116: 366–374.
Mohty M, Labopin M, Volin L, Gratwohl A, Socié G, Esteve J et al. Acute Leukemia Working Party of EBMT. Reduced-intensity versus conventional myeloablative conditioning allogeneic stem cell transplantation for patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a retrospective study from the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Blood 2010; 116: 4439–4443.
Bachanova V, Marks DI, Zhang MJ, Wang H, de Lima M, Aljurf MD et al. Ph+ ALL patients in first complete remission have similar survival after reduced intensity and myeloablative allogeneic transplantation: impact of tyrosine kinase inhibitor and minimal residual disease. Leukemia 2014; 28: 658–665.
Brüggemann M, Raff T, Flohr T, Gökbuget N, Nakao M, Droese J et al. German Multicenter Study Group for Adult Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Clinical significance of minimal residual disease quantification in adult patients with standard-risk acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 2006; 107: 1116–1123.
Ribera JM, Oriol A, Morgades M, Montesinos P, Sarrà J, González-Campos J et al. Treatment of high-risk philadelphia chromosome-negative acute lymphoblastic leukemia in adolescents and adults according to early cytologic response and minimal residual disease after consolidation assessed by flow cytometry: final results of the PETHEMA ALL-AR-03 Trial. J Clin Oncol 2014; 32: 1595–1604.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
NK received research funding from Medac/Germany. The remaining authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Author contributions
NK designed the study, interpreted the data and wrote the manuscript. UP assisted in the study design, analyzed the data, performed statistics and edited the manuscript. MB, MS, RT, CS, RA, HM, MH, CW, RGM, WB, GK, FA, NG, DH, AZ and DB assisted with data collection and edited the manuscript.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kröger, N., Bornhäuser, M., Stelljes, M. et al. Allogeneic stem cell transplantation after conditioning with treosulfan, etoposide and cyclophosphamide for patients with ALL: a phase II-study on behalf of the German Cooperative Transplant Study Group and ALL Study Group (GMALL). Bone Marrow Transplant 50, 1503–1507 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2015.202
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2015.202
This article is cited by
-
In Vitro Study of the Enzymatic and Nonenzymatic Conjugation of Treosulfan with Glutathione
European Journal of Drug Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics (2019)