Abstract
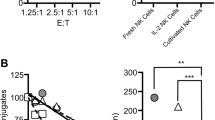
Natural cell-mediated cytotoxic activity in the mouse has been associated with two types of effector cells, the natural killer (NK) cell and the natural cytotoxic (NC) cell, which seem to differ with regard to their patterns of target selectivity, cell surface characteristics and susceptibility to regulatory factors1. During studies on the mechanism of action of cytotoxic molecules, it became evident that WEHI-164, the prototype NC target cell, was highly susceptible to direct lysis by both human and mouse recombinant tumour necrosis factor (TNF). Here we show that NC, but not NK activity mediated by normal splenocytes, is abrogated by rabbit antibodies to recombinant and natural TNF, respectively. Thus, the cell-mediated activity defined as NC is due to release of TNF by normal spleen cells and does not represent a unique natural effector mechanism.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stutman, O., Paige, C. J. & Feo Figarella, E. J. Immun. 121, 1819–1823 (1978).
Herberman, R. B. & Holden, H. T. Adv. Cancer Res. 27, 305–319 (1978).
Kumar, V., Luevano, E. & Bennett, M. J. exp. Med. 150, 531–534 (1979).
Minato, N., Reid, L. & Bloom, R. B. J. exp. Med. 154, 750–755 (1981).
Ortaldo, J. R. & Herberman, R. B. A. Rev. Immun. 2, 359–394 (1984).
Paige, C. J., Feo Figarella, E., Cuttito, M. J., Cahan, A. & Stutman, O. J. Immun. 121, 1827–1832 (1978).
Djeu, J., Heinbaugh, J. A., Holden, H. T. & Herberman, R. B. J. Immun. 122, 175–179 (1979).
Ortaldo, J. R. et al. J. Immun. 133, 779–784 (1984).
Djeu, J. Y., Lanza, E., Pastore, S. & Hapel, A. J. Nature 306, 788–789 (1983).
Henkart, P. A., Millard, P. J., Reynolds, C. W. & Henkart, M. P. J. exp. Med. 160, 75–93 (1984).
Wright, S. C., Weitzen, M. L., Kahle, R., Granger, G. A. & Bonavida, B. J. Immun. 130, 1479–1484 (1983).
Darzynkiewicz, Z., Williamson, B., Carswell, E. A. & Old, L. J. Cancer Res. 44, 83–90 (1984).
Iscove, N. N., Roitsch, C. A., Williams, N. & Guilbert, L. J. J. cell. Physiol. Suppl. 1, 65–78 (1982).
Rola-Pleszczynski, M. & Lieu, H. Cell. Immun. 82, 326–333 (1983).
Somura, K., Nakano, K., Abe, M., Nakata, K. & Yoshida, H. Gan To Kagaku Ryoha 12, 160–162 (1985).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ortaldo, J., Mason, L., Mathieson, B. et al. Mediation of mouse natural cytotoxic activity by tumour necrosis factor. Nature 321, 700–702 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1038/321700a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/321700a0
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.