Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Evidence of an active volcanic heat source beneath the Pine Island Glacier
Evidence of an active volcanic heat source beneath the Pine Island Glacier
The West Antarctic Ice Sheet sits atop an extensional rift system with volcano-like features, yet we do not know if any of these volcanoes are active, because identifying subglacial volcanism remains a challenge. Here, the authors find evidence in helium isotopes that a large volcanic heat source is emanating from beneath the fast-melting Pine Island Ice Glacier.
- Brice Loose
- , Alberto C. Naveira Garabato
- & Karen J. Heywood
-
Article
| Open Access Shallow magma diversions during explosive diatreme-forming eruptions
Shallow magma diversions during explosive diatreme-forming eruptions
Shallow magmatic feeder systems in monogenetic volcanic fields may determine how a volcano erupts. Here, the authors use numerical modeling to show that explosive excavation and infilling of eruptive craters affects local stress states, with feedbacks controlling sites and depths of crater-forming explosions.
- Nicolas Le Corvec
- , James D. Muirhead
- & James D. L. White
-
Article
| Open Access Disclosing the temperature of columnar jointing in lavas
Disclosing the temperature of columnar jointing in lavas
Columnar joints in lavas form during cooling, but the temperature this occurs at is unclear. Here, the authors perform thermo-mechanical experiments on basaltic rocks to examine the temperature of columnar joints in lavas and find that failure occurs at 890–840 °C, which is below the solidus temperature of 980 °C.
- Anthony Lamur
- , Yan Lavallée
- & Fabian B. Wadsworth
-
Article
| Open Access Immiscible hydrous Fe–Ca–P melt and the origin of iron oxide-apatite ore deposits
Immiscible hydrous Fe–Ca–P melt and the origin of iron oxide-apatite ore deposits
The origin of iron oxide-apatite deposits remains enigmatic and controversial. Here, the authors perform experiments on intermediate magmas and show that increasing aH2O and fO2 enlarges the two-liquid field thus allowing the Fe–Ca–P melt to separate easily from host silicic magma and produce iron oxide-apatite ores.
- Tong Hou
- , Bernard Charlier
- & Olivier Namur
-
Article
| Open Access Timescales of water accumulation in magmas and implications for short warning times of explosive eruptions
Timescales of water accumulation in magmas and implications for short warning times of explosive eruptions
Volatiles such as water play a key role in magma ascent and ultimately triggering explosive eruptions. Here, the authors show that water-rich melts with water concentrations of 6–9 wt.% can ascend rapidly to the surface over the timescales of hours to days with very short warning times.
- M. Petrelli
- , K. El Omari
- & D. Perugini
-
Article
| Open Access Understanding the plume dynamics of explosive super-eruptions
Understanding the plume dynamics of explosive super-eruptions
Super-eruptions such as Toba generate large co-ignimbrite plumes, but their behaviour is not fully understood. Here, the authors show that super-eruption plumes behave differently to Plinian eruptions and can generate over-plumes into the mesosphere, which would amplify their impact on the climate.
- Antonio Costa
- , Yujiro J. Suzuki
- & Takehiro Koyaguchi
-
Article
| Open Access Volcanic crystals as time capsules of eruption history
Volcanic crystals as time capsules of eruption history
Crystals can record the timing of volcanic eruptive triggers at depth by examining their zoning histories. Here, the authors analyse clinopyroxene crystal zoning from eruptions at Mount Etna, Italy from 1974-2014 and show that the intrusion of magma can trigger an eruption within 2 weeks of arrival.
- Teresa Ubide
- & Balz S. Kamber
-
Article
| Open Access Prodigious submarine landslides during the inception and early growth of volcanic islands
Prodigious submarine landslides during the inception and early growth of volcanic islands
As volcanic islands grow via subaerial shield-building and edifice growth, large submarine landslides occur. Here, the authors reconstruct the emergence of the Canary Islands via turbidites created by submarine landslides as the islands grew, showing that slides are multi-stage.
- James E. Hunt
- & Ian Jarvis
-
Article
| Open Access Andean mountain building and magmatic arc migration driven by subduction-induced whole mantle flow
Andean mountain building and magmatic arc migration driven by subduction-induced whole mantle flow
The Andean orogeny commenced in the Cretaceous, but was preceded by backarc extension starting in the Jurassic. Here, the author presents a 4D geodynamic subduction model reproducing the evolution of overriding plate deformation along with a progressive decrease in slab dip, explaining Jurassic-present arc migration.
- W. P. Schellart
-
Article
| Open Access Crystal plasticity as an indicator of the viscous-brittle transition in magmas
Crystal plasticity as an indicator of the viscous-brittle transition in magmas
The rheological behaviour of magma in shallow conditions may help determine a volcano’s eruptive style. Here, the authors perform deformation experiments on lava from Volcán de Colima to demonstrate that crystal plasticity may preclude failure at certain shallow magmatic conditions.
- J. E. Kendrick
- , Y. Lavallée
- & N. R. Varley
-
Article
| Open Access Caldera resurgence driven by magma viscosity contrasts
Caldera resurgence driven by magma viscosity contrasts
Following a large caldera creating volcanic eruption, caldera resurgence may occur as magma accumulation takes place, but this rarely leads to another a major eruption. Here, the authors using thermal and experimental models show that caldera resurgence is driven by magma viscosity contrasts.
- Federico Galetto
- , Valerio Acocella
- & Luca Caricchi
-
Article
| Open Access Volcanism in slab tear faults is larger than in island-arcs and back-arcs
Volcanism in slab tear faults is larger than in island-arcs and back-arcs
The volcanism of subduction settings concentrates in island-arcs and back-arc basins. Here, the authors show that the lithospheric tear faults bounding roll-backing slabs may focus huge volcanism with a volume of the erupted products exceeding that of the island-arcs edifices and back-arcs spreading centres.
- Luca Cocchi
- , Salvatore Passaro
- & Guido Ventura
-
Article
| Open Access Enhanced ice sheet melting driven by volcanic eruptions during the last deglaciation
Enhanced ice sheet melting driven by volcanic eruptions during the last deglaciation
The impact of volcanism on ice sheet melting during the last deglaciation is poorly understood and limited by a lack of suitable proxies. Here, the authors combine annually resolved records of ice sheet melting with numerical models to show that ice sheets are sensitive to high-latitude volcanic eruptions.
- Francesco Muschitiello
- , Francesco S. R. Pausata
- & Barbara Wohlfarth
-
Article
| Open Access The effect of giant lateral collapses on magma pathways and the location of volcanism
The effect of giant lateral collapses on magma pathways and the location of volcanism
Flank instability and lateral collapse are a potential hazard at volcanic edifices. Here, the authors use numerical simulations to show that at Fogo volcano, lateral collapse can trigger a significant deflection of magma pathways in the crust, demonstrating how volcanic edifices may evolve.
- Francesco Maccaferri
- , Nicole Richter
- & Thomas R. Walter
-
Correspondence
| Open Access Correspondence: Numerical modelling of the PERM anomaly and the Emeishan large igneous province
Correspondence: Numerical modelling of the PERM anomaly and the Emeishan large igneous province
- Trond H. Torsvik
- & Mathew Domeier
-
Article
| Open Access Taking the pulse of Mars via dating of a plume-fed volcano
Taking the pulse of Mars via dating of a plume-fed volcano
Mars hosts the solar system’s largest volcanoes, but their formation rates remain poorly constrained. Here, the authors have measured the crystallization and ejection ages of meteorites from a Martian volcano and find that its growth rate was much slower than analogous volcanoes on Earth.
- Benjamin E. Cohen
- , Darren F. Mark
- & Caroline L. Smith
-
Article
| Open Access Lithium enrichment in intracontinental rhyolite magmas leads to Li deposits in caldera basins
Lithium enrichment in intracontinental rhyolite magmas leads to Li deposits in caldera basins
Lithium is increasingly being utilized for modern technology in the form of lithium-ion batteries. Here, using in situ measurements of quartz-hosted melt inclusions, the authors demonstrate that preserved lake sediments within rhyolitic calderas have the potential to host large lithium-rich clay deposits.
- Thomas R. Benson
- , Matthew A. Coble
- & Gail A. Mahood
-
Article
| Open Access Initial pulse of Siberian Traps sills as the trigger of the end-Permian mass extinction
Initial pulse of Siberian Traps sills as the trigger of the end-Permian mass extinction
Although the mass end-Permian extinction is linked to large igneous provinces, its trigger remains unclear. Here, the authors propose that the abrupt change from flood lavas to sills resulted in the heating of sediments and led to the release of large-scale greenhouse gases to drive the end-Permian extinction.
- S. D. Burgess
- , J. D. Muirhead
- & S. A. Bowring
-
Article
| Open Access Clustering of arc volcanoes caused by temperature perturbations in the back-arc mantle
Clustering of arc volcanoes caused by temperature perturbations in the back-arc mantle
Volcanoes may cluster along volcanic arcs, but controls on cluster locations are still unclear. Here, using numerical models, the authors show that clustering along arcs is the result of inflow of hotter mantle material, and subdued inflow of colder material creating a 3D mantle flow pattern.
- Changyeol Lee
- & Ikuko Wada
-
Article
| Open Access End-Triassic mass extinction started by intrusive CAMP activity
End-Triassic mass extinction started by intrusive CAMP activity
The cause of the end-Triassic extinction remains controversial. Here, the authors present U-Pb age data showing that magmatic activity occurred 100 kyr before the earliest known eruptions, which links to changes in climate and biotic records indicating the importance of understanding the intrusive record.
- J.H.F.L. Davies
- , A. Marzoli
- & U. Schaltegger
-
Article
| Open Access Post-supereruption recovery at Toba Caldera
Post-supereruption recovery at Toba Caldera
Toba Caldera in Indonesia had one of the largest volcanic eruptions over the last 100 kyr and has since undergone periods of resurgence. Here, the authors present zircon and sediment age data showing resurgence started after the climactic eruption and lasted until 2.7 ka, advancing west and south.
- Adonara E. Mucek
- , Martin Danišík
- & Matthew A. Coble
-
Article
| Open Access Explosive eruption, flank collapse and megatsunami at Tenerife ca. 170 ka
Explosive eruption, flank collapse and megatsunami at Tenerife ca. 170 ka
Oceanic shield volcanoes flank failures can generate large tsunamis. Here, the authors provide evidence that two tsunamis impacted the coast of Tenerife 170 Ma, the first generated by volcano flank failure and the second following a debris avalanche of the edifice during an on-going ignimbrite-forming eruption.
- Raphaël Paris
- , Juan J. Coello Bravo
- & François Nauret
-
Article
| Open Access Progressive approach to eruption at Campi Flegrei caldera in southern Italy
Progressive approach to eruption at Campi Flegrei caldera in southern Italy
Forecasting eruptions at large calderas remains difficult. Here, the authors apply an elastic-brittle failure model to Campi Flegrei to show that successive episodes of unrest lead to a long-term accumulation of stress in the crust, such that conditions may be becoming more favourable to eruption.
- Christopher R.J. Kilburn
- , Giuseppe De Natale
- & Stefano Carlino
-
Article
| Open Access Petit-spot as definitive evidence for partial melting in the asthenosphere caused by CO2
Petit-spot as definitive evidence for partial melting in the asthenosphere caused by CO2
The genesis of primitive CO2-rich alkali magma at petit-spot volcanoes is still poorly understood. Here, the authors perform high pressure and temperature experiments to show that the CO2-rich melt is derived from the asthenosphere.
- Shiki Machida
- , Tetsu Kogiso
- & Naoto Hirano
-
Article
| Open Access Archaean zircons in Miocene oceanic hotspot rocks establish ancient continental crust beneath Mauritius
Archaean zircons in Miocene oceanic hotspot rocks establish ancient continental crust beneath Mauritius
There is growing evidence for the presence of continental fragments within the young oceanic basins, but this is still based on limited geological data. Here, the authors use zircon isotope geochronology to demonstrate the presence of Archaean continental crust beneath the young hotspot volcanoes of Mauritius.
- Lewis D. Ashwal
- , Michael Wiedenbeck
- & Trond H. Torsvik
-
Article
| Open Access Heterogeneity in mantle carbon content from CO2-undersaturated basalts
Heterogeneity in mantle carbon content from CO2-undersaturated basalts
Melting dynamics are affected by the amount of carbon in the Earth’s mantle. Le Voyeret al. report undegassed carbon concentrations from olivine-hosted melt inclusions from the Mid-Atlantic Ridge finding that carbon content varies by two orders of magnitude thus introducing heterogeneity into the upper mantle.
- M. Le Voyer
- , K.A. Kelley
- & E.H. Hauri
-
Article
| Open Access Observing eruptions of gas-rich compressible magmas from space
Observing eruptions of gas-rich compressible magmas from space
Satellite observations are an important tool in volcano monitoring, but observations such as ground deformation and gas emissions are treated independently. Here, the authors present a model coupling them through their link to magma volatile contents and storage depths prior to eruption
- Brendan McCormick Kilbride
- , Marie Edmonds
- & Juliet Biggs
-
Article
| Open Access Magmas near the critical degassing pressure drive volcanic unrest towards a critical state
Magmas near the critical degassing pressure drive volcanic unrest towards a critical state
Magmas may migrate through hydrothermal fluids, but magma-hydrothermal interactions are poorly understood. Here, Chiodini et al. use physical and volatile models showing that at a critical degassing pressure the release of magmatic gases can heat hydrothermal fluids triggering deformation leading to eruption.
- Giovanni Chiodini
- , Antonio Paonita
- & Jean Vandemeulebrouck
-
Article
| Open Access Role of syn-eruptive plagioclase disequilibrium crystallization in basaltic magma ascent dynamics
Role of syn-eruptive plagioclase disequilibrium crystallization in basaltic magma ascent dynamics
The quantification of timing for crystallization and exsolution processes are fundamental to our understanding of basaltic magma ascent dynamics. Here, the authors constrain timings to show that plagioclase reaches equilibrium in 1-2 hours, whereas ascent times were <1 hour.
- G. La Spina
- , M. Burton
- & F. Arzilli
-
Article
| Open Access Rapid laccolith intrusion driven by explosive volcanic eruption
Rapid laccolith intrusion driven by explosive volcanic eruption
Magmatic intrusions are thought to precede volcanic eruptions. However, Castro et al. present evidence that a laccolith was emplaced during the 2011 rhyolitic eruption of Cordón Caulle showing that eruptions may force the intrusion of magma into the shallow crust posing an unrecognized volcanic hazard.
- Jonathan M. Castro
- , Benoit Cordonnier
- & Yves Feisel
-
Article
| Open Access Post-eruptive flooding of Santorini caldera and implications for tsunami generation
Post-eruptive flooding of Santorini caldera and implications for tsunami generation
The Bronze Age eruption of Santorini is known to have generated tsunamis with caldera collapse as the likely mechanism. However, new bathymetric and seismic data presented by Nomikou et al. show that the entry of pyroclastic flows into the sea is the most likely tsunami-generating mechanism at Santorini.
- P. Nomikou
- , T. H. Druitt
- & M. M. Parks
-
Article
| Open Access Seismic evidence for a cold serpentinized mantle wedge beneath Mount St Helens
Seismic evidence for a cold serpentinized mantle wedge beneath Mount St Helens
Mount St Helens is the most active volcano in the Cascades but is located 50 km west of the arc axis. Hansen et al. use high resolution seismic data to image a boundary in Moho reflectivity beneath St Helens implying a serpentinized mantle wedge and a melt source region that lies to the east towards Mount Adams.
- S. M. Hansen
- , B. Schmandt
- & K. C. Creager
-
Article
| Open Access Surface uplift in the Central Andes driven by growth of the Altiplano Puna Magma Body
Surface uplift in the Central Andes driven by growth of the Altiplano Puna Magma Body
The Altiplano-Puna magma body is located in the world's second highest plateau, the Altiplano-Puna, but the influence of melt production in the surface uplift of the Central Andes is unclear. Perkinset al. link surface topography and isotactic modelling to constrain the melt production in the magma body.
- Jonathan P. Perkins
- , Kevin M. Ward
- & Noah J. Finnegan
-
Article
| Open Access A pulse of mid-Pleistocene rift volcanism in Ethiopia at the dawn of modern humans
A pulse of mid-Pleistocene rift volcanism in Ethiopia at the dawn of modern humans
Past volcanic eruptions along the densely populated Ethiopian Rift valley remain poorly constrained despite the present day hazard. Hutchison et al. show that a large volcanic flare up along a 200 km section of the rift occurred between 320–170 ka dramatically affecting the landscape and hominin population.
- William Hutchison
- , Raffaella Fusillo
- & Andrew T. Calvert
-
Article
| Open Access Pre-eruptive magmatic processes re-timed using a non-isothermal approach to magma chamber dynamics
Pre-eruptive magmatic processes re-timed using a non-isothermal approach to magma chamber dynamics
Zoned crystals may reflect magma chamber dynamics, where changes in temperature, pressure and timescale before volcanic eruption may be measured. Petrone et al. develop a new Non-Isothermal Diffusion Incremental Step model to reconstruct crystal lifetime histories to constrain pre-eruptive magmatic processes.
- Chiara Maria Petrone
- , Giuseppe Bugatti
- & Simone Tommasini
-
Article
| Open Access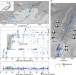 Oblique rift opening revealed by reoccurring magma injection in central Iceland
Oblique rift opening revealed by reoccurring magma injection in central Iceland
Deformation at divergent plate boundaries during rifting events is rarely observed and therefore poorly constrained. Ruch et al. show evidence of an oblique rift opening at the Bárðarbunga caldera, Iceland, which was one of the largest basaltic eruptions observed in the last 200 years
- Joël Ruch
- , Teng Wang
- & Sigurjón Jónsson
-
Article
| Open Access Magma storage in a strike-slip caldera
Magma storage in a strike-slip caldera
The Ilopango caldera, El Salvador has had a number of large explosive eruptions, but its magmatic plumbing system is unclear. Here, Saxby et al. image a strike-slip faulted low-density structure under the caldera and interpret it as a gas-charged magmatic reservoir beneath a shallow hydrothermal system.
- J. Saxby
- , J. Gottsmann
- & E. Gutiérrez
-
Article
| Open Access The feeder system of the Toba supervolcano from the slab to the shallow reservoir
The feeder system of the Toba supervolcano from the slab to the shallow reservoir
The Toba Caldera is the site of the largest Pleistocene eruption at 74,000 years ago, yet the magmatic plumbing system remains poorly understood. Here, Koulakov et al. present a new seismic tomography model highlighting a complex multilevel plumbing magmatic system under Toba.
- Ivan Koulakov
- , Ekaterina Kasatkina
- & Sergey Smirnov
-
Article
| Open Access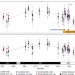 End-Cretaceous extinction in Antarctica linked to both Deccan volcanism and meteorite impact via climate change
End-Cretaceous extinction in Antarctica linked to both Deccan volcanism and meteorite impact via climate change
The cause of the end-Cretaceous mass extinction is still debated due to difficulties separating the influences of two closely-timed potential causal events (massive volcanism and meteorite impact). Here, the authors link the extinction to both kill mechanisms through a new paleotemperature record.
- Sierra V. Petersen
- , Andrea Dutton
- & Kyger C. Lohmann
-
Article
| Open Access Pliocene-Quaternary crustal melting in central and northern Tibet and insights into crustal flow
Pliocene-Quaternary crustal melting in central and northern Tibet and insights into crustal flow
The role of the low velocity-high conductivity zones (LV–HCZs) in developing the Tibetan Plateau has remained controversial. Here, Wang et al.present new geochemical and petrological data that show the LV–HCZs are sources of partial melt thus giving insight into the development of the Tibetan Plateau.
- Qiang Wang
- , Chris J. Hawkesworth
- & Yan-Hui Dong
-
Article
| Open Access Macrofossil evidence for a rapid and severe Cretaceous–Paleogene mass extinction in Antarctica
Macrofossil evidence for a rapid and severe Cretaceous–Paleogene mass extinction in Antarctica
Debate surrounds the causes, timing, and effects of the Cretaceous-Paleogene mass extinction, 66 Ma. Here, using new collections of marine macrofossils from Seymour Island, Antarctica, the authors show that the extinction was both rapid and severe in the high southern latitudes, contrary to previous studies.
- James D. Witts
- , Rowan J. Whittle
- & Vanessa C. Bowman
-
Article
| Open Access Mercury anomalies and the timing of biotic recovery following the end-Triassic mass extinction
Mercury anomalies and the timing of biotic recovery following the end-Triassic mass extinction
The association between Central Atlantic Magmatic Province (CAMP) eruption volatiles and the end-Triassic mass extinction remains ambiguous. Here, the authors present mercury and palaeontological evidence from the same archive and show that significant biotic recovery did not begin until CAMP eruptions ceased.
- Alyson M. Thibodeau
- , Kathleen Ritterbush
- & Frank A. Corsetti
-
Article
| Open Access Slow-moving and far-travelled dense pyroclastic flows during the Peach Spring super-eruption
Slow-moving and far-travelled dense pyroclastic flows during the Peach Spring super-eruption
Pyroclastic flows of the 18.8 Ma Peach Spring Tuff super-eruption travelled >170 km and entrained substrate blocks up to ∼1 m diameter. Here, the authors show that these flows had a dense base and speeds of ∼5-20 m s−1, fed by an eruption discharging magma at rates up to ∼107-108 m3 s−1for at least 2.5-10 h.
- O. Roche
- , D. C. Buesch
- & G. A. Valentine
-
Article
| Open Access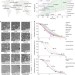 Volcanic ash melting under conditions relevant to ash turbine interactions
Volcanic ash melting under conditions relevant to ash turbine interactions
Volcanic ash is hazardous to jet engines, with high temperatures in turbines causing ash particles to melt and stick to the engine, adversely affecting turbine function. Here, the authors explore the spectrum of natural ash compositions and their behaviour and impact at high temperatures.
- Wenjia Song
- , Yan Lavallée
- & Donald B. Dingwell
-
Article
| Open Access Monitoring eruption activity using temporal stress changes at Mount Ontake volcano
Monitoring eruption activity using temporal stress changes at Mount Ontake volcano
Volcanic activity is often accompanied by small earthquakes, with focal mechanisms indicating stress state beneath volcanoes. Here, the authors demonstrate that quantitative evaluation of temporal stress changes is an effective tool for eruption monitoring.
- Toshiko Terakawa
- , Aitaro Kato
- & Takashi Okuda
-
Article
| Open Access Correlated compositional and mineralogical investigations at the Chang′e-3 landing site
Correlated compositional and mineralogical investigations at the Chang′e-3 landing site
The chemical compositions of young lava flows on the Moon have implications for late volcanism. Here, the authors present mineral distribution data from the Chang′e-3 Yutu rover in the northern Imbrium mare region, reporting unique compositional characteristics of a previously unsampled basalt type.
- Zongcheng Ling
- , Bradley L. Jolliff
- & Jianyu Wang
-
Article |
 Volcano seismicity and ground deformation unveil the gravity-driven magma discharge dynamics of a volcanic eruption
Volcano seismicity and ground deformation unveil the gravity-driven magma discharge dynamics of a volcanic eruption
Volcanic eruptions are thought to restore equilibrium when overpressure in the crust is induced by new magma rising from depth. Here, the authors use data from the 2007 Stromboli eruption as well as models to suggest that eruption is instead a consequence of the gravity-driven instability of the volcanic edifice.
- Maurizio Ripepe
- , Dario Delle Donne
- & Pasquale Poggi
-
Article |
 Bidecadal North Atlantic ocean circulation variability controlled by timing of volcanic eruptions
Bidecadal North Atlantic ocean circulation variability controlled by timing of volcanic eruptions
While present in palaeoclimate records, the drivers behind 20-year climate variability are poorly understood. Here, using climate simulations and in situand palaeo data, the authors present a possible link between volcanic eruptions, Great Salinity Anomalies and the Atlantic overturning circulation.
- Didier Swingedouw
- , Pablo Ortega
- & Roland Séférian
-
Article |
 Propagation style controls lava–snow interactions
Propagation style controls lava–snow interactions
How volcanoes and the cryosphere interact is of interest for understanding hazard mitigation at ice-clad volcanoes and for paleoclimate studies. Here, the authors provide quantitative details from an eruption in Kamchatka, demonstrating that two kinds of lava, ′a′a and pahoehoe, produced different snowpack responses.
- B. R. Edwards
- , A. Belousov
- & M. Belousova

 Crystal and melt inclusion timescales reveal the evolution of magma migration before eruption
Crystal and melt inclusion timescales reveal the evolution of magma migration before eruption