Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article |
 Localized high-concentration electrolytes get more localized through micelle-like structures
Localized high-concentration electrolytes get more localized through micelle-like structures
Liquid electrolytes in batteries are considered to be macroscopically homogeneous ionic transport media despite having a complex chemical composition and atomistic solvation structures. A micelle-like structure in a localized high-concentration electrolyte for which the solvent acts as a surfactant is reported.
- Corey M. Efaw
- , Qisheng Wu
- & Bin Li
-
Letter
| Open Access Probing lithium mobility at a solid electrolyte surface
Probing lithium mobility at a solid electrolyte surface
Understanding lithium dynamics in solid-state electrolytes used for Li-ion batteries can be challenging. Using nonlinear extreme-ultraviolet spectroscopies, a direct spectral signature of surface lithium ions showing a distinct blueshift relative to the bulk absorption spectra is observed in a prototypical solid-state electrolyte.
- Clarisse Woodahl
- , Sasawat Jamnuch
- & Michael Zuerch
-
Article |
 Dielectric control of reverse intersystem crossing in thermally activated delayed fluorescence emitters
Dielectric control of reverse intersystem crossing in thermally activated delayed fluorescence emitters
The role of the dielectric environment in thermally activated delayed fluorescence (TADF) is not yet fully understood. Here the authors reveal the relevance of environment–emitter interactions in gating the reverse intersystem crossing and its particular relevance in dipolar TADF emitters.
- Alexander J. Gillett
- , Anton Pershin
- & David Beljonne
-
Article |
 Cationic polymer-in-salt electrolytes for fast metal ion conduction and solid-state battery applications
Cationic polymer-in-salt electrolytes for fast metal ion conduction and solid-state battery applications
Polymer electrolytes provide a safe solution for future solid-state high-energy-density batteries, but combining high ionic conductivity and a high transference number is a challenge. A polymeric ionic liquid used as a polymer solvent is now shown to be promising for both sodium and potassium batteries.
- Fangfang Chen
- , Xiaoen Wang
- & Maria Forsyth
-
Review Article |
 Machine-learned potentials for next-generation matter simulations
Machine-learned potentials for next-generation matter simulations
Materials simulations are now ubiquitous for explaining material properties. This Review discusses how machine-learned potentials break the limitations of system-size or accuracy, how active-learning will aid their development, how they are applied, and how they may become a more widely used approach.
- Pascal Friederich
- , Florian Häse
- & Alán Aspuru-Guzik
-
Article |
 Insight into the effects of confined hydrocarbon species on the lifetime of methanol conversion catalysts
Insight into the effects of confined hydrocarbon species on the lifetime of methanol conversion catalysts
The methanol-to-hydrocarbons reaction on zeolites produces olefins from many sources, but catalyst stability is a major challenge. Here, by combining operando measurements and simulations, the formation and identification of deactivating carbonaceous species throughout the reaction are achieved.
- I. Lezcano-Gonzalez
- , E. Campbell
- & A. M. Beale
-
Article |
 Engineering high-energy-density sodium battery anodes for improved cycling with superconcentrated ionic-liquid electrolytes
Engineering high-energy-density sodium battery anodes for improved cycling with superconcentrated ionic-liquid electrolytes
Non-uniform metal deposition and dendrite formation reduce the efficiency, safety and life of batteries with metal anodes. The influence of these factors in a sodium electrolyte now shows how a molten-salt-like structure at the electrode surface results in dendrite-free metal cycling at higher rates.
- Dmitrii A. Rakov
- , Fangfang Chen
- & Maria Forsyth
-
Article |
 Self-assembled nanostructures in ionic liquids facilitate charge storage at electrified interfaces
Self-assembled nanostructures in ionic liquids facilitate charge storage at electrified interfaces
Understanding molecular interactions between ionic liquids and interfaces is crucial for electrochemical device applications. Self-assembled amphiphilic nanostructures in surface-active ionic liquids are shown to exhibit enhanced charge storage at electrified surfaces.
- Xianwen Mao
- , Paul Brown
- & T. Alan Hatton
-
News & Views |
 Charting stability space
Charting stability space
A comprehensive chemical space of potential inorganic ternary metal nitrides has been explored by computational methods as a guideline for their experimental synthesis and discovery.
- Ralf Riedel
- & Zhaoju Yu
-
Article |
 A map of the inorganic ternary metal nitrides
A map of the inorganic ternary metal nitrides
High-throughput computation is especially useful for materials screening where synthesis is challenging. Here, it is used to construct a stability map of ternary nitrides, allowing discovery of stable compounds and providing insight into principles that govern nitride stability.
- Wenhao Sun
- , Christopher J. Bartel
- & Gerbrand Ceder
-
News & Views |
 Realistic cataloguing of nanopores
Realistic cataloguing of nanopores
Despite an enormous number of nanopores that could, in principle, be formed in atomically thin materials, advanced modelling reveals that in typical experiments rather limited ensembles of most likely nanopores should be observed.
- Petr Král
-
Article |
 Addressing the isomer cataloguing problem for nanopores in two-dimensional materials
Addressing the isomer cataloguing problem for nanopores in two-dimensional materials
Nanopores in 2D materials have various possible lattice isomers, making relevant quantitative analysis difficult. An isomer-cataloguing framework is developed to address this problem, demonstrating remarkable agreement between simulated and experimental data.
- Ananth Govind Rajan
- , Kevin S. Silmore
- & Michael S. Strano
-
Perspective |
 Oxidation states and ionicity
Oxidation states and ionicity
This Perspective explores the history and usage of the concept of oxidation state, its relation to atomic charge and bonding, and opportunities that arise from applying this analysis to systems with mixed valence or correlated electrons.
- Aron Walsh
- , Alexey A. Sokol
- & C. Richard A. Catlow
-
Article |
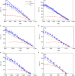 The mechanism of the ultrafast crystal growth of pure metals from their melts
The mechanism of the ultrafast crystal growth of pure metals from their melts
Molecular dynamic simulations reveal that the rapid crystal growth in pure metals is governed by a barrierless ordering process, correlating to the inherent crystalline structure in the liquid at the growth interface.
- Gang Sun
- , Jenny Xu
- & Peter Harrowell
-
News & Views |
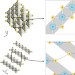 Illuminating interlayer interactions
Illuminating interlayer interactions
A synchrotron X-ray diffraction experiment demonstrates an unexpected accumulation of electron density in the interlayer region of TiS2, and provides a benchmark for theoretical models of weak interlayer bonding.
- Xiaohui Qiu
- & Wei Ji
-
-
News & Views |
 Designed and then realized
Designed and then realized
Simulation determined the crystal energy landscape of a set of molecular crystals, predicting ultrahigh surface area solids with high methane storage. These were then synthesized, showing the potential of computational structure-property mapping.
- Gregory J. O. Beran
-
Article |
 Design of efficient molecular organic light-emitting diodes by a high-throughput virtual screening and experimental approach
Design of efficient molecular organic light-emitting diodes by a high-throughput virtual screening and experimental approach
A high-throughput virtual screening approach is used to select molecules with efficient, thermally activated delayed fluorescence. The good performance of several selected emitters in organic LED applications has also been confirmed experimentally.
- Rafael Gómez-Bombarelli
- , Jorge Aguilera-Iparraguirre
- & Alán Aspuru-Guzik
-
-
Article |
 Exploring the origin of high optical absorption in conjugated polymers
Exploring the origin of high optical absorption in conjugated polymers
The photocurrent generated in organic photodetectors and solar cells can be enhanced by increasing light absorption in the active layer. It is now shown that an extended persistence length can increase the oscillator strength of conjugated polymers.
- Michelle S. Vezie
- , Sheridan Few
- & Jenny Nelson
-
Article |
 Polymer nanofilms with enhanced microporosity by interfacial polymerization
Polymer nanofilms with enhanced microporosity by interfacial polymerization
Here it is shown how ultrathin and microporous polymer membranes, fabricated using sterically contorted monomers, can achieve enhanced performance for solvent-based separations.
- Maria F. Jimenez-Solomon
- , Qilei Song
- & Andrew G. Livingston
-
Article |
 Fast diffusion of water nanodroplets on graphene
Fast diffusion of water nanodroplets on graphene
Molecular simulations suggest that nanodroplets of water and other liquids can be carried by thermally activated propagating ripples in graphene.
- Ming Ma
- , Gabriele Tocci
- & Gabriel Aeppli
-
-
-
News & Views |
 Zeroing in on ice
Zeroing in on ice
Computer simulations show that cubic and hexagonal ices nucleate through the formation of a tetragonal metastable ice phase.
- Ben Slater
- & David Quigley
-
-
Editorial |
 Crossing length scales
Crossing length scales
The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 2013 celebrates the use of computer simulations to model complex chemical systems using multiscale approaches. Taken in a broad sense, these ideas and techniques extend well beyond chemistry.
-
Article |
 Room-temperature metastability of multilayer graphene oxide films
Room-temperature metastability of multilayer graphene oxide films
Graphene oxide could potentially be used for numerous applications, particularly in electronics. Understanding its structural stability in an ambient atmosphere is essential for the realization of devices. A new study shows that multilayer graphene oxide is in fact metastable at room temperature.
- Suenne Kim
- , Si Zhou
- & Elisa Riedo
-
News & Views |
 Predictable porosity
Predictable porosity
The design of structures of organic nanoporous crystals has been hampered by the difficulty of placing functional moieties in a predictive manner. A modular strategy based on prefabricated organic nanocages having directional chiral interactions that self-assemble into the predicted crystals circumvents this problem.
- Neil B. McKeown
-
Letter |
 Anisotropic mechanical amorphization drives wear in diamond
Anisotropic mechanical amorphization drives wear in diamond
The only way diamond can be polished is by pressing it against small diamond crystals, but this works well only for certain crystallographic orientations. The details of this wear mechanism have now been uncovered in simulations that suggest wear occurs via a thin amorphous layer on the diamond surface.
- Lars Pastewka
- , Stefan Moser
- & Michael Moseler
-
Letter |
 Direct observation of local atomic order in a metallic glass
Direct observation of local atomic order in a metallic glass
The atomic configuration of metallic glasses is a long-standing issue important to the understanding of their properties. Nanobeam electron diffraction experiments now enable a direct determination of the local atomic order in a metallic glass.
- Akihiko Hirata
- , Pengfei Guan
- & Mingwei Chen
-
Editorial |
 A model approach to modelling
A model approach to modelling
The work by Roberto Car and Michele Parrinello on ab initio molecular dynamics published 25 years ago has had a huge impact on fundamental science and applications in a wide range of fields.
-
Commentary |
 A joint effort with lasting impact
A joint effort with lasting impact
The ramifications of the Car–Parrinello method, a 25-year-old unified approach to computing properties of materials from first principles, have reached out well-beyond materials science.
- Jürgen Hafner
-
Interview |
 A method to break all barriers
A method to break all barriers
Nature Materials asked Michele Parrinello about his research and the way in which his work with Roberto Car 25 years ago has influenced the materials science and quantum chemistry communities.
- Fabio Pulizzi
-
Letter |
 Ballistic nanofriction
Ballistic nanofriction
Friction between two surfaces is usually studied at low relative sliding speeds. A molecular dynamics study now explores friction at high speeds, showing the emergence of a ballistic friction regime, qualitatively different from standard drift friction. The findings might have important implications for applications in nanoelectromechanical systems.
- Roberto Guerra
- , Ugo Tartaglino
- & Erio Tosatti
-
News & Views |
 The genetics of grain boundaries
The genetics of grain boundaries
The prediction of interface structures is an uncertain and time-consuming task. A technique merging ab initio calculations with a genetic algorithm simplifies the process and provides suitable solutions of the atomic structures that would be hard to envisage a priori.
- W. Craig Carter
-
News & Views |
 How the weak become strong
How the weak become strong
β-sheet stack structures in protein crystals are held together with some of nature's weakest links: hydrogen bonds. It turns out that the size of the crystal stack makes a difference to its strength — and smaller is better.
- Christine Semmrich
- & Andreas R. Bausch

 Phase segregation and nanoconfined fluid O2 in a lithium-rich oxide cathode
Phase segregation and nanoconfined fluid O2 in a lithium-rich oxide cathode Flexing with the flow
Flexing with the flow Walter Kohn (1923–2016)
Walter Kohn (1923–2016) Boron clusters
Boron clusters Rapid unfolding
Rapid unfolding