Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Piezotransistive transduction of femtoscale displacement for photoacoustic spectroscopy
Piezotransistive transduction of femtoscale displacement for photoacoustic spectroscopy
Microelectromechanical systems—micrometre-sized devices with movable parts—make highly sensitive transducers. Here, the authors fabricate an integrated gallium nitride microcantilever and heterojunction field effect transistor that uses piezoelectric effects to measure displacement at the femtoscale level.
- Abdul Talukdar
- , M. Faheem Khan
- & Goutam Koley
-
Article
| Open Access An on-chip electrical transport spectroscopy approach for in situ monitoring electrochemical interfaces
An on-chip electrical transport spectroscopy approach for in situ monitoring electrochemical interfaces
In situprobing electrochemical interfaces is important for the development of improved electrocatalysts. Here, the authors present an on-chip electrical transport spectroscopy approach, which enablesin situmonitoring the dynamic electrochemical interface characteristics.
- Mengning Ding
- , Qiyuan He
- & Xiangfeng Duan
-
Article
| Open Access Non-plasmonic nanoantennas for surface enhanced spectroscopies with ultra-low heat conversion
Non-plasmonic nanoantennas for surface enhanced spectroscopies with ultra-low heat conversion
Metallic nanoantennas can enhance and confine electromagnetic fields, however, localized heating hinders many applications. Here, Caldarola et al.demonstrate both high near-field enhancement and ultra-low heat conversion in the visible-near infrared region using silicon dimer nanoantennas with 20 nm gaps.
- Martín Caldarola
- , Pablo Albella
- & Stefan A. Maier
-
Article
| Open Access Single-atom electron energy loss spectroscopy of light elements
Single-atom electron energy loss spectroscopy of light elements
Light atoms are hardly visible through standard microscopy techniques, because of their smaller scattering power and higher knock-on probability. Here, the authors present an approach to probe light atoms by means of electron energy loss spectroscopy, relying on inelastically scattered electrons.
- Ryosuke Senga
- & Kazu Suenaga
-
Article
| Open Access Direct observation of multistep energy transfer in LHCII with fifth-order 3D electronic spectroscopy
Direct observation of multistep energy transfer in LHCII with fifth-order 3D electronic spectroscopy
Photosynthesis is a complex process, involving the transfer of sunlight driven excitation energy to a reaction centre. Here, the authors directly observe the multistep excitation energy transitions in a light-harvesting complex using ultrafast fifth-order three-dimensional electronic spectroscopy.
- Zhengyang Zhang
- , Petar H. Lambrev
- & Howe-Siang Tan
-
Article
| Open Access Deep and high-resolution three-dimensional tracking of single particles using nonlinear and multiplexed illumination
Deep and high-resolution three-dimensional tracking of single particles using nonlinear and multiplexed illumination
Existing single-particle tracking techniques are limited in terms of penetration depth, tracking range or temporal resolution. Here, Perilloet al. demonstrate three-dimensional particle tracking up to 200-μm depth, with 35-nm spatial localization and 50-μs resolution using multiplexed two-photon excitation.
- Evan P. Perillo
- , Yen-Liang Liu
- & Andrew K. Dunn
-
Article
| Open Access Controllable synthesis of molybdenum tungsten disulfide alloy for vertically composition-controlled multilayer
Controllable synthesis of molybdenum tungsten disulfide alloy for vertically composition-controlled multilayer
The band gap modulation of two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenide alloy is essential for successful applications. Here, we show a controllable synthesis of Mo1−xWxS2 alloy and vertically composition-controlled Mo1−xWxS2multilayer, which is promising as a photoactive material.
- Jeong-Gyu Song
- , Gyeong Hee Ryu
- & Hyungjun Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of vibrational overtones by single-molecule resonant photodissociation
Observation of vibrational overtones by single-molecule resonant photodissociation
Studying the spectra of molecules typically requires large samples, which can be difficult to achieve for hard-to-generate ions. Here, the authors obtain spectra from single CaH+molecules in a three-ion Columbic crystal, observing new molecular transitions.
- Ncamiso B. Khanyile
- , Gang Shu
- & Kenneth R. Brown
-
Article
| Open Access Solubility design leading to high figure of merit in low-cost Ce-CoSb3 skutterudites
Solubility design leading to high figure of merit in low-cost Ce-CoSb3 skutterudites
Thermoelectric materials have the potential to convert waste heat into electricity. Although some of the more viable thermoelectric materials are based on expensive rare earth elements, here the authors replace Yb with low-cost Ce by engineering Ce solubility, thereby making Ce-CoSb3 a competitive thermoelectric.
- Yinglu Tang
- , Riley Hanus
- & G. Jeffrey Snyder
-
Article
| Open Access Creating semiconductor metafilms with designer absorption spectra
Creating semiconductor metafilms with designer absorption spectra
Ultrathin semiconductor metafilms can be designed to achieve near-unity absorption in specific spectral regions. Here, Kim et al. engineer nanoscale optical resonances in sub-50-nm-thick germanium nanobeams metafilms to demonstrate near-unity absorption in one or more desired wavelength regions.
- Soo Jin Kim
- , Pengyu Fan
- & Mark L. Brongersma
-
Article
| Open Access Transition of dislocation nucleation induced by local stress concentration in nanotwinned copper
Transition of dislocation nucleation induced by local stress concentration in nanotwinned copper
Metallic materials with a nanometre-scaled lamella structure can have properties that are very different from their coarser-grained counterparts. Here, the authors demonstrate how dislocations in such a material—nanotwinned copper—can nucleate in two distinctly different mechanisms depending on local stress
- N. Lu
- , K. Du
- & H. Q. Ye
-
Article
| Open Access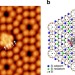 Chemical structure imaging of a single molecule by atomic force microscopy at room temperature
Chemical structure imaging of a single molecule by atomic force microscopy at room temperature
Atomic force microscopy is capable of resolving the chemical structure of a single molecule on a surface, usually at low temperatures. Here, the authors demonstrate that the chemical structure of a single molecule strongly adsorbed onto a silicon surface can be determined at room temperature.
- Kota Iwata
- , Shiro Yamazaki
- & Yoshiaki Sugimoto
-
Article
| Open Access Rational design of crystalline supermicroporous covalent organic frameworks with triangular topologies
Rational design of crystalline supermicroporous covalent organic frameworks with triangular topologies
Covalent organic frameworks are currently arousing considerable interest due to their desirable properties for a wide range of applications. Here, Jiang et al. report two such materials with triangular topologies which exhibit high hole mobility arising from extensive π-cloud delocalisation.
- Sasanka Dalapati
- , Matthew Addicoat
- & Donglin Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic structural evolution of supported palladium–ceria core–shell catalysts revealed by in situ electron microscopy
Dynamic structural evolution of supported palladium–ceria core–shell catalysts revealed by in situ electron microscopy
There is currently renewed interest in the use of core–shell catalysts for methane combustion. Here, the authors perform anex situ and in situelectron microscopy study to probe the structural evolution of palladium–cerium dioxide catalytic core–shell subunits over a wide temperature range.
- Shuyi Zhang
- , Chen Chen
- & Xiaoqing Pan
-
Article
| Open Access Towards experimental quantum-field tomography with ultracold atoms
Towards experimental quantum-field tomography with ultracold atoms
Full tomography of the quantum state of a many-body system becomes harder as more and more atoms are included. Here the authors borrow a concept from condensed-matter physics, continuous matrix-product states, and present an efficient approach for experimental quantum-field tomography.
- A. Steffens
- , M. Friesdorf
- & J. Eisert
-
Article
| Open Access Retrieving spin textures on curved magnetic thin films with full-field soft X-ray microscopies
Retrieving spin textures on curved magnetic thin films with full-field soft X-ray microscopies
The determination of the three-dimensional magnetic domain structures of nanostructures is an ongoing challenge. Here, Streubel et al.use two-dimensional X-ray microscopy to reconstruct three-dimensional domain structures in ferromagnetic thin-film cylinders.
- Robert Streubel
- , Florian Kronast
- & Denys Makarov
-
Article
| Open Access Determining the location and nearest neighbours of aluminium in zeolites with atom probe tomography
Determining the location and nearest neighbours of aluminium in zeolites with atom probe tomography
Substitution of framework silicon for aluminium in zeolites affects Brønsted acidity and subsequently catalytic activity. Here, the authors use atom probe tomography to obtain quantitative insights into the spatial distribution of individual aluminium atoms, including their distribution and segregation.
- Daniel E. Perea
- , Ilke Arslan
- & Bert M. Weckhuysen
-
Article
| Open Access Atomic species identification at the (101) anatase surface by simultaneous scanning tunnelling and atomic force microscopy
Atomic species identification at the (101) anatase surface by simultaneous scanning tunnelling and atomic force microscopy
Anatase is a pivotal material in devices for energy-harvesting applications and catalysis. Here, Stetsovych et al. demonstrate the potential of simultaneously combining atomic force microscopy and scanning tunnelling microscopy to identify the atomic species populating the (101) surface of anatase.
- Oleksandr Stetsovych
- , Milica Todorović
- & Oscar Custance
-
Article
| Open Access Complex structural dynamics of nanocatalysts revealed in Operando conditions by correlated imaging and spectroscopy probes
Complex structural dynamics of nanocatalysts revealed in Operando conditions by correlated imaging and spectroscopy probes
Studying a catalyst during reaction (operando conditions) can give significant insights into the changes a catalyst undergoes. Here, the authors use an operandoapproach to correlate X-ray spectroscopy and electron based imaging techniques to measure the dynamic changes in Pt nanoparticles during the catalytic hydrogenation of ethylene.
- Y. Li
- , D. Zakharov
- & A.I. Frenkel
-
Article
| Open Access Extreme ultraviolet imaging of three-dimensional magnetic reconnection in a solar eruption
Extreme ultraviolet imaging of three-dimensional magnetic reconnection in a solar eruption
Magnetic reconnection is a fundamental energy release process taking place in various astrophysical environments, but it is difficult to observe it directly. Here, the authors provide evidence of three-dimensional magnetic reconnection in a solar eruption using combined perspectives of two spacecraft.
- J. Q. Sun
- , X. Cheng
- & C. Fang
-
Article
| Open Access Probing three-dimensional sodiation–desodiation equilibrium in sodium-ion batteries by in situ hard X-ray nanotomography
Probing three-dimensional sodiation–desodiation equilibrium in sodium-ion batteries by in situ hard X-ray nanotomography
In situ3D visualization of sodium-ion battery processes is challenging due to the highly active sodium metal and the sluggish kinetics. Here, the authors present a X-ray tomography technique, which enables tracking the sodiation–desodiation process of a Sn anode in battery operation.
- Jiajun Wang
- , Christopher Eng
- & Jun Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Hyperbolic phonon-polaritons in boron nitride for near-field optical imaging and focusing
Hyperbolic phonon-polaritons in boron nitride for near-field optical imaging and focusing
Hyperbolic phonon polariton modes in natural hyperbolic materials could have uses in near-field optical imaging, guiding, and focusing applications. Here Li et al.demonstrate enlarged imaging and super-resolution focusing from a flat slab of hexagonal boron nitride enabled by hyperbolic phonon polariton modes.
- Peining Li
- , Martin Lewin
- & Thomas Taubner
-
Article
| Open Access A scanning cavity microscope
A scanning cavity microscope
Fluorescence from nanoparticles enables high-resolution optical imaging, but this approach is limited to those structures that emit light. Here, the authors demonstrate a microscope that uses a cavity to enhance the measurement of the alternative optical properties of absorption and dispersion.
- Matthias Mader
- , Jakob Reichel
- & David Hunger
-
Article |
 Resonant tunnelling in a quantum oxide superlattice
Resonant tunnelling in a quantum oxide superlattice
Quantum mechanical resonant tunnelling is believed to be only feasible in semiconductor-based heterostructures due to high crystalline quality required, which restricts the number of viable materials. Here, the authors demonstrate resonant tunnelling in a deliberately designed complex-oxide superlattice.
- Woo Seok Choi
- , Sang A. Lee
- & Ho Nyung Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Membranes with artificial free-volume for biofuel production
Membranes with artificial free-volume for biofuel production
The free-volume of a polymer is a key parameter in its ability to permit through transport of small molecules. Here, the authors develop a way of introducing different degrees of artificial free-volume to a polymer membrane, and thus tailor its penetrability for applications including biofuel purification.
- Nikos Petzetakis
- , Cara M. Doherty
- & Nitash P. Balsara
-
Article |
 Design and discovery of a novel half-Heusler transparent hole conductor made of all-metallic heavy elements
Design and discovery of a novel half-Heusler transparent hole conductor made of all-metallic heavy elements
Materials that are both electrically conducting and transparent to light are vital for optoelectronic devices, but are rare. Here, the authors perform a quantum mechanical search for such materials and identify the compound TaIrGe as an unexpected possibility, which they then synthesize.
- Feng Yan
- , Xiuwen Zhang
- & Alex Zunger
-
Article
| Open Access Spatial and temporal imaging of long-range charge transport in perovskite thin films by ultrafast microscopy
Spatial and temporal imaging of long-range charge transport in perovskite thin films by ultrafast microscopy
Determining the mechanism of charge carrier transport in solar cells is important for their development towards higher efficiencies. Here, the authors elucidate the spatial and temporal diffusion of charge carriers in hybrid perovskite thin films through ultrafast transient absorption microscopy.
- Zhi Guo
- , Joseph S. Manser
- & Libai Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Revealing the planar chemistry of two-dimensional heterostructures at the atomic level
Revealing the planar chemistry of two-dimensional heterostructures at the atomic level
The properties of 2D materials such as graphene can vary according to the quality and, for vertical devices, the interfaces between materials. Here, the authors report a method using TOF-SIMS, micro-Raman spectroscopy and atomic force microscopy to give high levels of detail of vertical 2D heterostructures.
- Harry Chou
- , Ariel Ismach
- & Andrei Dolocan
-
Article
| Open Access High-performance flexible perovskite solar cells exploiting Zn2SnO4 prepared in solution below 100 °C
High-performance flexible perovskite solar cells exploiting Zn2SnO4 prepared in solution below 100 °C
There has been impressive progress in the development of perovskite solar cells in recent years, but the best performing systems tend to be fabricated on glass surfaces. Here, the authors present a cell built on a polymer substrate, allowing flexibility whilst maintaining high efficiency.
- Seong Sik Shin
- , Woon Seok Yang
- & Sang Il Seok
-
Article
| Open Access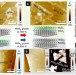 Atomically thin resonant tunnel diodes built from synthetic van der Waals heterostructures
Atomically thin resonant tunnel diodes built from synthetic van der Waals heterostructures
The family of two-dimensional materials is ever growing, but greater functionality can be realized by combining them together. Here, the authors report the direct synthesis of multijunction heterostructures made from graphene, tungsten diselenide and either molybdenum disulphide or molybdenum diselenide.
- Yu-Chuan Lin
- , Ram Krishna Ghosh
- & Joshua A. Robinson
-
Article
| Open Access The solvation of electrons by an atmospheric-pressure plasma
The solvation of electrons by an atmospheric-pressure plasma
Free, or solvated, electrons in a solution are known to form at the interface between a liquid and a gas. Here, the authors use absorption spectroscopy in a total internal reflection geometry to probe solvated electrons generated at a plasma in contact with the surface of an aqueous solution
- Paul Rumbach
- , David M. Bartels
- & David B. Go
-
Article
| Open Access Rhodium-catalysed C(sp2)–C(sp2) bond formation via C–H/C–F activation
Rhodium-catalysed C(sp2)–C(sp2) bond formation via C–H/C–F activation
Fluoroalkenes are found widely in biologically active compounds, but their introduction can be difficult or laborious. Here, the authors report a C–H/C–F activation strategy to introduce monofluoroalkenes into organic molecules in one step with good to excellent yields.
- Panpan Tian
- , Chao Feng
- & Teck-Peng Loh
-
Article
| Open Access Surface determination through atomically resolved secondary-electron imaging
Surface determination through atomically resolved secondary-electron imaging
Technical difficulties have so far limited the application of high-resolution secondary-electron microscopy in imaging surface structures. Here, the authors report a successful determination of surface reconstruction of strontium titanate, using the secondary-electron microscopy along with other techniques.
- J. Ciston
- , H. G. Brown
- & L. D. Marks
-
Article
| Open Access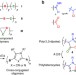 A palladium-catalysed multicomponent coupling approach to conjugated poly(1,3-dipoles) and polyheterocycles
A palladium-catalysed multicomponent coupling approach to conjugated poly(1,3-dipoles) and polyheterocycles
The requirement for multistep synthesis can render the fabrication of highly substituted polymers particularly troublesome. Here, the authors take advantage of metal-catalysed multicomponent polymerization to synthesize a large family of such materials with ease from single-pot reactions.
- David C. Leitch
- , Laure V. Kayser
- & Bruce A. Arndtsen
-
Article
| Open Access Enabling unassisted solar water splitting by iron oxide and silicon
Enabling unassisted solar water splitting by iron oxide and silicon
Water splitting using earth-abundant materials promises a low cost solution to the problem of large scale energy storage. Here, the authors fabricate a haematite and silicon-based high-efficiency water splitting device, which operates without the need for an externally applied bias.
- Ji-Wook Jang
- , Chun Du
- & Dunwei Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Crystallization of DNA-coated colloids
Crystallization of DNA-coated colloids
DNA-coated colloids have failed to achieve their promise of programmable self-assembly because they stick to each other like Velcro. Here Wang et al.overcome this problem by making clickable smooth colloids that are coated with short single-stranded DNA at high density.
- Yu Wang
- , Yufeng Wang
- & David J. Pine
-
Article
| Open Access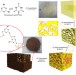 Synthesis of three-dimensionally interconnected sulfur-rich polymers for cathode materials of high-rate lithium–sulfur batteries
Synthesis of three-dimensionally interconnected sulfur-rich polymers for cathode materials of high-rate lithium–sulfur batteries
There is intensive research underway into the cathode development of lithium–sulphur batteries. Here, the authors present a battery with organosulfur-containing polymers as the cathode active materials which displays promising electrochemical performance.
- Hoon Kim
- , Joungphil Lee
- & Moon Jeong Park
-
Article
| Open Access General synthesis of complex nanotubes by gradient electrospinning and controlled pyrolysis
General synthesis of complex nanotubes by gradient electrospinning and controlled pyrolysis
Nanowires and nanotubes are ideal candidates for energy applications but inorganic multielement oxides are less well studied. Here, the authors propose a gradient-electrospinning followed by controlled-pyrolysis method to synthesize various controllable one dimensional metal oxide nanostructures.
- Chaojiang Niu
- , Jiashen Meng
- & Liqiang Mai
-
Article
| Open Access Polarization-independent actively tunable colour generation on imprinted plasmonic surfaces
Polarization-independent actively tunable colour generation on imprinted plasmonic surfaces
Plasmonic nanostructures are a promising alternative to conventional pixels, where their characteristics at the nanoscale offer many benefits. Franklin et al. combine plasmonic surfaces with liquid crystals to create voltage-tunable polarization-independent color pixels for reflective displays.
- Daniel Franklin
- , Yuan Chen
- & Debashis Chanda
-
Article
| Open Access Imaging screw dislocations at atomic resolution by aberration-corrected electron optical sectioning
Imaging screw dislocations at atomic resolution by aberration-corrected electron optical sectioning
Although screw dislocations impact on the properties of various engineering materials, their investigation on the atomic scale has been challenging. Here, the authors use optical sectioning in a scanning transmission electron microscope to achieve direct imaging of screw displacements around a screw dislocation core in GaN.
- H. Yang
- , J. G. Lozano
- & P. D. Nellist
-
Article
| Open Access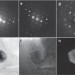 Scanning precession electron tomography for three-dimensional nanoscale orientation imaging and crystallographic analysis
Scanning precession electron tomography for three-dimensional nanoscale orientation imaging and crystallographic analysis
High-resolution microscopy allows imaging of information on the atomic scale. Here, by combining precession electron diffraction with scanning transmission electron microscopy, the authors demonstrate an efficient, alternative technique to determine the three-dimensional orientation of materials.
- Alexander S. Eggeman
- , Robert Krakow
- & Paul A. Midgley
-
Article |
 A carbon nanotube wall membrane for water treatment
A carbon nanotube wall membrane for water treatment
Carbon nanotubes have been proposed for many forms of water treatment, although ultrafiltration nanotube-based membranes with very high flow rates remain rare. Here, the authors fabricate a membrane delivering water permeability close to 30,000 litres per square meter per hour at 1 bar.
- Byeongho Lee
- , Youngbin Baek
- & Yong Hyup Kim
-
Article
| Open Access High-speed multiple-mode mass-sensing resolves dynamic nanoscale mass distributions
High-speed multiple-mode mass-sensing resolves dynamic nanoscale mass distributions
Nanomechanical resonators are sensitive to tiny changes in their mass. Here, the authors demonstrate a method for quickly measuring many resonator modes and use it to analyse the mass and position of multiple nanoparticles flowing in a fluid channel with a precision of 40 attograms and 150 nm, respectively.
- Selim Olcum
- , Nathan Cermak
- & Scott R. Manalis
-
Article
| Open Access Spatially and temporally resolved gas distributions around heterogeneous catalysts using infrared planar laser-induced fluorescence
Spatially and temporally resolved gas distributions around heterogeneous catalysts using infrared planar laser-induced fluorescence
Visualization of the gas distribution around working catalyst is crucial for understanding structure–activity relationships. Here, the authors show that gas distribution can be imaged in situwith high spatial and temporal resolution using infrared planar laser-induced fluorescence.
- Johan Zetterberg
- , Sara Blomberg
- & Edvin Lundgren
-
Article
| Open Access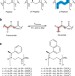 Triangular prism-shaped β-peptoid helices as unique biomimetic scaffolds
Triangular prism-shaped β-peptoid helices as unique biomimetic scaffolds
β-Peptoids are based on N-alkylated β-aminopropionic acid residues, which have been inspired by the more intensely studied peptoids and β-peptides. Here, the authors report X-ray crystal structures of oligomeric β-peptoids demonstrating secondary structures with this backbone.
- Jonas S. Laursen
- , Pernille Harris
- & Christian A. Olsen
-
Article
| Open Access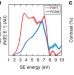 Sub-nanometre resolution imaging of polymer–fullerene photovoltaic blends using energy-filtered scanning electron microscopy
Sub-nanometre resolution imaging of polymer–fullerene photovoltaic blends using energy-filtered scanning electron microscopy
Morphological characterization of organic photovoltaic active layers is restricted by the lack of accurate chemical mapping tools. Here, the authors demonstrate an energy-filtered scanning electron microscopy technique, which enables sub-nanometre resolution imaging of an organic photovoltaic blend.
- Robert C. Masters
- , Andrew J. Pearson
- & Cornelia Rodenburg
-
Article
| Open Access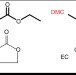 Radiolysis as a solution for accelerated ageing studies of electrolytes in Lithium-ion batteries
Radiolysis as a solution for accelerated ageing studies of electrolytes in Lithium-ion batteries
The degradation of organic solvents used in lithium-ion batteries reduces battery performance. Here, the authors present a radiolysis technique which is not only more efficient than conventional thermally activated ageing methods, but also allows mechanistic analysis of the degradation process.
- Daniel Ortiz
- , Vincent Steinmetz
- & Sophie Le Caër
-
Article
| Open Access Three-dimensional nanoscale molecular imaging by extreme ultraviolet laser ablation mass spectrometry
Three-dimensional nanoscale molecular imaging by extreme ultraviolet laser ablation mass spectrometry
Mass spectral analysis is used to map the composition of materials and surfaces in numerous fields. Here, the authors report a mass spectral technique based on extreme ultraviolet laser ablation that allows three-dimensional imaging of chemical composition in addition to giving highly sensitive nanoscale resolution.
- Ilya Kuznetsov
- , Jorge Filevich
- & Carmen S. Menoni
-
Article
| Open Access Optofluidic fabrication for 3D-shaped particles
Optofluidic fabrication for 3D-shaped particles
The current methods of fabricating three-dimensional particles include photolithography, layer-by-layer printing and several others. Here, Paulsen et al. demonstrate an optofluidic approach, whereby masked ultraviolet light is illuminated on photosensitive fluids whose cross-sections are shaped by fluid inertia.
- Kevin S. Paulsen
- , Dino Di Carlo
- & Aram J. Chung

 Mapping molecules in scanning far-field fluorescence nanoscopy
Mapping molecules in scanning far-field fluorescence nanoscopy