Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Imaging high-speed friction at the nanometer scale
Imaging high-speed friction at the nanometer scale
It has been a challenge to characterize microscopic origins of friction at high velocities. Here authors extend atomic force microscopy to develop a dynamic technique combining force sensitivity and spatial resolution and able to probe, at each image pixel, frictional forces at velocities up to several cm per second.
- Per-Anders Thorén
- , Astrid S. de Wijn
- & David B. Haviland
-
Article
| Open Access Nanoscale assembly of superconducting vortices with scanning tunnelling microscope tip
Nanoscale assembly of superconducting vortices with scanning tunnelling microscope tip
Scanning tunneling microscope (STM) is a powerful tool but local control of superconductivity with the STM tip is still lacking. Here, Geet al. show the use of an STM tip to control the local pinning in a superconductor through the heating effect, allowing to manipulate single superconducting vortex at nanoscale.
- Jun-Yi Ge
- , Vladimir N. Gladilin
- & Victor V. Moshchalkov
-
Article
| Open Access Scanning superlens microscopy for non-invasive large field-of-view visible light nanoscale imaging
Scanning superlens microscopy for non-invasive large field-of-view visible light nanoscale imaging
Rare subcellular events can be tracked by correlating structural-information gathered by imaging with specific-molecule fluorescent identification. Here, the authors achieve this correlation in a quick and non-invasive way using microsphere-based scanning superlens microscopy.
- Feifei Wang
- , Lianqing Liu
- & Wen Jung Li
-
Article
| Open Access Interrogation of bimetallic particle oxidation in three dimensions at the nanoscale
Interrogation of bimetallic particle oxidation in three dimensions at the nanoscale
Understanding bimetallic alloy oxidation is key to design of hollow-structured binary oxides and their optimization for applications, e.g., as catalysts. Here the authors combine real-time imaging and chemically-sensitive electron tomography to uncover unexpected complexity in possible morphological outcomes of bimetallic oxidation.
- Lili Han
- , Qingping Meng
- & Huolin L. Xin
-
Article
| Open Access Rapid mapping of polarization switching through complete information acquisition
Rapid mapping of polarization switching through complete information acquisition
Resolution of classical piezoresponse force microscopy is limited in data acquisition rates and energy scales. Here, Somnath et al. report an approach for rapid probing of ferroelectric switching using direct strain detection of material response to probe bias, enabling spectroscopic imaging at a rate of 3,504 times faster the current state of the art.
- Suhas Somnath
- , Alex Belianinov
- & Stephen Jesse
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic nuclear magnetic resonance field sensing with part-per-trillion resolution
Dynamic nuclear magnetic resonance field sensing with part-per-trillion resolution
The measurement of high magnetic fields has been limited to sensitivities in the nanotesla range. Here, the authors report advances in high-field magnetometry based on nuclear magnetic resonance, achieving resolution in the order of picoteslas or one part per trillion in relative terms.
- Simon Gross
- , Christoph Barmet
- & Klaas P. Pruessmann
-
Article
| Open Access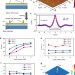 Kaleidoscopic imaging patterns of complex structures fabricated by laser-induced deformation
Kaleidoscopic imaging patterns of complex structures fabricated by laser-induced deformation
Complex surface micro- and nanostructures can be useful in many device applications, but are challenging in terms of controllability, low cost and high throughput. Here the authors have fabricated quasi 3D structures by the thermal deformation of simple two-dimensional laser-induced patterns.
- Haoran Zhang
- , Fengyou Yang
- & Qian Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Laser-induced phase separation of silicon carbide
Laser-induced phase separation of silicon carbide
Laser beam-induced processing is industrially relevant but often challenging to study in terms of underlying phase transformations. Here authors characterize formation of thin, phase-separated carbon and silicon layers on a silicon carbide substrate by laser-induced melting and solidification.
- Insung Choi
- , Hu Young Jeong
- & Keon Jae Lee
-
Correspondence
| Open Access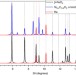 Correspondence: Strongly-driven Re+CO2 redox reaction at high-pressure and high-temperature
Correspondence: Strongly-driven Re+CO2 redox reaction at high-pressure and high-temperature
- D. Santamaria-Perez
- , C. McGuire
- & A. Muñoz
-
Correspondence
| Open Access Correspondence: Reply to ‘Strongly-driven Re+CO2 redox reaction at high-pressure and high-temperature’
Correspondence: Reply to ‘Strongly-driven Re+CO2 redox reaction at high-pressure and high-temperature’
- Mario Santoro
- , Federico A. Gorelli
- & Julien Haines
-
Article
| Open Access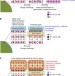 A stable lithium-rich surface structure for lithium-rich layered cathode materials
A stable lithium-rich surface structure for lithium-rich layered cathode materials
Surface modification of high-capacity lithium-rich layered oxides for improved capacity retention is an active area of battery materials research. Here authors demonstrate lithium-rich layered surfaces with a framework matching the host's, but with nickel atoms regularly arranged between layers.
- Sangryun Kim
- , Woosuk Cho
- & Jang Wook Choi
-
Article
| Open Access All-gas-phase synthesis of UiO-66 through modulated atomic layer deposition
All-gas-phase synthesis of UiO-66 through modulated atomic layer deposition
Thin films of metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) are promising for catalysis, gas storage, and microelectronics. Here, the authors introduce a vapour-phase synthesis of UiO-66 thin films, beginning with modulated atomic layer deposition of porous, amorphous films, followed by acetic acid vapour-enabled crystallization to the MOF structure.
- Kristian Blindheim Lausund
- & Ola Nilsen
-
Article
| Open Access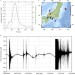 Prompt gravity signal induced by the 2011 Tohoku-Oki earthquake
Prompt gravity signal induced by the 2011 Tohoku-Oki earthquake
Earthquakes have been theorised to produce gravity signals that may arrive before seismic waves, but until now they had not been detected. Montagneret al. have detected prompt gravity signals from the 2011 Tohoku-Oki earthquake thus allowing an early warning of earthquakes before seismic wave arrival.
- Jean-Paul Montagner
- , Kévin Juhel
- & Philippe Lognonné
-
Article
| Open Access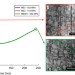 Phase transformation strengthening of high-temperature superalloys
Phase transformation strengthening of high-temperature superalloys
Nanoscale processes may directly impact macroscopic mechanical behaviour. Here authors describe a ‘phase-transformation strengthening’ mechanism in nickel-based high temperature alloys, allowing suppression of deleterious deformation processes at elevated temperatures by specific alloying elements.
- T. M. Smith
- , B. D. Esser
- & M. J. Mills
-
Article
| Open Access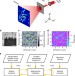 Phase retrieval by coherent modulation imaging
Phase retrieval by coherent modulation imaging
Robust coherent diffractive imaging generally requires many exposures that may damage samples. Here, the authors develop a single-shot X-ray imaging method applicable to general samples for materials and biological sciences, also enabling imaging of dynamic processes, using a pulsed X-ray laser.
- Fucai Zhang
- , Bo Chen
- & Ian K. Robinson
-
Article
| Open Access Structure-conserving spontaneous transformations between nanoparticles
Structure-conserving spontaneous transformations between nanoparticles
Ambient chemical transformations between nanoparticles are poorly explored in materials science. Here, the authors find that two atomically precise, isomorphic clusters of gold and silver can convert between each other in solution through a series of alloy clusters, preserving structure, topology, and metal-ligand stoichiometry.
- K. R. Krishnadas
- , Ananya Baksi
- & Thalappil Pradeep
-
Article
| Open Access High-energy electron emission from metallic nano-tips driven by intense single-cycle terahertz pulses
High-energy electron emission from metallic nano-tips driven by intense single-cycle terahertz pulses
High-energy electron sources are powerful tools for investigating dynamics at atomic and subatomic scales. Here, Li and Jones demonstrate the terahertz-driven emission of electrons with energies exceeding five kiloelectronvolts from nano-tips and study its dependence on the tip radius.
- Sha Li
- & R. R. Jones
-
Article
| Open Access Origin and structure of polar domains in doped molecular crystals
Origin and structure of polar domains in doped molecular crystals
Doping can introduce structural distortions in a molecular crystal in the form of polar domains. Here, the authors combine pyroelectric measurements and computation to reveal the molecular structure of such domains in centrosymmetric α-glycine crystals doped with L-amino acids.
- E. Meirzadeh
- , I. Azuri
- & I. Lubomirsky
-
Article
| Open Access Following lithiation fronts in paramagnetic electrodes with in situ magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging
Following lithiation fronts in paramagnetic electrodes with in situ magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging is a promising non-invasive approach to visualize paramagnetic materials in devices, but the short lifetime of signals currently limits its use. Here, the authors develop an approach which overcomes this hurdle to spectroscopically image lithiation fronts during battery operation.
- Mingxue Tang
- , Vincent Sarou-Kanian
- & Elodie Salager
-
Article
| Open Access Atomic intercalation to measure adhesion of graphene on graphite
Atomic intercalation to measure adhesion of graphene on graphite
Analysis of the mechanical properties of two-dimensional materials is important for device development. Here, the authors report a microscopic method for measuring the adhesion of graphene on top of highly ordered pyrolytic graphite, which exploits atomic-scale blisters formed upon neon atom intercalation.
- Jun Wang
- , Dan C. Sorescu
- & Petro Maksymovych
-
Article
| Open Access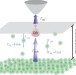 Time-resolved single dopant charge dynamics in silicon
Time-resolved single dopant charge dynamics in silicon
Probing individual impurities will become increasingly important as devices shrink towards the nanoscale. Here Rashidi et al., introduce a method based on time-resolved scanning tunnelling spectroscopy of surface dangling bonds to investigate the dynamics of individual dopants in silicon.
- Mohammad Rashidi
- , Jacob A. J. Burgess
- & Robert A. Wolkow
-
Article
| Open Access Scattering-type scanning near-field optical microscopy with low-repetition-rate pulsed light source through phase-domain sampling
Scattering-type scanning near-field optical microscopy with low-repetition-rate pulsed light source through phase-domain sampling
Low repetition rate lasers are suitable for studying nonlinear optical phenomena, while near-field microscopy allows high spatial resolution for nanomaterial characterisation. Here, Wang et al. enable scattering-type near-field microscopy with low repetition rate lasers through phase-domain sampling.
- Haomin Wang
- , Le Wang
- & Xiaoji G. Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Self-assembly of acetate adsorbates drives atomic rearrangement on the Au(110) surface
Self-assembly of acetate adsorbates drives atomic rearrangement on the Au(110) surface
The efficiency of a catalyst relies on the stability of intermediates on its surface. Here, the authors find that van der Waals interactions between acetate adsorbates on Au(110) provide a small but necessary energy contribution to stabilize the acetate and drive restructuring of the Au surface.
- Fanny Hiebel
- , Bonggeun Shong
- & Cynthia M. Friend
-
Article
| Open Access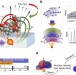 A quantum spin-probe molecular microscope
A quantum spin-probe molecular microscope
Single spin defects can allow high-resolution sensing of molecules under an applied magnetic field. Here, the authors propose a protocol for three-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging with angstrom-level resolution exploiting the dipolar field of a spin qubit, such as a diamond nitrogen-vacancy.
- V. S. Perunicic
- , C. D. Hill
- & L.C.L. Hollenberg
-
Article
| Open Access Imaging and controlling plasmonic interference fields at buried interfaces
Imaging and controlling plasmonic interference fields at buried interfaces
Visualizing surface plasmon polaritons at buried interfaces has remained elusive. Here, the authors develop a methodology to study the spatiotemporal evolution of buried near-fields within complex heterostructures, enabling the characterization of the next generation of plasmonic devices.
- Tom T. A. Lummen
- , Raymond J. Lamb
- & F. Carbone
-
Article
| Open Access Isotope analysis in the transmission electron microscope
Isotope analysis in the transmission electron microscope
Electron microscopy can reveal a material’s chemical structure down to the atomic level, but has so far been blind to isotopic differences. Here the authors are able to map isotope concentrations in graphene by measuring the probability of ejecting atoms, demonstrating a ‘mass spectrometer in the microscope’.
- Toma Susi
- , Christoph Hofer
- & Jani Kotakoski
-
Article
| Open Access Nanoscale probing of electron-regulated structural transitions in silk proteins by near-field IR imaging and nano-spectroscopy
Nanoscale probing of electron-regulated structural transitions in silk proteins by near-field IR imaging and nano-spectroscopy
Silk protein fibres are exceptionally strong, owing to their high β-sheet nanocrystal content. Here, the authors use an electron beam to guide silk β-sheet crystals through structural transitions, and visualize the changes by infrared near-field optics, achieving close to molecular-level resolution.
- Nan Qin
- , Shaoqing Zhang
- & Tiger H. Tao
-
Article
| Open Access The mechanism of eutectic growth in highly anisotropic materials
The mechanism of eutectic growth in highly anisotropic materials
The origins of non-periodic growth features observed in irregular eutectics have been a source of controversy. Here authors use time-resolved X-ray microtomography during eutectic growth of an alloy to show how competing models can be extended and reconciled.
- Ashwin J. Shahani
- , Xianghui Xiao
- & Peter W. Voorhees
-
Article
| Open Access Quantifying microstructural dynamics and electrochemical activity of graphite and silicon-graphite lithium ion battery anodes
Quantifying microstructural dynamics and electrochemical activity of graphite and silicon-graphite lithium ion battery anodes
Tomographic imaging of graphite-based anodes is challenging due to weak X-ray attenuation contrast. Here, the authors use operando propagation-based phase contrast tomography and digital volume correlation to study the electrochemical activity and microstructural dynamics in (silicon−) graphite electrodes.
- Patrick Pietsch
- , Daniel Westhoff
- & Vanessa Wood
-
Article
| Open Access Direct-write nanoscale printing of nanogranular tunnelling strain sensors for sub-micrometre cantilevers
Direct-write nanoscale printing of nanogranular tunnelling strain sensors for sub-micrometre cantilevers
Reducing the size of cantilever-based sensors increases the sensitivity and detection speed of techniques such as atomic force microscopy. Here, the authors demonstrate a nanomechanical readout method that can be easily scaled down in size by using electron co-tunnelling through a nanogranular metal.
- Maja Dukic
- , Marcel Winhold
- & Georg E. Fantner
-
Article
| Open Access Two-dimensional flow nanometry of biological nanoparticles for accurate determination of their size and emission intensity
Two-dimensional flow nanometry of biological nanoparticles for accurate determination of their size and emission intensity
Size and molecular composition of biological nanoparticles dictate their function, but cannot be simultaneously determined accurately. Here, Höök and others have subjected constrained biological nanoparticles on a lipid bilayer to hydrodynamic flow to quantify accurately both size and emission intensity.
- Stephan Block
- , Björn Johansson Fast
- & Fredrik Höök
-
Article
| Open Access Primary thermometry triad at 6 mK in mesoscopic circuits
Primary thermometry triad at 6 mK in mesoscopic circuits
Mesoscopic electrical circuits are an ideal platform to explore quantum phenomena, but this requires cooling the electrons to very low temperature, which is challenging. Here, the authors employ three different in situthermometers to report electronic quantum transport at 6mK in a micrometer-scale circuit.
- Z. Iftikhar
- , A. Anthore
- & F. Pierre
-
Article
| Open Access A physical zero-knowledge object-comparison system for nuclear warhead verification
A physical zero-knowledge object-comparison system for nuclear warhead verification
Zero-knowledge proofs can be used to prove that a statement is true without revealing why it is. Here the authors demonstrate a non-electronic fast neutron radiography technique to confirm that two objects are identical without revealing any details about their design or composition.
- Sébastien Philippe
- , Robert J. Goldston
- & Francesco d’Errico
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrasensitive mechanical detection of magnetic moment using a commercial disk drive write head
Ultrasensitive mechanical detection of magnetic moment using a commercial disk drive write head
The ability to detect weak magnetic moments is important for the study of nanomagnetism and spin-based quantum technologies. Here, the authors demonstrate nanoscale spin detection with high spin sensitivity using a commercial hard drive write head.
- Y. Tao
- , A. Eichler
- & C. L. Degen
-
Article
| Open Access Thermal control of sequential on-surface transformation of a hydrocarbon molecule on a copper surface
Thermal control of sequential on-surface transformation of a hydrocarbon molecule on a copper surface
On-surface chemical reactions provide an attractive route for making tailored nanostructures. Here the authors present a thermally-controlled sequential on-surface transformation of a hydrocarbon molecule, characterized via high-resolution atomic force microscopy and density functional theory calculations.
- Shigeki Kawai
- , Ville Haapasilta
- & Ernst Meyer
-
Article
| Open Access Non-destructive imaging of buried electronic interfaces using a decelerated scanning electron beam
Non-destructive imaging of buried electronic interfaces using a decelerated scanning electron beam
Imaging buried interfaces is necessary to assess the quality of electronic devices and their degradation mechanisms. Here, Hirohata et al. use energy-filtered scanning electron microscopy to image buried defects in an inorganic lateral spin-valve device, at the nanometre scale and non-destructively.
- Atsufumi Hirohata
- , Yasuaki Yamamoto
- & Andrew J. Vick
-
Article
| Open Access Magnetic measurements with atomic-plane resolution
Magnetic measurements with atomic-plane resolution
It has been predicted that electron beam probes may allow for the imaging of magnetism with atomic-scale resolution. Here, the authors demonstrate a scanning transmission electron microscopy method capable of resolving magnetic contrast from individual atomic planes.
- Ján Rusz
- , Shunsuke Muto
- & Claus M. Schneider
-
Article
| Open Access Atomic scale imaging of competing polar states in a Ruddlesden–Popper layered oxide
Atomic scale imaging of competing polar states in a Ruddlesden–Popper layered oxide
Competing phases in layered complex oxides are believed to be relevant for emergent phenomena, which still await to be witnessed. Here, Stone et al. report direct atomic-scale imaging of a multitude of polar phases in Ruddlesden-Popper oxide thin films, exhibiting diverse phenomena in a single structure.
- Greg Stone
- , Colin Ophus
- & Venkatraman Gopalan
-
Article
| Open Access Relating structure and composition with accessibility of a single catalyst particle using correlative 3-dimensional micro-spectroscopy
Relating structure and composition with accessibility of a single catalyst particle using correlative 3-dimensional micro-spectroscopy
The performance of catalytic materials is determined by small-scale chemical and structural variations over large volumes. Here the authors report a correlative spectroscopy approach capable of visualizing processes over multiple length scales, and model the effects of poisoning on mass transport.
- Yijin Liu
- , Florian Meirer
- & Bert M. Weckhuysen
-
Article
| Open Access Simultaneous atomic-resolution electron ptychography and Z-contrast imaging of light and heavy elements in complex nanostructures
Simultaneous atomic-resolution electron ptychography and Z-contrast imaging of light and heavy elements in complex nanostructures
The use of ptychography with electrons has been limited. Here, Yang et al. demonstrate that the combination of Z-contrast and phase imaging reveals the structure of complex nanomaterials. This practical tool can be used to solve the structure of a beam-sensitive carbon nanostructure at atomic-resolution.
- H. Yang
- , R. N. Rutte
- & P. D. Nellist
-
Article
| Open Access Mapping surface charge density of lipid bilayers by quantitative surface conductivity microscopy
Mapping surface charge density of lipid bilayers by quantitative surface conductivity microscopy
Surface charges on lipid bilayers deeply influence the way proteins interact with cellular membranes, yet their precise quantification has proven challenging. Here, the authors report on a quantitative method to map and evaluate surface charge densities under physiological conditions.
- Lasse Hyldgaard Klausen
- , Thomas Fuhs
- & Mingdong Dong
-
Article
| Open Access Multiparametric imaging with heterogeneous radiofrequency fields
Multiparametric imaging with heterogeneous radiofrequency fields
Magnetic resonance fingerprinting (MRF) requires a uniform B1+ radiofrequency field. Here the authors present plug-n-play MRF, a technique that enables multiparametric imaging with heterogeneous B1+fields, and demonstrate its utility in the presence of RF distortion caused by a metallic orthopaedic implant.
- Martijn A. Cloos
- , Florian Knoll
- & Daniel K. Sodickson
-
Article
| Open Access Controlling nanowire growth through electric field-induced deformation of the catalyst droplet
Controlling nanowire growth through electric field-induced deformation of the catalyst droplet
Semiconductor nanowires with precisely controlled structure can be grown by self-assembly using the vapor-liquid-solid process. Here, the authors report a more local growth control strategy using an electric field applied during growth to control nanowire diameter and growth direction.
- Federico Panciera
- , Michael M. Norton
- & Frances M. Ross
-
Article
| Open Access Synthesis of sodium polyhydrides at high pressures
Synthesis of sodium polyhydrides at high pressures
The only known compound of sodium and hydrogen is ionic NaH, but theory predicts the existence of polyhydrides at high pressure. Here, the authors report observations of the formation of polyhydrides above 40 GPa and 2000 K, supporting the idea of multicentre bonding in a material with unusual stoichiometry.
- Viktor V. Struzhkin
- , Duck Young Kim
- & Alexander F. Goncharov
-
Article
| Open Access Raman spectroscopic signature of fractionalized excitations in the harmonic-honeycomb iridates β- and γ-Li2IrO3
Raman spectroscopic signature of fractionalized excitations in the harmonic-honeycomb iridates β- and γ-Li2IrO3
Fractional excitations in quantum spin systems lead to exotic particles predicted in theory but difficult to observe in experiments. Here, Glamazda et al. report the dynamical Raman response of β- and γ-Li2IrO3is dominated by thermal damping of fermionic excitations, suggesting the emergence of Majorana fermions from spin fractionalization.
- A. Glamazda
- , P. Lemmens
- & K. -Y. Choi
-
Article
| Open Access Terahertz spectroscopy on Faraday and Kerr rotations in a quantum anomalous Hall state
Terahertz spectroscopy on Faraday and Kerr rotations in a quantum anomalous Hall state
Quantized magnetoelectric coupling, which induces exotic magneto-optical phenomena, awaits to be evidenced in topological insulators. Here, Okada et al. demonstrate Faraday and Kerr rotations of magnetic topological insulator surfaces in quantum anomalous Hall states by terahertz magneto-optics, indicating topological magnetoelectric effect.
- Ken N. Okada
- , Youtarou Takahashi
- & Yoshinori Tokura
-
Article
| Open Access Edge phonons in black phosphorus
Edge phonons in black phosphorus
Black phosphorus is an allotrope of phosphorous that, like graphite, can be exfoliated to create two-dimensional materials. Here, the authors use Raman spectroscopy and density functional theory calculations to investigate the anomalous behaviour of phonons near different black phosphorus edges.
- H. B. Ribeiro
- , C. E. P. Villegas
- & C. J. S. de Matos
-
Article
| Open Access Photo-induced enhanced Raman spectroscopy for universal ultra-trace detection of explosives, pollutants and biomolecules
Photo-induced enhanced Raman spectroscopy for universal ultra-trace detection of explosives, pollutants and biomolecules
Surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy is a sensitive technique capable of detecting single molecules via their vibrational fingerprints. Here, the authors demonstrate improved sensitivity with photo-induced enhanced Raman spectroscopy applied to trace-level detection of explosives and other analytes.
- Sultan Ben-Jaber
- , William J. Peveler
- & Ivan P. Parkin
-
Article
| Open Access Direct TEM observations of growth mechanisms of two-dimensional MoS2 flakes
Direct TEM observations of growth mechanisms of two-dimensional MoS2 flakes
MoS2 nanostructures are potentially useful in electronic applications. Here, Fei et al. show using in situ electron microscopy that MoS2grows in a vertical manner at low temperature, then rotates to horizontal structures, and finally develops in size by merging adjacent flakes at high temperature.
- Linfeng Fei
- , Shuijin Lei
- & Yu Wang

 Imaging electric field dynamics with graphene optoelectronics
Imaging electric field dynamics with graphene optoelectronics