News & Views |
Featured
-
-
News & Views |
Tyrosine-kinase inhibitors—new standard for NSCLC therapy
A clinical trial of patients with pharmacogenomically selected non-small-cell lung cancer clearly demonstrated an improvement in progression-free survival after gefitinib treatment compared with standard chemotherapy. This report is the first to suggest that personalized therapy based on pharmacogenomics could be standardized in the treatment of lung cancer.
- Nagahiro Saijo
-
Review Article |
 Molecular mechanisms of metastasis in breast cancer—clinical applications
Molecular mechanisms of metastasis in breast cancer—clinical applications
Circulating tumor cells (CTCs) have a crucial role in the metastatic cascade, tumor dissemination and progression. Furthermore, CTCs are involved in treatment failure, therapy resistance and disease progression. New therapeutic possibilities are offered by the established clinical prognostic and predictive value of CTCs with the additional possibility of using them for the real-time monitoring of systemic-therapy efficacy. This Review discusses the future clinical applications of CTCs in breast cancer including the incorporation of CTCs as end points in clinical trials and the blockade of tumor dissemination and self seeding via the therapeutic targeting of CTCs.
- Michal Mego
- , Sendurai A. Mani
- & Massimo Cristofanilli
-
News & Views |
Nilotinib and dasatinib—new 'magic bullets' for CML?
The efficacy of nilotinib and dasatinib as frontline treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia has been documented in small phase II studies. Now, two clinical trials have assessed the effectiveness of second-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitors in comparison with standard dose imatinib at 1 year. Will these results change our current practice?
- Massimo Breccia
-
Research Highlight |
 PARP inhibitor olaparib is safe and effective in patients with BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations
PARP inhibitor olaparib is safe and effective in patients with BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations
- Lisa Hutchinson
-
-
Review Article |
 Future directions of bone-targeted therapy for metastatic breast cancer
Future directions of bone-targeted therapy for metastatic breast cancer
Bone is the most common site of breast cancer metastasis, resulting in substantial morbidity and mortality. A number of therapies are being developed, including bisphosphonates, which target factors that promote tumor growth in bone. The authors of this Review outline the underlying mechanisms that drive this pathological process, and highlight potential molecular targets that will improve therapeutic interventions for metastatic breast cancer. Tools that assess response in individual patients and guide appropriate treatment are also discussed.
- Tomifumi Onishi
- , Naoki Hayashi
- & Naoto T. Ueno
-
Review Article |
 Making the best of PARP inhibitors in ovarian cancer
Making the best of PARP inhibitors in ovarian cancer
Inhibitors of poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase (PARP) have shown promise as therapeutic agents for the treatment of ovarian cancers with mutations inBRCA1 or BRCA2. By exploiting the synthetic lethal interaction that exists between PARP inhibition and BRCA mutations, these agents specifically kill cancer cells by targeting their DNA repair system. The authors of this Review describe the importance of BRCAmutations for the efficacy of PARP inhibitors. They also discuss the preclinical and clinical trial results of PARP inhibitors, the challenges related to the use of these agents, and future directions.
- Susana Banerjee
- , Stan B. Kaye
- & Alan Ashworth
-
Opinion |
 Off-tumor target—beneficial site for antiangiogenic cancer therapy?
Off-tumor target—beneficial site for antiangiogenic cancer therapy?
Antiangiogenic therapy inhibits tumor growth by targeting the blood vessels of the tumor. Antiangiogenic therapy often correlates with longer survival in patients without affecting tumor growth. This positive response may be due to the off-tumor target effects of antiangiogenic drugs. In this article, Yihai Cao describes the potential mechanisms underlying the benefits of targeting off-tumor sites, and how these events improve outcomes in patients with cancer-associated systemic syndromes.
- Yihai Cao
-
Research Highlight |
 Activated PI3K/AKT confers resistance to trastuzumab but not lapatinib
Activated PI3K/AKT confers resistance to trastuzumab but not lapatinib
- Lisa Hutchinson
-
News & Views |
 Denileukin diftitox—a step towards a 'magic bullet' for CTCL
Denileukin diftitox—a step towards a 'magic bullet' for CTCL
Investigators found that denileukin diftitox, which targets the interleukin-2 receptor, achieves objective response rates in 44% of patients with cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, with a median duration of response of 7.8 months and 2% incidence of severe vascular leak syndrome. The inclusion of a placebo arm in the study revealed several additional interesting observations.
- Marshall E. Kadin
- & Eric C. Vonderheid
-
-
-
Research Highlight |
Lapatinib is effective in patients with p95HER2-positive tumors
- Lisa Hutchinson
-
News & Views |
 Pazopanib: carving a niche in a crowded therapeutic landscape
Pazopanib: carving a niche in a crowded therapeutic landscape
Encouraging data have been reported from a randomized, double-blind, phase III trial comparing pazopanib therapy to placebo in treatment-naive and cytokine-refractory patients with advanced renal-cell carcinoma. The challenge that lies ahead is determining where pazopanib fits into the crowded therapeutic algorithms for this disease.
- Sumanta Kumar Pal
- & Robert A. Figlin
-
News & Views |
Importance of patient selection for EGFR TKIs in lung cancer
Platinum-based chemotherapy has been the standard first-line treatment for patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer for decades. However, a recent study has shown the superiority of gefitinib treatment in comparison with chemotherapy in a molecularly selected cohort of patients harboring sensitizing EGFR mutations. These results demonstrate the importance of incorporating molecular selection into the design of lung cancer trials that use EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors.
- Ariel Lopez-Chavez
- & Giuseppe Giaccone
-
Review Article |
 Molecular circuits of solid tumors: prognostic and predictive tools for bedside use
Molecular circuits of solid tumors: prognostic and predictive tools for bedside use
The rapid pace of research in cancer biology, and the advent of molecular targeted therapies has made personalized medicine a reality. This knowledge has generated a vast panel of molecular biomarkers. This Review presents the molecular, prognostic and predictive factors for the six solid tumors associated with the highest mortality. The authors discuss the key biomarkers for each disease site according to its associated clinicopathological presentation and specific associated molecular interactions.
- Charles Ferté
- , Fabrice André
- & Jean-Charles Soria
-
Review Article |
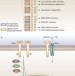 Understanding resistance to EGFR inhibitors—impact on future treatment strategies
Understanding resistance to EGFR inhibitors—impact on future treatment strategies
EGFR is one of the most studied targets in oncology, and several inhibitors have shown promising results in selected patient populations. However, intrinsic and acquired resistance to these targeted therapies is increasingly recognized. The authors of this Review describe the successful translation of EGFR inhibitors to the clinic, and highlight the mechanisms of resistance to these agents that limit their long-term efficacy. Understanding these processes will allow researchers to develop therapies that overcome resistance and ultimately lead to more successful outcomes.
- Deric L. Wheeler
- , Emily F. Dunn
- & Paul M. Harari
-
Review Article |
 Targeted therapy in non-small-cell lung cancer—is it becoming a reality?
Targeted therapy in non-small-cell lung cancer—is it becoming a reality?
Survival outcomes for advanced or metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer remain poor; however, molecular targeted agents offer new opportunities provided that patients are selected for treatment according to their tumor profile. This Review highlights the promising activity shown with novel targeted therapies that interfere with the IGF-1R pathway and agents that inhibit the EML4-ALK fusion protein. Aberrations in other key signaling pathways that have been identified as crucial targets, especially in resistant patients, are also discussed.
- Filip Janku
- , David J. Stewart
- & Razelle Kurzrock
-
-
Case Study |
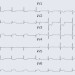 A case of variant angina in a patient under chronic treatment with sorafenib
A case of variant angina in a patient under chronic treatment with sorafenib
A 63-year-old male patient under chronic treatment with sorafenib for an unresectable multifocal hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) presented with suspected variant angina. Spontaneous spasm occurred during cardiac catheterization and was revealed during coronary angiogram with the unusual feature of a retrograde transient filling of a contralateral branch. Italo Porto and colleagues contend that the effects of sorafenib treatment were primarily responsible for the major cardiovascular event observed in this case, and suggest that clinicians should be aware of this possible severe complication of sorafenib therapy.
- Italo Porto
- , Andrea Leo
- & Filippo Crea
-
Review Article |
 mTOR signaling and drug development in cancer
mTOR signaling and drug development in cancer
Mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) has a key role in several pathways that are involved in cell growth and cancer. In this Review, Dr. Dancey outlines the mechanisms of action and performance of current mTOR inhibitors in clinical trials. Second-generation inhibitors are also discussed along with strategies that should be used to improve outcomes achieved with mTOR inhibitors.
- Janet Dancey
-
News & Views |
Thalidomide in lung cancer therapy—what have we learned?
Disappointing phase III results for thalidomide combined with gemcitabine and carboplatin in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer might be related to poor efficacy of targeted therapies in unselected patients. We argue that current trial designs are flawed because they expose large numbers of such patients to potentially harmful treatment, and suggest that future research strategies should prioritize identification of predictive markers.
- Martin Reck
- & Ulrich Gatzemeier
-
Review Article |
 Management of breast cancer with targeted agents: importance of heterogenicity
Management of breast cancer with targeted agents: importance of heterogenicity
Breast cancer is a heterogeneous disease with different molecular drivers regulating its growth, survival and treatment response. Drug development efforts have resulted in agents against new molecular targets that are active against only those tumors with the targeted molecular alteration or phenotype. The authors critically discuss the recently established and investigational strategies for the treatment of the main breast cancer subtypes.
- Serena Di Cosimo
- & José Baselga
-
News & Views |
Optimal first-line therapy for NSCLC with EGFR mutations
Activating mutations in EGFR are characteristic of patients with lung cancer who have high sensitivity to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors, such as gefitinib and erlotinib. The randomized IPASS study by Mok and colleagues confirmed that patients with EGFR mutations have a higher response rate, longer progression-free survival and improved quality of life when treated with first-line gefinitib instead of chemotherapy.
- Joel W. Neal
- & Lecia V. Sequist
-
News & Views |
Tailored treatment for ovarian cancer: are we there yet?
First-line platinum and taxane chemotherapy improves the prognosis of patients with epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC), however, about 80% of patients relapse and long-term survival is poor. The development of drug resistance is the main cause of treatment failure; therefore, the identification of new compounds that interfere with tumor growth and survival is a priority.
- Cristiana Sessa
- & Gianluca Del Conte
-
-
News & Views |
Sunitinib versus interferon-α in metastatic RCC
Motzer and colleagues present updated results from a multicenter, phase III trial of sunitinib versus interferon-α as first-line treatment for patients with metastatic renal-cell carcinoma. The observed improvement in overall survival for patients treated with sunitinib further establishes this agent as the reference standard for first-line treatment of good-risk and intermediate-risk patients with metastatic renal cancer.
- Jason E. Faris
- & M. Dror Michaelson

 Farletuzumab—promising new agent in ovarian cancer
Farletuzumab—promising new agent in ovarian cancer