Review Article |
Featured
-
-
-
Review Article |
 Beyond the margins: real-time detection of cancer using targeted fluorophores
Beyond the margins: real-time detection of cancer using targeted fluorophores
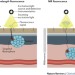
Intraoperative fluorescence enables highly specific real-time detection of tumours at the time of surgery. In particular, near-infrared (NIR) fluorescence is a promising tool currently being tested in clinical settings. Zhang et al. discuss the latest developments in NIR fluorophores, cancer-targeting strategies, and detection instrumentation for intraoperative cancer detection, as well as the challenges associated with their effective application in clinical settings.
- Ray R. Zhang
- , Alexandra B. Schroeder
- & Jamey P. Weichert
-
Review Article |
 Rethinking the metastatic cascade as a therapeutic target
Rethinking the metastatic cascade as a therapeutic target
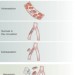
The treatment of microscopic metastatic disease is based on the assumption that micrometastases and overt metastases will respond to the same interventions; however, clinical observations illustrate this assumption is incorrect. The authors discuss our existing understanding of the metastatic cascade, emerging therapeutic targets involved in the metastatic process, and how novel anti-metastatic therapies might be developed for clinical use.
- Lida A. Mina
- & George W. Sledge Jr
-
Review Article |
 Synthetic lethal approaches to breast cancer therapy
Synthetic lethal approaches to breast cancer therapy
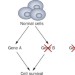
Synthetic lethality has emerged as a novel approach to treat cancer. Inhibitors of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase, a target that has synthetic lethality withBRCAmutations, have already shown promise in clinical trials. The authors of this Review describe the clinical application of synthetic lethality for patients with breast cancer, and discuss biomarkers that can be used to select patients who will respond to this therapy. Other potential genes that could be involved in synthetic lethality, and are thus new targets, are also explored.
- Farah L. Rehman
- , Christopher J. Lord
- & Alan Ashworth
-

 The roles and implications of RNA m6A modification in cancer
The roles and implications of RNA m6A modification in cancer